|
1
|
Pavenstadt H, Kriz W and Kretzler M: Cell
biology of the glomerular podocyte. Physiol Rev. 83:253–307. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Greka A and Mundel P: Cell biology and
pathology of podocytes. Annu Rev Physiol. 74:299–323. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Gubler MC: Podocyte differentiation and
hereditary proteinuria/nephrotic syndromes. J Am Soc Nephrol.
14(Suppl 1): S22–S26. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
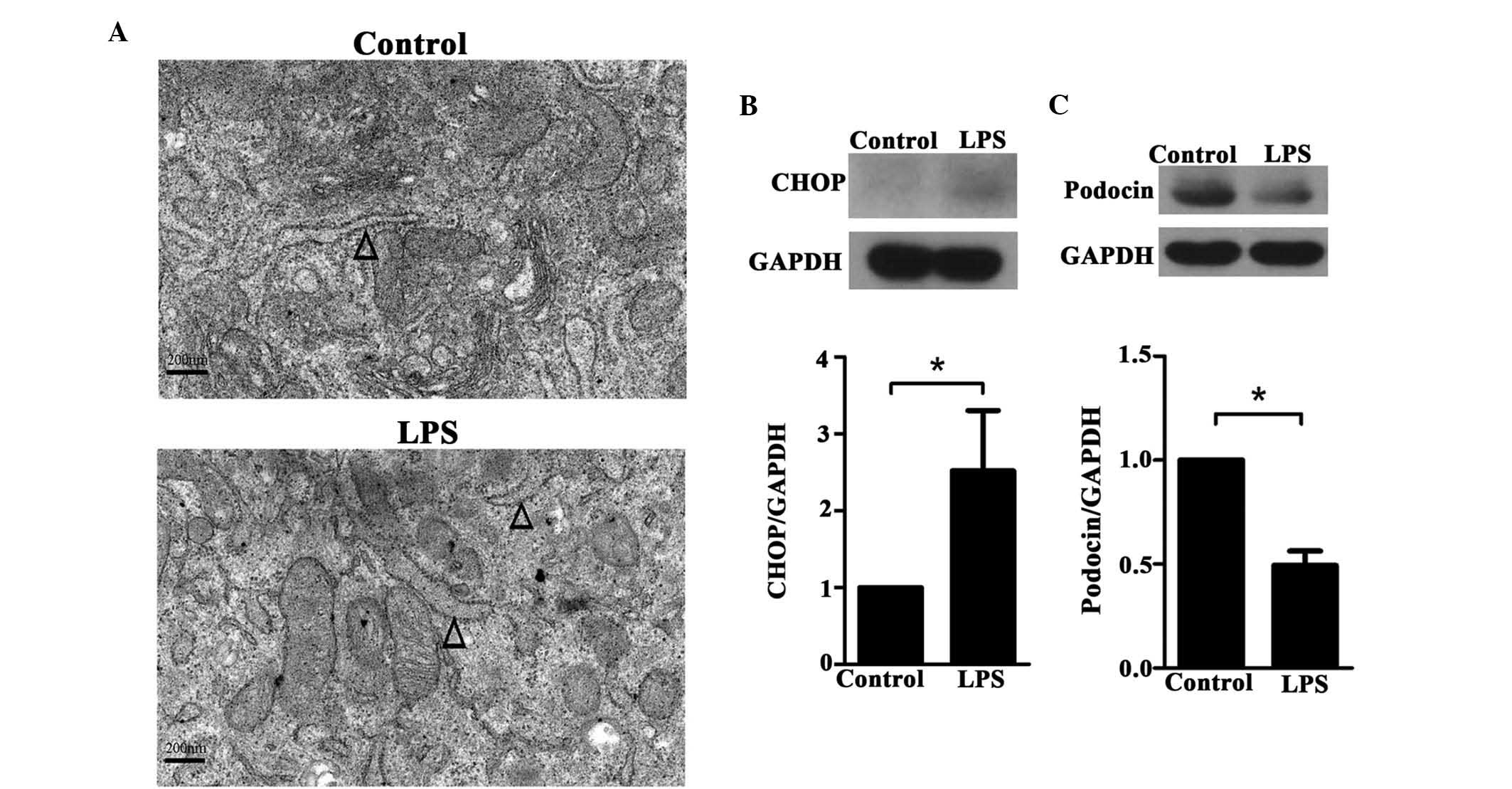
4
|
Patrakka J and Tryggvason K: New insights
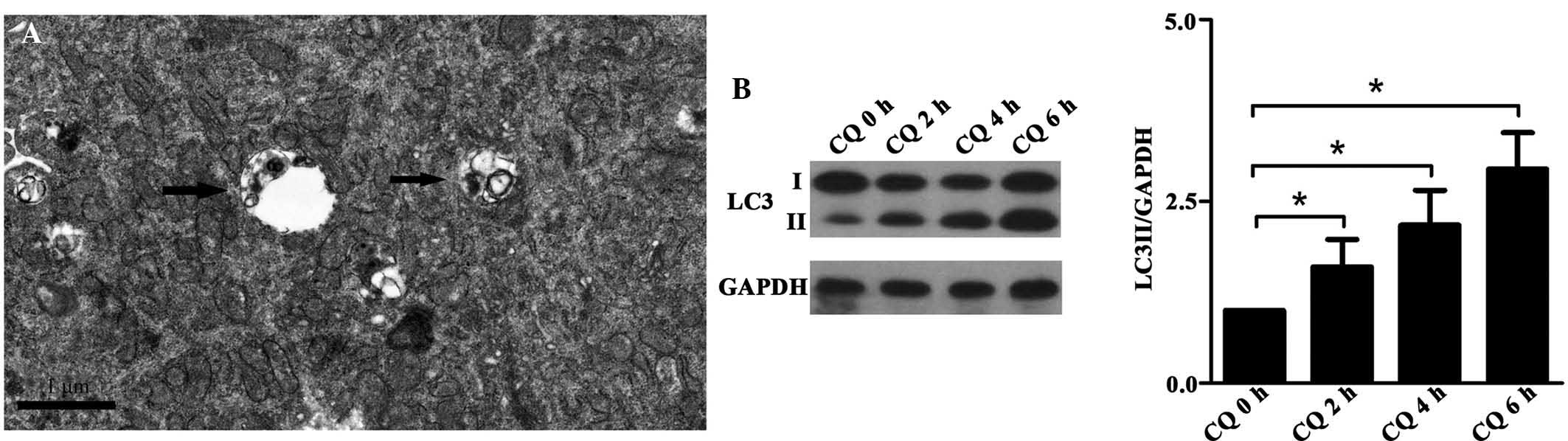
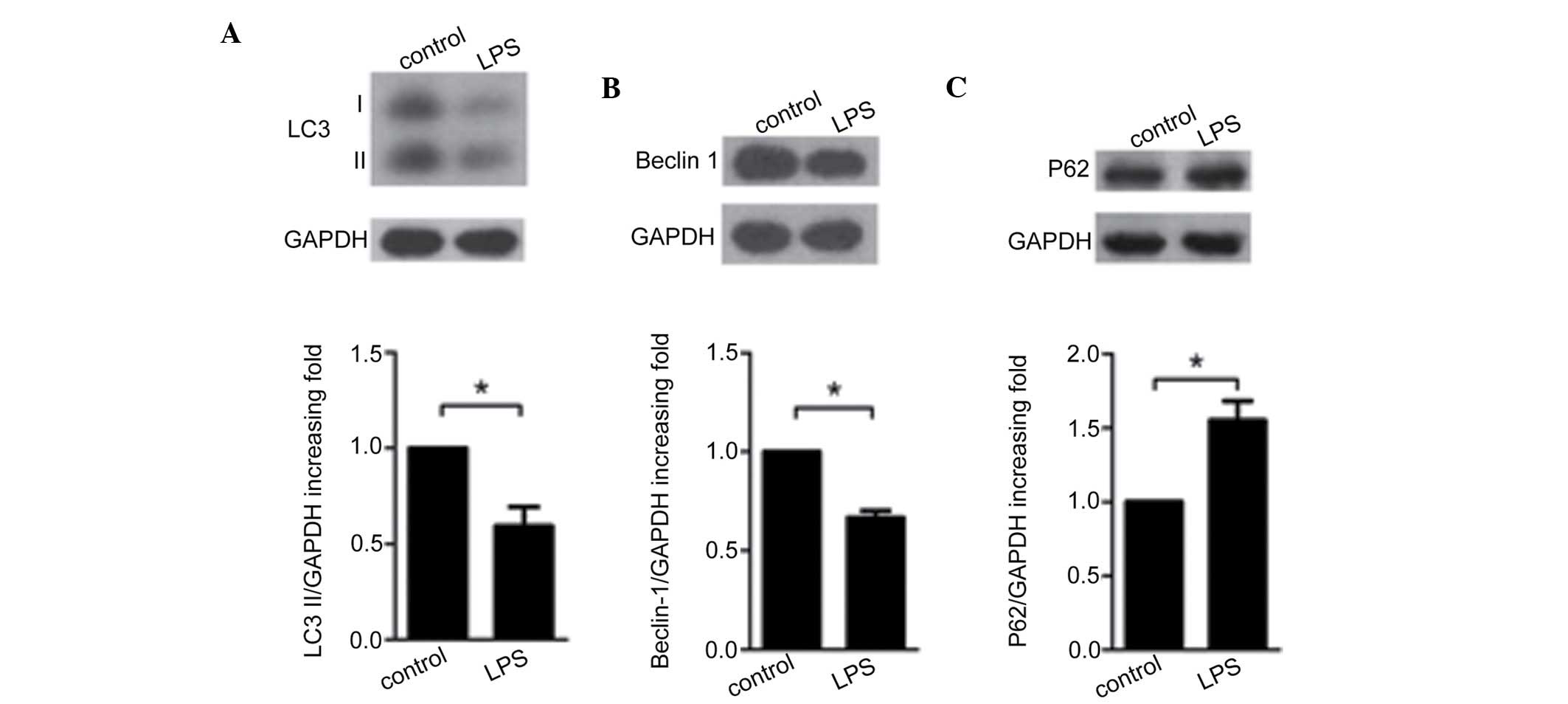
into the role of podocytes in proteinuria. Nat Rev Nephrol.
5:463–468. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
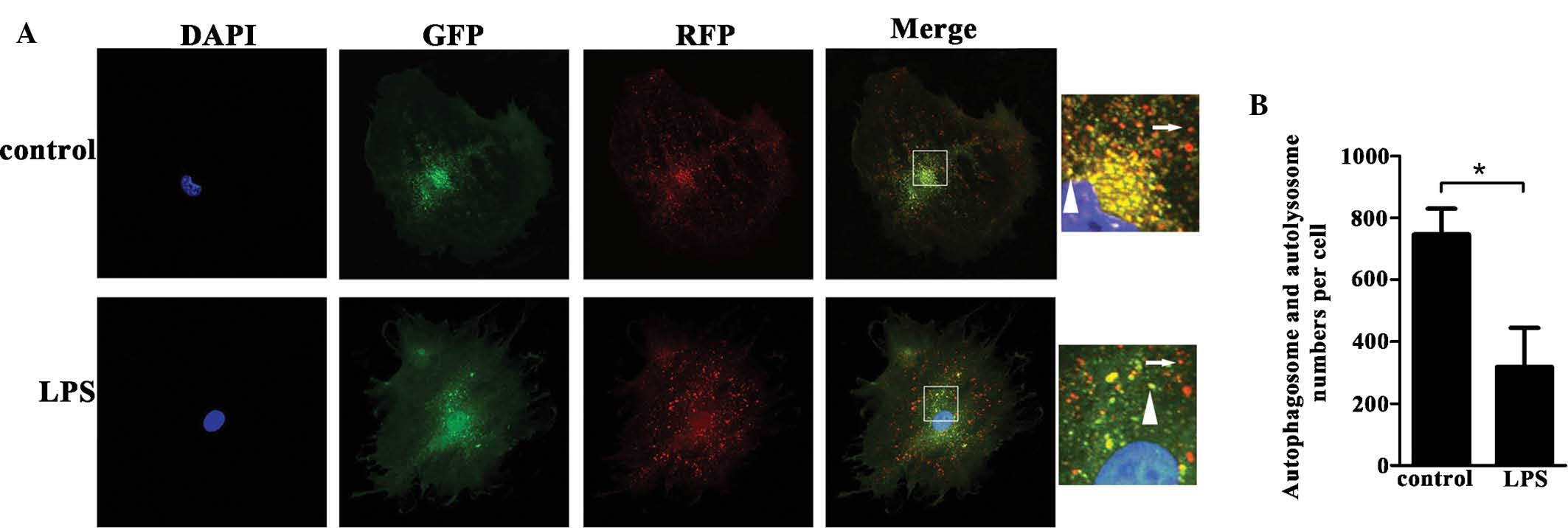
|
5
|
Yu CC, Fornoni A, Weins A, Hakroush S,
Maiguel D, Sageshima J, Chen L, Ciancio G, Faridi MH, Behr D, et
al: Abatacept in B7-1-positive proteinuric kidney disease. N Engl J
Med. 369:2416–2423. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Reiser J, von Gersdorff G, Loos M, Oh J,
Asanuma K, Giardino L, Rastaldi MP, Calvaresi N, Watanabe H,
Schwarz K, et al: Induction of B7-1 in podocytes is associated with
nephrotic syndrome. J Clin Invest. 113:1390–1397. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wei C, Moller CC, Altintas MM, Li J,
Schwarz K, Zacchigna S, Xie L, Henger A, Schmid H, Rastaldi MP, et
al: Modification of kidney barrier function by the urokinase
receptor. Nat Med. 14:55–63. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Saurus P, Kuusela S, Lehtonen E, Hyvönen
ME, Ristola M, Fogarty CL, Tienari J, Lassenius MI, Forsblom C,
Lehto M, et al: Podocyte apoptosis is prevented by blocking the
Toll-like receptor pathway. Cell Death Dis. 6:e17522015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kumagai T, Baldwin C, Aoudjit L, Nezvitsky
L, Robins R, Jiang R and Takano T: Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B
inhibition protects against podocyte injury and proteinuria. Am J
Pathol. 184:2211–2224. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang B, Shi W, Ma J, Sloan A, Faul C, Wei
C, Reiser J, Yang Y, Liu S and Wang W: The calcineurin-NFAT pathway
allows for urokinase receptor-mediated beta3 integrin signaling to
cause podocyte injury. J Mol Med (Berl). 90:1407–1420. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Zhang B, Xie S, Shi W and Yang Y:
Amiloride off-target effect inhibits podocyte urokinase receptor
expression and reduces proteinuria. Nephrol Dial Transplant.
27:1746–1755. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Mizushima N, Levine B, Cuervo AM and
Klionsky DJ: Autophagy fights disease through cellular
self-digestion. Nature. 451:1069–1075. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hartleben B, Gödel M, Meyer-Schwesinger C,
Liu S, Ulrich T, Köbler S, Wiech T, Grahammer F, Arnold SJ,
Lindenmeyer MT, et al: Autophagy influences glomerular disease
susceptibility and maintains podocyte homeostasis in aging mice. J
Clin Invest. 120:1084–1096. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mundel P, Reiser J, Zúñiga Mejía Borja A,
Pavenstädt H, Davidson GR, Kriz W and Zeller R: Rearrangements of
the cytoskeleton and cell contacts induce process formation during
differentiation of conditionally immortalized mouse podocyte cell
lines. Exp Cell Res. 236:248–58. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Srivastava T, Sharma M, Yew KH, Sharma R,
Duncan RS, Saleem MA, McCarthy ET, Kats A, Cudmore PA, Alon US, et
al: LPS and PAN-induced podocyte injury in an in vitro model of
minimal change disease: changes in TLR profile. J Cell Commun
Signal. 7:49–60. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
16
|
Reiser J, von Gersdorff G, Loos M, Oh J,
Asanuma K, Giardino L, Rastaldi MP, Calvaresi N, Watanabe H,
Schwarz K, et al: Induction of B7 1 in podocytes is associated with
nephrotic syndrome. J Clin Invest. 113:1390–1397. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Howell GM, Gomez H, Collage RD, Loughran
P, Zhang X, Escobar DA, Billiar TR, Zuckerbraun BS and Rosengart
MR: Augmenting autophagy to treat acute kidney injury during
endotoxemia in mice. PLoS One. 8:e695202013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mei S, Livingston M, Hao J, Li L, Mei C
and Dong Z: Autophagy is activated to protect against endotoxic
acute kidney injury. Sci Rep. 6:221712016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Klionsky DJ and Emr SD: Autophagy as a
regulated pathway of cellular degradation. Science. 290:1717–1721.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Komatsu M, Waguri S, Chiba T, Murata S,
Iwata J, Tanida I, Ueno T, Koike M, Uchiyama Y and Kominami E: Loss
of autophagy in the central nervous system causes neurodegeneration
in mice. Nature. 441:880–884. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Maiuri MC, Zalckvar E, Kimchi A and
Kroemer G: Self-eating and self-killing: Crosstalk between
autophagy and apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 8:741–752. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen YM, Zhou Y, Go G, Marmerstein JT,
Kikkawa Y and Miner JH: Laminin beta2 gene missense mutation
produces endoplasmic reticulum stress in podocytes. J Am Soc
Nephrol. 24:1223–1233. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yu CC, Fornoni A, Weins A, Hakroush S,
Maiguel D, Sageshima J, Chen L, Ciancio G, Faridi MH, Behr D, et
al: Abatacept in B7 1 positive proteinuric kidney disease. N Engl J
Med. 369:2416–2423. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ma J, Zhang B, Liu S, Xie S, Yang Y, Ma J,
Deng Y, Wang W, Xu L, Li R, et al: 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D(3)
inhibits podocyte uPAR expression and reduces proteinuria. PLoS
One. 8:e649122013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zeng C, Fan Y, Wu J, Shi S, Chen Z, Zhong
Y, Zhang C, Zen K and Liu Z: Podocyte autophagic activity plays a
protective role in renal injury and delays the progression of
podocytopathies. J Pathol. 234:203–213. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Klionsky DJ, Abdalla FC, Abeliovich H,
Abraham RT, Acevedo-Arozena A, Adeli K, Agholme L, Agnello M,
Agostinis P, Aguirre-Ghiso JA, et al: Guidelines for the use and
interpretation of assays for monitoring autophagy. Autophagy.
8:445–544. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bjorkoy G, Lamark T, Brech A, Outzen H,
Perander M, Overvatn A, Stenmark H and Johansen T: p62/SQSTM1 forms
protein aggregates degraded by autophagy and has a protective
effect on huntingtin-induced cell death. J Cell Biol. 171:603–614.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhou C, Zhong W, Zhou J, Sheng F, Fang Z,
Wei Y, Chen Y, Deng X, Xia B and Lin J: Monitoring autophagic flux
by an improved tandem fluorescent-tagged LC3 (mTagRFP-mWasabi-LC3)
reveals that high-dose rapamycin impairs autophagic flux in cancer
cells. Autophagy. 8:1215–1226. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Cybulsky AV, Takano T, Papillon J, Kitzler
TM and Bijian K: Endoplasmic reticulum stress in glomerular
epithelial cell injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 301:F496–F508.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Wu L, Feng Z, Cui S, Hou K, Tang L, Zhou
J, Cai G, Xie Y, Hong Q, Fu B and Chen X: Rapamycin upregulates
autophagy by inhibiting the mTOR-ULK1 pathway, resulting in reduced
podocyte injury. PLoS One. 8:e637992013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Seglen PO and Gordon PB: 3-Methyladenine:
Specific inhibitor of autophagic/lysosomal protein degradation in
isolated rat hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 79:1889–1892.
1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mackeh R, Perdiz D, Lorin S, Codogno P and
Poüs C: Autophagy and microtubules-new story, old players. J Cell
Sci. 126:1071–1080. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|