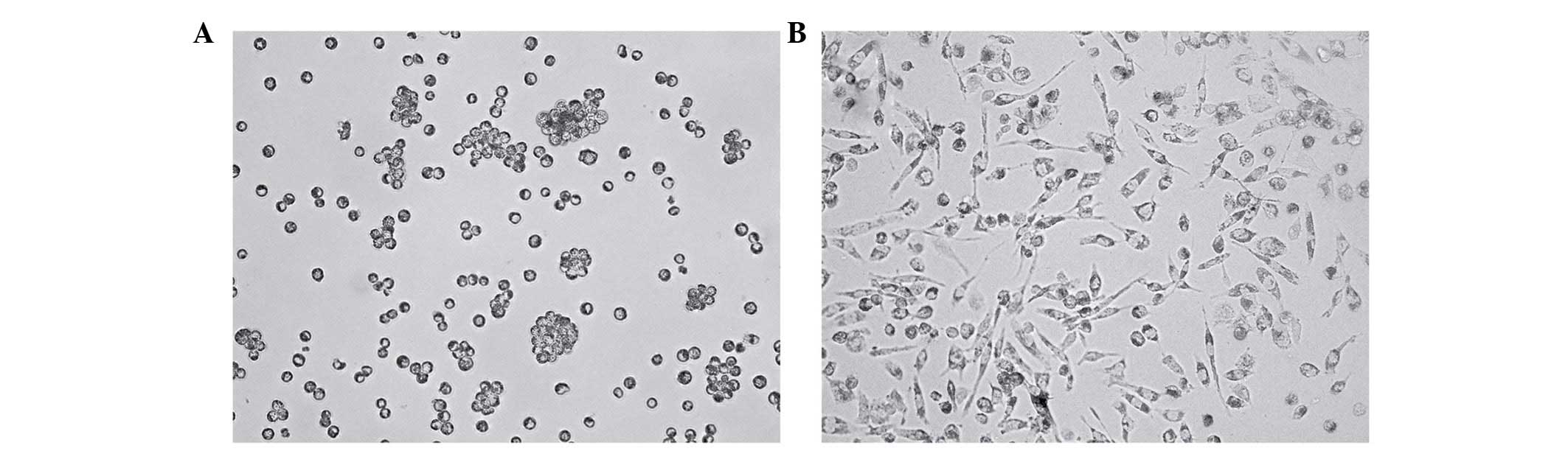
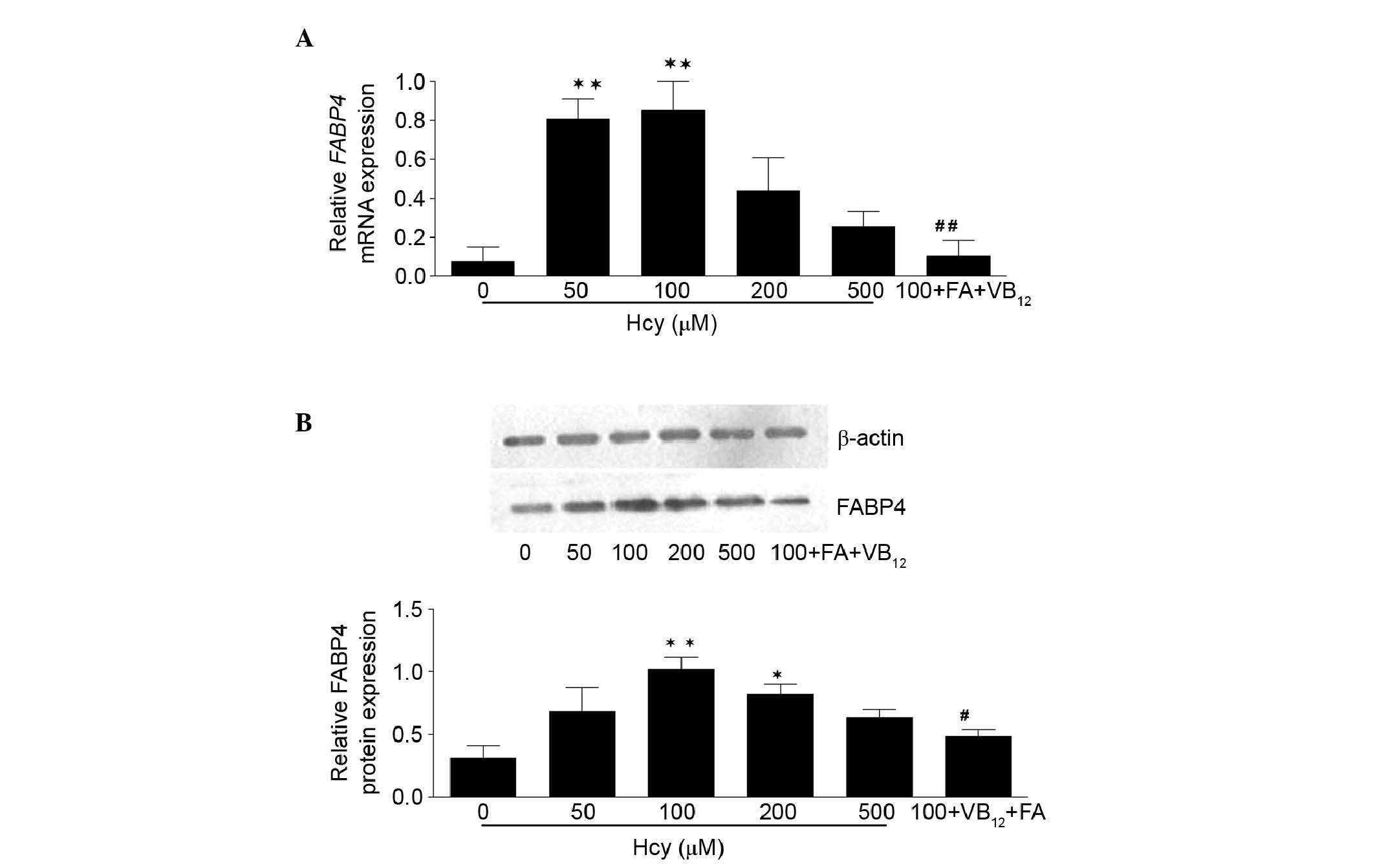
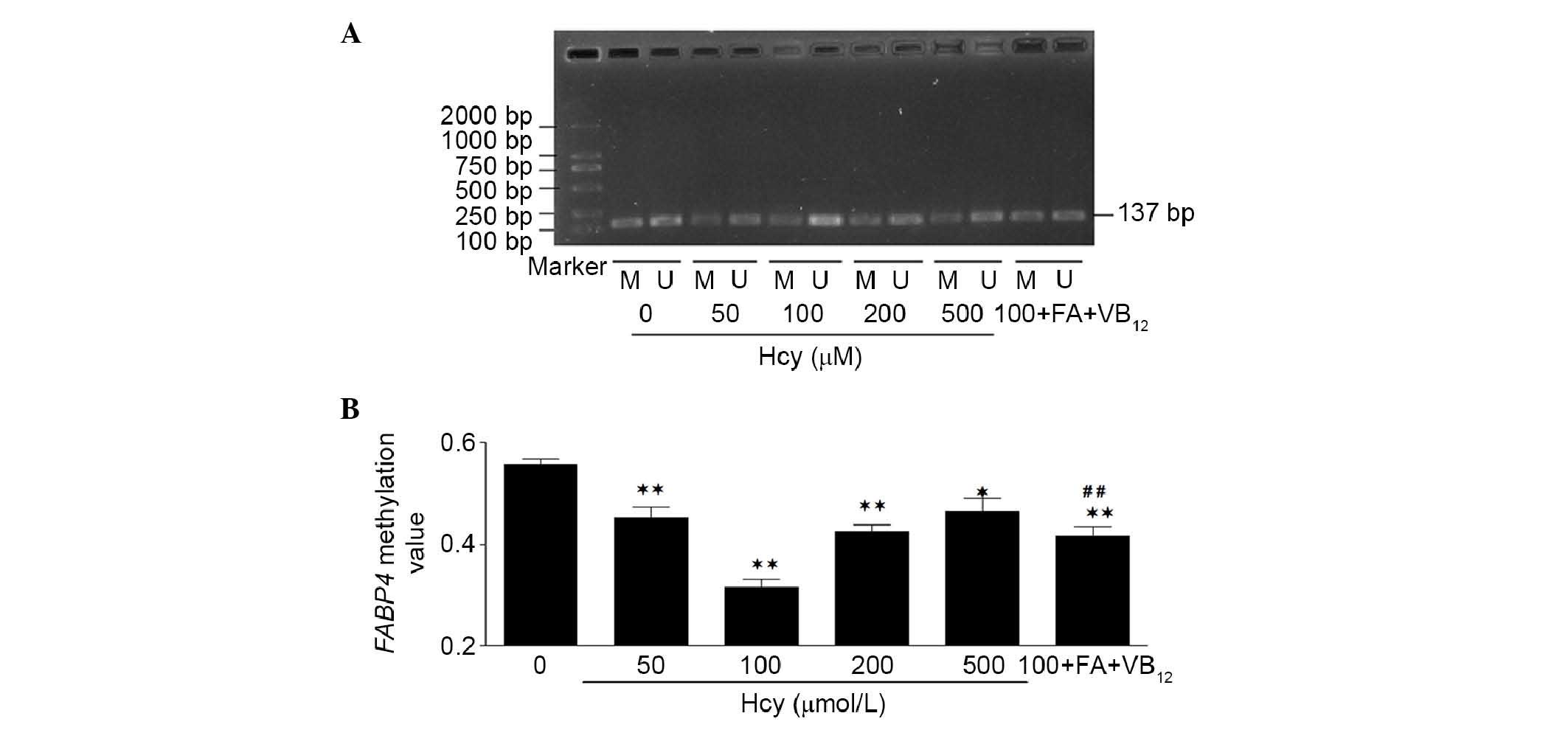
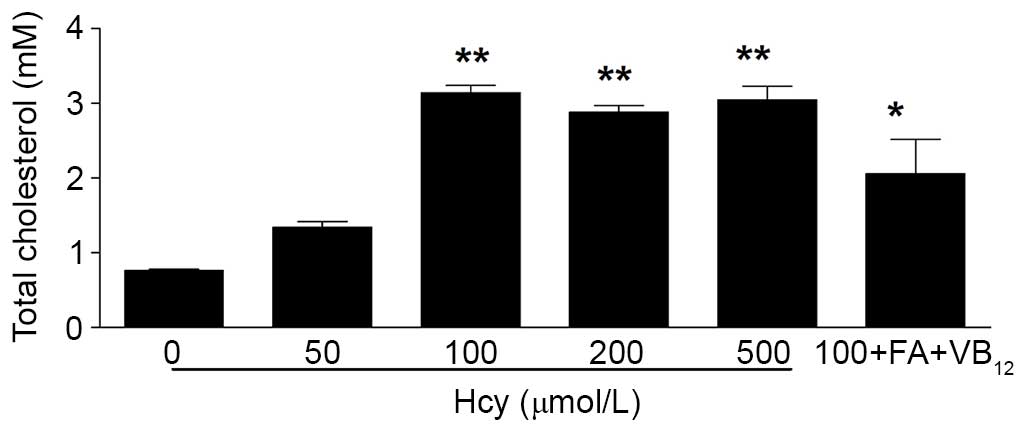
|
1
|
Furuhashi M and Hotamisligil GS: Fatty
acid-binding proteins: Role in metabolic diseases and potential as
drug targets. Nat Rev Drug Disc. 7:489–503. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Cabré A, Babio N, Lázaro I, Bulló M,
Garcia-Arellano A, Masana L and Salas-Salvadó J: FABP4 predicts
atherogenic dyslipidemia development. The PREDIMED study.
Atherosclerosis. 222:229–234. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Furuhashi M, Ishimura S, Ota H and Miura
T: Lipid chaperones and metabolic inflammation. Int J Inflam.
2011:6426122011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Fu Y, Luo N and Lopes-Virella MF: Oxidized
LDL induces the expression of ALBP/aP2 mRNA and protein in human
THP-1 macrophages. J Lipid Res. 41:2017–2023. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pelton PD, Zhou L, Demarest KT and Burris
TP: PPARgamma activation induces the expression of the adipocyte
fatty acid binding protein gene in human monocytes. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 261:456–458. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fu Y, Luo N, Lopes-Virella MF and Garvey
WT: The adipocyte lipid binding protein (ALBP/aP2) gene facilitates
foam cell formation in human THP-1 macrophages. Atherosclerosis.
165:259–269. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tehlivets O: Homocysteine as a risk factor
for atherosclerosis: Is its conversion to s-adenosyl-L-homocysteine
the key to deregulated lipid metabolism? J Lipids. 2011:7028532011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li L, Xie J, Zhang M and Wang S:
Homocysteine harasses the imprinting expression of IGF2 and H19 by
demethylation of differentially methylated region between IGF2/H19
genes. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 41:464–471. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Yi-Deng J, Tao S, Hui-Ping Z, Jian-Tuan X,
Jun C, Gui-Zhong L and Shu-Ren W: Folate and ApoE DNA methylation
induced by homo-cysteine in human monocytes. DNA Cell Biol.
26:737–744. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ma S, Zhang H, Sun W, Gong H, Wang Y, Ma
C, Wang J, Cao C, Yang X, Tian J and Jiang Y: Hyperhomocysteinemia
induces cardiac injury by up-regulation of p53-dependent Noxa and
Bax expression through the p53 DNA methylation in ApoE(−/−) mice.
Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 45:391–400. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Deng G, Nguyen A, Tanaka H, Matsuzaki K,
Bell I, Mehta KR, Terdiman JP, Waldman FM, Kakar S, Gum J, et al:
Regional hypermethylation and global hypomethylation are associated
with altered chromatin conformation and histone acetylation in
colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer. 118:2999–3005. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Subramanyam MA, Diez-Roux AV, Pilsner JR,
Villamor E, Donohue KM, Liu Y and Jenny NS: Social factors and
leukocyte DNA methylation of repetitive sequences: The multi-ethnic
study of atherosclerosis. PLoS One. 8:e540182013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sharma P, Senthil kumar RD, Brahmachari V,
Sundaramoorthy E, Mahajan A, Sharma A and Sengupta S: Mining
literature for a comprehensive pathway analysis: A case study for
retrieval of homocysteine related genes for genetic and epigenetic
studies. Lipids Health Dis. 5:12006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yideng J, Zhihong L, Jiantuan X, Jun C,
Guizhong L and Shuren W: Homocysteine-mediated PPARalpha, gamma DNA
methylation and its potential pathogenic mechanism in monocytes.
DNA Cell Biol. 27:143–150. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Jiang Y, Zhang H, Sun T, Wang J, Sun W,
Gong H, Yang B, Shi Y and Wei J: The comprehensive effects of
hyperlipidemia and hyperhomocysteinemia on pathogenesis of
atherosclerosis and DNA hypomethylation in ApoE−/− mice. Acta
Biochim Biophys Sin. 44:866–875. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Liang Y, Yang X, Ma L, Cai X, Wang L, Yang
C, Li G, Zhang M, Sun W and Jiang Y: Homocysteine-mediated
cholesterol efflux via ABCA1 and ACAT1 DNA methylation in THP-1
monocyte-derived foam cells. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai).
45:220–228. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Wang XQ, Yang K, He YS, Lu L and Shen WF:
Receptor mediated elevation in FABP4 levels by advanced glycation
end products induces cholesterol and triacylglycerol accumulation
in THP-1 macrophages. Lipids. 46:479–486. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Veeranna V, Zalawadiya SK, Niraj A,
Pradhan J, Ference B, Burack RC, Jacob S and Afonso L: Homocysteine
and reclassification of cardiovascular disease risk. J Am Coll
Cardiol. 58:1025–1033. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yang AN, Zhang HP, Sun Y, Yang XL, Wang N,
Zhu G, Zhang H, Xu H, Ma SC, Zhang Y, Li GZ, Jia YX, Cao J and
Jiang YD: High-methionine diets accelerate atherosclerosis by
HHcy-mediated FABP4 gene demethylation pathway via DNMT1 in
ApoE(−/−) mice. FEBS Lett. 589:3998–4009. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Makowski L, Brittingham KC, Reynolds JM,
Suttles J and Hotamisligil GS: The fatty acid-binding protein, aP2,
coordinates macrophage cholesterol trafficking and inflammatory
activity. Macrophage expression of aP2 impacts peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor gamma and IkappaB kinase
activities. J Biol Chem. 280:12888–12895. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fu Y, Luo N and Lopes-Virella MF: Oxidized
LDL induces the expression of ALBP/aP2 mRNA and protein in human
THP-1 macrophages. J Lipid Res. 41:2017–2023. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Miller AL: The methionine-homocysteine
cycle and its effects on cognitive diseases. Altern Med Rev.
8:7–19. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tuncman G, Erbay E, Hom X, De Vivo I,
Campos H, Rimm EB and Hotamisligil GS: A genetic variant at the
fatty acid-binding protein aP2 locus reduces the risk for
hypertriglyceridemia, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:6970–6975. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Furuhashi M, Fuseya T, Murata M, Hoshina
K, Ishimura S, Mita T, Watanabe Y, Omori A, Matsumoto M, Sugaya T,
et al: Local production of fatty acid-binding protein 4 in
epicardial/perivascular fat and macrophages is linked to coronary
atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 36:825–834. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Huang Y, Peng K, Su J, Huang Y, Xu Y and
Wang S: Different effects of homocysteine and oxidized low density
lipoprotein on methylation status in the promoter region of the
estrogen receptor a gene. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai).
39:19–26. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Yideng J, Jianzhong Z, Ying H, Juan S,
Jinge Z, Shenglan W, Xiaoqun H and Shuren W: Homocysteine-mediated
expression of SAHH, DNMTs, MBD2, and DNA hypomethylation potential
pathogenic mechanism in VSMCs. DNA Cell Biol. 26:603–611. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jiang Y, Sun T, Xiong J, Cao J, Li G and
Wang S: Hyperhomocysteinemia-mediated DNA hypomethylation and its
potential epigenetic role in rats. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin
(Shanghai). 39:657–667. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Zaina S, Lindholm MW and Lund G: Nutrition
and aberrant DNA methylation patterns in atherosclerosis: More than
just hyperhomocysteinemia? J Nutr. 135:5–8. 2005.
|
|
29
|
Moore KJ and Freeman MW: Targeting innate
immunity for CV benefit. Drug Discov Today Ther Strateg. 5:15–23.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|