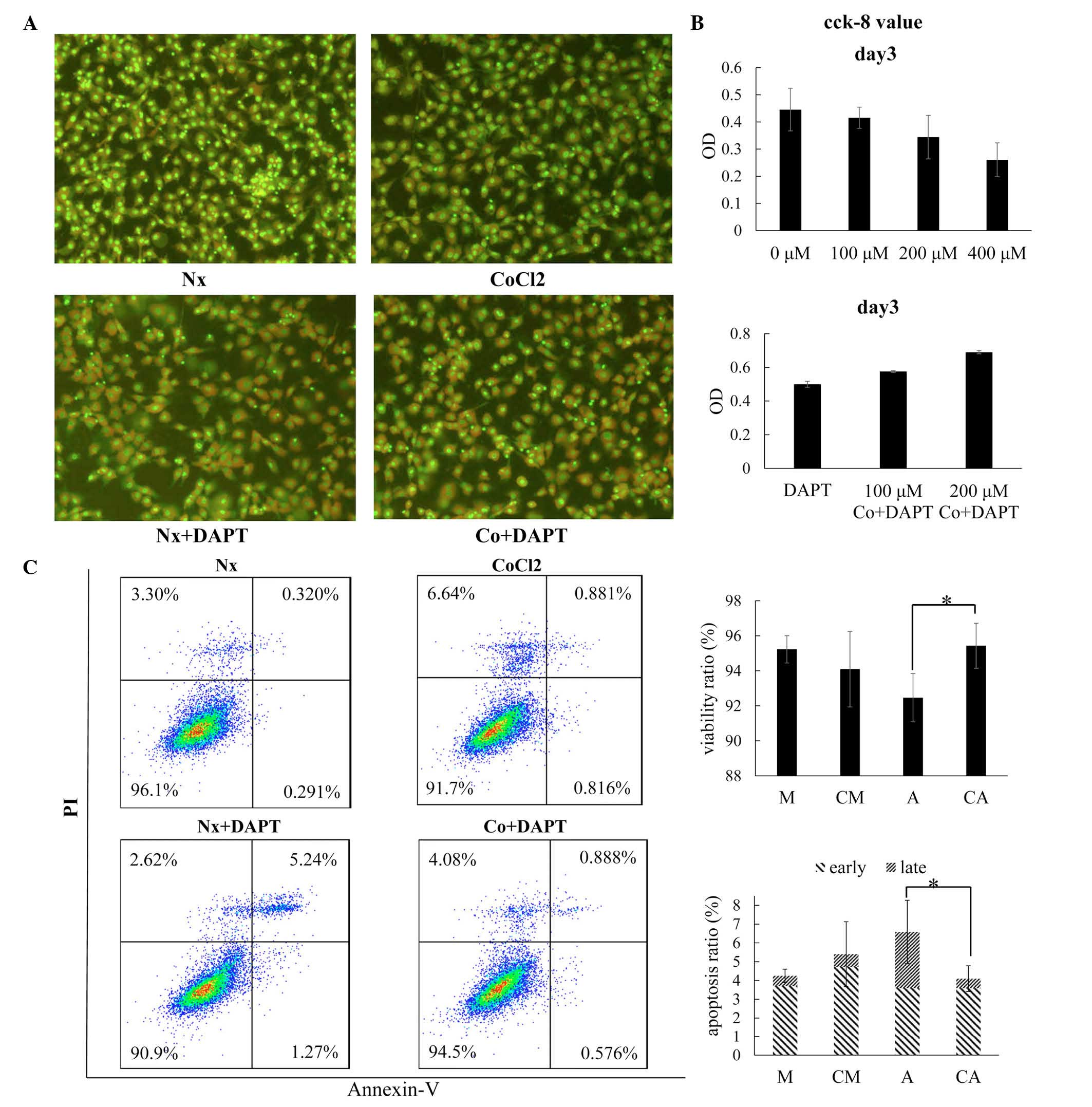
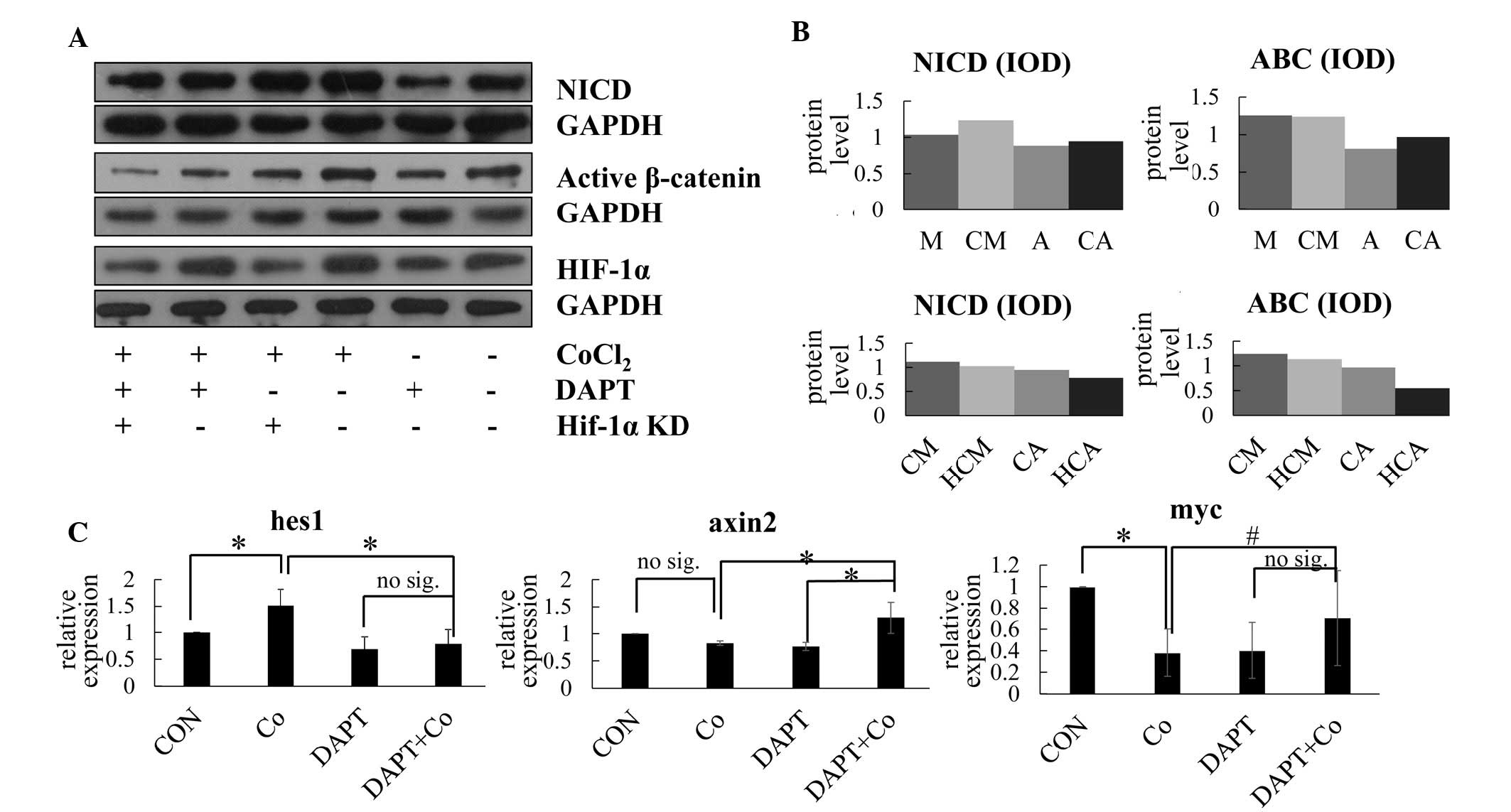
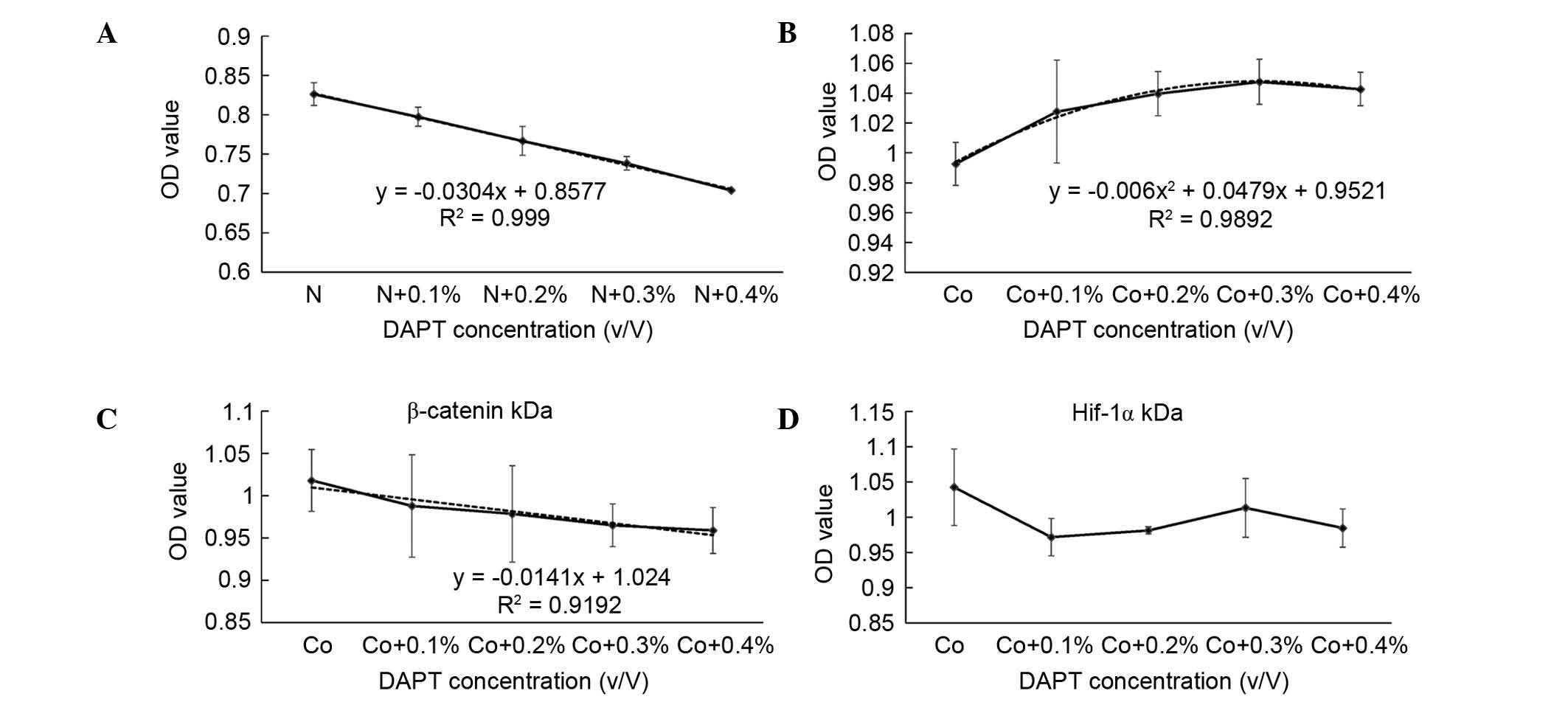
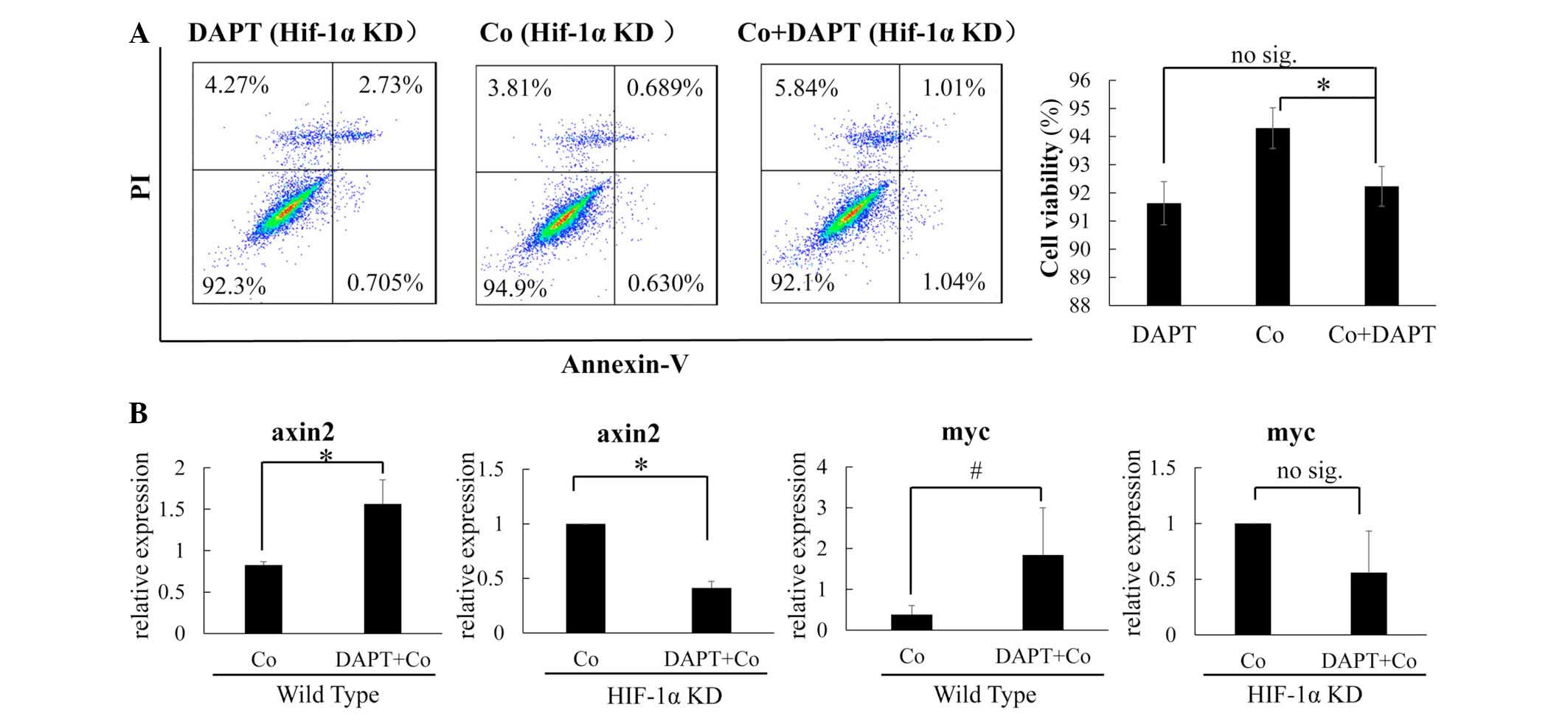
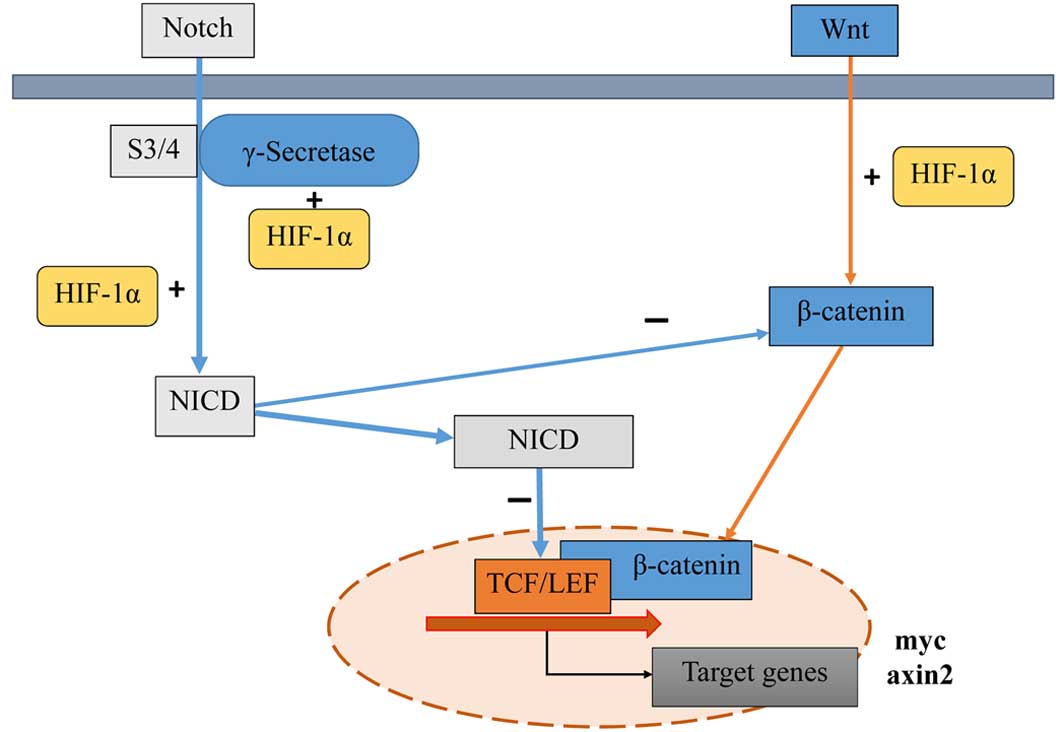
|
1
|
Collu GM, Hidalgo-Sastre A and Brennan K:
Wnt-Notch signalling crosstalk in development and disease. Cell Mol
Life Sci. 71:3553–3567. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hayward P, Kalmar T and Arias AM:
Wnt/Notch signalling and information processing during development.
Development. 135:411–424. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Deregowski V, Gazzerro E, Priest L,
Rydziel S and Canalis E: Notch 1 overexpression inhibits
osteoblastogenesis by suppressing Wnt/beta-catenin but not bone
morphogenetic protein signaling. J Biol Chem. 281:6203–6210. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lin GL and Hankenson KD: Integration of
BMP, Wnt and notch signaling pathways in osteoblast
differentiation. J Cell Biochem. 112:3491–3501. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Abdallah BM, Jafari A, Zaher W, Qiu W and
Kassem M: Skeletal (stromal) stem cells: An update on intracellular
signaling pathways controlling osteoblast differentiation. Bone.
70:28–36. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Kusumbe AP, Ramasamy SK and Adams RH:
Coupling of angiogenesis and osteogenesis by a specific vessel
subtype in bone. Nature. 507:323–328. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Maes C, Carmeliet G and Schipani E:
Hypoxia-driven pathways in bone development, regeneration and
disease. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 8:358–366. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gustafsson MV, Zheng X, Pereira T, Gradin
K, Jin S, Lundkvist J, Ruas JL, Poellinger L, Lendahl U and
Bondesson M: Hypoxia requires notch signaling to maintain the
undifferentiated cell state. Dev Cell. 9:617–628. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Villa JC, Chiu D, Brandes AH, Escorcia FE,
Villa CH, Maguire WF, Hu CJ, de Stanchina E, Simon MC, Sisodia SS,
et al: Nontranscriptional role of Hif-1α in activation of
γ-secretase and notch signaling in breast cancer. Cell Rep.
8:1077–1092. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Genetos DC, Toupadakis CA, Raheja LF, Wong
A, Papanicolaou SE, Fyhrie DP, Loots GG and Yellowley CE: Hypoxia
decreases sclerostin expression and increases Wnt signaling in
osteoblasts. J Cell Biochem. 110:457–467. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen D, Li Y, Zhou Z, Wu C, Xing Y, Zou X,
Tian W and Zhang C: HIF-1α inhibits Wnt signaling pathway by
activating Sost expression in osteoblasts. PLoS One. 8:e659402013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Chen D, Li Y, Zhou Z, Xing Y, Zhong Y, Zou
X, Tian W and Zhang C: Synergistic inhibition of Wnt pathway by
HIF-1α and osteoblast-specific transcription factor osterix (Osx)
in osteoblasts. PLoS One. 7:e529482012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Hubbi ME and Semenza GL: Regulation of
cell proliferation by hypoxia-inducible factors. Am J Physiol Cell
Physiol. 309:C775–C782. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Braunschweig L, Meyer AK, Wagenführ L and
Storch A: Oxygen regulates proliferation of neural stem cells
through Wnt/β-catenin signalling. Mol Cell Neurosci. 67:84–92.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Meldrum A, Coats P, Orr D and Horgan P:
Vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and signalling pathways –
effect of hypoxia on vascular remodelling. Atherosclerosis.
241:e762015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Canalis E: Wnt signalling in osteoporosis:
Mechanisms and novel therapeutic approaches. Nat Rev Endocrinol.
9:575–583. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Xu N, Liu H, Qu F, Fan J, Mao K, Yin Y,
Liu J, Geng Z and Wang Y: Hypoxia inhibits the differentiation of
mesenchymal stem cells into osteoblasts by activation of Notch
signaling. Exp Mol Pathol. 94:33–39. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Chan MC, Holt-Martyn JP, Schofield CJ and
Ratcliffe PJ: Pharmacological targeting of the HIF hydroxylases – a
new field in medicine development. Mol Aspects Med. Jan
11–2016.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Moriyama H, Moriyama M, Isshi H, Ishihara
S, Okura H, Ichinose A, Ozawa T, Matsuyama A and Hayakawa T: Role
of notch signaling in the maintenance of human mesenchymal stem
cells under hypoxic conditions. Stem Cells Dev. 23:2211–2224. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kim HA, Koo BK, Cho JH, Kim YY, Seong J,
Chang HJ, Oh YM, Stange DE, Park JG, Hwang D and Kong YY: Notch1
counteracts WNT/β-catenin signaling through chromatin modification
in colorectal cancer. J Clin Invest. 122:3248–3259. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kwon C, Cheng P, King IN, Andersen P,
Shenje L, Nigam V and Srivastava D: Notch post-translationally
regulates β-catenin protein in stem and progenitor cells. Nat Cell
Biol. 13:1244–1251. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Andersen P, Uosaki H, Shenje LT and Kwon
C: Non-canonical Notch signaling: Emerging role and mechanism.
Trends Cell Biol. 22:257–265. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hayward P, Brennan K, Sanders P, Balayo T,
DasGupta R, Perrimon N and Martinez Arias A: Notch modulates Wnt
signalling by associating with Armadillo/β-catenin and regulating
its transcriptional activity. Development. 132:1819–1830. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Utting JC, Robins SP, Brandao-Burch A,
Orriss IR, Behar J and Arnett TR: Hypoxia inhibits the growth,
differentiation and bone-forming capacity of rat osteoblasts. Exp
Cell Res. 312:1693–1702. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|