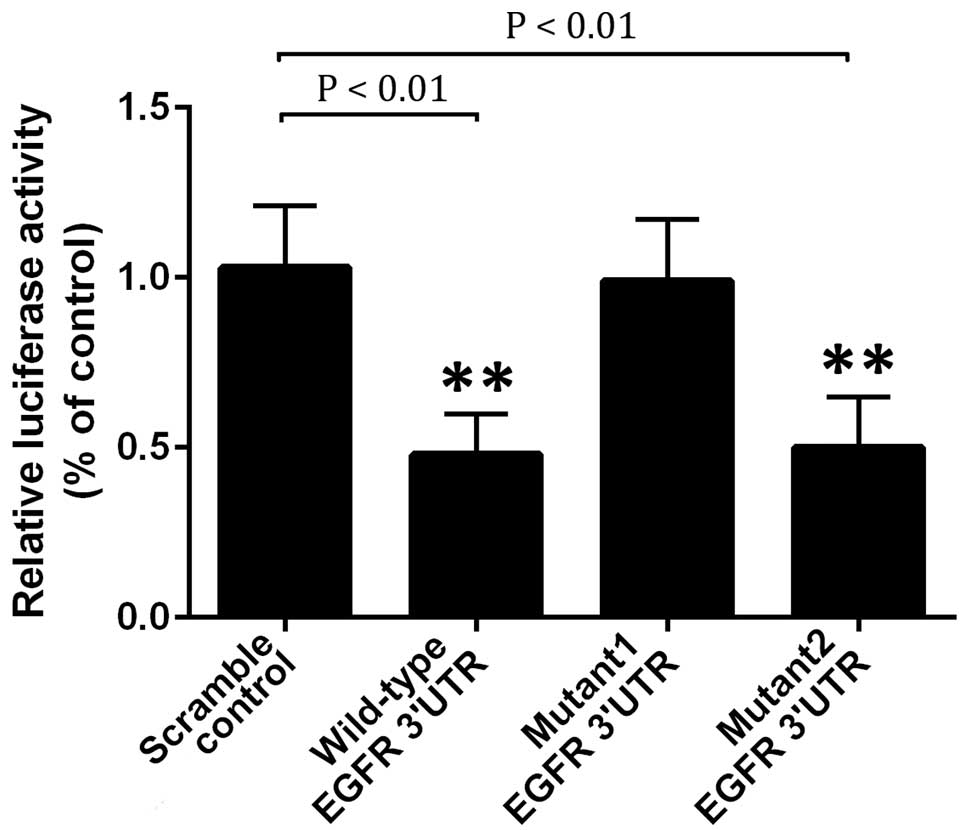
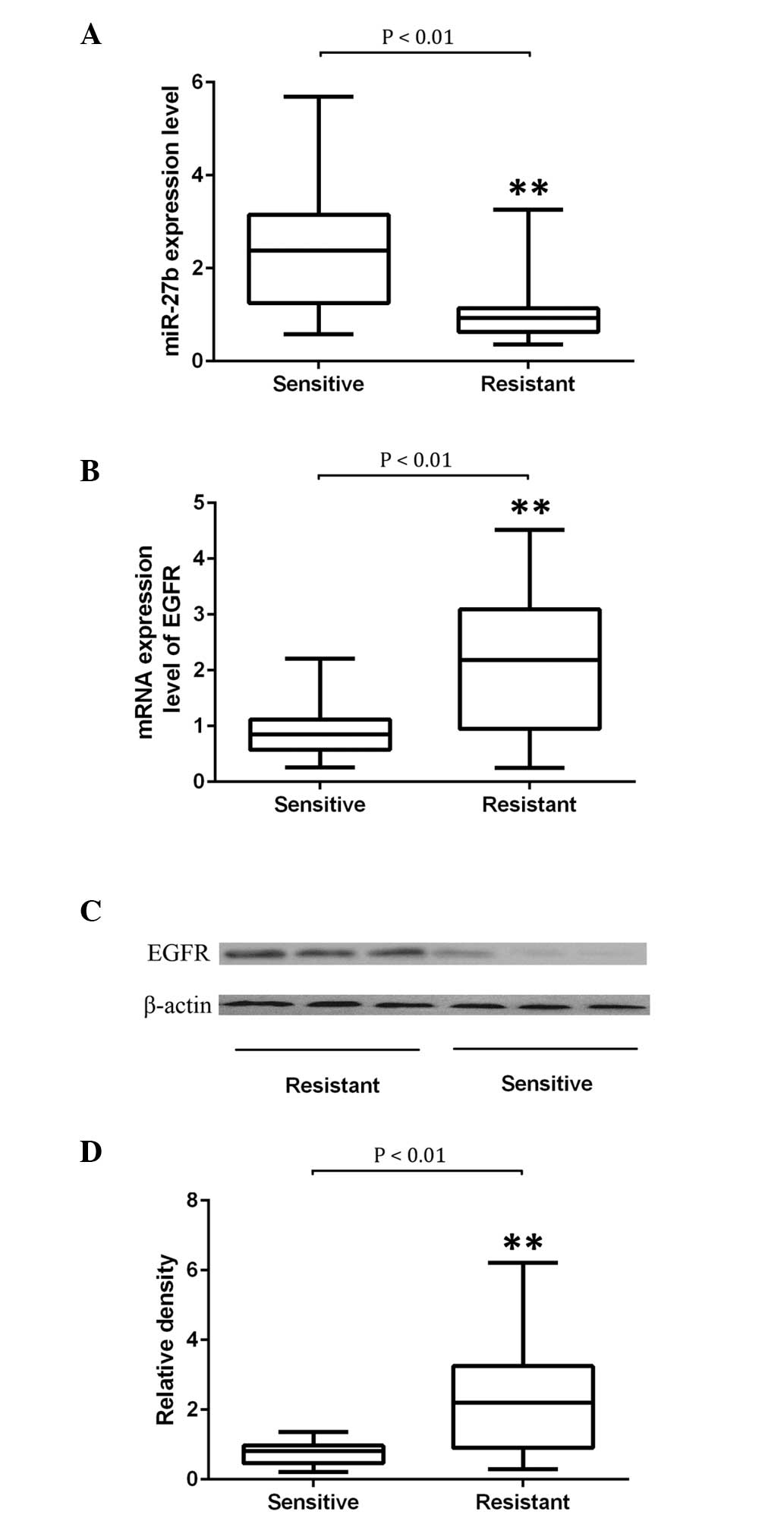
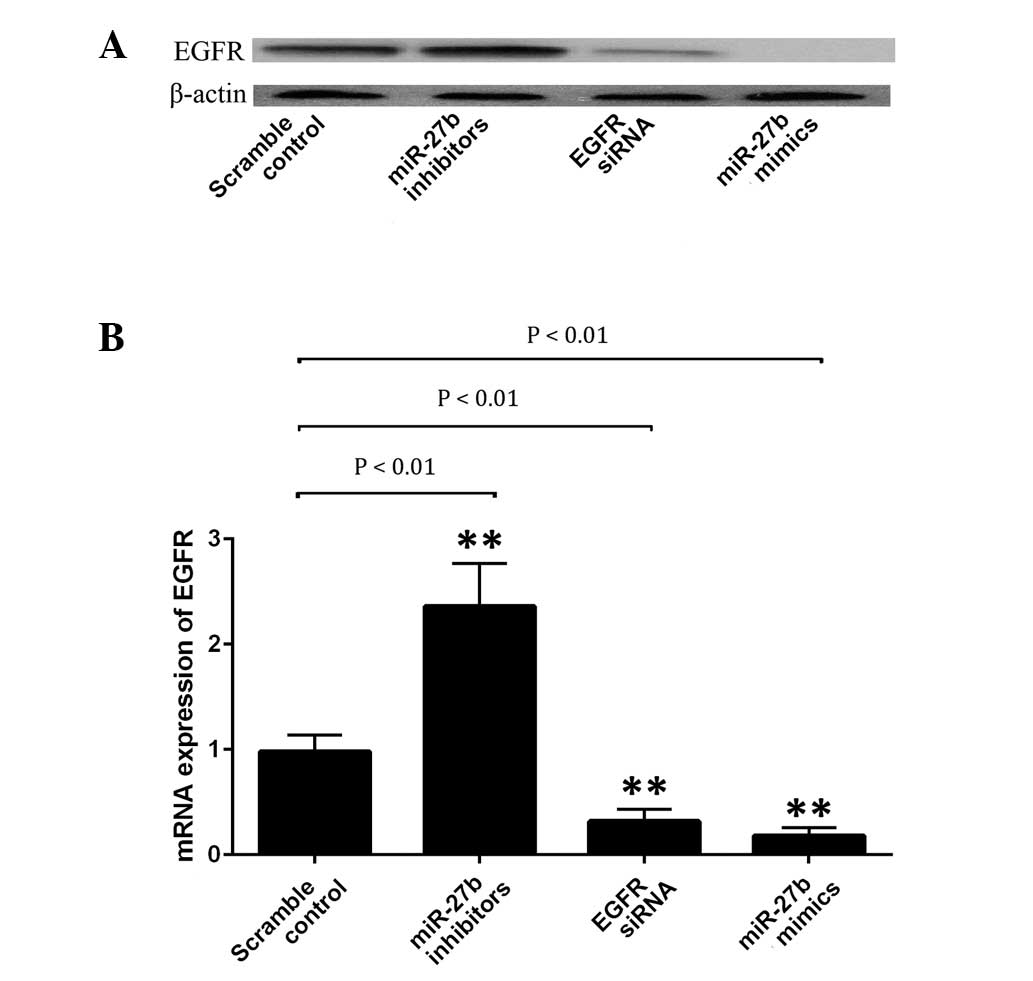
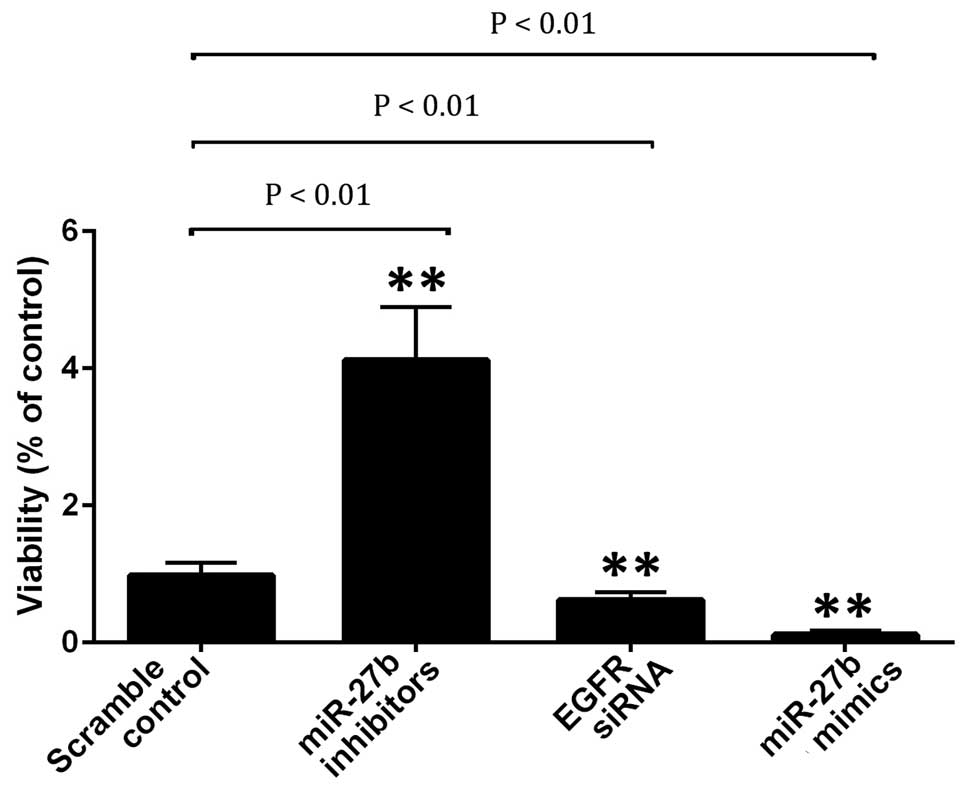
|
1
|
Jalal SI, Ademuyiwa FO and Hanna NH: The
role of maintenance chemotherapy in advanced nonsmall cell lung
cancer. Curr Opin Oncol. 21:110–115. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Edelman MJ and Gandara DR: Promising new
agents in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer
Chemother Pharmacol. 37:385–393. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Peng Y, Yu S, Li H, Xiang H, Peng J and
Jiang S: MicroRNAs: Emerging roles in adipogenesis and obesity.
Cell Signal. 26:1888–1896. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Palumbo S, Miracco C, Pirtoli L and
Comincini S: Emerging roles of microRNA in modulating cell-death
processes in malignant glioma. J Cell Physiol. 229:277–286. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Liu R, Liu X, Zheng Y, Gu J, Xiong S,
Jiang P, Jiang X, Huang E, Yang Y, Ge D and Chu Y: MicroRNA-7
sensitizes non-small cell lung cancer cells to paclitaxel. Oncol
Lett. 8:2193–2200. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ning FL, Wang F, Li ML, Yu ZS, Hao YZ and
Chen SS: MicroRNA-182 modulates chemosensitivity of human non-small
cell lung cancer to cisplatin by targeting PDCD4. Diagn Pathol.
9:1432014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang F, Li Y, Wu H, Qi K, You J, Li X, Zu
L, Pan Z, Wang Y, Li Y, et al: MiR-192 confers cisplatin resistance
by targeting Bim in lung cancer. Zhongguo fei ai za zhi.
17:384–390. 2014.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jiang Z, Yin J, Fu W, Mo Y, Pan Y, Dai L,
Huang H, Li S and Zhao J: MiRNA 17 family regulates
cisplatin-resistant and metastasis by targeting TGFβR2 in NSCLC.
PLoS One. 9:e946392014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Rui W, Bing F, Hai-Zhu S, Wei D and
Long-Bang C: Identification of microRNA profiles in
docetaxel-resistant human non-small cell lung carcinoma cells
(SPC-A1). J Cell Mol Med. 14:206–214. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Walker S: Updates in non-small cell lung
cancer. Clin J Oncol Nurs. 12:587–96. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gkiozos I, Charpidou A and Syrigos K:
Developments in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer.
Anticancer Res. 27:2823–2827. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bernstein ED, Herbert SM and Hanna NH:
Chemotherapy and radiotherapy in the treatment of resectable
non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 13:291–301. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pirker R: Adjuvant chemotherapy in
patients with completely resected non-small cell lung cancer.
Transl Lung Cancer Res. 3:305–310. 2014.
|
|
15
|
Bi N and Wang L: Superiority of
concomitant chemoradiation over sequential chemoradiation in
inoperable, locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer: Challenges
in the selection of appropriate chemotherapy. Semin Radiat Oncol.
25:122–132. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Matikas A, Mistriotis D, Georgoulias V and
Kotsakis A: Current and future approaches in the management of
non-small-cell lung cancer patients with resistance to EGFR TKIs.
Clin Lung Cancer. 16:252–261. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pilkington G, Boland A, Brown T, Oyee J,
Bagust A and Dickson R: A systematic review of the clinical
effectiveness of first-line chemotherapy for adult patients with
locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer. Thorax.
Feb 6–2015.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Paul I and Jones JM: Apoptosis block as a
barrier to effective therapy in non small cell lung cancer. World J
Clin Oncol. 5:588–594. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Horwitz SB: Taxol (paclitaxel): Mechanisms
of action. Ann Oncol. 5(Suppl 6): S3–S6. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Geney R, Ungureanu M, Li D and Ojima I:
Overcoming multidrug resistance in taxane chemotherapy. Clin Chem
Lab Med. 40:918–925. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
McGrogan BT, Gilmartin B, Carney DN and
McCann A: Taxanes, microtubules and chemoresistant breast cancer.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1785:96–132. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tay FC, Lim JK, Zhu H, Hin LC and Wang S:
Using artificial microRNA sponges to achieve microRNA
loss-of-function in cancer cells. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 81:117–127.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Wan L, Zhang L, Fan K and Wang J: MiR-27b
targets LIMK1 to inhibit growth and invasion of NSCLC cells. Mol
Cell Biochem. 390:85–91. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ye J, Wu X, Wu D, Wu P, Ni C, Zhang Z,
Chen Z, Qiu F, Xu J and Huang J: miRNA-27b targets vascular
endothelial growth factor C to inhibit tumor progression and
angiogenesis in colorectal cancer. PLoS One. 8:e606872013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ishteiwy RA, Ward TM, Dykxhoorn DM and
Burnstein KL: The microRNA-23b/-27b cluster suppresses the
metastatic phenotype of castration-resistant prostate cancer cells.
PLoS One. 7:e521062012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Lee JJ, Drakaki A, Iliopoulos D and Struhl
K: MiR-27b targets PPARγ to inhibit growth, tumor progression and
the inflammatory response in neuroblastoma cells. Oncogene.
31:3818–3825. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Jin L, Wessely O, Marcusson EG, Ivan C,
Calin GA and Alahari SK: Prooncogenic factors miR-23b and miR-27b
are regulated by Her2/Neu, EGF, and TNF-α in breast cancer. Cancer
Res. 73:2884–2896. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J and Ward E: Cancer
statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 60:277–300. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gu J, Ding JY, Lu CL, Lin ZW, Chu YW, Zhao
GY, Guo J and Ge D: Overexpression of CD88 predicts poor prognosis
in non-small-cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 81:259–265. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Edelman MJ: Novel taxane formulations and
microtubule-binding agents in non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin Lung
Cancer. 10:S30–S34. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Morales-Cano D, Calviño E, Rubio V,
Herráez A, Sancho P, Tejedor MC and Diez JC: Apoptosis induced by
paclitaxel via Bcl-2, Bax and caspases 3 and 9 activation in NB4
human leukaemia cells is not modulated by ERK inhibition. Exp
Toxicol Pathol. 65:1101–1108. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kavallaris M: Microtubules and resistance
to tubulin-binding agents. Nat Rev Cancer. 10:194–204. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wan YF, Guo XQ, Wang ZH, Ying K and Yao
MH: Effects of paclitaxel on proliferation and apoptosis in human
acute myeloid leukemia HL-60 cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 25:378–384.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Xu R, Sato N, Yanai K, Akiyoshi T, Nagai
S, Wada J, Koga K, Mibu R, Nakamura M and Katano M: Enhancement of
paclitaxel-induced apoptosis by inhibition of mitogen-activated
protein kinase pathway in colon cancer cells. Anticancer Res.
29:261–270. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|