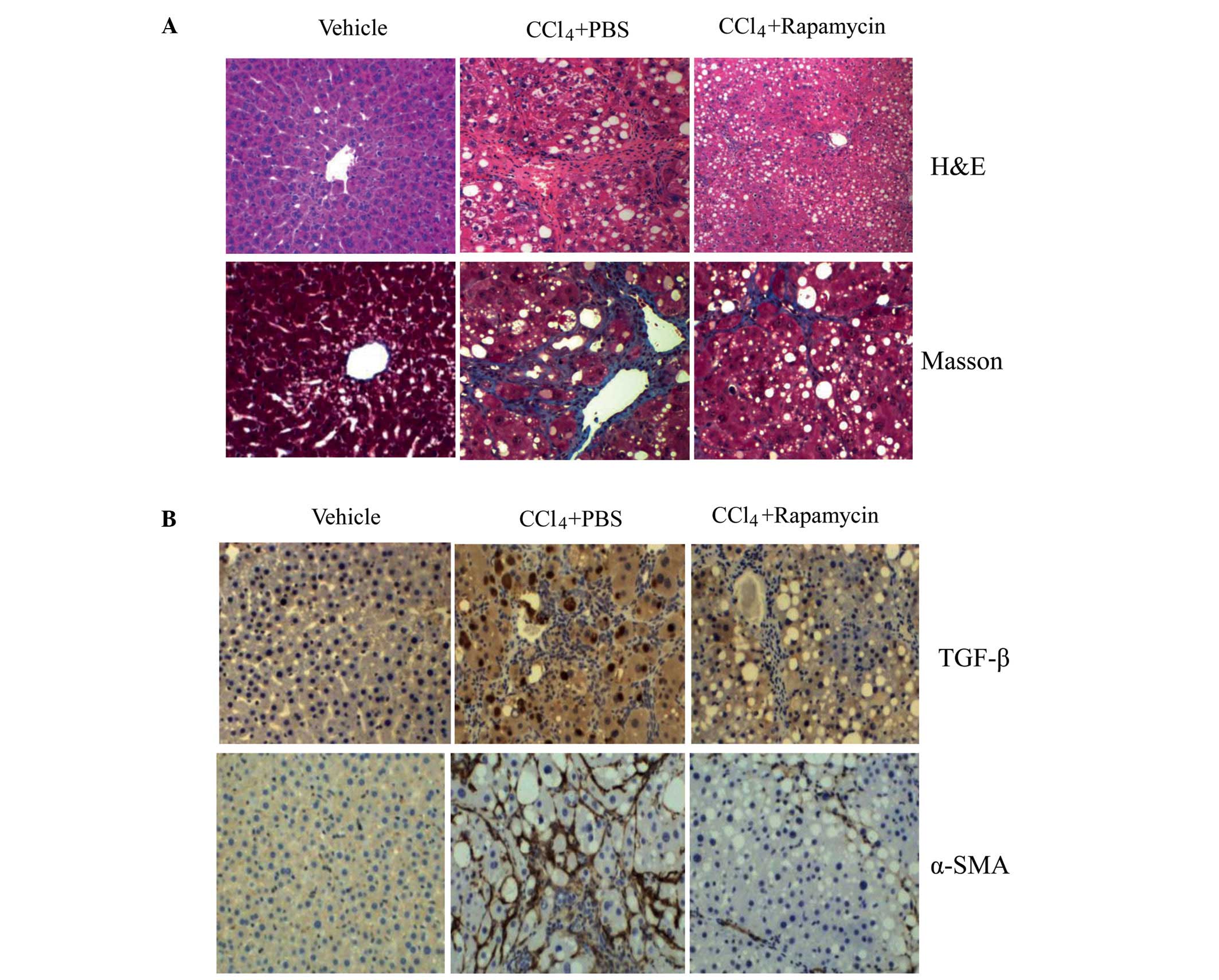
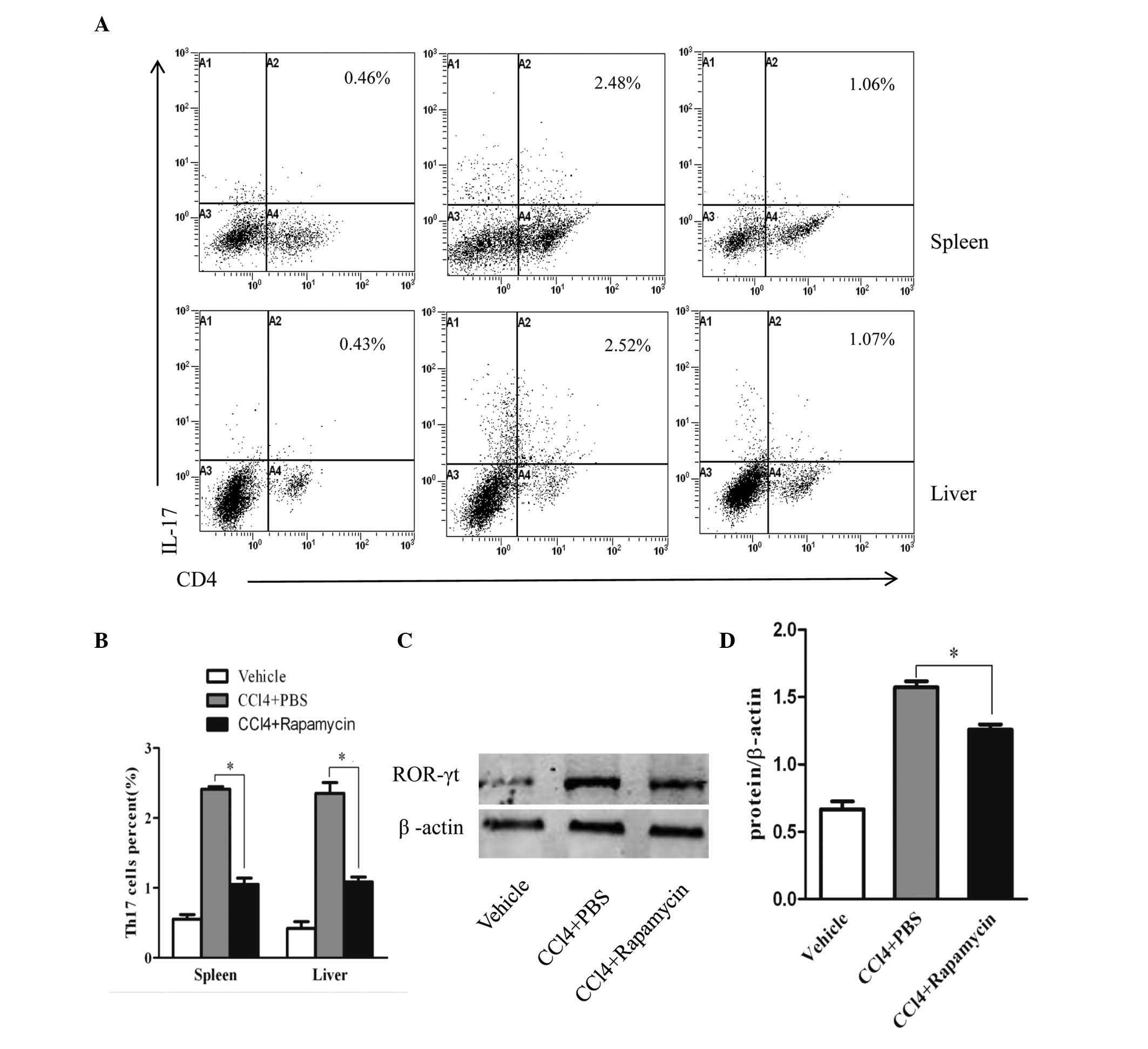
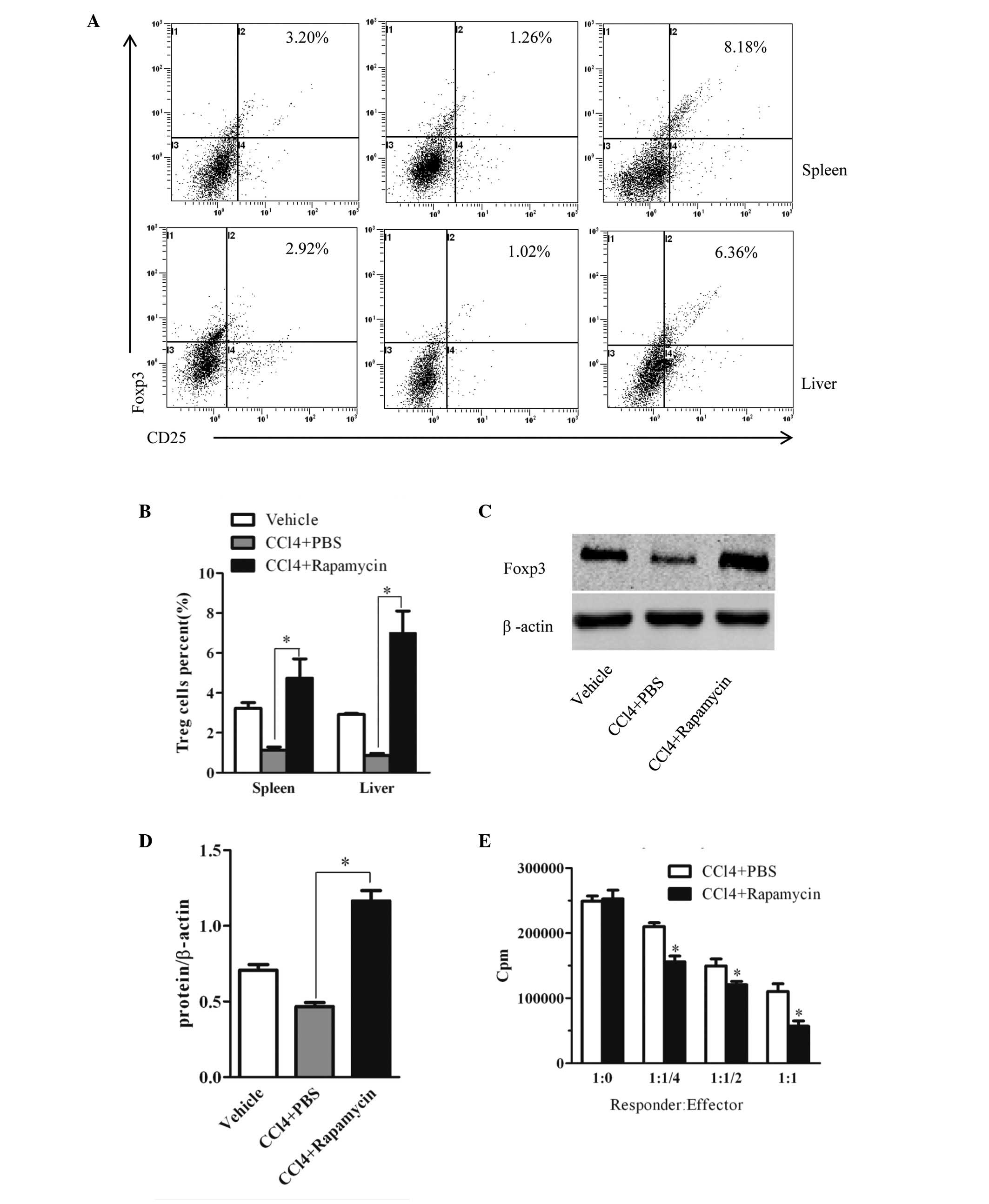
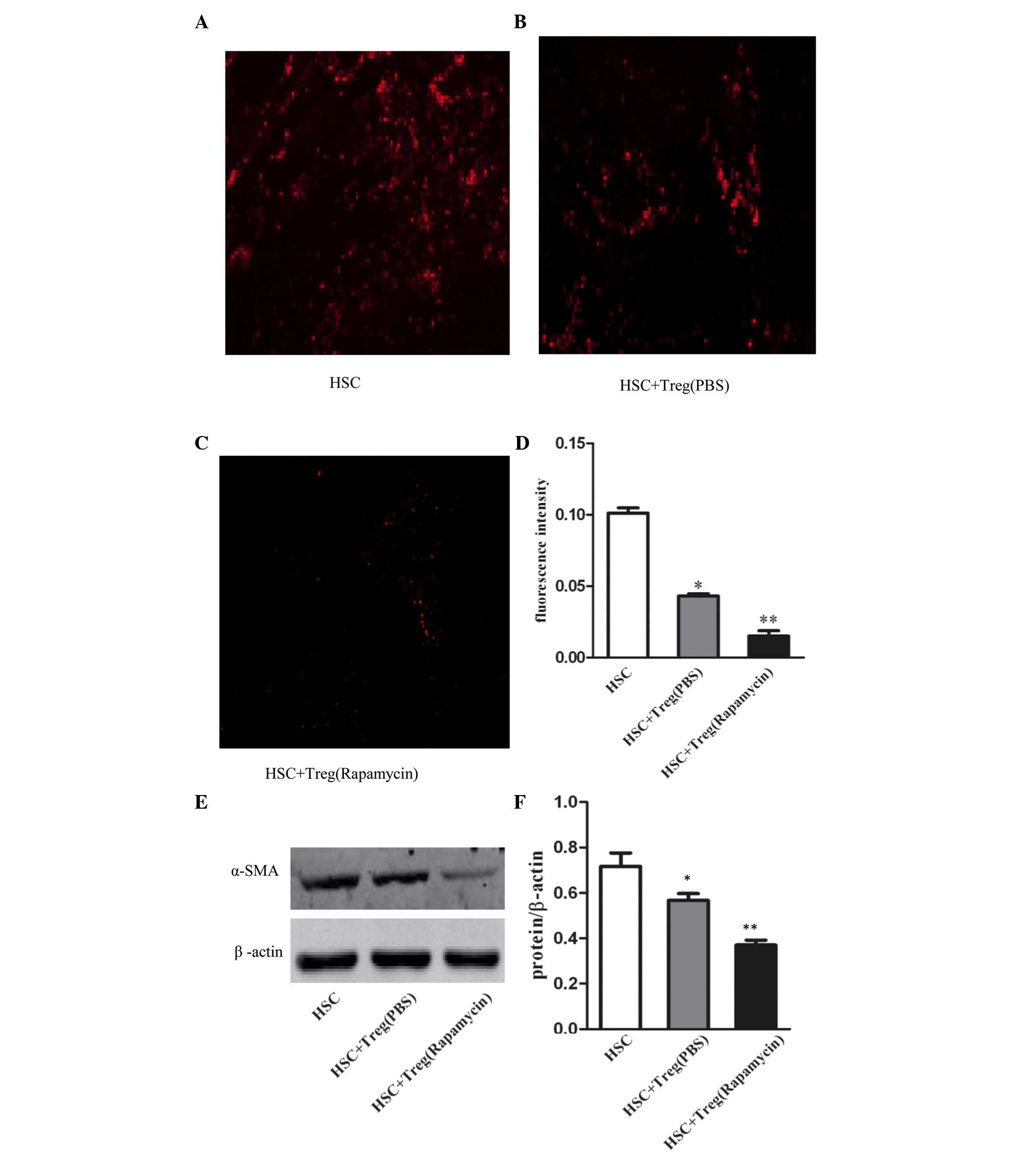
|
1
|
Racanelli V and Rehermann B: The liver as
an immunological organ. Hepatology. 43(2 Suppl 1): S54–S62. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Crispe IN: The liver as a lymphoid organ.
Annu Rev Immunol. 27:147–163. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lan RY, Salunga TL, Tsuneyama K, Lian ZX,
Yang GX, Hsu W, Moritoki Y, Ansari AA, Kemper C, Price J, et al:
Hepatic IL-17 responses in human and murine primary biliary
cirrhosis. J Autoimmun. 32:43–51. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Wang L, Chen S and Xu K: IL-17 expression
is correlated with hepatitis B-related liver diseases and fibrosis.
Int J Mol Med. 27:385–392. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sun HQ, Zhang JY, Zhang H, Zou ZS, Wang FS
and Jia JH: Increased Th17 cells contribute to disease progression
in patients with HBV-associated liver cirrhosis. J Viral Hepat.
19:396–403. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Workman CJ, Szymczak-Workman AL, Collison
LW, Pillai MR and Vignali DA: The development and function of
regulatory T cells. Cell Mol Life Sci. 66:2603–2622. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sakaguchi S, Yamaguchi T, Nomura T and Ono
M: Regulatory T cells and immune tolerance. Cell. 133:775–787.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fenoglio D, Bernuzzi F, Battaglia F,
Parodi A, Kalli F, Negrini S, De Palma R, Invernizzi P and Filaci
G: Th17 and regulatory T lymphocytes in primary biliary cirrhosis
and systemic sclerosis as models of autoimmune fibrotic diseases.
Autoimmun Rev. 12:300–304. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li J, Qiu SJ, She WM, Wang FP, Gao H, Li
L, Tu CT, Wang JY, Shen XZ and Jiang W: Significance of the balance
between regulatory T (Treg) and T helper 17 (Th17) cells during
hepatitis B virus related liver fibrosis. PLoS One. 7:e393072012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yasumi Y, Takikawa Y, Endo R and Suzuki K:
Interleukin-17 as a new marker of severity of acute hepatic injury.
Hepatol Res. 37:248–254. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sun XF, Gu L, Deng WS and Xu Q: Impaired
balance of T helper 17/T regulatory cells in carbon
tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis in mice. World J
Gastroenterol. 20:2062–2070. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shin HJ, Baker J, Leveson-Gower DB, Smith
AT, Sega EI and Negrin RS: Rapamycin and IL-2 reduce lethal acute
graft-versus-host disease associated with increased expansion of
donor type CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells. Blood.
118:2342–2350. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kopf H, de la Rosa GM, Howard OM and Chen
X: Rapamycin inhibits differentiation of Th17 cells and promotes
generation of FoxP3+ T regulatory cells. Int Immunopharmacol.
7:1819–1824. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yin H, Li X, Zhang B, Liu T, Yuan B, Ni Q,
Hu S and Gu H: Sirolimus ameliorates inflammatory responses by
switching the Treg/Th17 profile in murine colitis. Immunology.
139:494–502. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hennig M, Bauer D, Wasmuth S, Busch M,
Walscheid K, Thanos S and Heiligenhaus A: Everolimus improves
experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis. Exp Eye Res. 105:43–52.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Battaglia M, Stabilini A and Roncarolo MG:
Rapamycin selectively expands CD4+CD25+FoxP3+ regulatory T cells.
Blood. 105:4743–4748. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Qu Y, Zhang B, Zhao L, Liu G, Ma H, Rao E,
Zeng C and Zhao Y: The effect of immunosuppressive drug rapamycin
on regulatory CD4+CD25+Foxp3+T cells in mice. Transpl Immunol.
17:153–161. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ogino H, Nakamura K, Ihara E, Akiho H and
Takayanagi R: CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells suppress Th17-responses
in an experimental colitis model. Dig Dis Sci. 56:376–386. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Copple BL, Bai S, Burgoon LD and Moon JO:
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α regulates the expression of genes in
hypoxic hepatic stellate cells important for collagen deposition
and angiogenesis. Liver Int. 31:230–244. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Chen CH, Kuo LM, Chang Y, Wu W, Goldbach
C, Ross MA, Stolz DB, Chen L, Fung JJ, Lu L and Qian S: In vivo
immune modulatory activity of hepatic stellate cells in mice.
Hepatology. 44:1171–1181. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Friedman SL: Evolving challenges in
hepatic fibrosis. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 7:425–436. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mack DG, Falta MT, McKee AS, Martin AK,
Simonian PL, Crawford F, Gordon T, Mercer RR, Hoover MD, Marrack P,
et al: Regulatory T cells modulate granulomatous inflammation in an
HLA-DP2 transgenic murine model of beryllium-induced disease. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 111:8553–8558. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Eastaff-Leung N, Mabarrack N, Barbour A,
Cummins A and Barry S: Foxp3+ regulatory T cells, Th17 effector
cells and cytokine environment in inflammatory bowel disease. J
Clin Immunol. 30:80–89. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Shah K, Lee WW, Lee SH, Kim SH, Kang SW,
Craft J and Kang I: Dysregulated balance of Th17 and Th1 cells in
systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res Ther. 12:R532010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lohr J, Knoechel B, Wang JJ, Villarino AV
and Abbas AK: Role of IL-17 and regulatory T lymphocytes in a
systemic autoimmune disease. J Exp Med. 203:2785–2791. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rong G, Zhou Y, Xiong Y, Zhou L, Geng H,
Jiang T, Zhu Y, Lu H, Zhang S, Wang P, et al: Imbalance between T
helper type 17 and T regulatory cells in patients with primary
biliary cirrhosis: The serum cytokine profile and peripheral cell
population. Clin Exp Immunol. 156:217–225. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kong X, Feng D, Wang H, Hong F, Bertola A,
Wang FS and Gao B: Interleukin-22 induces hepatic stellate cell
senescence and restricts liver fibrosis in mice. Hepatology.
56:1150–1159. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fontenot JD, Gavin MA and Rudensky AY:
Foxp3 programs the development and function of CD4+CD25+ regulatory
T cells. Nat Immunol. 4:330–336. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ivanov II, McKenzie BS, Zhou L, Tadokoro
CE, Lepelley A, Lafaille JJ, Cua DJ and Littman DR: The orphan
nuclear receptor RORgammat directs the differentiation program of
proinflammatory IL-17+ T helper cells. Cell. 126:1121–1133. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yin H, Li X, Zhang B, Liu T, Yuan B, Ni Q,
Hu S and Gu H: Sirolimus ameliorates inflammatory responses by
switching the regulatory T/T helper type 17 profile in murine
colitis. Immunology. 139:494–502. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Viglietta V, Baecher-Allan C, Weiner HL
and Hafler DA: Loss of functional suppression by CD4+CD25+
regulatory T cells in patients with multiple sclerosis. J Exp Med.
199:971–979. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lawson JM, Tremble J, Dayan C, Beyan H,
Leslie RD, Peakman M and Tree TI: Increased resistance to
CD4+CD25hi regulatory T cell-mediated suppression in patients with
type 1 diabetes. Clin Exp Immunol. 154:353–359. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Smyk-Pearson S, Golden-Mason L, Klarquist
J, Burton JR Jr, Tester IA, Wang CC, Culbertson N, Vandenbark AA
and Rosen HR: Functional suppression by FoxP3+CD4+CD25 (high)
regulatory T cells during acute hepatitis C virus infection. J
Infect Dis. 197:46–57. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Battaglia M, Stabilini A, Migliavacca B,
Horejs-Hoeck J, Kaupper T and Roncarolo MG: Rapamycin promotes
expansion of functional CD4+CD25+FOXP3+ regulatory T cells of both
healthy subjects and type 1 diabetic patients. J Immunol.
177:8338–8347. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Tresoldi E, Dell'Albani I, Stabilini A,
Jofra T, Valle A, Gagliani N, Bondanza A, Roncarolo MG and
Battaglia M: Stability of human rapamycin-expanded CD4+CD25+ T
regulatory cells. Haematologica. 96:1357–1365. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Saxena A, Dobaczewski M, Rai V, Haque Z,
Chen W, Li N and Frangogiannis NG: Regulatory T cells are recruited
in the infarcted mouse myocardium and may modulate fibroblast
phenotype and function. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
307:H1233–H1242. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Huang GC, Zhang JS and Tang QQ:
Involvement of C/EBP-alpha gene in in vitro activation of rat
hepatic stellate cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 324:1309–1318.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|