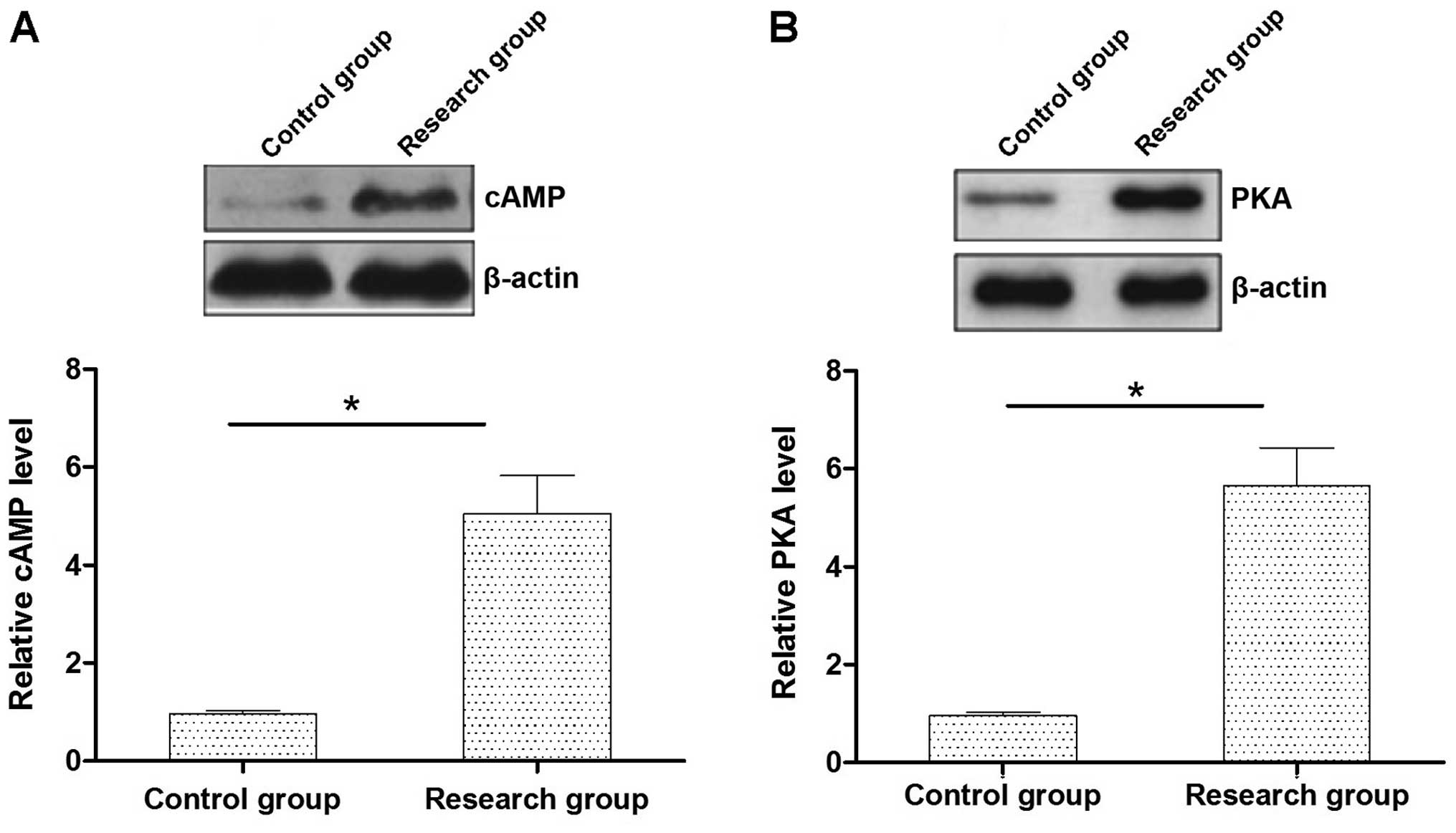
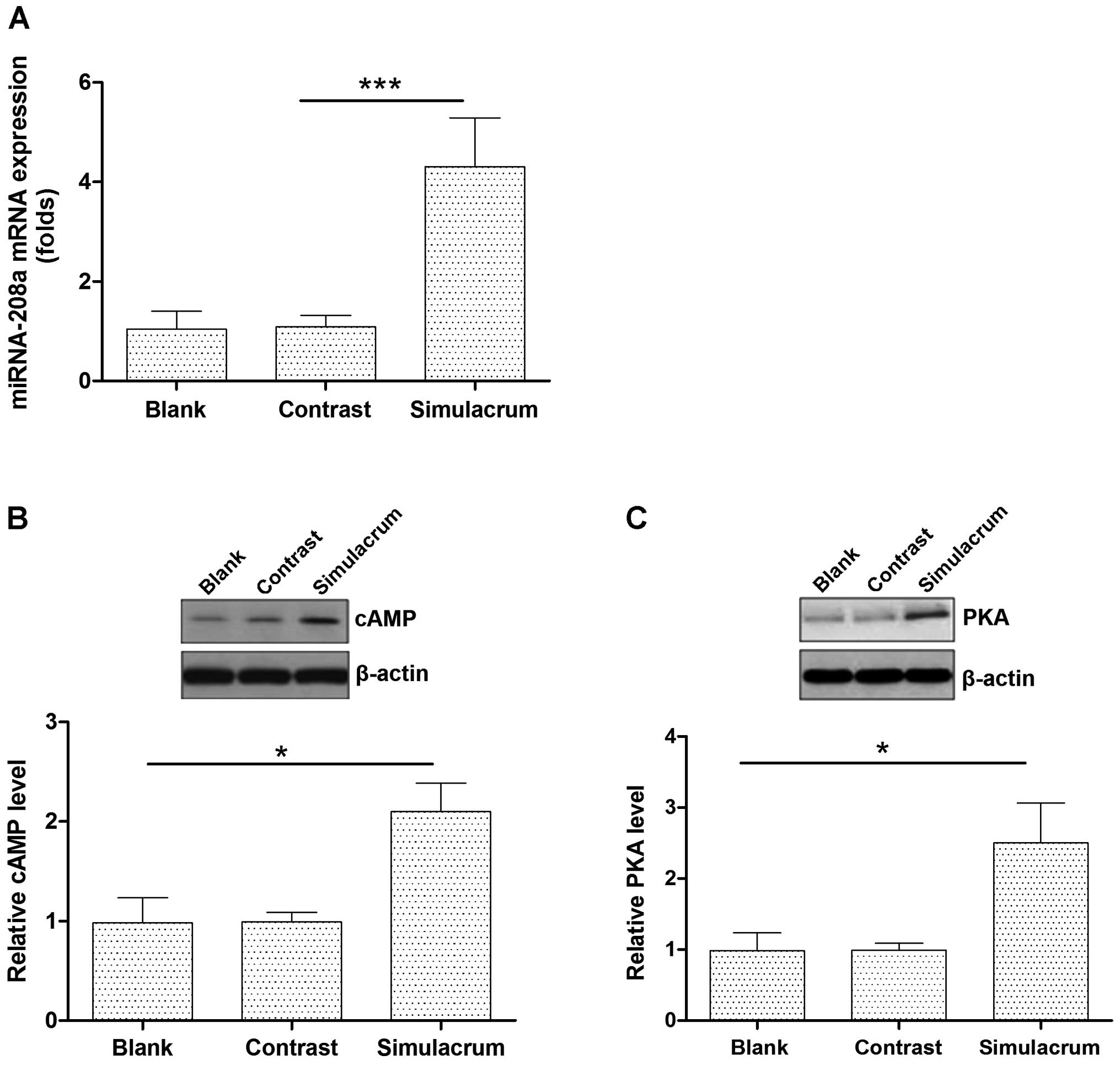
|
1
|
Li Z, Ying X, Chen H, Ye P, Shen Y, Pan W
and Zhang L: MicroRNA-194 inhibits the epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in gastric cancer cells by targeting FoxM1. Dig Dis Sci.
59:2145–2152. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lewis BP, Burge CB and Bartel DP:
Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that
thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 120:15–20.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cheng Y, Liu X, Yang J, Lin Y, Xu DZ, Lu
Q, Deitch EA, Huo Y, Delphin ES and Zhang C: MicroRNA-145, a novel
smooth muscle cell phenotypic marker and modulator, controls
vascular neointimal lesion formation. Circ Res. 105:158–166. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Suárez Y, Fernández-Hernando C, Pober JS
and Sessa WC: Dicer dependent microRNAs regulate gene expression
and functions in human endothelial cells. Circ Res. 100:1164–1173.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Callis TE, Pandya K, Seok HY, Tang RH,
Tatsuguchi M, Huang ZP, Chen JF, Deng Z, Gunn B, Shumate J, et al:
MicroRNA-208a is a regulator of cardiac hypertrophy and conduction
in mice. J Clin Invest. 119:2772–2786. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Newby AC: Metalloproteinases promote
plaque rupture and myocardial infarction: A persuasive concept
waiting for clinical translation. Matrix Biol. 44–46:157–66. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Zhang Y, Zhou ZG, Wang L, Zhang P, Wang
MJ, Cui CF, Guan JT, Chen KL and Zhan L: Clinicopathological
significance of microRNA-21 and miR-125 expression in colorectal
cancer. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 12:623–626. 2009.In
Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Du J, Yang S, An D, Hu F, Yuan W, Zhai C
and Zhu T: BMP-6 inhibits microRNA-21 expression in breast cancer
through repressing deltaEF1 and AP-1. Cell Res. 19:487–496. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang JG, Wang JJ, Zhao F, Liu Q, Jiang K
and Yang GH: MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) represses tumor suppressor PTEN
and promotes growth and invasion in non-small cell lung cancer
(NSCLC). Clin Chim Acta. 411:846–852. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bae HJ, Noh JH, Kim JK, Eun JW, Jung KH,
Kim MG, Chang YG, Shen Q, Kim SJ, Park WS, et al: MicroRNA-29c
functions as a tumor suppressor by direct targeting oncogenic SIRT1
in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene. 33:2557–2567. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Fan DN, Tsang FH, Tam AH, Au SL, Wong CC,
Wei L, Lee JM, He X, Ng IO and Wong CM: Histone lysine
methyltransferase, suppressor of variegation 3–9 homolog 1,
promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression and is negatively
regulated by microRNA-125b. Hepatology. 57:637–647. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Zhu H and Fan GC: Role of microRNAs in the
reperfused myocardium towards post-infarct remodelling. Cardiovasc
Res. 94:284–292. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
14
|
Rane S, He M, Sayed D, Vashistha H,
Malhotra A, Sadoshima J, Vatner DE, Vatner SF and Abdellatif M:
Downregulation of miR-199a derepresses hypoxia-inducible
factor-1alpha and Sirtuin 1 and recapitulates hypoxia
preconditioning in cardiac myocytes. Circ Res. 104:879–886. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Raghunandan R and Ingram VM:
Hyperphosphorylation of the cytoskeletal protein Tau by the
MAP-kinase PK40erk2: regulation by prior phosphorylation with
cAMP-dependent protein kinase A. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
215:1056–1066. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fantidis P: The role of intracellular
3′5′-cyclic adenosine mono-phosphate (cAMP) in atherosclerosis.
Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 8:464–472. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|