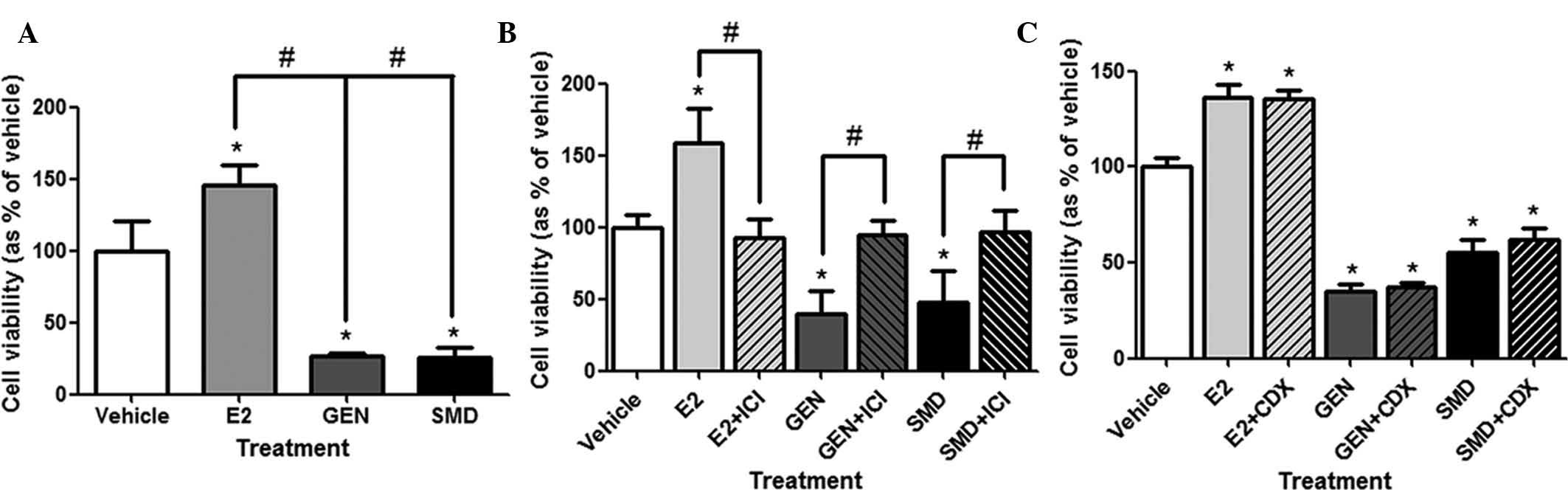
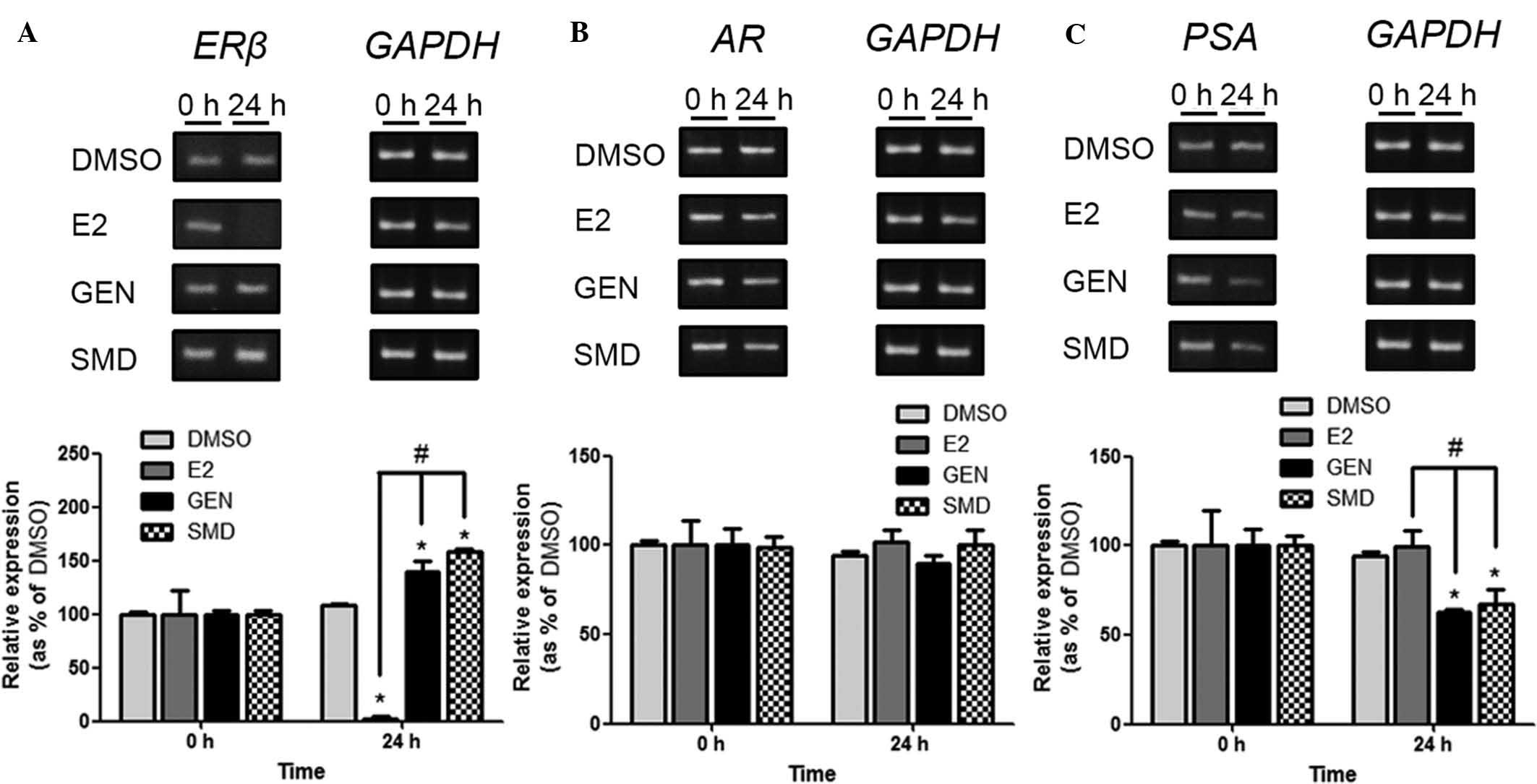
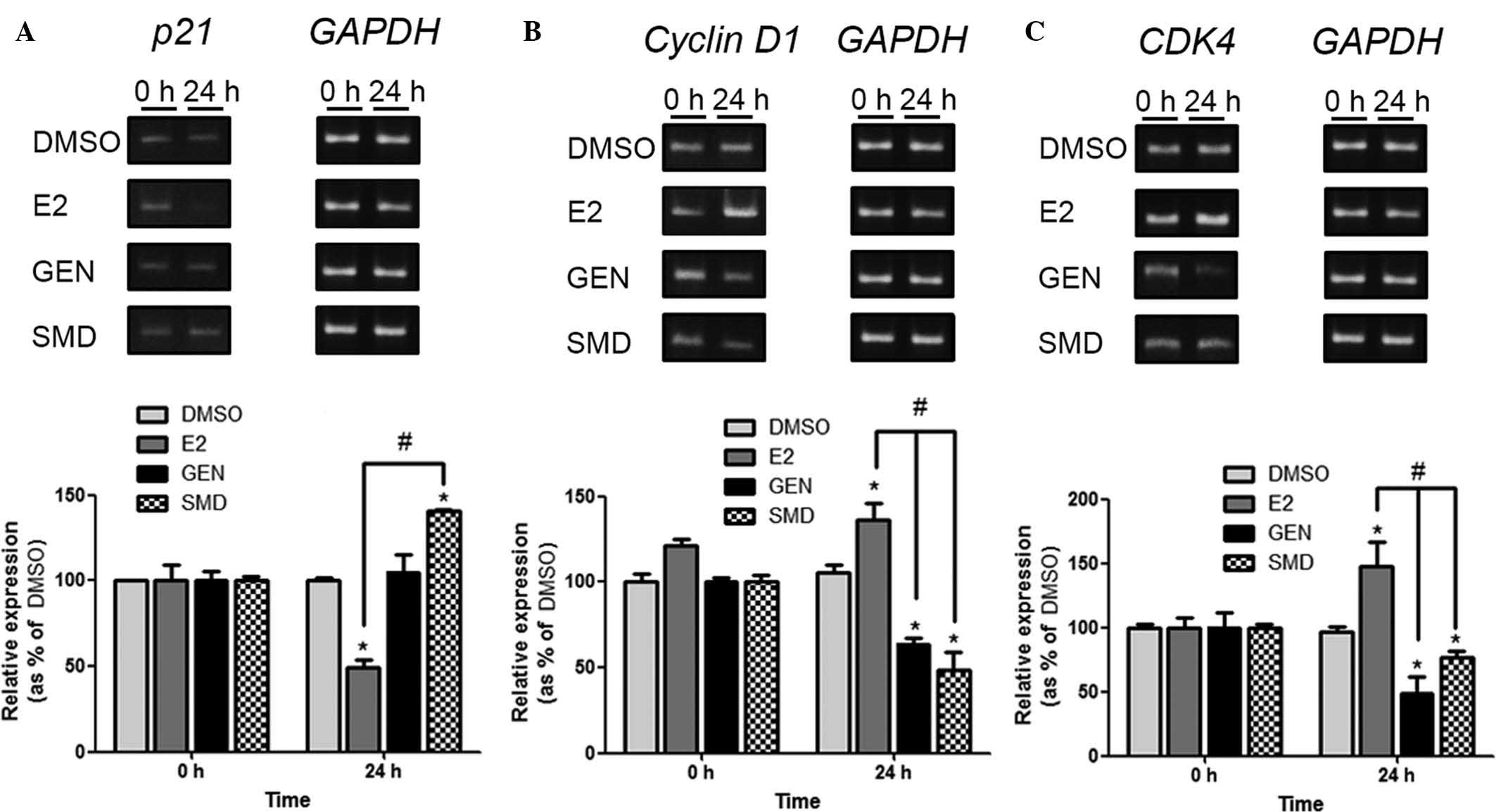
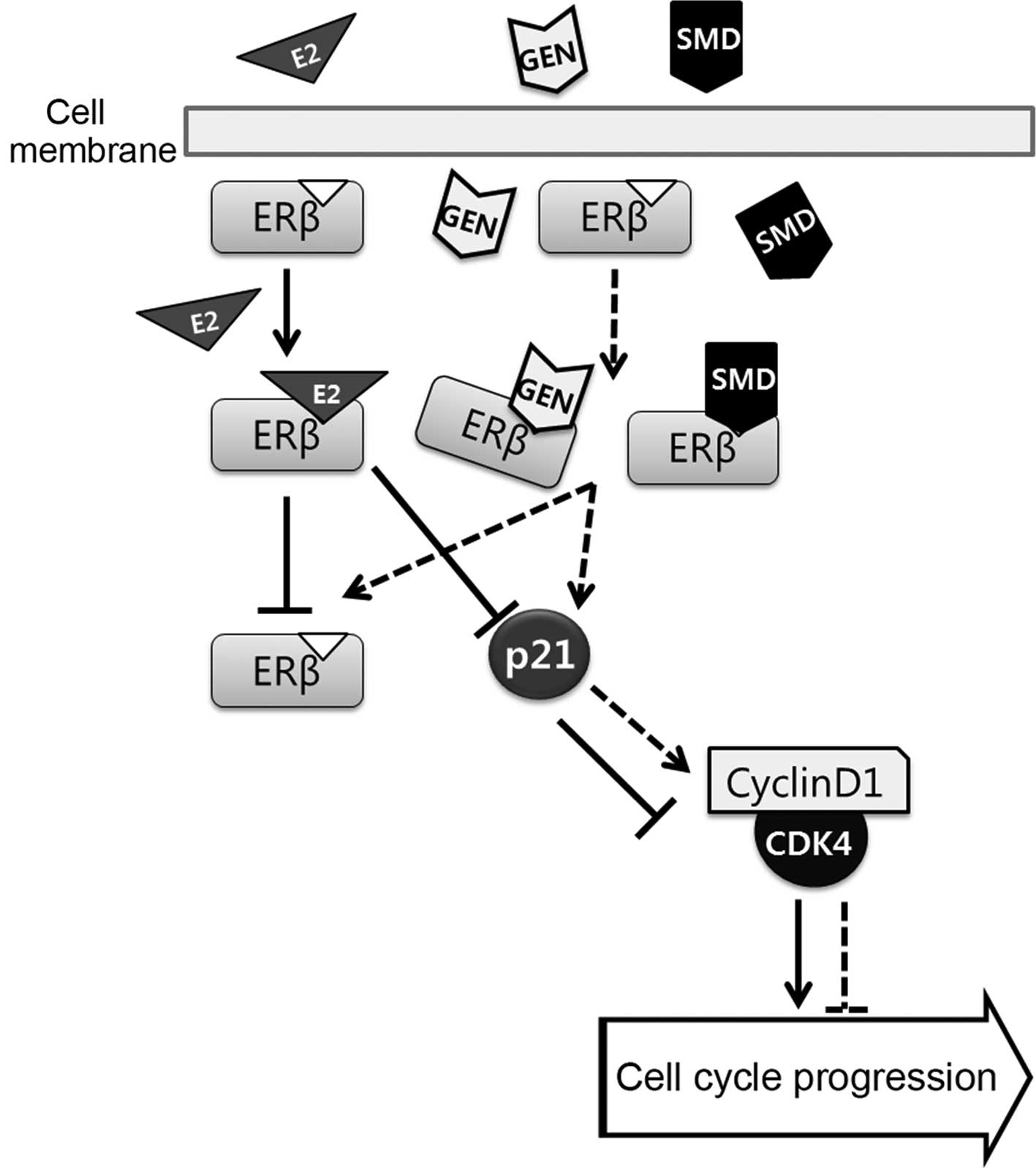
|
1
|
Ogimoto I, Shibata A and Fukuda K: World
Cancer Research fund/american institute of cancer research 1997
recommendations: Applicability to digestive tract cancer in Japan.
Cancer Causes Control. 11:9–23. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Torfadottir JE, Steingrimsdottir L, Mucci
L, Aspelund T, Kasperzyk JL, Olafsson O, Fall K, Tryggvadottir L,
Harris TB, Launer L, et al: Milk intake in early life and risk of
advanced prostate cancer. Am J Epidemiol. 175:144–153. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
3
|
Chung MS, Lee SH, Lee DH, Kim SJ, Kim CS,
Lee KS, Jung JI, Kim SW, Lee YS and Chung BH: Practice patterns of
Korean urologists for screening and managing prostate cancer
according to PSA level. Yonsei Med J. 53:1136–1141. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Castro B, Sánchez P, Torres JM, Preda O,
del Moral RG and Ortega E: Bisphenol A exposure during adulthood
alters expression of aromatase and 5α-reductase isozymes in rat
prostate. PLoS One. 8:e559052013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Saad F and Asselah J: Chemotherapy for
prostate cancer: Clinical practice in Canada. Can Urol Assoc J.
7:S5–S10. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Weng C, Cai J, Wen J, Yuan H, Yang K,
Imperato-McGinley J and Zhu YS: Differential effects of estrogen
receptor ligands on regulation of dihydrotestosterone-induced cell
proliferation in endothelial and prostate cancer cells. Int J
Oncol. 42:327–337. 2013.
|
|
7
|
Basak S, Pookot D, Noonan EJ and Dahiya R:
Genistein down-regulates androgen receptor by modulating
HDAC6-Hsp90 chaperone function. Mol Cancer Ther. 7:3195–3202. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Matsumura K, Tanaka T, Kawashima H and
Nakatani T: Involvement of the estrogen receptor beta in
genistein-induced expression of p21 (waf1/cip1) in PC-3 prostate
cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 28:709–714. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Messina MJ: Legumes and soybeans: Overview
of their nutritional profiles and health effects. Am J Clin Nutr.
70(Suppl 3): S439–S450. 1999.
|
|
10
|
Smith S, Sepkovic D, Bradlow HL and Auborn
KJ: 3,3′-Diindolylmethane and genistein decrease the adverse
effects of estrogen in LNCaP and PC-3 prostate cancer cells. J
Nutr. 138:2379–2385. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ahmad A, Biersack B, Li Y, Bao B, Kong D,
Ali S, Banerjee S and Sarkar FH: Perspectives on the role of
isoflavones in prostate cancer. AAPS J. 15:991–1000. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hwang KA, Kang NH, Yi BR, Lee HR, Park MA
and Choi KC: Genistein, a soy phytoestrogen, prevents the growth of
BG-1 ovarian cancer cells induced by 17β-estradiol or bisphenol A
via the inhibition of cell cycle progression. Int J Oncol.
42:733–740. 2013.
|
|
13
|
Hwang KA, Park MA, Kang NH, Yi BR, Hyun
SH, Jeung EB and Choi KC: Anticancer effect of genistein on BG-1
ovarian cancer growth induced by 17 β-estradiol or bisphenol A via
the suppression of the crosstalk between estrogen receptor α and
insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor signaling pathways. Toxicol
Appl Pharmacol. 272:637–646. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kang NH, Hwang KA, Kim TH, Hyun SH, Jeung
EB and Choi KC: Induced growth of BG-1 ovarian cancer cells by
17β-estradiol or various endocrine disrupting chemicals was
reversed by resveratrol via downregulation of cell cycle
progression. Mol Med Rep. 6:151–156. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kang NH, Hwang KA, Lee HR, Choi DW and
Choi KC: Resveratrol regulates the cell viability promoted by
17β-estradiol or bisphenol A via down-regulation of the cross-talk
between estrogen receptor α and insulin growth factor-1 receptor in
BG-1 ovarian cancer cells. Food Chem Toxicol. 59:373–379. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Seo YJ, Kim BS, Chun SY, Park YK, Kang KS
and Kwon TG: Apoptotic effects of genistein, biochanin-A and
apigenin on LNCaP and PC-3 cells by p21 through transcriptional
inhibition of polo-like kinase-1. J Korean Med Sci. 26:1489–1494.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liu ZM, Ho SC, Chen YM and Woo J: A
six-month randomized controlled trial of whole soy and isoflavones
daidzein on body composition in equol-producing postmenopausal
women with prehypertension. J Obes. 3597632013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Matthews VL, Knutsen SF, Beeson WL and
Fraser GE: Soy milk and dairy consumption is independently
associated with ultrasound attenuation of the heel bone among
postmenopausal women: The adventist health study-2. Nutr Res.
31:766–775. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Keshavarz SA, Nourieh Z, Attar MJ and
Azadbakht L: Effect of soymilk consumption on waist circumference
and cardiovascular risks among overweight and obese female adults.
Int J Prev Med. 3:798–805. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jacobsen BK, Knutsen SF and Fraser GE:
Does high soy milk intake reduce prostate cancer incidence? The
adventist health study (United States). Cancer Causes Control.
9:553–557. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Sugiyama Y, Masumori N, Fukuta F, Yoneta
A, Hida T, Yamashita T, Minatoya M, Nagata Y, Mori M, Tsuji H, et
al: Influence of isoflavone intake and equol-producing intestinal
flora on prostate cancer risk. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 14:1–4.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cassidy A, Brown JE, Hawdon A, Faughnan
MS, King LJ, Millward J, Zimmer-Nechemias L, Wolfe B and Setchell
KD: Factors affecting the bioavailability of soy isoflavones in
humans after ingestion of physiologically relevant levels from
different soy foods. J Nutr. 136:45–51. 2006.
|
|
23
|
deVere White RW, Tsodikov A, Stapp EC,
Soares SE, Fujii H and Hackman RM: Effects of a high dose,
aglycone-rich soy extract on prostate-specific antigen and serum
isoflavone concentrations in men with localized prostate cancer.
Nutr Cancer. 62:1036–1043. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Rodriguez-Roque MJ, Rojas-Graü MA,
Elez-Martinez P and Martin-Belloso O: Soymilk phenolic compounds,
isoflavones and antioxidant activity as affected by in vitro
gastrointestinal digestion. Food Chem. 136:206–212. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Park MA, Hwang KA and Choi KC: Diverse
animal models to examine potential role (s) and mechanism of
endocrine disrupting chemicals on the tumor progression and
prevention: Do they have tumorigenic or anti-tumorigenic property?
Lab Anim Res. 27:265–273. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Lee HR, Kim TH and Choi KC: Functions and
physiological roles of two types of estrogen receptors, ERα and
ERβ, identified by estrogen receptor knockout mouse. Lab Anim Res.
28:71–76. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hwang KA, Park SH, Yi BR and Choi KC: Gene
alterations of ovarian cancer cells expressing estrogen receptors
by estrogen and bisphenol a using microarray analysis. Lab Anim
Res. 27:99–107. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cheng J, Lee EJ, Madison LD and Lazennec
G: Expression of estrogen receptor beta in prostate carcinoma cells
inhibits invasion and proliferation and triggers apoptosis. FEBS
Lett. 566:169–172. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tate PL, Bibb R and Larcom LL: Milk
stimulates growth of prostate cancer cells in culture. Nutr Cancer.
63:1361–1366. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kang NH, Hwang KA, Yi BR, Lee HJ, Jeung
EB, Kim SU and Choi KC: Human amniotic fluid-derived stem cells
expressing cytosine deaminase and thymidine kinase inhibits the
growth of breast cancer cells in cellular and xenograft mouse
models. Cancer Gene Ther. 19:412–419. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Takagi A, Kano M and Kaga C: Possibility
of breast cancer prevention: use of soy isoflavones and fermented
soy beverage produced using probiotics. Int J Mol Sci.
16:10907–10920. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Butkutė B, Lemežienė N, Dabkevičienė G, et
al: Source of variation of isoflavone concentrations in perennial
clover species. Pharmacogn Mag. 10(Suppl 1): S181–S188. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Mahmoud AM, Yang W and Bosland MC: Soy
isoflavones and prostate cancer: A review of molecular mechanisms.
J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 140:116–132. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang Q, Ge X, Tian X, Zhang Y, Zhang J and
Zhang P: Soy isoflavone: The multipurpose phytochemical (Review).
Biomed Rep. 1:697–701. 2013.
|
|
35
|
Castagnetta LA, Miceli MD, Sorci CM,
Pfeffer U, Farruggio R, Oliveri G, Calabrò M and Carruba G: Growth
of LNCaP human prostate cancer cells is stimulated by estradiol via
its own receptor. Endocrinology. 136:2309–2319. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gao AM, Ke ZP, Shi F, Sun GC and Chen H:
Chrysin enhances sensitivity of BEL-7402/ADM cells to doxorubicin
by suppressing PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 and ERK/Nrf2 pathway. Chem Biol
Interact. 206:100–108. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chang Y and Choue R: Plasma
pharmacokinetics and urinary excretion of isoflavones after
ingestion of soy products with different aglycone/glucoside ratios
in South Korean women. Nutr Res Pract. 7:393–399. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Liu D, Liu J, Lin B, et al: Lewis y
regulate cell cycle related factors in ovarian carcinoma cell RMG-I
in Vitro via ERK and Akt signaling pathways. Int J Mol Sci.
13:828–839. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Li W, Winters A, Poteet E, Ryou MG, Lin S,
Hao S, Wu Z, Yuan F, Hatanpaa KJ, Simpkins JW and Yang SH:
Involvement of estrogen receptor β5 in the progression of glioma.
Brain Res. 1503:97–107. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Sherr CJ: The Pezcoller lecture: Cancer
cell cycles revisited. Cancer Res. 60:3689–3695. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|