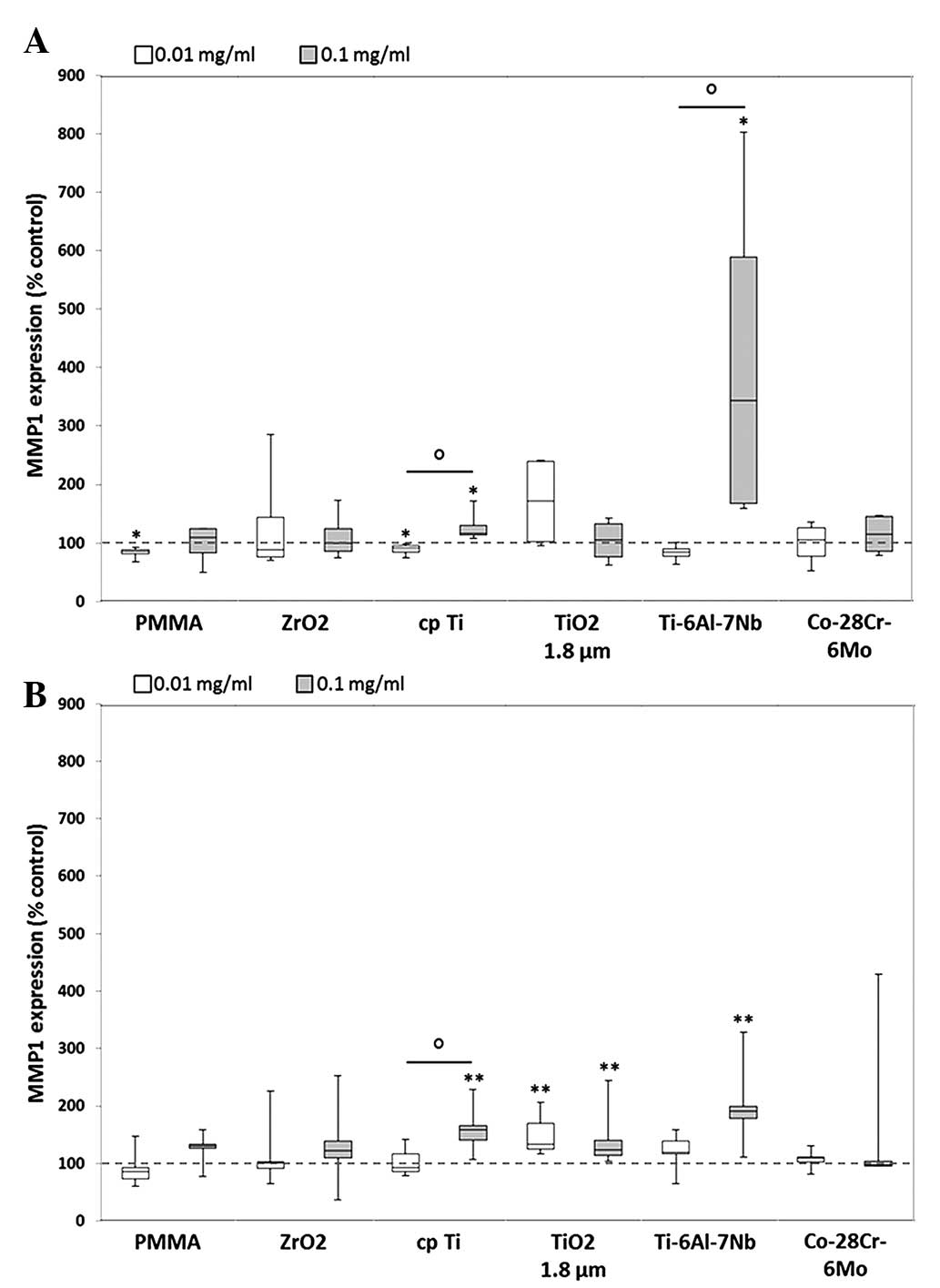
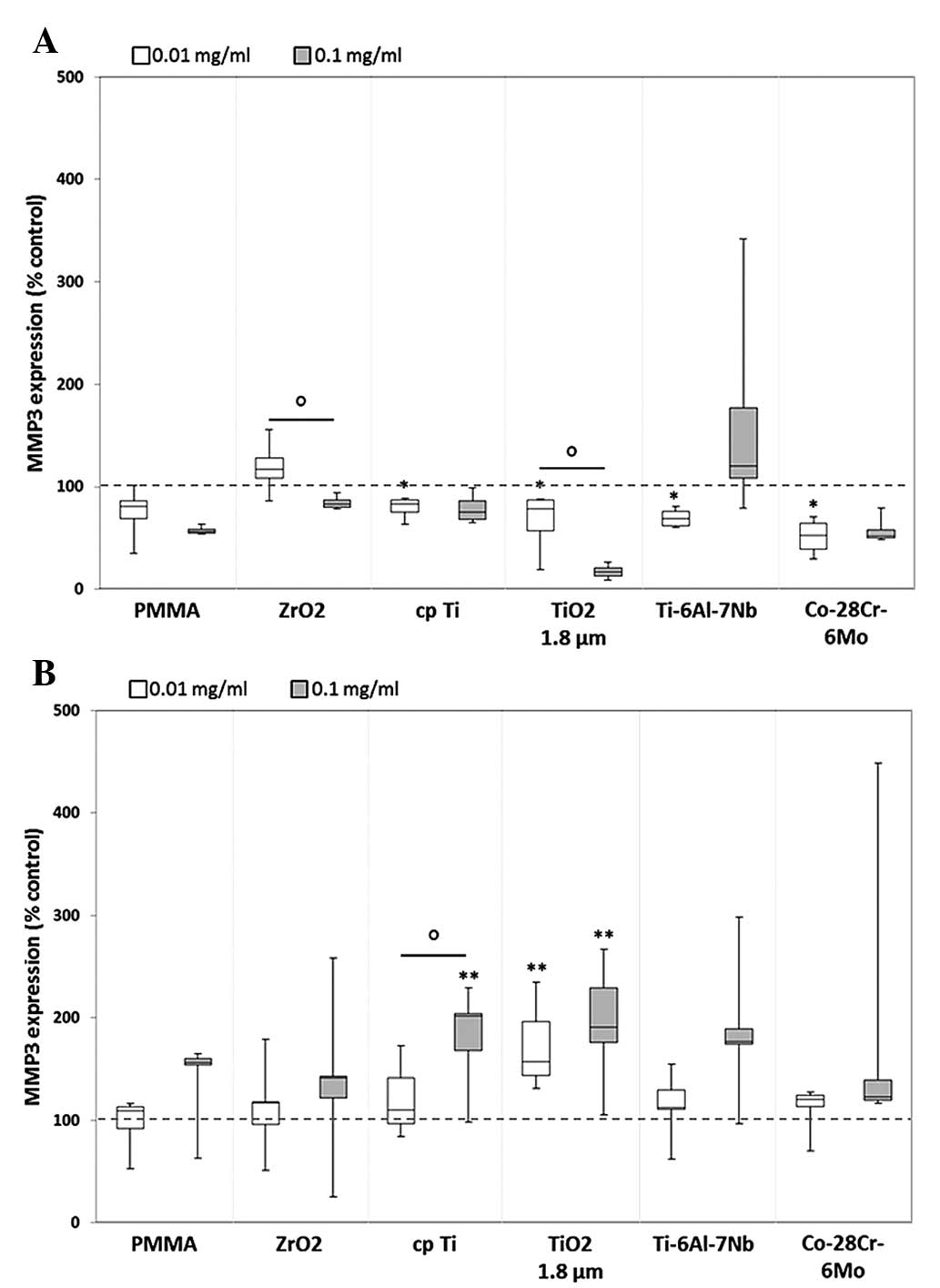
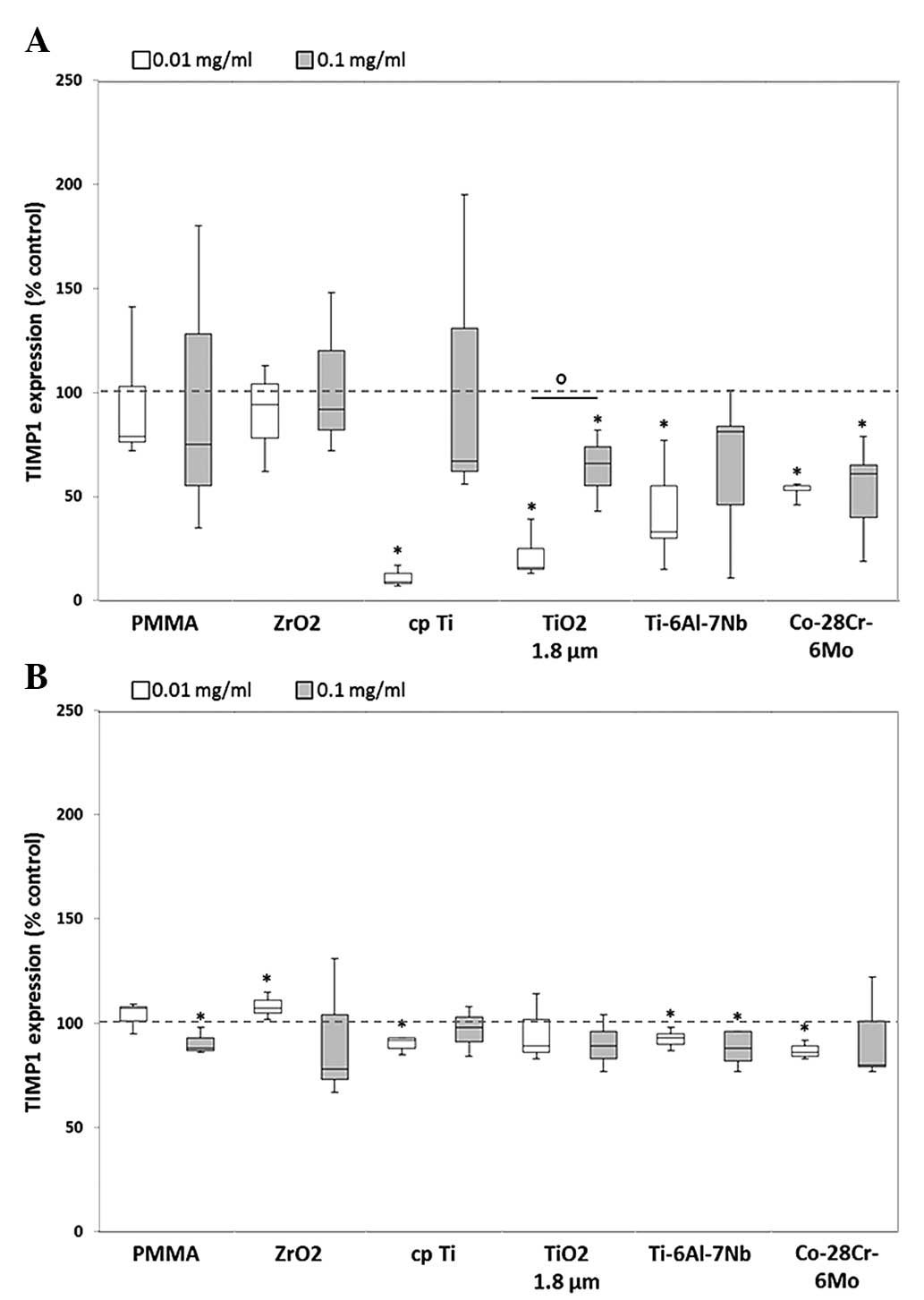
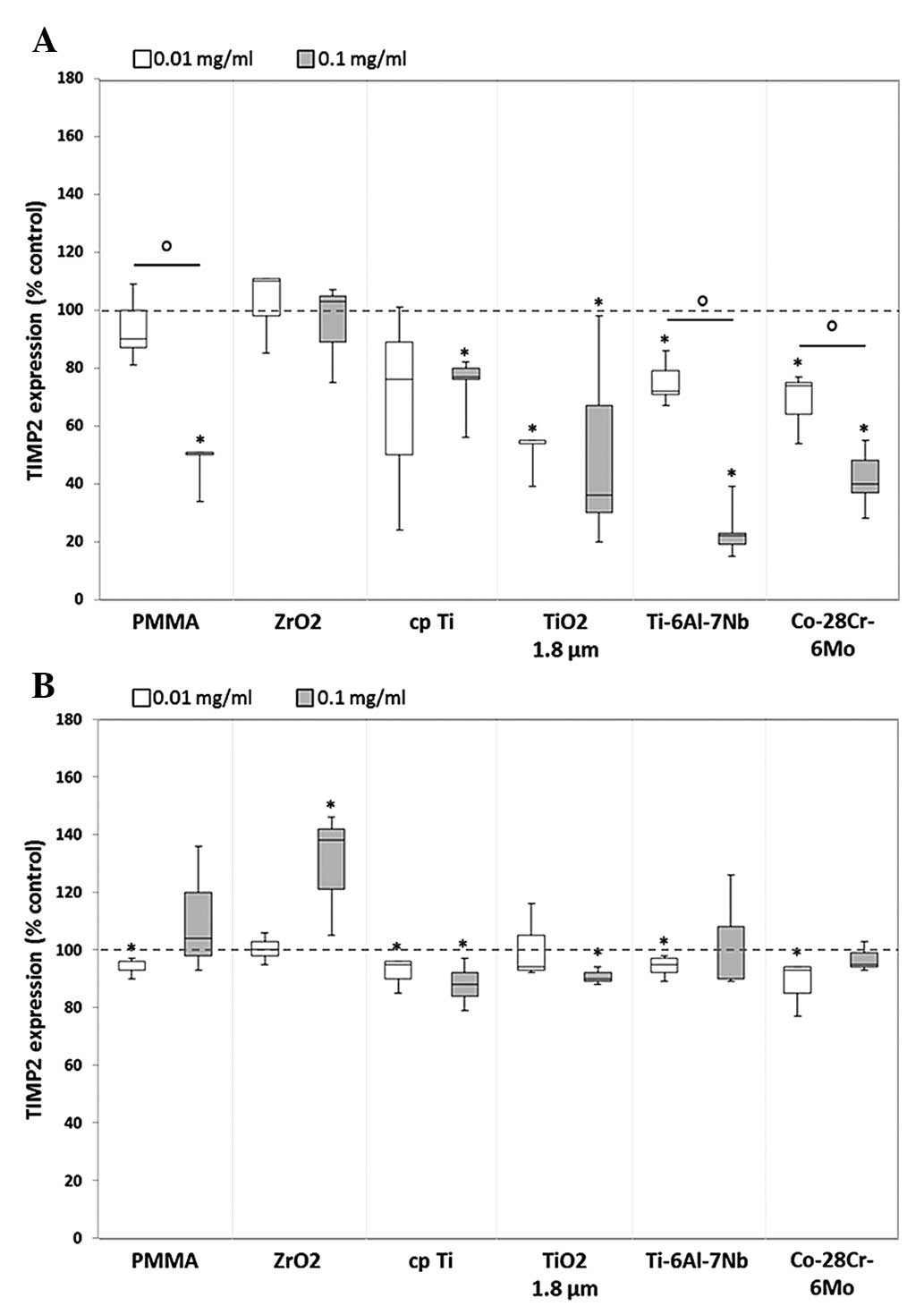
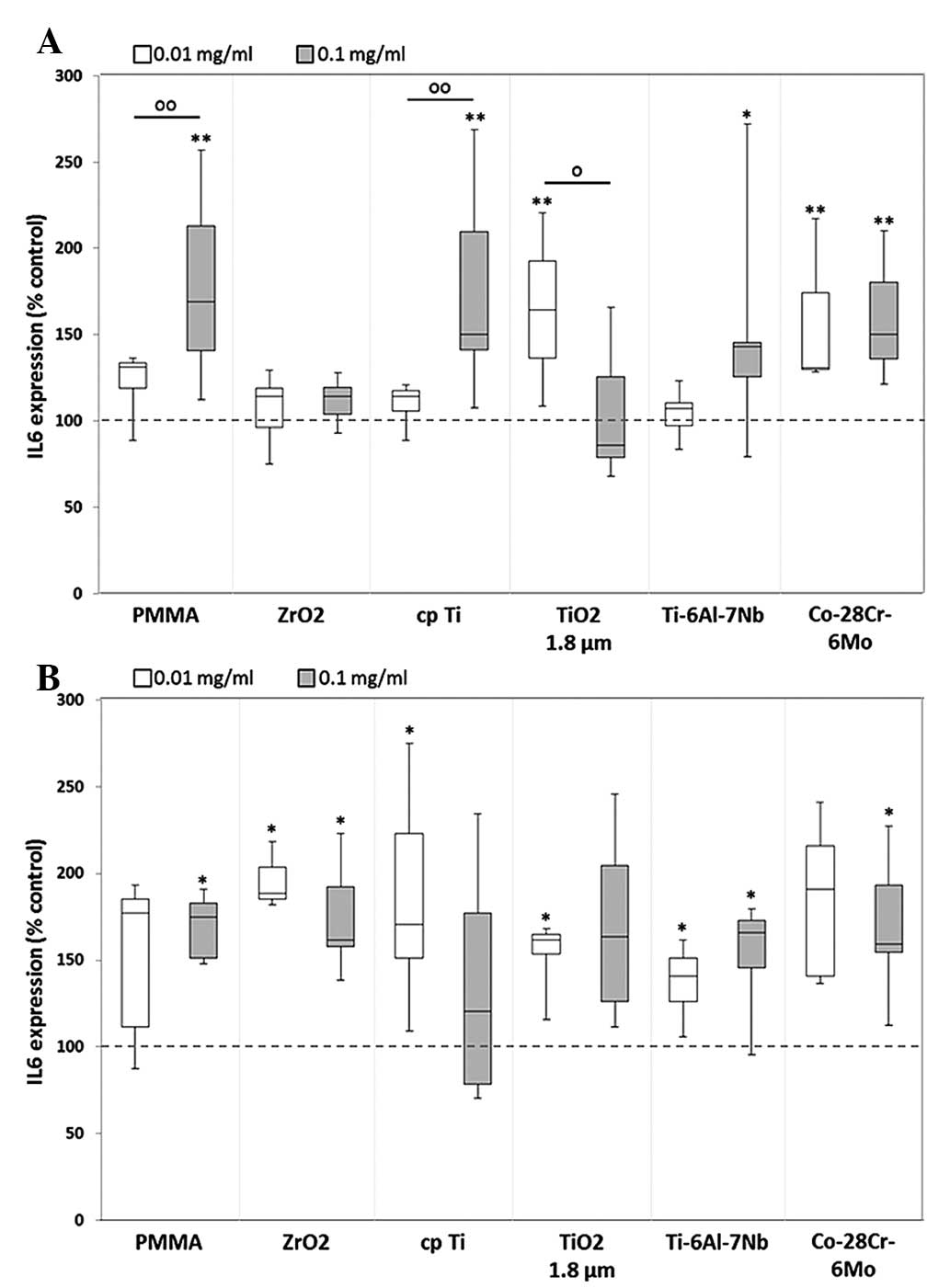
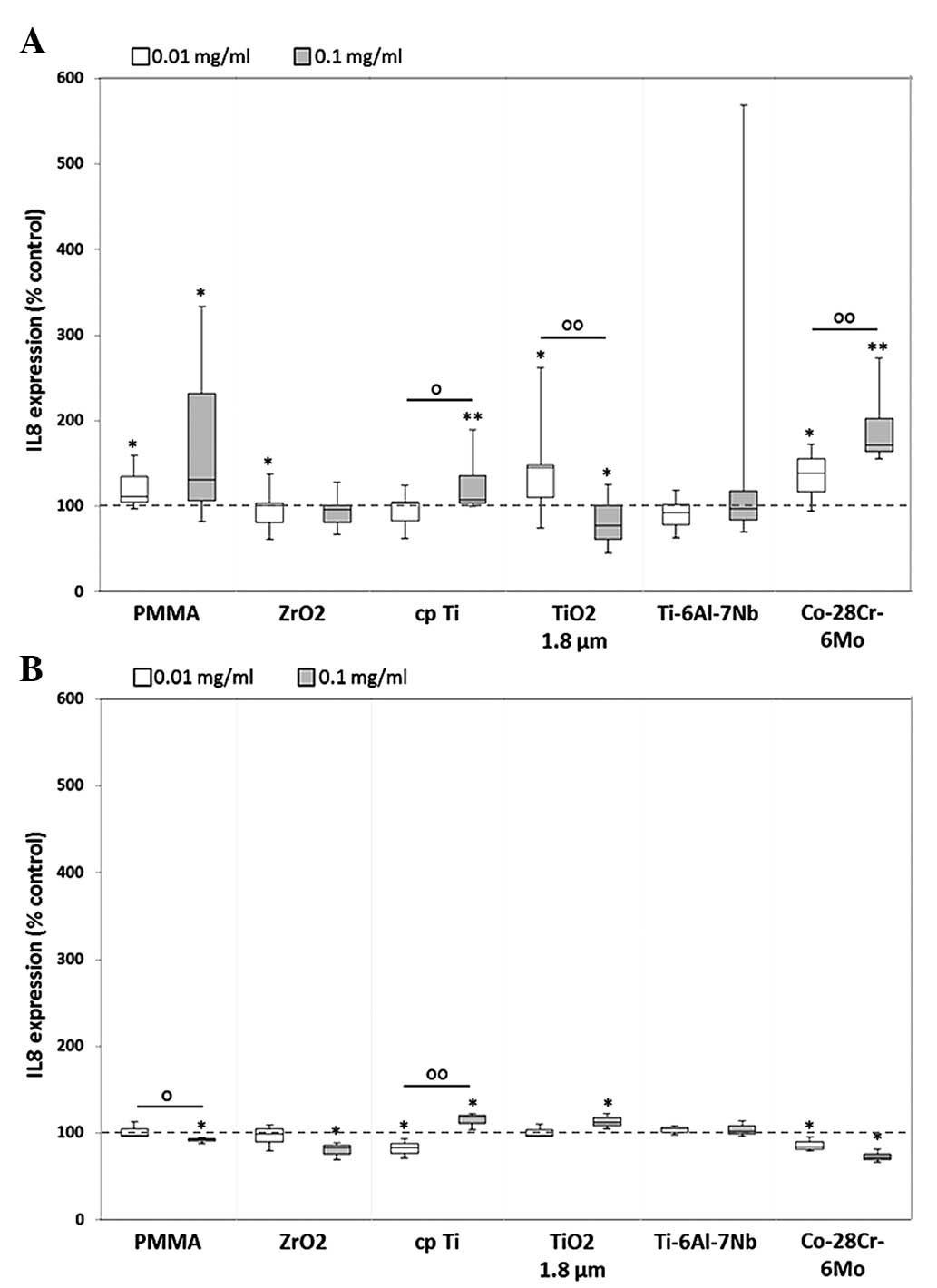
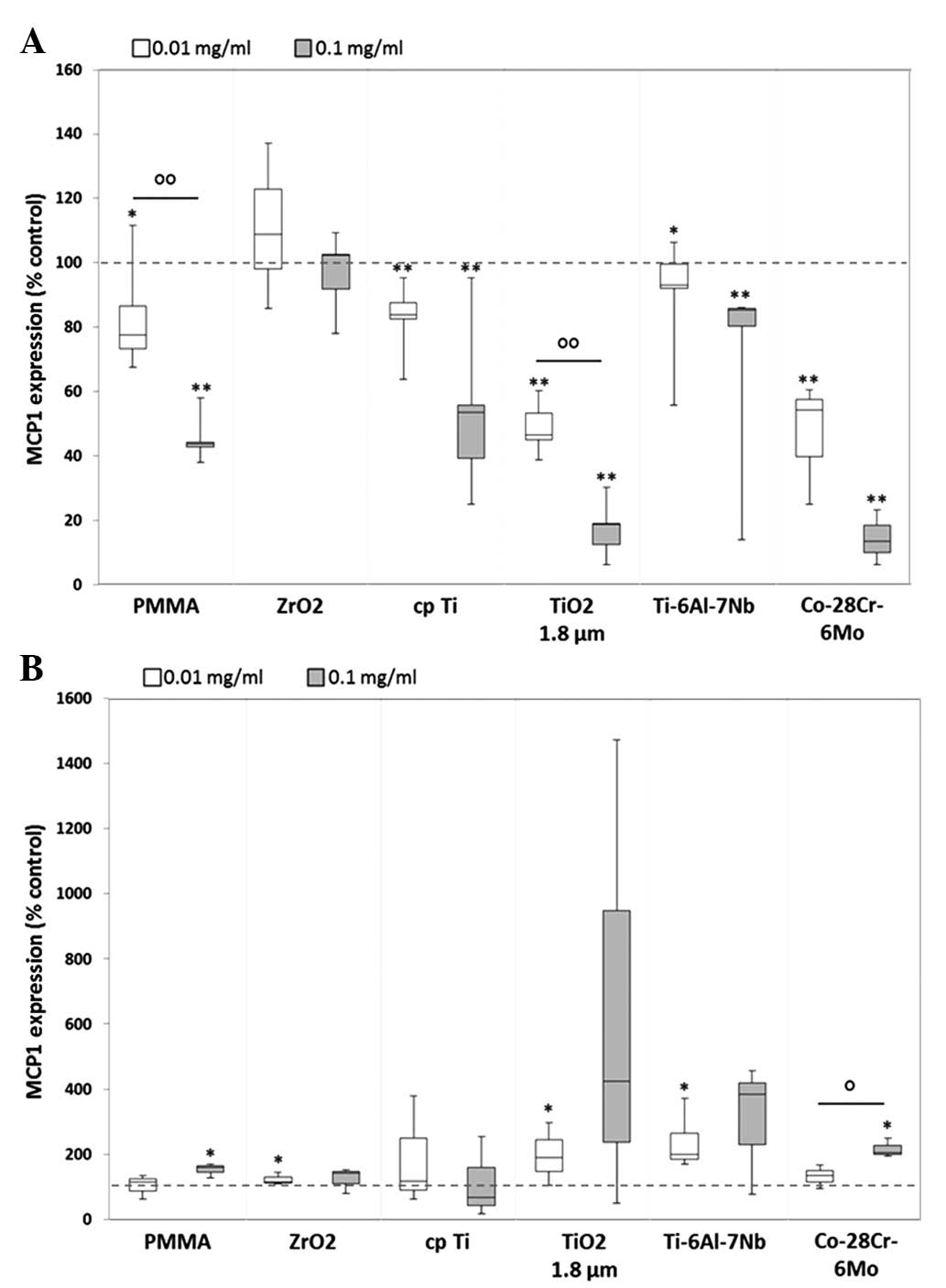
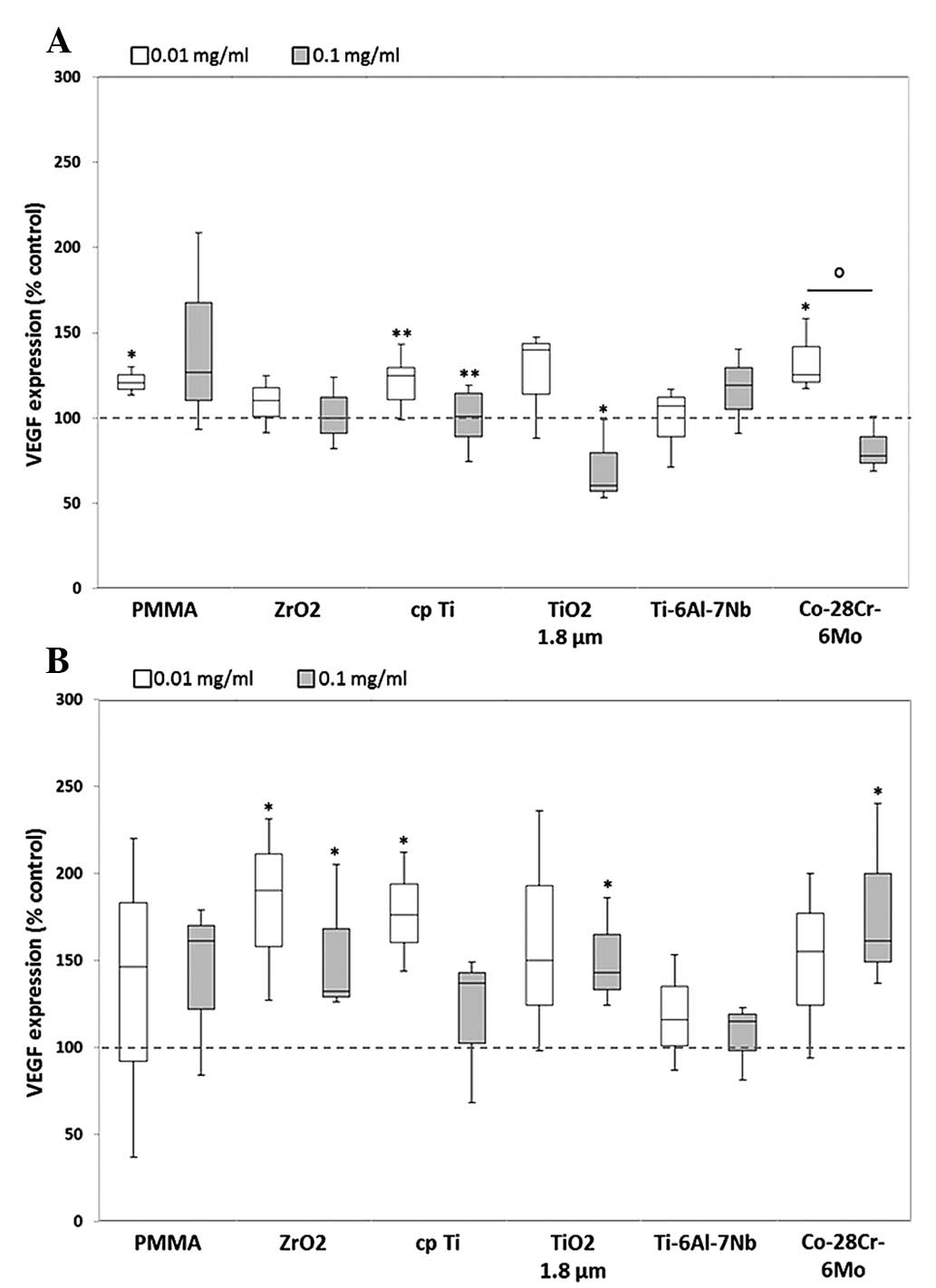
|
1
|
Bader R, Steinhauser E, Holzwarth U,
Schmitt M and Mittelmeier W: A novel test method for evaluation of
the abrasive wear behaviour of total hip stems at the interface
between implant surface and bone cement. Proc Inst Mech Eng H.
218:223–230. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jacobs JJ, Roebuck KA, Archibeck M, Hallab
NJ and Glant TT: Osteolysis: Basic science. Clin Orthop Relat Res.
393:71–77. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Willert HG and Semlitsch M: Tissue
reactions to plastic and metallic wear products of joint
endoprostheses. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 333:4–14. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lochner K, Fritsche A, Jonitz A, Hansmann
D, Mueller P, Mueller-Hilke B and Bader R: The potential role of
human osteoblasts for periprosthetic osteolysis following exposure
to wear particles. Int J Mol Med. 28:1055–1063. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Syggelos SA, Aletras AJ, Smirlaki I and
Skandalis SS: Extracellular matrix degradation and tissue
remodeling in periprosthetic loosening and osteolysis: Focus on
matrix metalloproteinases, their endogenous tissue inhibitors and
the proteasome. Biomed Res Int. 2013:2308052013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Tuan RS, Lee FY, T Konttinen Y, Wilkinson
JM and Smith RL; Implant Wear Symposium 2007 Biologic Work Group:
What are the local and systemic biologic reactions and mediators to
wear debris and what host factors determine or modulate the
biologic response to wear particles? J Am Acad Orthop Surg.
16(Suppl 1): 42–48. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Nakashima Y, Sun DH, Maloney WJ, Goodman
SB, Schurman DJ and Smith RL: Induction of matrix metalloproteinase
expression in human macrophages by orthopaedic particulate debris
in vitro. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 80:694–700. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Diehl P, Hantke B, Hennig M, Tschesche H,
Mittelmeier W, Schmitt M and Muehlenweg B: Protein expression of
MMP-13, uPA and PAI-1 in pseudocapsular and interface tissue around
implants of loose artificial hip joints and in osteoarthritis. Int
J Mol Med. 13:711–715. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nich C, Takakubo Y, Pajarinen J, Ainola M,
Salem A, Sillat T, Rao AJ, Raska M, Tamaki Y, Takagi M, et al:
Macrophages-Key cells in the response to wear debris from joint
replacements. J Biomed Mater Res A. 101:3033–3045. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Rooprai HK, Rucklidge GJ, Panou C and
Pilkington GJ: The effects of exogenous growth factors on matrix
metalloproteinase secretion by human brain tumour cells. Br J
Cancer. 82:52–55. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Tasaki K, Shintani Y, Saotome T, Andoh A,
Fujiyama Y, Hozawa S and Bamba T: Pro-inflammatory cytokine-induced
matrix metalloproteinase-1 (MMP-1) secretion in human pancreatic
periacinar myofibroblasts. Pancreatology. 3:414–421. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Andersson MK, Lundberg P, Ohlin A, Perry
MJ, Lie A, Stark A and Lerner UH: Effects on osteoclast and
osteoblast activities in cultured mouse calvarial bones by synovial
fluids from patients with a loose joint prosthesis and from
osteoarthritis patients. Arthritis Res Ther. 9:R182007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kular J, Tickner J, Chim SM and Xu J: An
overview of the regulation of bone remodelling at the cellular
level. Clin Biochem. 45:863–873. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Koreny T, Tunyogi-Csapó M, Gál I, Vermes
C, Jacobs JJ and Glant TT: The role of fibroblasts and
fibroblast-derived factors in periprosthetic osteolysis. Arthritis
Rheum. 54:3221–3232. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yao J, Cs-Szabó G, Jacobs JJ, Kuettner KE
and Glant TT: Suppression of osteoblast function by titanium
particles. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 79:107–112. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Goodman S, Aspenberg P, Song Y, Knoblich
G, Huie P, Regula D and Lidgren L: Tissue ingrowth and
differentiation in the bone-harvest chamber in the presence of
cobalt-chromium-alloy and high-density-polyethylene particles. J
Bone Joint Surg Am. 77:1025–1035. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Schulze C, Lochner K, Jonitz A, Lenz R,
Duettmann O, Hansmann D and Bader R: Cell viability, collagen
synthesis and cytokine expression in human osteoblasts following
incubation with generated wear particles using different bone
cements. Int J Mol Med. 32:227–234. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Trindade MC, Lind M, Sun D, Schurman DJ,
Goodman SB and Smith RL: In vitro reaction to orthopaedic
biomaterials by macrophages and lymphocytes isolated from patients
undergoing revision surgery. Biomaterials. 22:253–259. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Keeney M, Waters H, Barcay K, Jiang X, Yao
Z, Pajarinen J, Egashira K, Goodman SB and Yang F: Mutant MCP-1
protein delivery from layer-by-layer coatings on orthopedic
implants to modulate inflammatory response. Biomaterials.
34:10287–9525. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bader R, Mittelmeier W, Steinhauser E,
Brehm P, Brem R, Tübel J, Choungthong P, Winklmair D, Schmitt M and
Holzwarth U: Abriebverhalten von zementierten
Hüftendoprothesen-Stielen-Einfluss der
Knochenzement-Zusammensetzung. Materialprüfung. 47:175–180. 2005.In
German.
|
|
21
|
Lenz R, Mittelmeier W, Hansmann D, Brem R,
Diehl P, Fritsche A and Bader R: Response of human osteoblasts
exposed to wear particles generated at the interface of total hip
stems and bone cement. J Biomed Mater Res A. 89:370–378. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Park EK, Jung HS, Yang HI, Yoo MC, Kim C
and Kim KS: Optimized THP-1 differentiation is required for the
detection of responses to weak stimuli. Inflamm Res. 56:45–50.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Brew K, Dinakarpandian D and Nagase H:
Tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases: Evolution, structure and
function. Biochem Biophys Acta. 1477:267–283. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bitar D and Parvizi J: Biological response
to prosthetic debris. World J Orthop. 6:172–189. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Goodman SB, Gibon E and Yao Z: The basic
science of periprosthetic osteolysis. Instr Course Lect.
62:201–206. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Vermes C, Chandrasekaran R, Jacobs JJ,
Galante JO, Roebuck KA and Glant TT: The effects of particulate
wear debris, cytokines and growth factors on the functions of MG-63
osteoblasts. J Bone Joint Surg. 83-A:201–211. 2001.
|
|
27
|
Sasaki K, Takagi M, Mandelin J, Takei I,
Santavirta S, Ida H, Ogino T and Konttinen YT: Quantitative
analysis of mRNA expression of TIMPs in the periprosthetic
interface tissue of loose hips by real-time PCR system. J Biomed
Mater Res. 58:605–612. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Naidu MD, Chander R and Nair PM: Effect of
gamma irradiation on chemical and biological properties of
lipopolysaccharides from Salmonella typhimurium. Indian J Exp Biol.
36:588–92. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zittermann SI and Issekutz AC: Endothelial
growth factors VEGF and bFGF differentially enhance monocyte and
neutrophil recruitment to inflammation. J Leukoc Biol. 80:247–257.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Otto M, Kriegsmann J, Gehrke T and Bertz
S: Wear particles: Key to aseptic prosthetic loosening? Pathologe.
27:447–460. 2006.In German. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Fritz EA, Glant TT, Vermes C, Jacobs JJ
and Roebuck KA: Titanium particles induce the immediate early
stress responsive chemokines IL-8 and MCP-1 in osteoblasts. J
Orthop Res. 20:490–498. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Fritz EA, Jacobs JJ, Glant TT and Roebuck
KA: Chemokine IL-8 induction by particulate wear debris in
osteoblasts is mediated by NF-kappaB. J Orthop Res. 23:1249–1257.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|