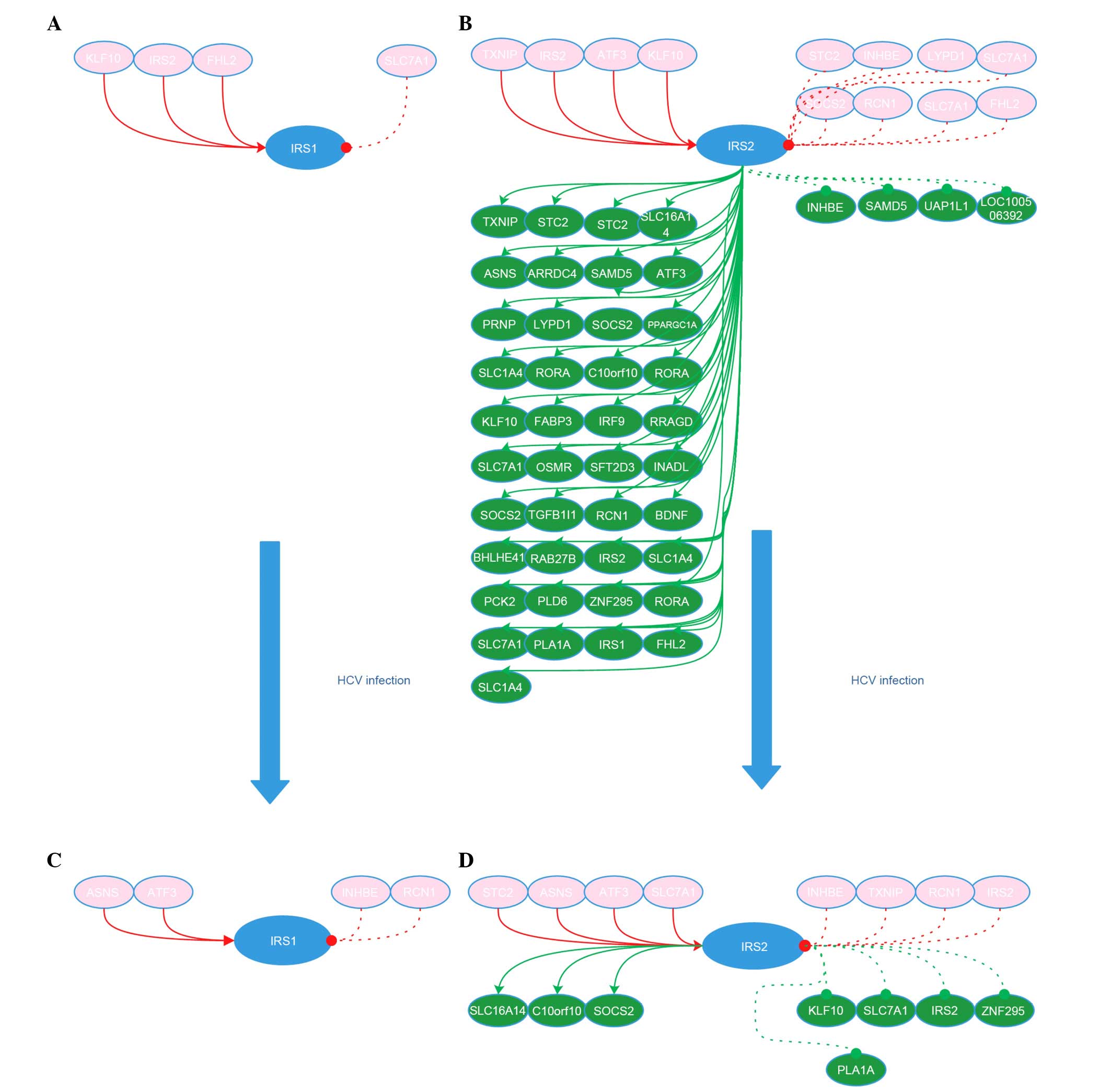
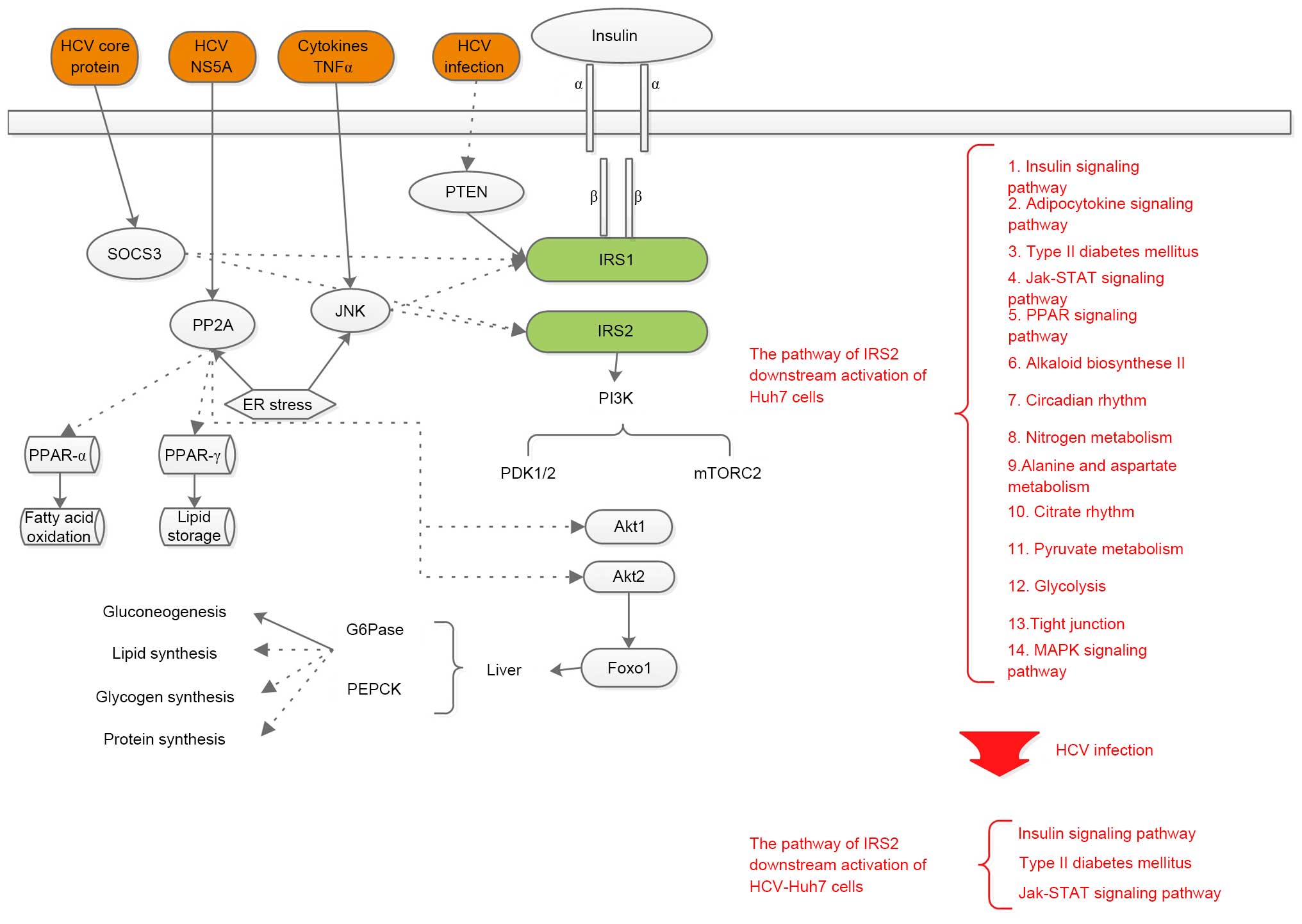
|
1
|
Serfaty L and Capeau J: Hepatitis C,
insulin resistance and diabetes: Clinical and pathogenic data.
Liver Int. 29(Suppl 2): 13–25. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Koike K and Moriya K: Metabolic aspects of
hepatitis C viral infection: Steatohepatitis resembling but
distinct from NASH. J Gastroenterol. 40:329–336. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jian Wu Y, Shu Chen L and Gui Qiang W:
Effects of fatty liver and related factors on the efficacy of
combination antiviral therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis C.
Liver Int. 26:166–172. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Xiong J, Lu Y, Feng J, Yuan D, Tian M,
Chang Y, Fu C, Wang G, Zeng H and Miao W: Tetrahymena functional
genomics database (TetraFGD): An integrated resource for
Tetrahymena functional genomics. Database (Oxford).
12:bat0082013.
|
|
5
|
Wang Y, Joshi T, Zhang XS, Xu D and Chen
L: Inferring gene regulatory networks from multiple microarray
datasets. Bioinformatics. 22:2413–2420. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Huang DW, Sherman BT, Tan Q, Collins JR,
Alvord WG, Roayaei J, Stephens R, Baseler MW, Lane HC and Lempicki
RA: The DAVID Gene Functional Classification Tool: A novel
biological module-centric algorithm to functionally analyze large
gene lists. Genome Biol. 8:R1832007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dennis G Jr, Sherman BT, Hosack DA, Yang
J, Gao W, Lane HC and Lempicki RA: DAVID: Database for Annotation,
Visualization, and Integrated Discovery. Genome Biol. 4:32003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Kadowaki T: Insights into insulin
resistance and type 2 diabetes from knockout mouse models. J Clin
Invest. 106:459–465. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ueki K, Yamauchi T, Tamemoto H, Tobe K,
Yamamoto-Honda R, Kaburagi Y, Akanuma Y, Yazaki Y, Aizawa S, Nagai
R and Kadowaki T: Restored insulin-sensitivity in IRS-1-deficient
mice treated by adenovirus-mediated gene therapy. J Clin Invest.
105:1437–1445. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Micallef JM, Kaldor JM and Dore GJ:
Spontaneous viral clearance following acute hepatitis C infection:
A systematic review of longitudinal studies. J Viral Hepat.
13:34–41. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Allison ME, Wreghitt T, Palmer CR and
Alexander GJ: Evidence for a link between hepatitis C virus
infection and diabetes mellitus in a cirrhotic population. J
Hepatol. 21:1135–1139. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cavaghan MK, Ehrmann DA and Polonsky KS:
Interactions between insulin resistance and insulin secretion in
the development of glucose intolerance. J Clin Invest. 106:329–333.
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kahn BB: Type 2 diabetes: When insulin
secretion fails to compensate for insulin resistance. Cell.
92:593–596. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Campbell PJ, Mandarino LJ and Gerich JE:
Quantification of the relative impairment in actions of insulin on
hepatic glucose production and peripheral glucose uptake in
non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Metabolism. 37:15–21.
1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Romero-Gómez M, Del Mar Viloria M, Andrade
RJ, Salmerón J, Diago M, Fernández-Rodríguez CM, Corpas R, Cruz M,
Grande L, Vázquez L, et al: Insulin resistance impairs sustained
response rate to peginterferon plus ribavirin in chronic hepatitis
C patients. Gastroenterology. 128:636–641. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Romero-Gómez M: Insulin resistance and
hepatitis C. World J Gastroenterol. 12:7075–7080. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Arao M, Murase K, Kusakabe A, Yoshioka K,
Fukuzawa Y, Ishikawa T, Tagaya T, Yamanouchi K, Ichimiya H,
Sameshima Y and Kakumu S: Prevalence of diabetes mellitus in
Japanese patients infected chronically with hepatitis C virus. J
Gastroenterol. 38:355–360. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mason AL, Lau JY, Hoang N, Qian K,
Alexander GJ, Xu L, Guo L, Jacob S, Regenstein FG, Zimmerman R, et
al: Association of diabetes mellitus and chronic hepatitis C virus
infection. Hepatology. 29:328–333. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fraser GM, Harman I, Meller N, Niv Y and
Porath A: Diabetes mellitus is associated with chronic hepatitis C
but not chronic hepatitis B infection. Isr J Med Sci. 32:526–530.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Caronia S, Taylor K, Pagliaro L, Carr C,
Palazzo U, Petrik J, O'Rahilly S, Shore S, Tom BD and Alexander GJ:
Further evidence for an association between non-insulin-dependent
diabetes mellitus and chronic hepatitis C virus infection.
Hepatology. 30:1059–1063. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mehta SH, Brancati FL, Sulkowski MS,
Strathdee SA, Szklo M and Thomas DL: Prevalence of type 2 diabetes
mellitus among persons with hepatitis C virus infection in the
United States. Ann Intern Med. 133:592–599. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Grimbert S, Valensi P, Lévy-Marchal C,
Perret G, Richardet JP, Raffoux C, Trinchet JC and Beaugrand M:
High prevalence of diabetes mellitus in patients with chronic
hepatitis C. A case-control study. Gastroenterol Clin Biol.
20:544–548. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ozyilkan E, Erbaş T, Simşek H, Telatar F,
Kayhan B and Telatar H: Increased prevalence of hepatitis C virus
antibodies in patients with diabetes mellitus. J Intern Med.
235:283–284. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Simó R, Hernández C, Genescà J, Jardí R
and Mesa J: High prevalence of hepatitis C virus infection in
diabetic patients. Diabetes Care. 19:998–1000. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zein NN, Abdulkarim AS, Wiesner RH, Egan
KS and Persing DH: Prevalence of diabetes mellitus in patients with
end-stage liver cirrhosis due to hepatitis C, alcohol, or
cholestatic disease. J Hepatol. 32:209–217. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hui JM, Sud A, Farrell GC, Bandara P, Byth
K, Kench JG, McCaughan GW and George J: Insulin resistance is
associated with chronic hepatitis C virus infection and fibrosis
progression [corrected]. Gastroenterology. 125:1695–1704. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Alexander GJ: An association between
hepatitis C virus infection and type 2 diabetes mellitus: What is
the connection? Ann Intern Med. 133:650–652. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Oliveira CP, Kappel CR, Siqueira ER, Lima
VM, Stefano JT, Michalczuk MT, Marini SS, Barbeiro HV, Soriano FG,
Carrilho FJ, et al: Effects of hepatitis C virus on cardiovascular
risk in infected patients: A comparative study. Int J Cardiol.
164:221–226. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Shintani Y, Fujie H, Miyoshi H, Tsutsumi
T, Tsukamoto K, Kimura S, Moriya K and Koike K: Hepatitis C virus
infection and diabetes: Direct involvement of the virus in the
development of insulin resistance. Gastroenterology. 126:840–848.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zekri AR, Ashour MS, Hassan A, Alam El-Din
HM, El-Shehaby AM and Abu-Shady MA: Cytokine profile in Egyptian
hepatitis C virus genotype-4 in relation to liver disease
progression. World J Gastroenterol. 11:6624–6630. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Greenberg AS and McDaniel ML: Identifying
the links between obesity, insulin resistance and beta-cell
function: Potential role of adipocyte-derived cytokines in the
pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes. Eur J Clin Invest. 32(Suppl 3):
24–34. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kawaguchi T, Yoshida T, Harada M, Hisamoto
T, Nagao Y, Ide T, Taniguchi E, Kumemura H, Hanada S, Maeyama M, et
al: Hepatitis C virus down-regulates insulin receptor substrates 1
and 2 through up-regulation of suppressor of cytokine signaling 3.
Am J Pathol. 165:1499–1508. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kawaguchi T, Ide T, Taniguchi E, Hirano E,
Itou M, Sumie S, Nagao Y, Yanagimoto C, Hanada S and Koga H:
Clearance of HCV improves insulin resistance, beta-cell function,
and hepatic expression of insulin receptor substrate 1 and 2. Am J
Gastroenterol. 102:570–576. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Aytug S, Reich D, Sapiro LE, Bernstein D
and Begum N: Impaired IRS-1/PI3-kinase signaling in patients with
HCV: A mechanism for increased prevalence of type 2 diabetes.
Hepatology. 38:1384–1392. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Banerjee S, Saito K, Ait-Goughoulte M,
Meyer K, Ray RB and Ray R: Hepatitis C virus core protein
upregulates serine phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate-1
and impairs the downstream akt/protein kinase B signaling pathway
for insulin resistance. J Virol. 82:2606–2612. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
36
|
Lecube A, Hernández C, Genescà J and Simó
R: Proinflammatory cytokines, insulin resistance, and insulin
secretion in chronic hepatitis C patients: A case-control study.
Diabetes Care. 29:1096–1101. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Liu J, Wang B, Wang W, Sun M, Li Y, Jia X,
Zhai S and Dang S: Computational networks of activating
transcription 3 gene in Huh7 cell lines and hepatitis C
virus-infected Huh7 cell lines. Mol Med Rep. 12:1239–1246.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Brüning JC, Michael MD, Winnay JN, Hayashi
T, Hörsch D, Accili D, Goodyear LJ and Kahn CR: A muscle-specific
insulin receptor knockout exhibits features of the metabolic
syndrome of NIDDM without altering glucose tolerance. Mol Cell.
2:559–569. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kulkarni RN, Brüning JC, Winnay JN, Postic
C, Magnuson MA and Kahn CR: Tissue-specific knockout of the insulin
receptor in pancreatic beta cells creates an insulin secretory
defect similar to that in type 2 diabetes. Cell. 96:329–339. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Vassen L, Wegrzyn W and Klein-Hitpass L:
Human insulin receptor substrate-2: Gene organization and promoter
characterization. Diabetes. 48:1877–1880. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Withers DJ, Gutierrez JS, Towery H, Burks
DJ, Ren JM, Previs S, Zhang Y, Bernal D, Pons S, Shulman GI, et al:
Disruption of IRS-2 causes type 2 diabetes in mice. Nature.
391:900–904. 1998. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Araki E, Lipes MA, Patti ME, Brüning JC,
Haag B III, Johnson RS and Kahn CR: Alternative pathway of insulin
signalling in mice with targeted disruption of the IRS-1 gene.
Nature. 372:186–190. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Tamemoto H, Kadowaki T, Tobe K, Yagi T,
Sakura H, Hayakawa T, Terauchi Y, Ueki K, Kaburagi Y, Satoh S, et
al: Insulin resistance and growth retardation in mice lacking
insulin receptor substrate-1. Nature. 372:182–186. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Taniguchi CM, Ueki K and Kahn R:
Complementary roles of IRS-1 and IRS-2 in the hepatic regulation of
metabolism. J Clin Invest. 115:718–727. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Anai M, Funaki M, Ogihara T, Terasaki J,
Inukai K, Katagiri H, Fukushima Y, Yazaki Y, Kikuchi M, Oka Y and
Asano T: Altered expression levels and impaired steps in the
pathway to phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activation via insulin
receptor substrates 1 and 2 in Zucker fatty rats. Diabetes.
47:13–23. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kerouz NJ, Hörsch D, Pons S and Kahn CR:
Differential regulation of insulin receptor substrates-1 and -2
(IRS-1 and IRS-2) and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase isoforms in
liver and muscle of the obese diabetic (ob/ob) mouse. J Clin
Invest. 100:3164–3172. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Miyamoto H, Moriishi K, Moriya K, Murata
S, Tanaka K, Suzuki T, Miyamura T, Koike K and Matsuura Y:
Involvement of the PA28gamma-dependent pathway in insulin
resistance induced by hepatitis C virus core protein. J Virol.
81:1727–1735. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Tonelli J, Li W, Kishore P, Pajvani UB,
Kwon E, Weaver C, Scherer PE and Hawkins M: Mechanisms of early
insulin-sensitizing effects of thiazolidinediones in type 2
diabetes. Diabetes. 53:1621–1629. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Wu HS, Yu JH, Li YY, Yang YS, He QJ, Lou
YJ and Ji RY: Insulin-sensitizing effects of a novel alpha-methyl-
alpha -phenoxylpropionate derivative in vitro. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
28:417–422. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Mousavinasab F, Tähtinen T, Jokelainen J,
Koskela P, Vanhala M, Oikarinen J, Keinänen-Kiukaanniemi S and
Laakso M: Effect of the Pro12Ala polymorphism of the PPARg2 gene on
serum adiponectin changes: Endocrine. 27:307–309. 2005.
|
|
51
|
Yessoufou A and Wahli W: Multifaceted
roles of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) at the
cellular and whole organism levels. Swiss Med Wkly.
140:w130712010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Bardot O, Aldridge TC, Latruffe N and
Green S: PPAR-RXR heterodimer activates a peroxisome proliferator
response element upstream of the bifunctional enzyme gene. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 192:37–45. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
de Gottardi A, Pazienza V, Pugnale P,
Bruttin F, Rubbia-Brandt L, Juge-Aubry CE, Meier CA, Hadengue A and
Negro F: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha and
-gamma mRNA levels are reduced in chronic hepatitis C with
steatosis and genotype 3 infection. Aliment Pharmacol Ther.
23:107–114. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Eslam M, Khattab MA and Harrison SA:
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors and hepatitis C virus.
Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 4:419–431. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Patsouris D, Mandard S, Voshol PJ, Escher
P, Tan NS, Havekes LM, Koenig W, März W, Tafuri S, Wahli W, et al:
PPARalpha governs glycerol metabolism. J Clin Invest. 114:94–103.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Jiang G, Dallas-Yang Q, Li Z, Szalkowski
D, Liu F, Shen X, Wu M, Zhou G, Doebber T, Berger J, et al:
Potentiation of insulin signaling in tissues of Zucker obese rats
after acute and long-term treatment with PPARgamma agonists.
Diabetes. 51:2412–2419. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Dharancy S, Malapel M, Perlemuter G,
Roskams T, Cheng Y, Dubuquoy L, Podevin P, Conti F, Canva V,
Philippe D, et al: Impaired expression of the peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor alpha during hepatitis C virus
infection. Gastroenterology. 128:334–342. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Clément S, Pascarella S and Negro F:
Hepatitis C virus infection: Molecular pathways to steatosis,
insulin resistance and oxidative stress. Viruses. 1:126–143. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Ozcan U, Cao Q, Yilmaz E, Lee AH, Iwakoshi
NN, Ozdelen E, Tuncman G, Görgün C, Glimcher LH and Hotamisligil
GS: Endoplasmic reticulum stress links obesity, insulin action, and
type 2 diabetes. Science. 306:457–461. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Hotamisligil GS: Role of endoplasmic
reticulum stress and c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase pathways in
inflammation and origin of obesity and diabetes. Diabetes. 54(Suppl
2): S73–78. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Christen V, Treves S, Duong FH and Heim
MH: Activation of endoplasmic reticulum stress response by
hepatitis viruses up-regulates protein phosphatase 2A. Hepatology.
46:558–565. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Wu Z, Jiao P, Huang X, Feng B, Feng Y,
Yang S, Hwang P, Du J, Nie Y, Xiao G and Xu H: MAPK phosphatase-3
promotes hepatic gluconeogenesis through dephosphorylation of
forkhead box O1 in mice. J Clin Invest. 120:3901–3911. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Yan L, Lavin VA, Moser LR, Cui Q, Kanies C
and Yang E: PP2A regulates the pro-apoptotic activity of FOXO1. J
Biol Chem. 283:7411–7420. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Deng X, Zhang W, O-Sullivan I, Williams
JB, Dong Q, Park EA, Raghow R, Unterman TG and Elam MB: FoxO1
inhibits sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c (SREBP-1c)
gene expression via transcription factors Sp1 and SREBP-1c. J Biol
Chem. 287:20132–20143. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Zhang K, Li L, Qi Y, Zhu X, Gan B, DePinho
RA, Averitt T and Guo S: Hepatic suppression of Foxo1 and Foxo3
causes hypoglycemia and hyperlipidemia in mice. Endocrinology.
153:631–646. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Zhang W, Patil S, Chauhan B, Guo S, Powell
DR, Le J, Klotsas A, Matika R, Xiao X, Franks R, et al: FoxO1
regulates multiple metabolic pathways in the liver: effects on
gluconeogenic, glycolytic, and lipogenic gene expression. J Biol
Chem. 281:10105–10117. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Gao TT, Qin ZL, Ren H, Zhao P and Qi ZT:
Inhibition of IRS-1 by hepatitis C virus infection leads to insulin
resistance in a PTEN-dependent manner. Virol J. 12:122015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Persico M, Masarone M, La Mura V, Persico
E, Moschella F, Svelto M, Bruno S and Torella R: Clinical
expression of insulin resistance in hepatitis C and B virus-related
chronic hepatitis: Differences and similarities. World J
Gastroenterol. 15:462–466. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Eguchi Y, Mizuta T, Ishibashi E, Kitajima
Y, Oza N, Nakashita S, Hara M, Iwane S, Takahashi H, Akiyama T, et
al: Hepatitis C virus infection enhances insulin resistance induced
by visceral fat accumulation. Liver Int. 29:213–220. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Squillace N, Lapadula G, Torti C, Orlando
G, Mandalia S, Nardini G, Beghetto B, Costarelli S and Guaraldi G:
Hepatitis C virus antibody-positive patients with HIV infection
have a high risk of insulin resistance: A cross-sectional study.
HIV Med. 9:151–159. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Moucari R, Asselah T, Cazals-Hatem D,
Voitot H, Boyer N, Ripault MP, Sobesky R, Martinot-Peignoux M,
Maylin S, Nicolas-Chanoine MH, et al: Insulin resistance in chronic
hepatitis C: Association with genotypes 1 and 4, serum HCV RNA
level, and liver fibrosis. Gastroenterology. 134:416–423. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|