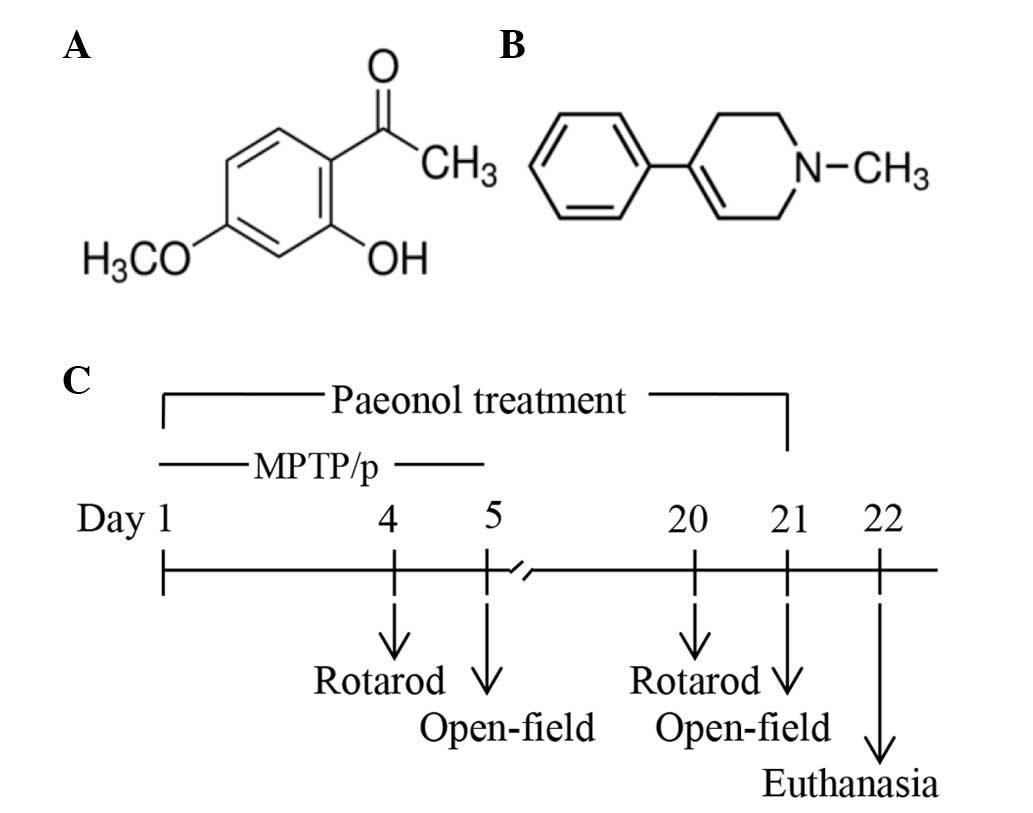
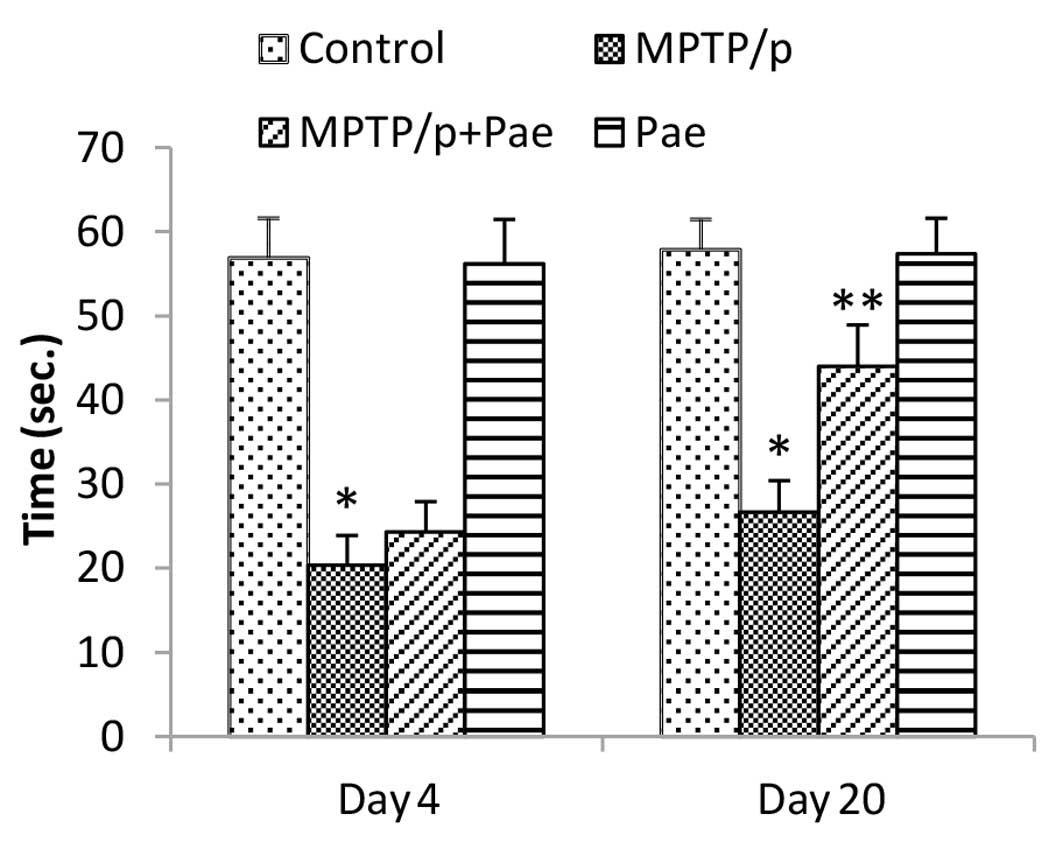
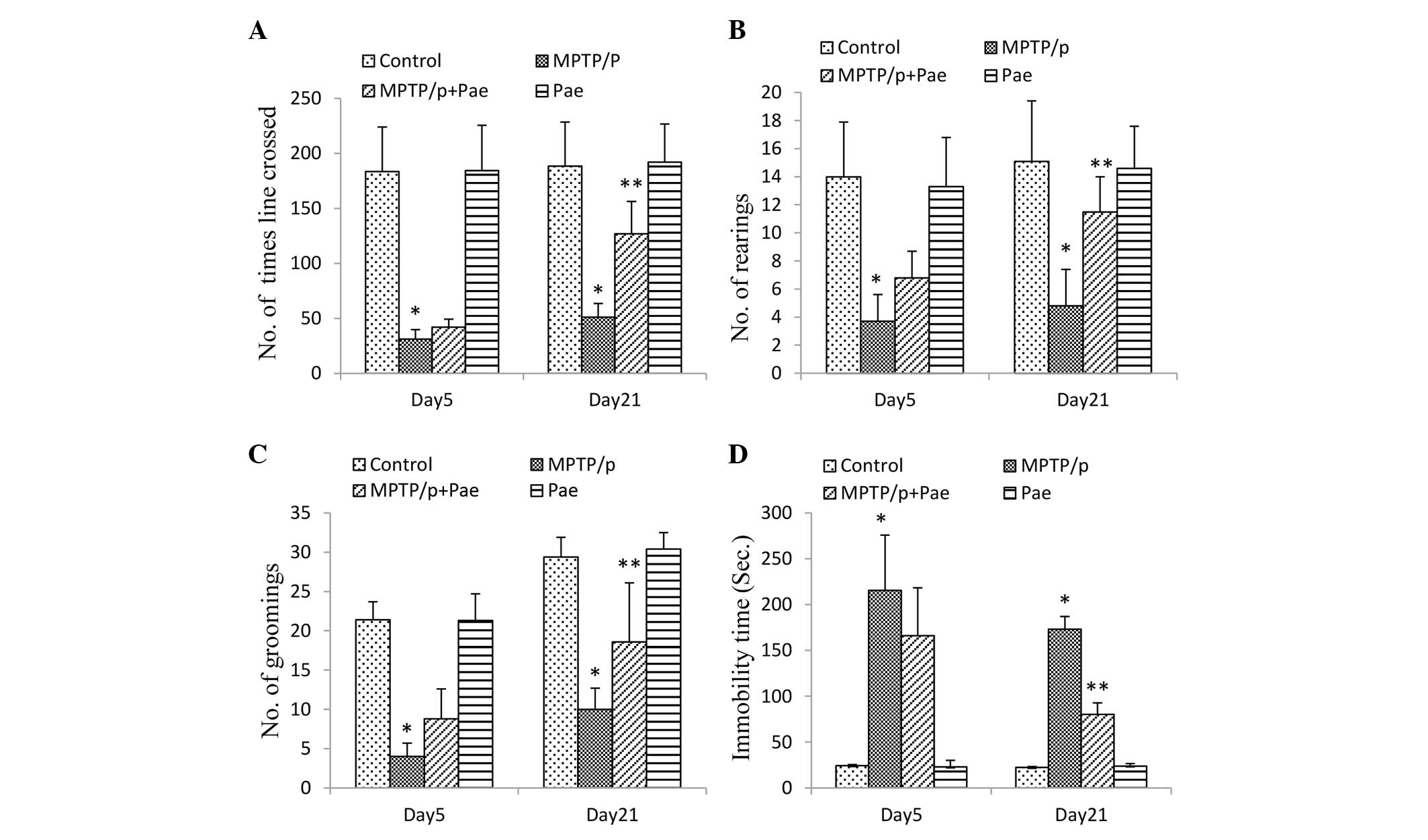
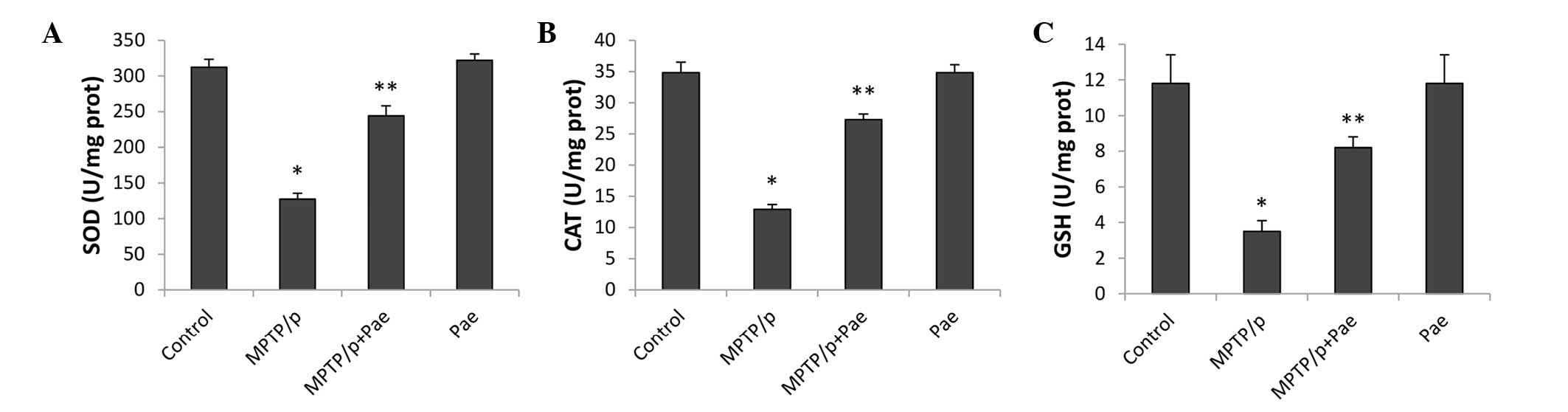
|
1
|
Meissner WG, Frasier M, Gasser T, Goetz
CG, Lozano A, Piccini P, Obeso JA, Rascol O, Schapira A, Voon V, et
al: Priorities in Parkinson's disease research. Nat Rev Drug
Discov. 10:377–393. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kowal SL, Dall TM, Chakrabarti R, Storm MV
and Jain A: The current and projected economic burden of
Parkinson's disease in the United States. Mov Disord. 28:311–318.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Guillot TS, Richardson JR, Wang MZ, Li YJ,
Taylor TN, Ciliax BJ, Zachrisson O, Mercer A and Miller GW: PACAP38
increases vesicular monoamine transporter 2 (VMAT2) expression and
attenuates methamphetamine toxicity. Neuropeptides. 42:423–434.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Klegeris A and McGeer PL: R-(−)-Deprenyl
inhibits monocytic THP-1 cell neurotoxicity independently of
monoamine oxidase inhibition. Exp Neurol. 166:458–464. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hartmann A: Postmortem studies in
Parkinson's disease. Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 6:281–293.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Birkmayer W and Hornykiewicz O: The
L-3,4-dioxyphenylalanine (DOPA)-effect in Parkinson-akinesia. Wien
Klin Wochenschr. 73:787–788. 1961.In German. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Morin N, Morissette M, Grégoire L, Rajput
A, Rajput AH and Di Paolo T: Contribution of brain serotonin
subtype 1B receptors in levodopa-induced motor complications.
Neuropharmacology. 99:356–368. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Winner B, Desplats P, Hagl C, Klucken J,
Aigner R, Ploetz S, Laemke J, Karl A, Aigner L, Masliah E, et al:
Dopamine receptor activation promotes adult neurogenesis in an
acute Parkinson model. Exp Neurol. 219:543–552. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Abdel-Salam OM: Drugs used to treat
Parkinson's disease, present status and future directions. CNS
Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 7:321–342. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tan W, Xue-bin C, Tian Z, Xiao-wu C,
Pei-pei H, Zhi-bin C and Bei-sha T: Effects of simvastatin on the
expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase and brain-derived
neurotrophic factor in a lipopolysaccharide-induced rat model of
Parkinson disease. Int J Neurosci. 126:278–286. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Chen B, Ning M and Yang G: Effect of
paeonol on antioxidant and immune regulatory activity in
hepatocellular carcinoma rats. Molecules. 17:4672–4683. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fu PK, Wu CL, Tsai TH and Hsieh CL:
Anti-inflammatory and anticoagulative effects of paeonol on
LPS-induced acute lung injury in rats. Evid Based Complement
Alternat Med. 2012:8375132012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lau CH, Chan CM, Chan YW, Lau KM, Lau TW,
Lam FC, Law WT, Che CT, Leung PC, Fung KP, et al: Pharmacological
investigations of the anti-diabetic effect of Cortex Moutan and its
active component paeonol. Phytomedicine. 14:778–784. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li M, Tan SY and Wang XF: Paeonol exerts
an anticancer effect on human colorectal cancer cells through
inhibition of PGE2 synthesis and COX-2 expression. Oncol
Rep. 32:2845–2853. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang H, Geng ZM, Hu ZW, Wang SY and Zhao
B: Neuroprotective effects of paeonol in a cell model of Parkinson
disease. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 44:30–36. 2015.In
Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lin C, Lin HY, Chen JH, Tseng WP, Ko PY,
Liu YS, Yeh WL and Lu DY: Effects of paeonol on
anti-neuroinflammatory responses in microglial cells. Int J Mol
Sci. 16:8844–8860. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mounsey RB, Mustafa S, Robinson L, Ross
RA, Riedel G, Pertwee RG and Teismann P: Increasing levels of the
endocannabinoid 2-AG is neuroprotective in the
1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine mouse model of
Parkinson's disease. Exp Neurol. 273:36–44. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
He XJ and Nakayama H: Transiently impaired
neurogenesis in MPTP mouse model of Parkinson's disease.
Neurotoxicology. 50:46–55. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lau YS, Patki G, Das-Panja K, Le WD and
Ahmad SO: Neuroprotective effects and mechanisms of exercise in a
chronic mouse model of Parkinson's disease with moderate
neurodegeneration. Eur J Neurosci. 33:1264–1274. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hsieh CL, Cheng CY, Tsai TH, Lin IH, Liu
CH, Chiang SY, Lin JG, Lao CJ and Tang NY: Paeonol reduced cerebral
infarction involving the superoxide anion and microglia activation
in ischemia-reperfusion injured rats. J Ethnopharmacol.
106:208–215. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhong SZ, Ge QH, Qu R, Li Q and Ma SP:
Paeonol attenuates neurotoxicity and ameliorates cognitive
impairment induced by d-galactose in ICR mice. J Neurol Sci.
277:58–64. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Petroske E, Meredith GE, Callen S,
Totterdell S and Lau YS: Mouse model of Parkinsonism: A comparison
between subacute MPTP and chronic MPTP/probenecid treatment.
Neuroscience. 106:589–601. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tarantini S, Hertelendy P, Tucsek Z,
Valcarcel-Ares MN, Smith N, Menyhart A, Farkas E, Hodges EL, Towner
R, Deak F, et al: Pharmacologically-induced neurovascular
uncoupling is associated with cognitive impairment in mice. J Cereb
Blood Flow Metab. 35:1871–1881. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Carter RJ, Morton J and Dunnett SB: Motor
coordination and balance in rodents. Curr Protoc Neurosci Unit
8.12. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Sedelis M, Hofele K, Auburger GW, Morgan
S, Huston JP and Schwarting RK: MPTP susceptibility in the mouse:
Behavioral, neurochemical, and histological analysis of gender and
strain differences. Behav Genet. 30:171–182. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Aguirre-Vidal Y, Montes S, Tristan-López
L, Anaya-Ramos L, Teiber J, Ríos C, Baron-Flores V and
Monroy-Noyola A: The neuroprotective effect of lovastatin on
MPP(+)-induced neurotoxicity is not mediated by PON2.
Neurotoxicology. 48:166–170. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Palencia G, Garcia E, Osorio-Rico L,
Trejo-Solís C, Escamilla-Ramírez A and Sotelo J: Neuroprotective
effect of thalidomide on MPTP-induced toxicity. Neurotoxicology.
47:82–87. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Patil SP, Jain PD, Ghumatkar PJ, Tambe R
and Sathaye S: Neuroprotective effect of metformin in MPTP-induced
Parkinson's disease in mice. Neuroscience. 277:747–754. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jackson-Lewis V, Blesa J and Przedborski
S: Animal models of Parkinson's disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord.
18(Suppl 1): S183–S185. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Zang LY and Misra HP: Generation of
reactive oxygen species during the monoamine oxidase-catalyzed
oxidation of the neurotoxicant,
1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine. J Biol Chem.
268:16504–16512. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Patil SP, Jain PD, Sancheti JS, Ghumatkar
PJ, Tambe R and Sathaye S: Neuroprotective and neurotrophic effects
of Apigenin and Luteolin in MPTP induced parkinsonism in mice.
Neuropharmacology. 86:192–202. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang XL, Xing GH, Hong B, Li XM, Zou Y,
Zhang XJ and Dong MX: Gastrodin prevents motor deficits and
oxidative stress in the MPTP mouse model of Parkinson's disease:
Involvement of ERK1/2-Nrf2 signaling pathway. Life Sci. 114:77–85.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Gaki GS and Papavassiliou AG: Oxidative
stress-induced signaling pathways implicated in the pathogenesis of
Parkinson's disease. Neuromolecular Med. 16:217–230. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhang J, Perry G, Smith MA, Robertson D,
Olson SJ, Graham DG and Montine TJ: Parkinson's disease is
associated with oxidative damage to cytoplasmic DNA and RNA in
substantia nigra neurons. Am J Pathol. 154:1423–1429. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Jenner P and Olanow CW: Oxidative stress
and the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease. Neurology. 47(6 Suppl
3): S161–S170. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Maj MC, Tkachyova I, Patel P, Addis JB,
Mackay N, Levandovskiy V, Lee J, Lang AE, Cameron JM and Robinson
BH: Oxidative stress alters the regulatory control of p66Shc and
Akt in PINK1 deficient cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
399:331–335. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Weydert CJ and Cullen JJ: Measurement of
superoxide dismutase, catalase and glutathione peroxidase in
cultured cells and tissue. Nat Protoc. 5:51–66. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Selvakumar GP, Janakiraman U, Essa MM,
Justin Thenmozhi A and Manivasagam T: Escin attenuates behavioral
impairments, oxidative stress and inflammation in a chronic
MPTP/probenecid mouse model of Parkinson's disease. Brain Res.
1585:23–36. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Tansey MG and Goldberg MS:
Neuroinflammation in Parkinson's disease: Its role in neuronal
death and implications for therapeutic intervention. Neurobiol Dis.
37:510–518. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Hirsch EC, Hunot S, Damier P and Faucheux
B: Glial cells and inflammation in Parkinson's disease: A role in
neurodegeneration? Ann Neurol. 44(3 Suppl 1): S115–S120. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hirsch EC and Hunot S: Neuroinflammation
in Parkinson's disease: A target for neuroprotection? Lancet
Neurol. 8:382–397. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Rossol M, Heine H, Meusch U, Quandt D,
Klein C, Sweet MJ and Hauschildt S: LPS-induced cytokine production
in human monocytes and macrophages. Crit Rev Immunol. 31:379–446.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Sarkar S, Chigurupati S, Raymick J, Mann
D, Bowyer JF, Schmitt T, Beger RD, Hanig JP, Schmued LC and Paule
MG: Neuroprotective effect of the chemical chaperone, trehalose in
a chronic MPTP-induced Parkinson's disease mouse model.
Neurotoxicology. 44:250–262. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Whitton PS: Inflammation as a causative
factor in the aetiology of Parkinson's disease. Br J Pharmacol.
150:963–976. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Niranjan R: The role of inflammatory and
oxidative stress mechanisms in the pathogenesis of Parkinson's
disease: Focus on astrocytes. Mol Neurobiol. 49:28–38. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Tseng YT, Hsu YY, Shih YT and Lo YC:
Paeonol attenuates microglia-mediated inflammation and oxidative
stress-induced neurotoxicity in rat primary microglia and cortical
neurons. Shock. 37:312–318. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Daubner SC, Le T and Wang S: Tyrosine
hydroxylase and regulation of dopamine synthesis. Arch Biochem
Biophys. 508:1–12. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
48
|
Fukuda T, Takahashi J and Tanaka J:
Tyrosine hydroxylase-immunoreactive neurons are decreased in number
in the cerebral cortex of Parkinson's disease. Neuropathology.
19:10–13. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Episcopo FL, Tirolo C, Testa N, Caniglia
S, Morale MC and Marchetti B: Reactive astrocytes are key players
in nigrostriatal dopaminergic neurorepair in the MPTP mouse model
of Parkinson's disease: Focus on endogenous neurorestoration. Curr
Aging Sci. 6:45–55. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Weissmiller AM and Wu C: Current advances
in using neurotrophic factors to treat neurodegenerative disorders.
Transl Neurodegener. 1:142012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Dai L, Wang D, Meng H, Zhang K, Fu L, Wu Y
and Bai Y: Association between the BDNF G196A and C270T
polymorphisms and Parkinson's disease: A meta-analysis. Int J
Neurosci. 123:675–683. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Scalzo P, Kummer A, Bretas TL, Cardoso F
and Teixeira AL: Serum levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor
correlate with motor impairment in Parkinson's disease. J Neurol.
257:540–545. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Salehi Z and Mashayekhi F: Brain-derived
neurotrophic factor concentrations in the cerebrospinal fluid of
patients with Parkinson's disease. J Clin Neurosci. 16:90–93. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|