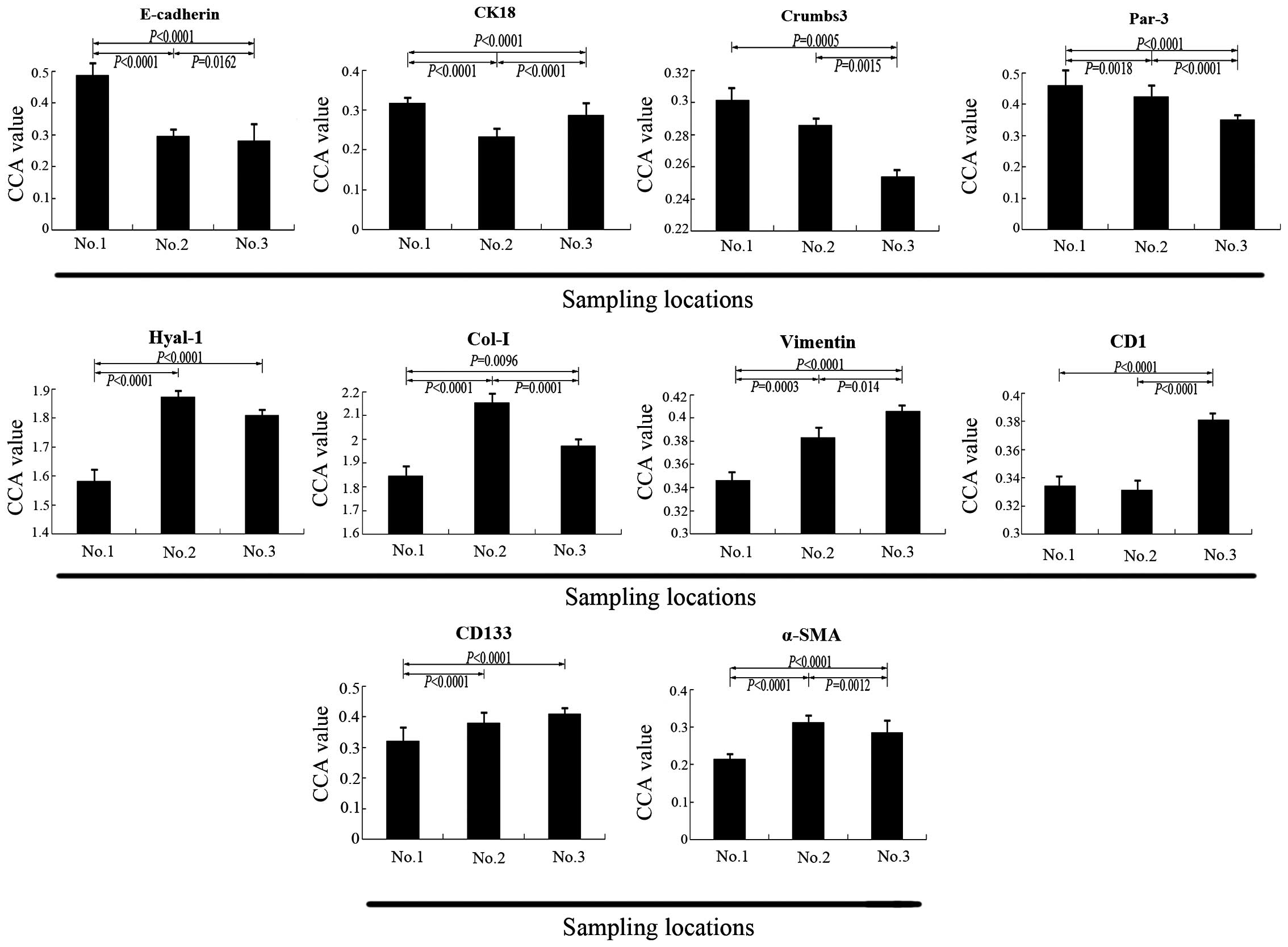
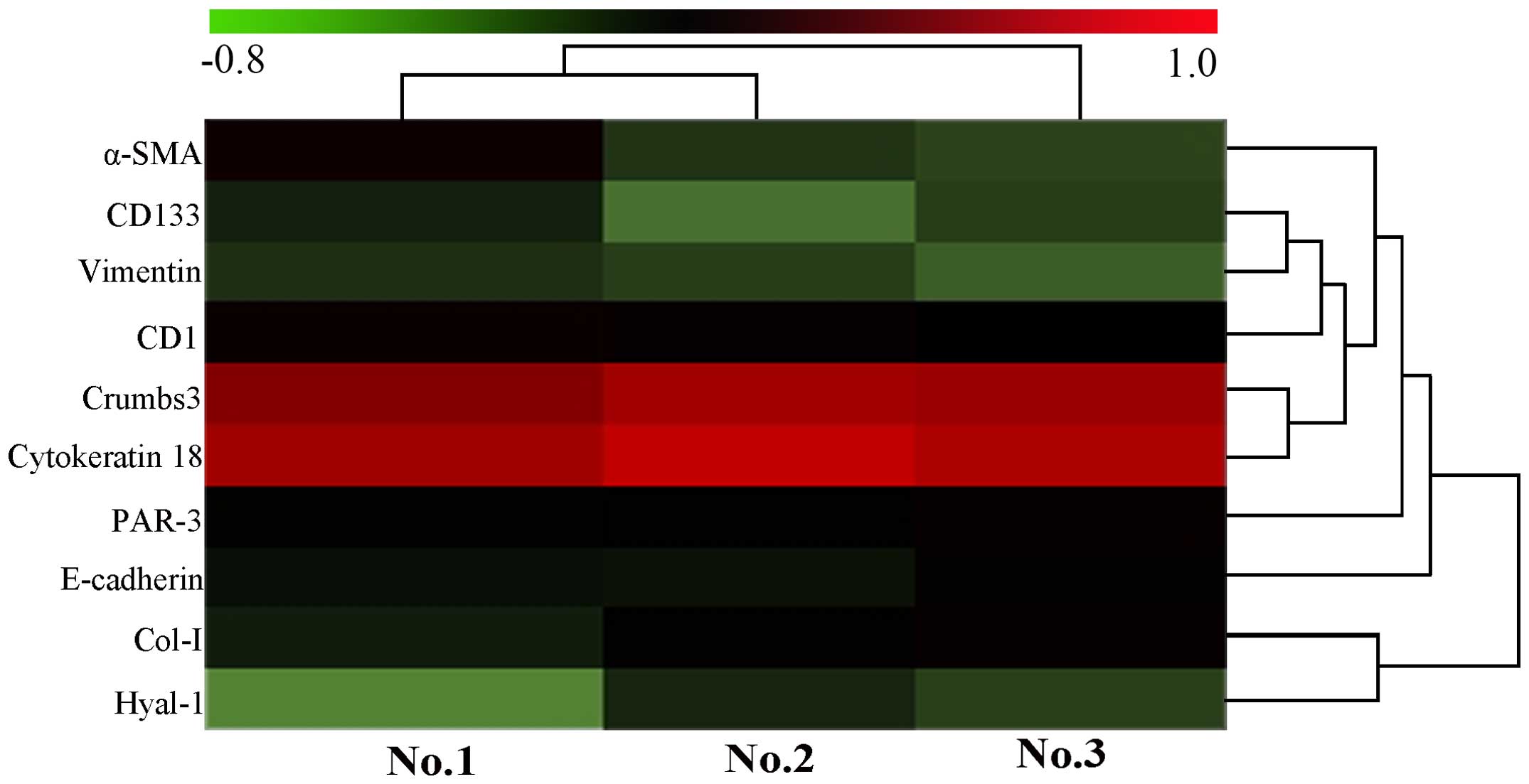
|
1
|
Brücher BL and Jamall IS: Epistemology of
the origin of cancer: A new paradigm. BMC Cancer. 14:3312014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Paget S: The distribution of secondary
growths in cancer of the breast 1889. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
8:98–101. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Korkaya H, Liu S and Wicha MS: Breast
cancer stem cells, cytokine networks, and the tumor
microenvironment. J Clin Invest. 121:3804–3809. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Felsher DW: Cancer revoked: Oncogenes as
therapeutic targets. Nat Rev Cancer. 3:375–380. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li R and Pendergast AM: Arg kinase
regulates epithelial cell polarity by targeting β1-integrin and
small GTPase pathways. Curr Biol. 21:1534–1542. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hammoudi A, Song F, Reed KR, Jenkins RE,
Meniel VS, Watson AJ, Pritchard DM, Clarke AR and Jenkins JR:
Proteomic profiling of a mouse model of acute intestinal Apc
deletion leads to identification of potential novel biomarkers of
human colorectalcancer (CRC). Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
440:364–370. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Elsum IA, Martin C and Humbert PO:
Scribble regulates an EMT polarity pathway through modulation of
MAPK-ERK signaling to mediate junction formation. J Cell Sci.
126:3990–3999. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sfakianos J, Togawa A, Maday S, Hull M,
Pypaert M, Cantley L, Toomre D and Mellman I: Par3 functions in the
biogenesis of the primary cilium in polarized epithelial cells. J
Cell Biol. 179:1133–1140. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Reed MJ, Damodarasamy M, Chan CK, Johnson
MN, Wight TN and Vernon RB: Cleavage of hyaluronan is impaired in
aged dermal wounds. Matrix Biol. 32:45–51. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
10
|
Tlsty TD and Hein PW: Know thy neighbor:
Stromal cells can contribute oncogenic signals. Curr Opin Genet
Dev. 11:54–59. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Weinberg R and Mihich E: Eighteenth annual
pezcoller symposium: Tumor microenvironment and heterotypic
interactions. Cancer Res. 66:11550–11553. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Roncucci L, Pedroni M, Vaccina F, Benatti
P, Marzona L and De Pol A: Aberrant crypt foci in colorectal
carcinogenesis. Cell and crypt dynamics. Cell Prolif. 33:1–18.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Guo F, Wang Q, Zhou Y, Wu L, Ma X, Liu F,
Huang F and Qin G: Lentiviral vector-mediated FoxO1 overexpression
inhibits extracellular matrix protein secretion under high glucose
conditions in mesangial cells. J Cell Biochem. 117:74–83. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Kolliopoulos C, Bounias D, Bouga H,
Kyriakopoulou D, Stavropoulos M and Vynios DH: Hyaluronidases and
their inhibitors in the serum of colorectal carcinoma patients. J
Pharm Biomed Anal. 83:299–304. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Barreto SC, Hopkins CA, Bhowmick M and Ray
A: Extracellular matrix in obesity-cancer interactions. Horm Mol
Biol Clin Investig. 22:63–77. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Abu El-Asrar AM, De Hertogh G, van den
Eynde K, Alam K, Van Raemdonck K, Opdenakker G, Van Damme J, Geboes
K and Struyf S: Myofibroblasts in proliferative diabetic
retinopathy can originate from infiltrating fibrocytes and through
endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EndoMT). Exp Eye Res.
132:179–189. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Noah TK, Lo YH, Price A, Chen G, King E,
Washington MK, Aronow BJ and Shroyer NF: SPDEF functions as a
colorectal tumor suppressor by inhibiting β-catenin activity.
Gastroenterology. 144:1012–1023.e6. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Grosse-Gehling P, Fargeas CA, Dittfeld C,
Garbe Y, Alison MR, Corbeil D and Kunz-Schughart LA: CD133 as a
biomarker for putative cancer stem cells in solid tumours:
Limitations, problems and challenges. J Pathol. 229:355–378. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Wang P: Suppression of DACH1 promotes
migration and invasion of colorectal cancer via activating
TGF-β-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 460:314–319. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lai DW, Liu SH, Karlsson AI, Lee WJ, Wang
KB, Chen YC, Shen CC, Wu SM, Liu CY, Tien HR, et al: The novel Aryl
hydrocarbon receptor inhibitor biseugenol inhibits gastric tumor
growth and peritoneal dissemination. Oncotarget. 5:7788–7804. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Knösel T, Emde V, Schlüns K, Schlag PM,
Dietel M and Petersen I: Cytokeratin profiles identify diagnostic
signatures in colorectal cancer using multiplex analysis of tissue
microarrays. Cell Oncol. 28:167–175. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cernat L, Blaj C, Jackstadt R, Brandl L,
Engel J, Hermeking H, Jung A, Kirchner T and Horst D: Colorectal
cancers mimic structural organization of normal colonic crypts.
PLoS One. 9:e1042842014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Milicic A, Harrison LA, Goodlad RA, Hardy
RG, Nicholson AM, Presz M, Sieber O, Santander S, Pringle JH,
Mandir N, et al: Ectopic expression of P-cadherin correlates with
promoter hypomethylation early in colorectal carcinogenesis and
enhanced intestinal crypt fission in vivo. Cancer Res.
68:7760–7768. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Whiteman EL, Liu CJ, Fearon ER and
Margolis B: The transcription factor snail represses Crumbs3
expression and disrupts apicobasal polarity complexes. Oncogene.
27:3875–3879. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ribeiro AL and Okamoto OK: Combined
effects of pericytes in the tumor microenvironment. Stem Cells Int.
2015:8684752015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kim MJ, Lee YS, Han GY, Lee HN, Ahn C and
Kim CW: Profilin 2 promotes migration, invasion, and stemness of
HT29 human colorectal cancer stem cells. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem.
79:1438–1446. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chen CC, Sureshbabul M, Chen HW, Lin YS,
Lee JY, Hong QS, Yang YC and Yu SL: Curcumin suppresses metastasis
via Sp-1, FAK inhibition and E-Cadherin upregulation in colorectal
cancer. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013:5416952013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Ng L, Wan TM, Lam CS, Chow AK, Wong SK,
Man JH, Li HS, Cheng NS, Pak RC, Cheung AH, et al: Post-operative
plasma osteopontin predicts distant metastasis in human colorectal
cancer. PLoS One. 10:e01262192015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kim YJ, Kang HB, Yim HS, Kim JH and Kim
JW: NDRG2 positively regulates E-cadherin expression and prolongs
overall survival in colon cancer patients. Oncol Rep. 30:1890–1898.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Elsum IA, Martin C and Humbert PO:
Scribble regulates an EMT polarity pathway through modulation of
MAPK-ERK signaling to mediate junction formation. J Cell Sci.
126:3990–3999. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Karp CM, Tan TT, Mathew R, Nelson D,
Mukherjee C, Degenhardt K, Karantza-Wadsworth V and White E: Role
of the polarity determinant crumbs in suppressing mammalian
epithelial tumor progression. Cancer Res. 68:4105–4115. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sfakianos J, Togawa A, Maday S, Hull M,
Pypaert M, Cantley L, Toomre D and Mellman I: Par3 functions in the
biogenesis of the primary cilium in polarized epithelial cells. J
Cell Biol. 179:1133–1140. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liu J, Zhang W, Liu J, Lu X, Long Y, Zhou
Y and Liu S: Expressions of connexin and par-3 in the distal margin
of rectal cancer after ultra-low anterior resection. J Huazhong
Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 29:330–334. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Mack NA, Porter AP, Whalley HJ, Schwarz
JP, Jones RC, Khaja AS, Bjartell A, Anderson KI and Malliri A:
β2-syntrophin and Par-3 promote an apicobasal Rac activity gradient
at cell-cell junctions by differentially regulating Tiam1 activity.
Nat Cell Biol. 14:1169–1180. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wong CS, Wong VW, Chan CM, Ma BB, Hui EP,
Wong MC, Lam MY, Au TC, Chan WH, Cheuk W and Chan AT:
Identification of 5-fluorouracil response proteins in colorectal
carcinoma cell line SW480 by two-dimensional electrophoresis and
MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. Oncol Rep. 20:89–98. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang P: Suppression of DACH1 promotes
migration and invasion of colorectal cancer via activating
TGF-β-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 460:314–319. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chen Y, Cha Z, Fang W, Qian B, Yu W, Li W,
Yu G and Gao Y: The prognostic potential and oncogenic effects of
PRR11 expression in hilar cholangiocarcinoma. Oncotarget.
6:20419–20433. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ji Q, Liu X, Han Z, Zhou L, Sui H, Yan L,
Jiang H, Ren J, Cai J and Li Q: Resveratrol suppresses
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer through
TGF-β1/Smads signaling pathway mediated Snail/E-cadherin
expression. BMC Cancer. 15:972015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Lee WS, Woo EY, Kwon J, Park MJ, Lee JS,
Han YH and Bae IH: Bcl-w enhances mesenchymal changes and
invasiveness of glioblastoma cells by inducing nuclear accumulation
of β-catenin. PLoS One. 8:e680302013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Matsumoto K, Arao T, Tanaka K, Kaneda H,
Kudo K, Fujita Y, Tamura D, Aomatsu K, Tamura T, Yamada Y, et al:
mTOR signal and hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha regulate CD133
expression in cancer cells. Cancer Res. 69:7160–7164. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Pistollato F, Abbadi S, Rampazzo E,
Persano L, Della Puppa A, Frasson C, Sarto E, Scienza R, D'avella D
and Basso G: Intratumoral hypoxic gradient drives stem cells
distribution and MGMT expression in glioblastoma. Stem Cells.
28:851–862. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ding Q, Yoshimitsu M, Kuwahata T, Maeda K,
Hayashi T, Obara T, Miyazaki Y, Matsubara S, Natsugoe S and Takao
S: Establishment of a highly migratory subclone reveals that CD133
contributes to migration and invasion through
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in pancreatic cancer. Hum Cell.
25:1–8. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Tlsty TD and Coussens LM: Tumor stroma and
regulation of cancer development. Annu Rev Pathol. 1:119–150. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Herrera A, Herrera M, Alba-Castellón L,
Silva J, García V, Loubat-Casanovas J, Alvarez-Cienfuegos A, Miguel
García J, Rodriguez R, Gil B, et al: Protumorigenic effects of
Snail-expression fibroblasts on colon cancer cells. Int J Cancer.
134:2984–2990. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Yang MC, Wang CJ, Liao PC, Yen CJ and Shan
YS: Hepatic stellate cells secretes type I collagen to trigger
epithelial mesenchymal transition of hepatoma cells. Am J Cancer
Res. 4:751–763. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Feng Y, Xu X, Zhang Y, Ding J, Wang Y,
Zhang X, Wu Z, Kang L, Liang Y, Zhou L, et al: HPIP is upregulated
in colorectal cancer and regulates colorectal cancer cell
proliferation, apoptosis and invasion. Sci Rep. 5:94292015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zhang HS, Yan B, Li XB, Fan L, Zhang YF,
Wu GH, Li M and Fang J: PAX2 protein induces expression of cyclin
D1 through activating AP-1 protein and promotes proliferation of
colon cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 287:44164–44172. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Park EJ, Chung HJ, Park HJ, Kim GD, Ahn YH
and Lee SK: Suppression of Src/ERK and GSK-3/β-catenin signaling by
pinosylvin inhibits the growth of human colorectal cancer cells.
Food Chem Toxicol. 55:424–433. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Hayashido Y, Kitano H, Sakaue T, Fujii T,
Suematsu M, Sakurai S and Okamoto T: Overexpression of integrin αv
facilitates proliferation and invasion of oral squamous cell
carcinoma cells via MEK/ERK signaling pathway that is activated by
interaction of integrin αvβ8 with type I collagen. Int J Oncol.
45:1875–1882. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Nykopp TK, Pasonen-Seppänen S, Tammi MI,
Tammi RH, Kosma VM, Anttila M and Sironen R: Decreased
hyaluronidase 1 expression is associated with early disease
recurrence in human endometrial cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 137:152–159.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Song L, Liu D, Wang B, He J, Zhang S, Dai
Z, Ma X and Wang X: miR-494 suppresses the progression of breast
cancer in vitro by targeting CXCR4 through the Wnt/β-catenin
signaling pathway. Oncol Rep. 34:525–531. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Cao F, Miao Y, Xu K and Liu P: Lethal (2)
giant larvae: An indispensable regulator of cell polarity and
cancer development. Int J Biol Sci. 11:380–389. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Mayne R, Vail MS and Miller EJ:
Characterization of the collagen chains synthesized by cultured
smooth muscle cells derived from rhesus monkey thoracic aorta.
Biochemistry. 17:446–452. 1978. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Brücher BL and Jamall IS: Cell-cell
communication in the tumor microenvironment, carcinogenesis and
anticancer treatment. Cell Physiol Biochem. 34:213–243. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Yamanaka T, Horikoshi Y, Suzuki A,
Sugiyama Y, Kitamura K, Maniwa R, Nagai Y, Yamashita A, Hirose T,
Ishikawa H and Ohno S: Par-6 regulates aPKC activity in a novel way
and mediates cell-cell contact-induced formation of the epithelial
junctional complex. Genes Cells. 6:721–731. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Guo J, Niu R, Huang W, Zhou M, Shi J,
Zhang L and Liao H: Growth factors from tumor microenvironment
possibly promote the proliferation of glioblastoma-derived
stem-like cells in vitro. Pathol Oncol Res. 18:1047–1057. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Itoh M, Sasaki H, Furuse M, Ozaki H, Kita
T and Tsukita S: Junctional adhesion molecule (JAM) binds to PAR-3:
A possible mechanism for the recruitment of PAR-3 to tight
junctions. J Cell Biol. 154:491–497. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Ebnet K, Suzuki A, Horikoshi Y, Hirose T,
Meyer Zu, Brickwedde MK, Ohno S and Vestweber D: The cell polarity
protein ASIP/PAR-3 directly associates with junctional adhesion
molecule (JAM). EMBO J. 20:3738–3748. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Lokeshwar VB, Rubinowicz D, Schroeder GL,
Forgacs E, Minna JD, Block NL, Nadji M and Lokeshwar BL: Stromal
and epithelial expression of tumor markers hyaluronic acid and
HYAL1 hyaluronidase in prostate cancer. J Biol Chem.
276:11922–11932. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Lokeshwar VB, Young MJ, Goudarzi G, Iida
N, Yudin AI, Cherr GN and Selzer MG: Identification of bladder
tumor-derived hyaluronidase: Its similarity to HYAL1. Cancer Res.
59:4464–44670. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
McCrea PD, Gu D and Balda MS: Junctional
music that the nucleus hears: Cell-cell contact signaling and the
modulation of gene activity. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.
1:a0029232009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Menzel EJ and Farr C: Hyaluronidase and
its substrate hyaluronan: Biochemistry, biological activities and
therapeutic uses. Cancer Lett. 131:3–11. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Turley EA, Noble PW and Bourguignon LY:
Signaling properties of hyaluronan receptors. J Biol Chem.
277:4589–4592. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Paiva P, Van Damme MP, Tellbach M, Jones
RL, Jobling T and Salamonsen LA: Expression patterns of hyaluronan,
hyaluronan synthases and hyaluronidases indicate a role for
hyaluronan in the progression of endometrial cancer. Gynecol Oncol.
98:193–202. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Wang F, Grigorieva EV, Li J, Senchenko VN,
Pavlova TV, Anedchenko EA, Kudryavtseva AV, Tsimanis A, Angeloni D,
Lerman MI, et al: HYAL1 and HYAL2 inhibit tumour growth in vivo but
not in vitro. PLoS One. 3:e30312008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Lokeshwar VB, Cerwinka WH and Lokeshwar
BL: HYAL1 hyaluronidase: A molecular determinant of bladder tumor
growth and invasion. Cancer Res. 65:2243–2250. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Kramer MW, Golshani R, Merseburger AS,
Knapp J, Garcia A, Hennenlotter J, Duncan RC, Soloway MS, Jorda M,
Kuczyk MA, et al: HYAL-1 hyaluronidase: A potential prognostic
indicator for progression to muscle invasion and recurrence in
bladder cancer. Eur Urol. 57:86–93. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
69
|
Wakitani S, Kimura T, Hirooka A, Ochi T,
Yoneda M, Yasui N, Owaki H and Ono K: Repair of rabbit articular
surfaces with allograft chodnrocytes embedded in collagen gel. J
Bone Joint Surg Br. 71:74–80. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Frenkel SR, Toolan B, Menche D, Pitman MI
and Pachence JM: Chondrocyte transplantation using a collagen
bilayer matrix for cartilage repair. J Bone Joint Surg Br.
79:831–836. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Schuppan D, Schmid M, Somasundaram R,
Ackermann R, Ruehl M, Nakamura T and Riecken EO: Collagens in the
liver extracellular matrix bind hepatocyte growth factor.
Gastroenterology. 114:139–152. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Kauppila S, Stenbäck F, Risteli J, Jukkola
A and Risteli L: Aberrant type I and III collagen gene expression
in human breast cancer in vivo. J Pathol. 186:262–268. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Minamoto T, Ooi A, Okada Y, Mai M, Nagai Y
and Nakanishi I: Desmoplastic reaction of gastric carcinoma: A
light- and electron microscopic immunohistochemical analysis using
collagen type-specific antibodies. Hum Pathol. 19:815–821. 1988.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Bosman FT, de Bruïne A, Flohil C, van der
Wurff A, ten Kate J and Dinjens WW: Epithelial-stromal interactions
in colon cancer. Int J Dev Biol. 37:203–211. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Dahlman T, Lammerts E, Wik M, Bergström D,
Grimelius L, Westermark K, Rubin K and Heldin NE: Fibrosis in
undifferentiated (anaplastic) thyroid carcinomas: Evidence for a
dual action of tumour cells in collagen type I synthesis. J Pathol.
191:376–386. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Pietras K and Ostman A: Hallmarks of
cancer: Interactions with the tumor stroma. Exp Cell Res.
316:1324–1331. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Niehans GA, Kratzke RA, Froberg MK, Aeppli
DM, Nguyen PL and Geradts J: G1 checkpoint protein and p53
abnormalities occur in most invasive transitional cell carcinomas
of the urinary bladder. Br J Cancer. 80:1175–1184. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Mani SA, Guo W, Liao MJ, Eaton EN, Ayyanan
A, Zhou AY, Brooks M, Reinhard F, Zhang CC, Shipitsin M, et al: The
epithelial-mesenchymal transition generates cells with properties
of stem cells. Cell. 133:704–715. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Huang R, Wang G, Song Y, Tang Q, You Q,
Liu Z, Chen Y, Zhang Q, Li J, Muhammand S, et al: Colorectal cancer
stem cell and chemo-resistant colorectal cancer cell phenotypes and
increased sensitivity to Notch pathway inhibitor. Mol Med Rep.
12:2417–2424. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Alao JP: The regulation of cyclin D1
degradation: Roles in cancer development and the potential for
therapeutic invention. Mol Cancer. 6:242007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Ricci-Vitiani L, Lombardi DG, Pilozzi E,
Biffoni M, Todaro M, Peschle C and De Maria R: Identification and
expansion of human colon-cancer-initiating cells. Nature.
445:111–115. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
O'Brien CA, Pollett A, Gallinger S and
Dick JE: A human colon cancer cell capable of initiating tumour
growth in immunodeficient mice. Nature. 445:106–110. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Gilcrease MZ: Integrin signaling in
epithelial cells. Cancer Lett. 247:1–25. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Takada Y, Ye X and Simon S: The integrins.
Genome Biol. 8:2152007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Iwatsuki H, Sasaki K, Suda M and Itano C:
Vimentin intermediate filament protein as differentiation marker of
optic vesicle epithelium in the chick embryo. Acta Histochem.
101:369–382. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Gilles C, Polette M, Zahm JM, Tournier JM,
Volders L, Foidart JM and Birembaut P: Vimentin contributes to
human mammary epithelial cell migration. J Cell Sci. 112:4615–4625.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Shattil SJ, Kim C and Ginsberg MH: The
final steps of integrin activation: The end game. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 11:288–300. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Box C, Rogers SJ, Mendiola M and Eccles
SA: Tumour-microenvironmental interactions: Paths to progression
and targets for treatment. Semin Cancer Biol. 20:128–138. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Hammoudi A, Song F, Reed KR, Jenkins RE,
Meniel VS, Watson AJ, Pritchard DM, Clarke AR and Jenkins JR:
Proteomic profiling of a mouse model of acute intestinal Apc
deletion leads to identification of potential novel biomarkers of
human colorectal cancer (CRC). Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
440:364–370. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|