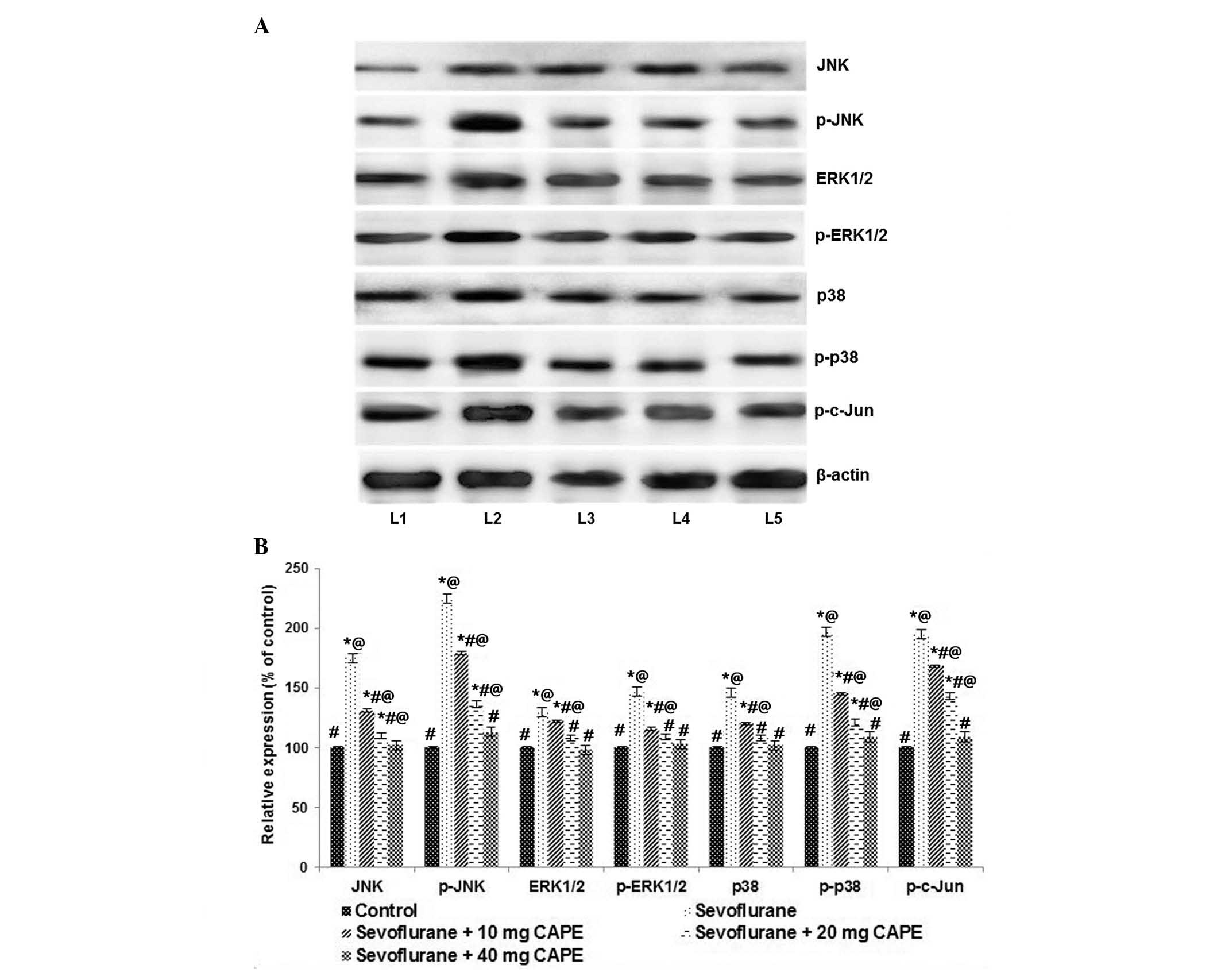
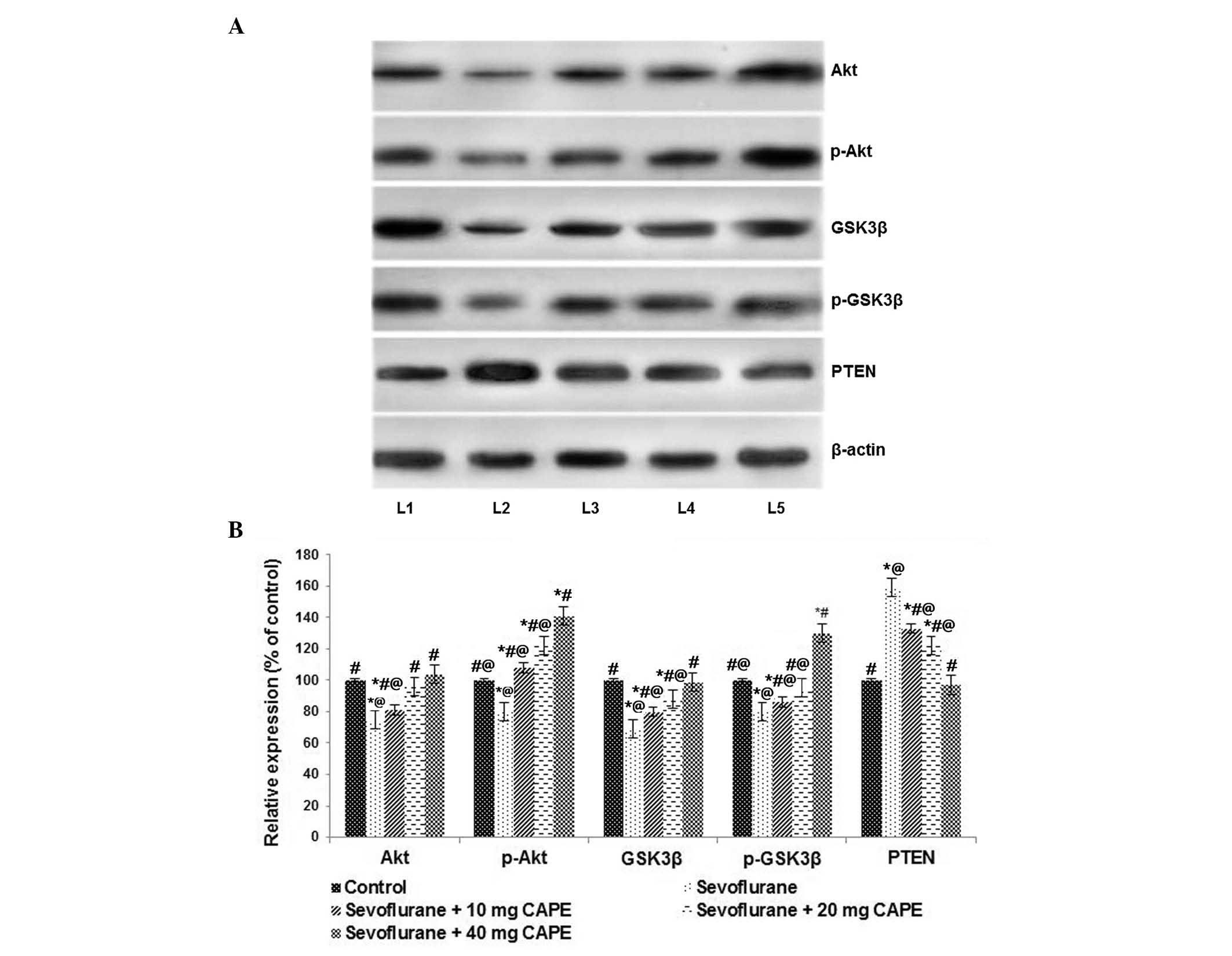
|
1
|
Istaphanous GK and Loepke AW: General
anesthetics and the developing brain. Curr Opin Anesthesiol.
22:368–373. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Patel SS and Goa KL: Sevoflurane: A review
of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties and its
clinical use in general anaesthesia. Drugs. 51:658–700. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Johnson SA, Young C and Olney JW:
Isoflurane-induced neuroapoptosis in the developing brain of
nonhypoglycemic mice. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol. 20:21–28. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Brambrink AM, Evers AS, Avidan MS, Farber
NB, Smith DJ, Zhang X, Dissen GA, Creeley CE and Olney JW:
Isoflurane-induced neuroapoptosis in theneonatal rhesus macaque
brain. Anesthesiology. 112:834–841. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li Y, Liu C, Zhao Y, Hu K, Zhang J, Zeng
M, Luo T, Jiang W and Wang H: Sevoflurane induces short-term
changes in proteins in the cerebral cortices of developing rats.
Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 57:380–390. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Li Y, Wang F, Liu C, Zeng M, Han X, Luo T,
Jiang W, Xu J and Wang H: JNK pathway may be involved in
isoflurane-induced apoptosis in the hippocampi of neonatal rats.
Neurosci Lett. 545:17–22. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jevtovic-Todorovic V, Hartman RE, Izumi Y,
Benshoff ND, Dikranian K, Zorum-ski CF, Olney JW and Wozniak DF:
Early exposure to common anesthetic agents causes widespread
neurodegeneration in the developing rat brain and persistent
learning deficits. J Neurosci. 23:876–882. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhu C, Gao J, Karlsson N, Li Q, Zhang Y,
Huang Z, Li H, Kuhn HG and Blomgren K: Isoflurane anesthesia
induced persistent, progressive memory impairment, caused a loss of
neural stem cells and reduced neurogenesis in young, but not adult,
rodents. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 30:1017–1030. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Stratmann G, Sall JW, May LD, Bell JS,
Magnusson KR, Rau V, Visrodia KH, Alvi RS, Ku B, Lee MT and Dai R:
Isoflurane differentially affects neurogenesis and long-term
neurocognitive function in 60 day-old and 7 day-old rats.
Anesthesiology. 110:834–848. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
DiMaggio C, Sun LS and Li G: Early
childhood exposure to anesthesia and risk of developmental and
behavioral disorders in a sibling birth cohort. Anesth Analg.
113:1143–1151. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ing C, DiMaggio C, Whitehouse A, Hegarty
MK, Brady J, von Ungern-Sternberg BS, Davidson A, Wood AJ, Li G and
Sun LS: Long-term differences in language and cognitive function
after childhood exposure to anesthesia. Pediatrics. 130:e476–e485.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Satomoto M, Satoh Y, Terui K, Miyao H,
Takishima K, Ito M and Imaki J: Neonatal exposure to sevoflurane
induces abnormal social behaviors and deficits in fear conditioning
in mice. Anesthesiology. 110:628–637. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kodama M, Satoh Y, Otsubo Y, Araki Y,
Yonamine R, Masui K and Kazama T: Neonatal desflurane exposure
induces more robust neuroapoptosis than do isoflurane and
sevoflurane and impairs working memory. Anesthesiology.
115:979–991. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shih J, May LD, Gonzalez HE, Lee EW, Alvi
RS, Sall JW, Rau V, Bickler PE, Lalchandani GR, Yusupova M, et al:
Delayed environmental enrichment reverses sevoflurane-induced
memory impairment in rats. Anesthesiology. 116:586–602. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wei HF, Liang G, Yang H, Wang Q, Hawkins
B, Madesh M, Wang S and Eckenhoff RG: The common inhalational
anesthetic isoflurane induces apoptosis via activation of inositol
1,4,5-trisphosphate receptors. Anesthesiology. 108:251–260. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lunardi N, Ori C, Erisir A and
Jevtovic-Todorovic V: General anesthesia causes long-lasting
disturbances in the ultrastructural properties of developing
synapses in young rats. Neurotox Res. 17:179–188. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Zhao X, Yang Z, Liang G, Wu Z, Peng Y,
Joseph DJ, Inan S and Wei H: Dual effects of isoflurane on
proliferation, differentiation and survival in human
neuroprogenitor cells. Anesthesiology. 118:537–549. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Soriano SG, Liu Q, Li J, Liu JR, Han XH,
Kanter JL, Bajic D and Ibla JC: Ketamine activates cell cycle
signaling and apoptosis in the neonatal rat brain. Anesthesiology.
112:1155–1163. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sinner B, Friedrich O, Zink W, Zausig Y
and Graf BM: The toxic effects of s(+)-ketamine on differentiating
neurons in vitro as a consequence of suppressed neuronal
Ca2+ oscillations. Anesth Analg. 113:1161–1169. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhao YL, Xiang Q, Shi QY, Li SY, Tan L,
Wang JT, Jin XG and Luo AL: GABAergic excitotoxicity injury of the
immature hippocampal pyramidal neurons' exposure to isoflurane.
Anesth Analg. 113:1152–1160. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Brambrink AM, Evers AS, Avidan MS, Farber
NB, Smith DJ, Martin LD, Dissen GA, Creeley CE and Olney JW:
Ketamine-induced neuroapoptosis in the fetal and neonatal rhesus
macaque brain. Anesthesiology. 116:372–384. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Istaphanous GK, Ward CG, Nan X, Hughes EA,
Mccann JC, McAuliffe JJ, Danzer SC and Loepke AW: Characterization
and quantification of isoflurane-induced developmental apoptotic
cell death in mouse cerebral cortex. Anesth Analg. 116:845–854.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Mousa A and Bakhiet M: Role of cytokine
signaling during nervous system development. Int J Mol Sci.
14:13931–13957. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Harper SJ and Wilkie N: MAPKs: New targets
for neurodegeneration. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 7:187–200. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kaminska B, Gozdz A, Zawadzka M,
Ellert-Miklaszewska A and Lipko M: MAPK signal transduction
underlying brain inflammation and gliosis as therapeutic target.
Anat Rec (Hoboken). 292:1902–1913. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Wang WY, Yang R, Hu SF, Wang H, Ma ZW and
Lu Y: N-stearoyl-l-tyrosine ameliorates sevoflurane induced
neuroapoptosis via MEK/ERK1/2MAPK signaling pathway in the
developing brain. Neurosci Lett. 541:167–172. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sanders RD, Sun P, Patel S, Li M, Maze M
and Ma D: Dexmedetomidine provides cortical neuroprotection: Impact
on anaesthetic-induced neuroapoptosisin the rat developing brain.
Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 54:710–716. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Li Y, Zeng M, Chen W, Liu C, Wang F, Han
X, Zuo Z and Peng S: Dexmedetomidine reduces isoflurane-induced
neuroapoptosis partly by pre-serving PI3K/Akt pathway in the
hippocampus of neonatal rats. PLoS One. 9:e936392014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Zhao Y, Liang G, Chen Q, Joseph DJ, Meng
Q, Eckenhoff RG, Eckenhoff MF and Wei H: Anesthetic-induced
neurodegeneration mediated via inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate
receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 333:14–22. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bai T, Dong DS and Pei L: Resveratrol
mitigates isoflurane-induced neuroapoptosis by inhibiting the
activation of the Akt-regulated mitochondrial apoptotic signaling
pathway. Int J Mol Med. 32:819–826. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Demestre M, Messerli SM, Celli N,
Shahhossini M, Kluwe L, Mautner V and Maruta H: CAPE (caffeic acid
phenethyl ester)-based propolis extract (Bio 30) suppresses the
growth of human neurofibromatosis (NF) tumor xenografts in mice.
Phytother Res. 23:226–230. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Natarajan K, Singh S, Burke TR Jr,
Grunberger D and Aggarwal BB: Caffeic acid phenethyl ester is a
potent and specific inhibitor of activation of nuclear
transcription factor NF-kappaB. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
93:9090–9095. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Lin HP, Jiang SS and Chuu CP: Caffeic acid
phenethyl ester causes p21 induction, Akt signaling reduction and
growth inhibition in PC-3 human prostate cancer cells. PLoS One.
7:e312862012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Orban Z, Mitsiades N, Burke TR, Tsokos M
and Chrousos GP: Caffeic acid phenethyl ester induces leukocyte
apoptosis, modulates nuclear factor-kappaB and suppresses acute
inflammation. Neuroimmunomodulation. 7:99–105. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Irmak MK, Fadillioglu E, Sogut S, Erdogan
H, Gulec M, Ozer M, Yagmurca M and Gozukara ME: Effects of caffeic
acid phenethyl ester and alpha-tocopherol on reperfusion injury in
rat brain. Cell Biochem Funct. 21:283–289. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Altug ME, Serarslan Y, Bal R, Kontas T,
Ekici F, Melek IM, Aslan H and Duman T: Caffeic acid phenethyl
ester protects rabbit brains against permanent focal ischemia by
antioxidant action: A biochemical and planimetric study. Brain Res.
1201:135–142. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kurauchi Y, Hisatsune A, Isohama Y,
Mishima S and Katsuki H: Caffeic acid phenethyl ester protects
nigral dopaminergic neurons via dual mechanisms involving haem
oxygenase-1 and brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Br J Pharmacol.
166:1151–1168. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Istaphanous GK, Howard J, Nan X, Hughes
EA, McCann JC, McAuliffe JJ, Danzer SC and Loepke AW: Comparison of
the neuroapoptotic properties of equipotent anesthetic
concentrations of desflurane, isoflurane, or sevoflurane in
neonatal mice. Anesthesiology. 114:578–587. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Bloomfield SM, McKinney J, Smith L and
Brisman J: Reliability of S100B in predicting severity of central
nervous system injury. Neurocritical Care. 6:121–138. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wang S, Peretich K, Zhao Y, Liang G, Meng
Q and Wei H: Anesthesia induced neurodegeneration in fetal rat
brains. Pediatr Res. 66:435–440. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Li B, Du T, Li H, Gu L, Zhang H, Huang J,
Hertz L and Peng L: Signaling pathways for transactivation by
dexmedetomidine of epidermal growth factor receptors in astrocytes
and its paracrine effect on neurons. Br J Pharmacol. 154:191–203.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Pearn ML, Hu Y, Niesman IR, Patel HH,
Drummond JC, Roth DM, Akassoglou K, Patel PM and Head BP: Propofol
neurotoxicity is mediated by p75 neurotrophin receptor activation.
Anesthesiology. 116:352–361. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
43
|
Creeley C, Dikranian K, Dissen G, Martin
L, Olney J and Brambrink A: Propofol induced apoptosis of neurones
and oligodendrocytes in fetal and neonatal rhesus macaque brain. Br
J Anaesth. 110:i29–i38. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Liang G, Ward C, Peng J, Zhao Y, Huang B
and Wei H: Isoflurane causes greater neurodegeneration than an
equivalent exposure of sevoflurane in the developing brain of
neonatal mice. Anesthesiology. 112:1325–1334. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Dong Y, Zhang G, Zhang B, Moir RD, Xia W,
Marcantonio ER, Culley DJ, Crosby G, Tanzi RE and Xie Z: The common
inhalational anesthetic sevoflurane induces apoptosis and increases
beta-amyloid protein levels. Arch Neurol. 66:620–631. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zheng SQ, An LX, Cheng1 X and Wang YJ:
Sevoflurane causes neuronal apoptosis and adaptability changes of
neonatal rats. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 57:1167–1174. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Du T, Li B, Liu S, Zang P, Prevot V, Hertz
L and Peng L: ERK phosphorylationin intact, adult brain by
alpha(2)-adrenergic trans-activation of EGF receptors. Neurochem
Int. 55:593–600. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zhang X, Wang J, Qian W, Zhao J, Sun L,
Qian Y and Xiao H: Dexmedetomidine inhibits tumor necrosis
factor-alpha and interleukin 6 inlipopolysaccharide-stimulated
astrocytes by suppression of c-Jun N-terminalkinases. Inflammation.
37:942–949. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Yang H, Liang G, Hawkins BJ, Madesh M,
Pierwola A and Wei H: Inhalational anesthetics induce cell damage
by disruption of intracellular calcium homeostasis with different
potencies. Anesthesiology. 109:243–250. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Flick RP, Katusic SK, Colligan RC, Wilder
RT, Voigt RG, Olson MD, Sprung J, Weaver AL, Schroeder DR and
Warner DO: Cognitive and behavioral outcomes after early exposure
to anesthesia and surgery. Pediatrics. 128:e1053–e1061. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Bong CL, Allen JC and Kim JT: The effects
of exposure to general anesthesia in infancy on academic
performance at age 12. Anesth Analg. 117:1419–1428. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Fang F, Xue Z and Cang J: Sevoflurane
exposure in 7 day-old rats affects neurogenesis, neurodegeneration
and neurocognitive function. Neurosci Bull. 28:499–508. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Oppenheim RW: Cell death during
development of the nervous system. Annu Rev Neurosci. 14:453–501.
1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Rakic S and Zecevic N: Programmed cell
death in the developing human telencephalon. Eur J Neurosci.
12:2721–2734. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Blomgren K, Leist M and Groc L:
Pathological apoptosis in the developing brain. Apoptosis.
12:993–1010. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Loepke AW and Soriano SG: An assessment of
the effects of general anesthetics on developing brain structure
and neurocognitive function. Anesth Analg. 106:1681–1707. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Gown AM and Willingham MC: Improved
detection of apoptotic cells in archival paraffin sections:
Immunohistochemistry using antibodies to cleaved caspase 3. J
Histochem Cytochem. 50:449–454. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Zhao H, Yenari MA, Cheng D, Sapolsky RM
and Steinberg GK: Bcl-2 overexpression protects against neuron loss
within the ischemic margin following experimental stroke and
inhibits cytochrome c translocation and caspase-3 activity. J
Neurochem. 85:1026–1036. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Chong ZZ, Li F and Maiese K: Oxidative
stress in the brain: Novel cellular targets that govern survival
during neurodegenerative disease. Prog Neurobiol. 75:207–246. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Hou J, Wang S, Shang YC, Chong ZZ and
Maiese K: Erythropoietin employs cell longevity pathways of SIRT1
to foster endothelial vascular integrity during oxidant stress.
Curr Neurovasc Res. 8:220–235. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Koh PO: Nicotinamide attenuates the
ischemic brain injury-induced decrease of Akt activation and Bad
phosphorylation. Neurosci Lett. 498:105–109. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Yon JH, Daniel-Johnson J, Carter LB and
Jevtovic-Todorovic V: Anesthesia induces neuronal cell death in the
developing rat brain via the intrinsic and extrinsic apoptotic
pathways. Neuroscience. 135:815–827. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Peltier J, O'Neill A and Schaffer DV:
PI3K/Akt and CREB regulate adult neural hippocampal progenitor
proliferation and differentiation. Dev Neurobiol. 67:1348–1361.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Wyatt LA, Filbin MT and Keirstead HS: PTEN
inhibition enhances neurite outgrowth in human embryonic stem
cell-derived neuronal progenitor cells. J Comp Neurol.
522:2741–2755. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Ojeda L, Gao J, Hooten KG, Wang E,
Thonhoff JR, Dunn TJ, Gao T and Wu P: Critical role of
PI3K/Akt/GSK3β in motoneuron specification from human neural stem
cells in response to FGF2 and EGF. PLoS One. 6:e234142011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Luo HR, Hattori H, Hossain MA, Hester L,
Huang Y, Lee-Kwon W, Donowitz M, Nagata E and Snyder SH: Akt as a
mediator of cell death. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:11712–11717.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Song G, Ouyang G and Bao S: The activation
of Akt/PKB signaling pathway and cell survival. J Cell Mol Med.
9:59–71. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Yeste-Velasco M, Folch J, Casadesús G,
Smith MA, Pallàs M and Camins A: Neuroprotection by c-Jun
NH2-terminal kinase inhibitor SP600125 against potassium
deprivation-induced apoptosis involves the Akt pathway and
inhibition of cell cycle reentry. Neuroscience. 159:1135–1147.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Wang W, Shi L, Xie Y, Ma C, Li W, Su X,
Huang S, Chen R, Zhu Z, Mao Z, et al: SP600125, a new JNK
inhibitor, protects dopaminergic neurons in the MPTP model of
Parkinson's disease. Neurosci Res. 48:195–202. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Kuan CY and Burke RE: Targeting the JNK
signaling pathway for stroke and Parkinson's diseases therapy. Curr
Drug Targets CNS Neurol Disord. 4:63–67. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Walker CL, Walker MJ, Liu NK, Risberg EC,
Gao X, Chen J and Xu XM: Systemic bisperoxovanadium activates
Akt/mTOR, reduces autophagy and enhances recovery following
cervical spinal cord injury. PLoS One. 7:e300122012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Guan QH, Pei DS, Zhang QG, Hao ZB, Xu TL
and Zhang GY: The neuroprotective action of SP600125, a new
inhibitor of JNK, on transient brain ischemia/reperfusion-induced
neuronal death in rat hippocampal CA1 via nuclear and non-nuclear
pathways. Brain Res. 1035:51–59. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Han JY, Jeong EY, Kim YS, Roh GS, Kim HJ,
Kang SS, Cho GJ and Choi WS: C-jun N-terminal kinase regulates the
interaction between 14-3-3 and bad in ethanol-induced cell death. J
Neurosci Res. 86:3221–3229. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Fan J, Xu G, Nagel DJ, Hua Z, Zhang N and
Yin G: A model of ischemia and reperfusion increases JNK activity,
inhibits the association of bad and 14-3-3 and induces apoptosis of
rabbit spinal neurocytes. Neurosci Lett. 473:196–201. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Liao Z, Cao D, Han X, Liu C, Peng J, Zuo
Z, Wang F and Li Y: Both JNK and P38 MAPK pathways participate in
the protection by dexmedetomidine against isoflurane-induced
neuroapoptosis in the hippocampus of neonatal rats. Brain Res Bull.
107:69–78. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Zheng S and Zuo Z: Isoflurane
preconditioning induces neuroprotection against ischemia via
activation of P38 mitogen-activated protein kinases. Mol Pharmacol.
65:1172–1180. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|