|
1
|
Udompataikul M and Limpa-o-vart D:
Comparative trial of 5% dexpanthenol in water-in-oil formulation
with 1% hydrocortisone ointment in the treatment of childhood
atopic dermatitis: A pilot study. J Drugs Dermatol. 11:366–374.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Amin K: The role of mast cells in allergic
inflammation. Respir Med. 106:9–14. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Sampson HA: Atopic dermatitis. Ann
Allergy. 69:469–479. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Schneider L, Tilles S, Lio P, Boguniewicz
M, Beck L, Lebovidge J, et al: Atopic dermatitis: A practice
parameter update 2012. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 131:295–299. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hashimoto Y, Takaoka A, Sugimoto M, Honma
Y, Sakurai T, Futaki N and Arai I: Itch-associated scratching
contributes to the development of dermatitis and
hyperimmunoglobulinaemia E in NC/Nga mice. Exp Dermatol.
20:820–825. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Leung DY and Soter NA: Cellular and
immunologic mechanisms in atopic dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol.
44(Suppl 1): S1–S12. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Miraglia del Giudice M, Decimo F, Leonardi
S, Maioello N, Amelio R, Capasso A, Capristo C and Capristo AF:
Immune dysregulation in atopic dermatitis. Allergy Asthma Proc.
27:451–455. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wierenga EA, Snoek M, Jansen HM, Bos JD,
van Lier RA and Kapsenberg ML: Human atopen-specific types 1 and 2
T helper cell clones. J Immunol. 147:2942–2949. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Szegedi A, Baráth S, Nagy G, Szodoray P,
Gál M, Sipka S, Bagdi E, Banham AH and Krenács L: Regulatory T
cells in atopic dermatitis: epidermal dendritic cell clusters may
contribute to their local expansion. Br J Dermatol. 160:984–993.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Oyoshi MK, He R, Kumar L, Yoon J and Geha
RS: Cellular and molecular mechanisms in atopic dermatitis. Adv
Immunol. 102:135–226. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Eyerich K, Pennino D, Scarponi C, Foerster
S, Nasorri F, Behrendt H, Ring J, Traidl-Hoffmann C, Albanesi C and
Cavani A: IL-17 in atopic eczema: Linking allergen-specific
adaptive and microbial-triggered innate immune response. J Allergy
Clin Immunol. 123:59–66.e4. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Nakae S, Komiyama Y, Nambu A, Sudo K,
Iwase M, Homma I, Sekikawa K, Asano M and Iwakura Y:
Antigen-specific T cell sensitization is impaired in
IL-17-deficient mice, causing suppression of allergic cellular and
humoral responses. Immunity. 17:375–387. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hengge UR, Ruzicka T, Schwartz RA and Cork
MJ: Adverse effects of topical glucocorticosteroids. J Am Acad
Dermatol. 54:1–15; quiz 16–18. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Yang G, Choi CH, Lee K, Lee M, Ham I and
Choi HY: Effects of Catalpa ovata stem bark on atopic
dermatitis-like skin lesions in NC/Nga mice. J Ethnopharmacol.
145:416–423. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
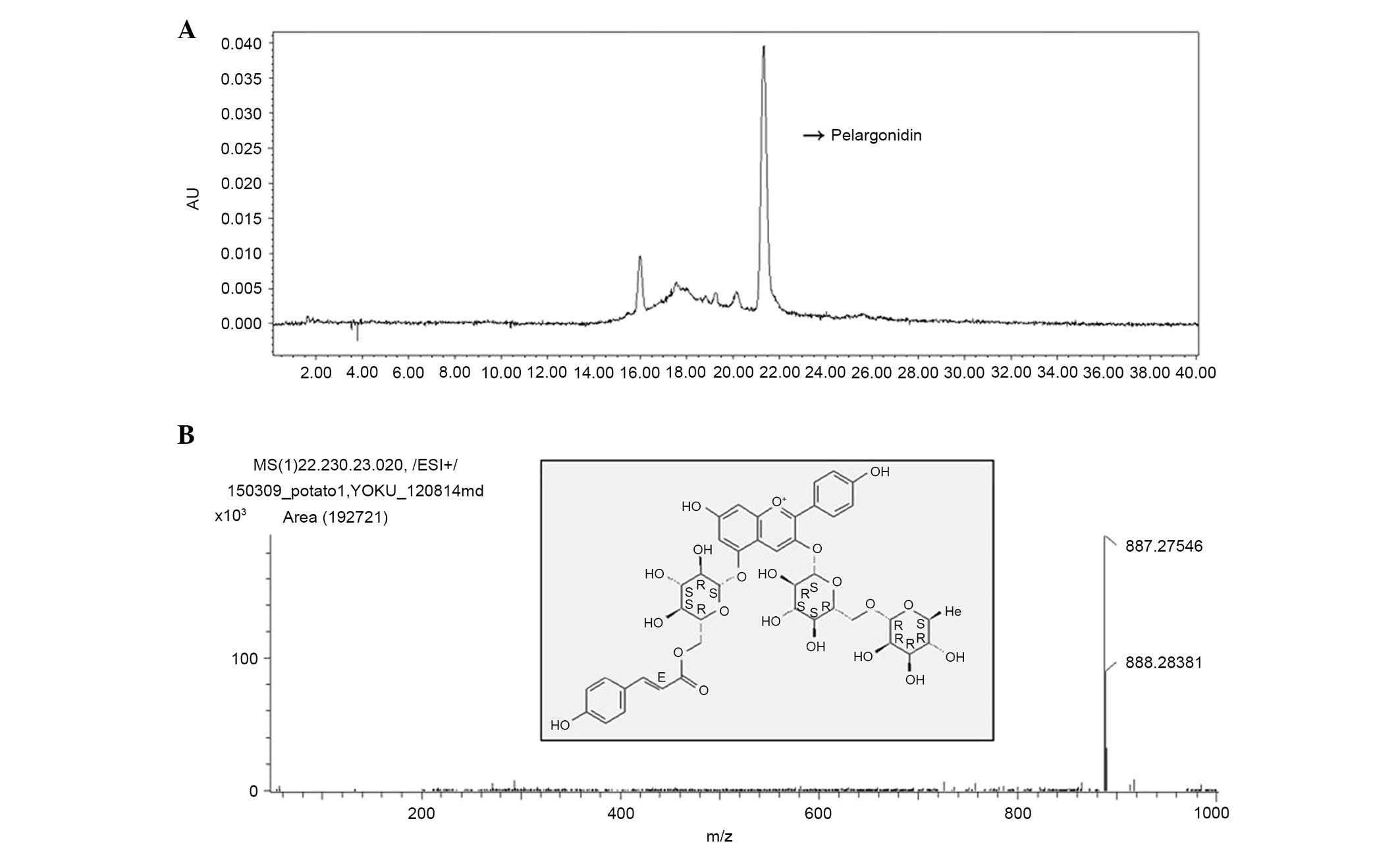
Ieri F, Innocenti M, Andrenelli L, Vecchio
V and Mulinacci N: Rapid HPLC/DAD/MS method to determine phenolic
acids, glycoalkaloids and anthocyanins in pigmented potatoes
(Solanum tuberosum L.) and correlations with variety and
geographical origin. Food Chemistry. 125:750–759. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Mulinacci N, Ieri F, Giaccherini C,
Innocenti M, Andrenelli L, Canova G, Saracchi M and Casiraghi MC:
Effect of cooking on the anthocyanins, phenolic acids,
glycoalkaloids, and resistant starch content in two pigmented
cultivars of Solanum tuberosum L. J Agric Food Chem.
56:11830–11837. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Afaq F, Malik A, Syed D, Maes D, Matsui MS
and Mukhtar H: Pomegranate fruit extract modulates UV-B-mediated
phosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein kinases and activation
of nuclear factor kappa B in normal human epidermal keratinocytes
paragraph sign. Photochem Photobiol. 81:38–45. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Suto H, Matsuda H, Mitsuishi K, Hira K,
Uchida T, Unno T, Ogawa H and Ra C: NC/Nga mice: A mouse model for
atopic dermatitis. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 120(Suppl 1): S70–S75.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
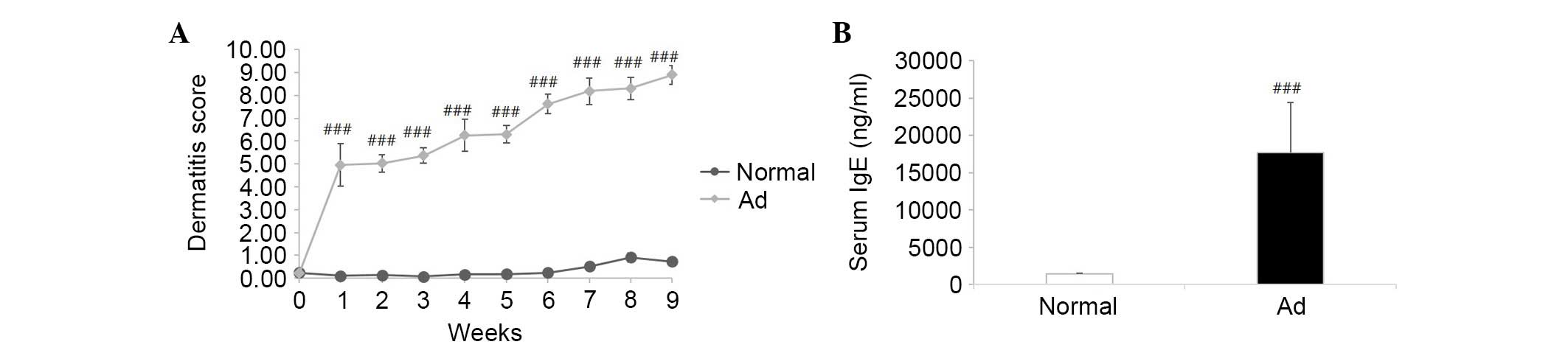
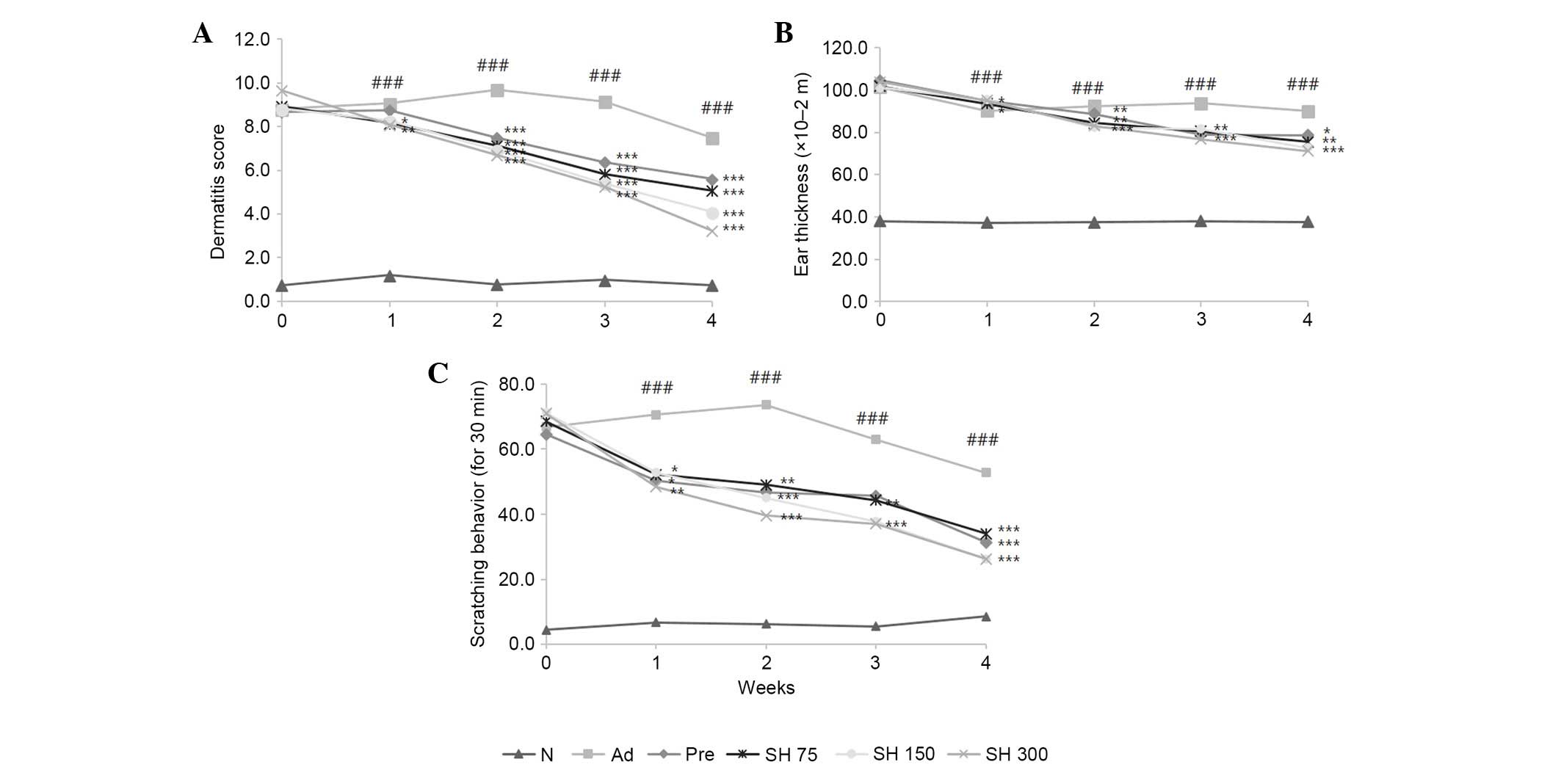
Takano N, Arai I and Kurachi M: Analysis
of the spontaneous scratching behavior by NC/Nga mice: A possible
approach to evaluate antipruritics for subjects with atopic
dermatitis. Eur J Pharmacol. 471:223–228. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mihara K, Kuratani K, Matsui T, Nakamura M
and Yokota K: Vital role of the itch-scratch response in
development of spontaneous dermatitis in NC/Nga mice. Br J
Dermatol. 151:335–345. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Wesolowski J and Paumet F: The impact of
bacterial infection on mast cell degranulation. Immunol Res.
51:215–226. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lee TY, Kim DJ, Won JN, Lee IH, Sung MH
and Poo H: Oral administration of poly-gamma-glutamate ameliorates
atopic dermatitis in Nc/Nga mice by suppressing Th2-biased immune
response and production of IL-17A. J Invest Dermatol. 134:704–711.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Koga C, Kabashima K, Shiraishi N,
Kobayashi M and Tokura Y: Possible pathogenic role of Th17 cells
for atopic dermatitis. J Invest Dermatol. 128:2625–2630. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bieber T: Atopic dermatitis. N Engl J Med.
358:1483–1494. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Akdis M, Simon HU, Weigl L, Kreyden O,
Blaser K and Akdis CA: Skin homing (cutaneous lymphocyte-associated
antigen-positive) CD8+ T cells respond to superantigen and
contribute to eosinophilia and IgE production in atopic dermatitis.
J Immunol. 163:466–475. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Akdis CA, Akdis M, Simon D, Dibbert B,
Weber M, Gratzl S, Kreyden O, Disch R, Wüthrich B, Blaser K and
Simon HU: T cells and T cell-derived cytokines as pathogenic
factors in the nonallergic form of atopic dermatitis. J Invest
Dermatol. 113:628–634. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kim GD, Kim TH, Park YS, Ahn HJ, Cho JJ
and Park CS: Immune response against
2,4-dinitrofluorobenzene-induced atopic dermatitis-like clinical
manifestation is suppressed by spermidine in NCNga mice. Scand J
Immunol. 81:221–228. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lin YT, Wang CT, Chao PS, Lee JH, Wang LC,
Yu HH, Yang YH and Chiang BL: Skin-homing CD4+
Foxp3+ T cells exert Th2-like function after
staphylococcal superantigen stimulation in atopic dermatitis
patients. Clin Exp Allergy. 41:516–525. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Werfel T: The role of leukocytes,
keratinocytes, and allergen-specific IgE in the development of
atopic dermatitis. J Invest Dermatol. 129:1878–1891. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hinz D, Bauer M, Röder S, Olek S, Huehn J,
Sack U, Borte M, Simon JC and Lehmann I: Cord blood Tregs with
stable FOXP3 expression are influenced by prenatal environment and
associated with atopic dermatitis at the age of one year. Allergy.
67:380–389. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
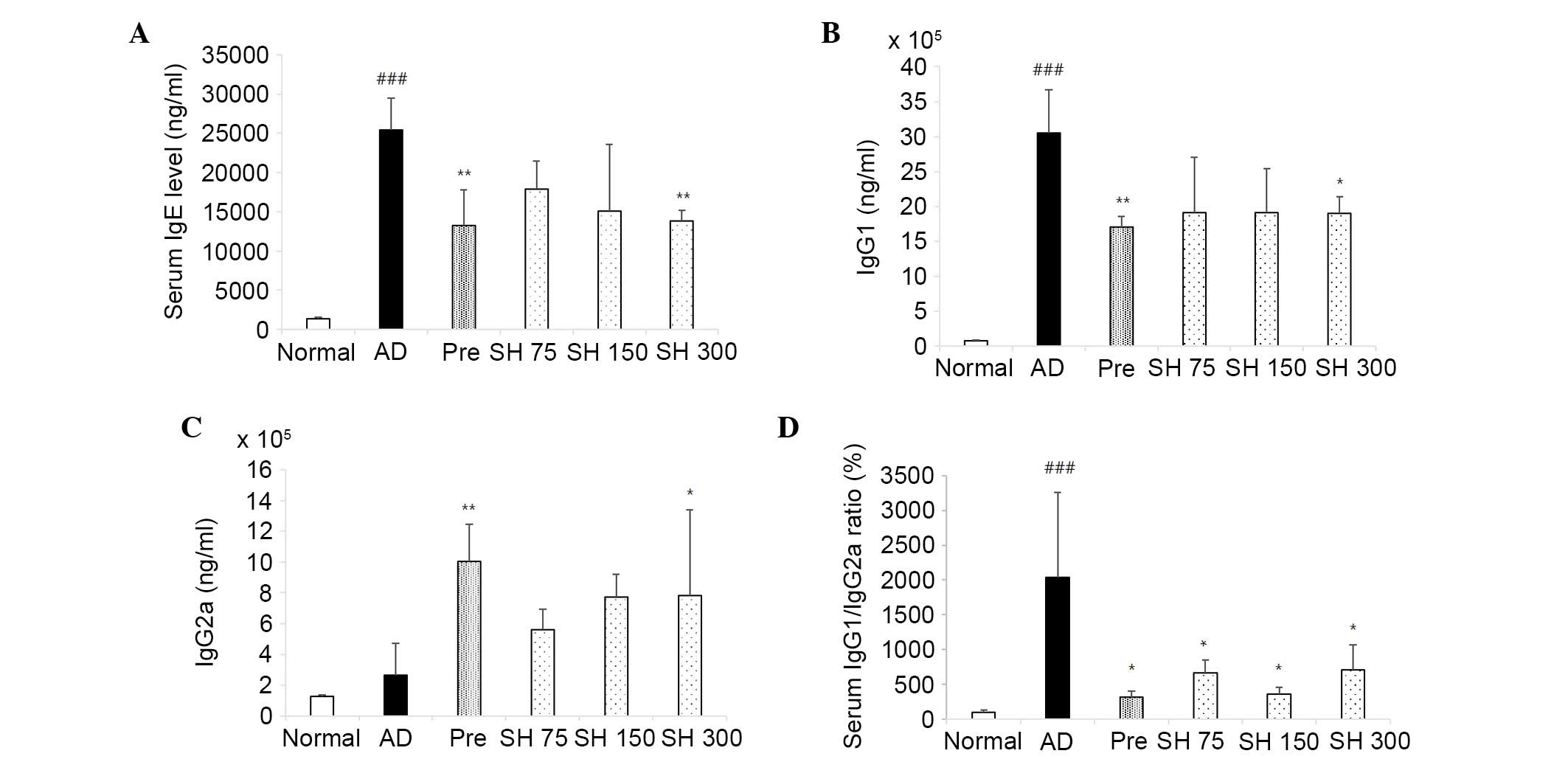
Mountford AP, Fisher A and Wilson RA: The
profile of IgG1 and IgG2a antibody responses in mice exposed to
Schistosoma mansoni. Parasite Immunol. 16:521–527. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
N'Dri D, Mazzeo T, Zaupa M, Ferracane R,
Fogliano V and Pellegrini N: Effect of cooking on the total
antioxidant capacity and phenolic profile of some whole-meal
African cereals. J Sci Food Agric. 93:29–36. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Eichhorn S and Winterhalter P:
Anthocyanins from pigmented potato (Solanum tuberosum L.)
varieties. Food Research International. 38:943–948. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Han KH, Sekikawa M, Shimada K, Hashimoto
M, Hashimoto N, Noda T, Tanaka H and Fukushima M: Anthocyanin-rich
purple potato flake extract has antioxidant capacity and improves
antioxidant potential in rats. Br J Nutr. 96:1125–1133. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Afaq F, Saleem M, Krueger CG, Reed JD and
Mukhtar H: Anthocyanin- and hydrolyzable tannin-rich pomegranate
fruit extract modulates MAPK and NF-kappaB pathways and inhibits
skin tumorigenesis in CD-1 mice. Int J Cancer. 113:423–433. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Zhang EY, Chen AY and Zhu BT: Mechanism of
dinitrochlorobenzene-induced dermatitis in mice: Role of specific
antibodies in pathogenesis. PLoS One. 4:e77032009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Vestergaard C, Yoneyama H, Murai M,
Nakamura K, Tamaki K, Terashima Y, Imai T, Yoshie O, Irimura T,
Mizutani H and Matsushima K: Overproduction of Th2-specific
chemokines in NC/Nga mice exhibiting atopic dermatitis-like
lesions. J Clin Invest. 104:1097–1105. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kishimoto T and Hirano T: Molecular
regulation of B lymphocyte response. Annu Rev Immunol. 6:485–512.
1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Hussain Z, Katas H, Mohd Amin MC and
Kumolosasi E: Efficient immuno-modulation of TH1/TH2 biomarkers in
2,4-dinitroflu-orobenzene-induced atopic dermatitis:
Nanocarrier-mediated transcutaneous co-delivery of
anti-inflammatory and antioxidant drugs. PLoS One. 9:e1131432014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Niebuhr M and Werfel T: Innate immunity,
allergy and atopic dermatitis. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol.
10:463–468. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wollenberg A, Kraft S, Hanau D and Bieber
T: Immunomorphological and ultrastructural characterization of
Langerhans cells and a novel, inflammatory dendritic epidermal cell
(IDEC) population in lesional skin of atopic eczema. J Invest
Dermatol. 106:446–453. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Bieber T: The pro- and anti-inflammatory
properties of human antigen-presenting cells expressing the high
affinity receptor for IgE (Fc epsilon RI). Immunobiology.
212:499–503. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Novak N, Valenta R, Bohle B, Laffer S,
Haberstok J, Kraft S and Bieber T: FcepsilonRI engagement of
Langerhans cell-like dendritic cells and inflammatory dendritic
epidermal cell-like dendritic cells induces chemotactic signals and
different T-cell phenotypes in vitro. J Allergy Clin Immunol.
113:949–957. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Kasraie S, Niebuhr M, Baumert K and Werfel
T: Functional effects of interleukin 31 in human primary
keratinocytes. Allergy. 66:845–852. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Meyer N, Zimmermann M, Bürgler S, Bassin
C, Woehrl S, Moritz K, Rhyner C, Indermitte P, Schmid-Grendelmeier
P, Akdis M, et al: IL-32 is expressed by human primary
keratinocytes and modulates keratinocyte apoptosis in atopic
dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 125:858–865.e810. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Klunker S, Trautmann A, Akdis M, Verhagen
J, Schmid-Grendelmeier P, Blaser K and Akdis CA: A second step of
chemotaxis after transendothelial migration: Keratinocytes
undergoing apoptosis release IFN-gamma-inducible protein 10,
monokine induced by IFN-gamma, and IFN-gamma-inducible
alpha-chemoattractant for T cell chemotaxis toward epidermis in
atopic dermatitis. J Immunol. 171:1078–1084. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Homey B, Steinhoff M, Ruzicka T and Leung
DY: Cytokines and chemokines orchestrate atopic skin inflammation.
J Allergy Clin Immunol. 118:178–189. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Sokol CL and Luster AD: The chemokine
system in innate immunity. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 7:pii:
a016303. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Nakatani T, Kaburagi Y, Shimada Y, Inaoki
M, Takehara K, Mukaida N and Sato S: CCR4 memory CD4+ T lymphocytes
are increased in peripheral blood and lesional skin from patients
with atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 107:353–358. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Amerio P, Frezzolini A, Feliciani C,
Verdolini R, Teofoli P, De Pità O and Puddu P: Eotaxins and CCR3
receptor in inflammatory and allergic skin diseases: Therapeutical
implications. Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy. 2:81–94. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Esnault S, Benbernou N, Lavaud F, Shin HC,
Potron G and Guenounou M: Differential spontaneous expression of
mRNA for IL-4, IL-10, IL-13, IL-2 and interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma)
in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) from atopic patients.
Clin Exp Immunol. 103:111–118. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Conti P, Pang X, Boucher W, Letourneau R,
Reale M, Barbacane RC, Thibault J and Theoharides TC: Impact of
Rantes and MCP-1 chemokines on in vivo basophilic cell recruitment
in rat skin injection model and their role in modifying the protein
and mRNA levels for histidine decarboxylase. Blood. 89:4120–4127.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Imai T, Baba M, Nishimura M, Kakizaki M,
Takagi S and Yoshie O: The T cell-directed CC chemokine TARC is a
highly specific biological ligand for CC chemokine receptor 4. J
Biol Chem. 272:15036–15042. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Schröder JM and Mochizuki M: The role of
chemokines in cutaneous allergic inflammation. Biol Chem.
380:889–896. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Galli SJ, Nakae S and Tsai M: Mast cells
in the development of adaptive immune responses. Nat Immunol.
6:135–142. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|