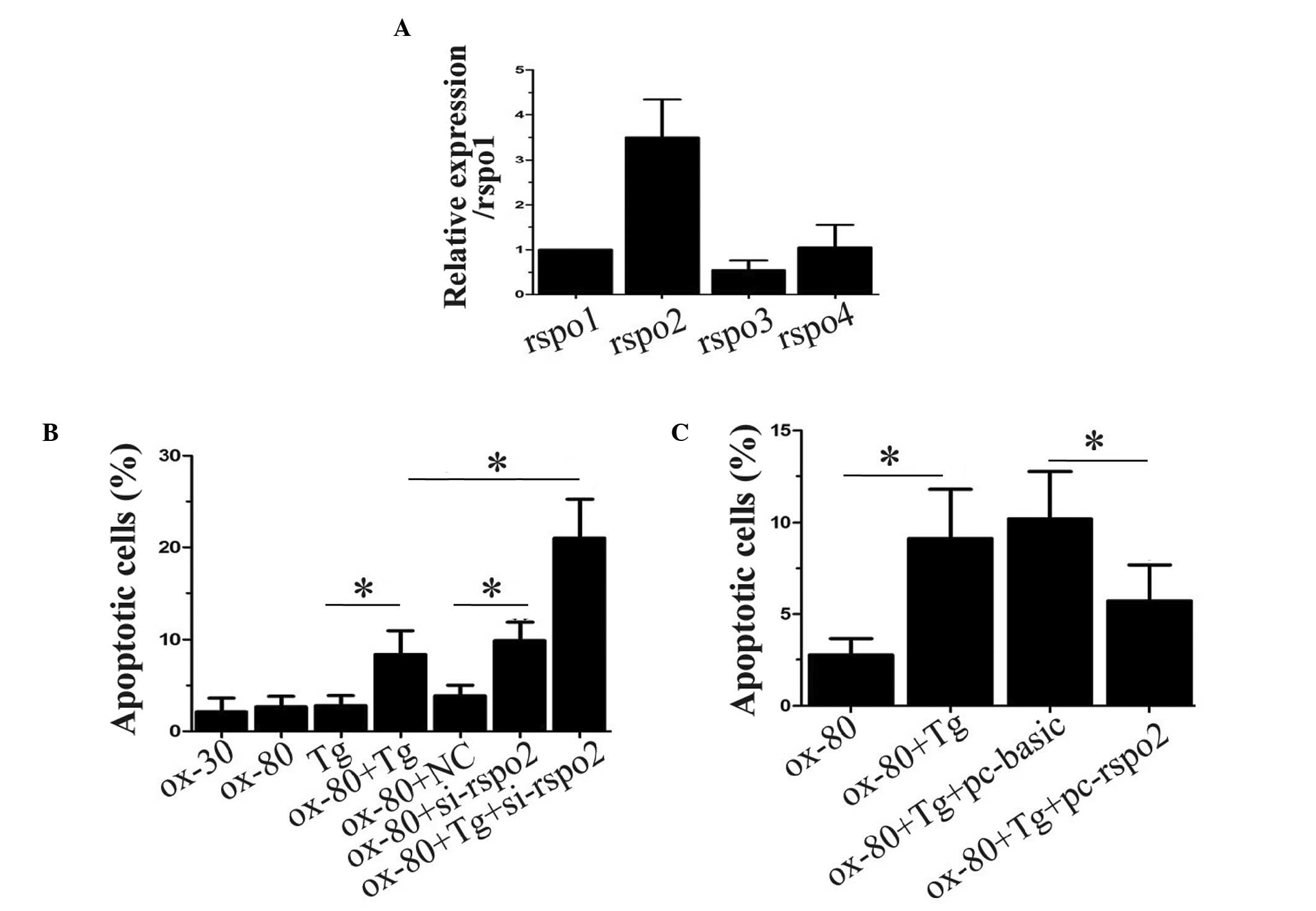
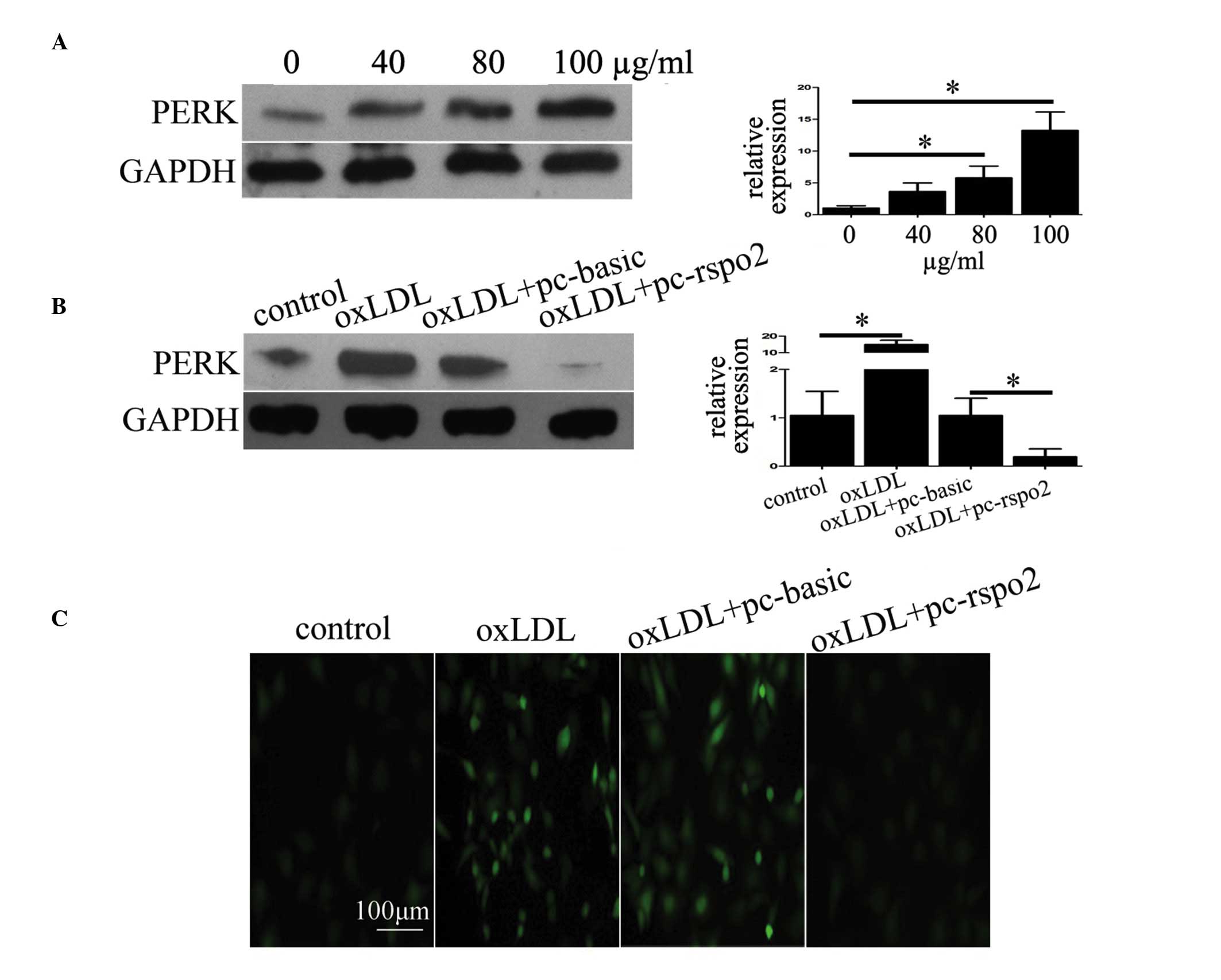
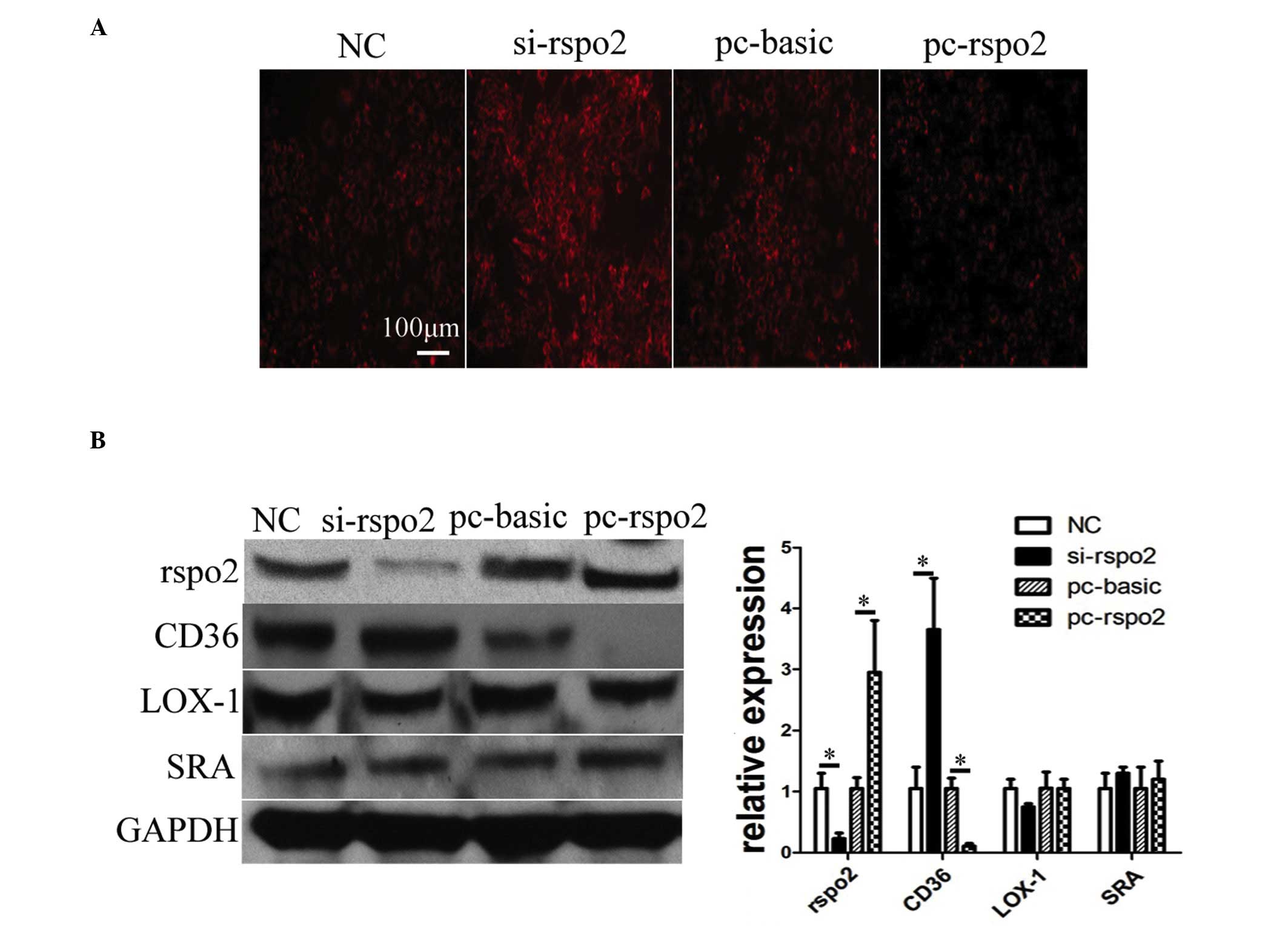
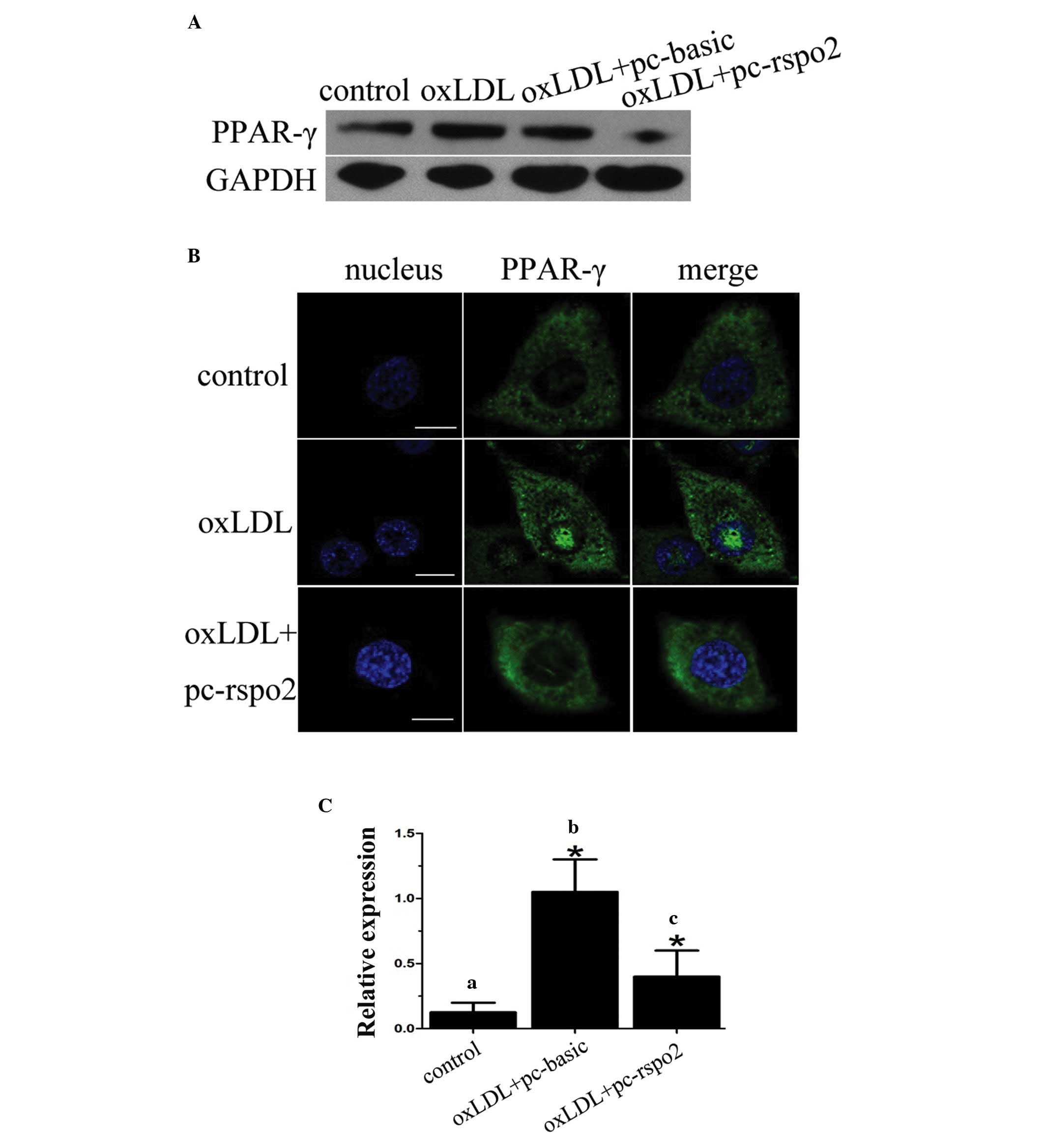
|
1
|
Braunwald E: Shattuck
lecture-cardiovascular medicine at the turn of the millennium:
Triumphs, concerns and opportunities. N Engl J Med. 337:1360–1369.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lloyd-Jones D, Adams RJ, Brown TM,
Carnethon M, Dai S, De Simone G, Ferguson TB, Ford E, Furie K,
Gillespie C, et al: Executive summary: Heart disease and stroke
statistics-2010 update: A report from the American Heart
Association. Circulation. 121:948–954. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Libby P, Ridker PM and Maseri A:
Inflammation and atherosclerosis. Circulation. 105:1135–1143. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Waldo SW, Li Y, Buono C, Zhao B, Billings
EM, Chang J and Kruth HS: Heterogeneity of human macrophages in
culture and in atherosclerotic plaques. Am J Pathol. 172:1112–1126.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Moore KJ and Tabas I: Macrophages in the
pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Cell. 145:341–355. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chang YC, Huang KX, Huang AC, Ho YC and
Wang CJ: Hibiscus anthocyanins-rich extract inhibited LDL oxidation
and oxLDL-mediated macrophages apoptosis. Food Chem Toxicol.
44:1015–1023. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Deigner HP, Claus R, Bonaterra GA, Gehrke
C, Bibak N, Blaess M, Cantz M, Metz J and Kinscherf R: Ceramide
induces aSMase expression: Implications for oxLDL-induced
apoptosis. FASEB J. 15:807–814. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Seimon TA, Nadolski MJ, Liao X, Magallon
J, Nguyen M, Feric NT, Koschinsky ML, Harkewicz R, Witztum JL,
Tsimikas S, et al: Atherogenic lipids and lipoproteins trigger
CD36-TLR2-dependent apoptosis in macrophages undergoing endoplasmic
reticulum stress. Cell Metab. 12:467–482. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Erbay E, Babaev VR, Mayers JR, Makowski L,
Charles KN, Snitow ME, Fazio S, Wiest MM, Watkins SM, Linton MF and
Hotamisligil GS: Reducing endoplasmic reticulum stress through a
macrophage lipid chaperone alleviates atherosclerosis. Nat Med.
15:1383–1391. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Oh J, Riek AE, Weng S, Petty M, Kim D,
Colonna M, Cella M and Bernal-Mizrachi C: Endoplasmic reticulum
stress controls M2 macrophage differentiation and foam cell
formation. J Biol Chem. 287:11629–11641. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Giovannini C, Varì R, Scazzocchio B,
Sanchez M, Santangelo C, Filesi C, D'Archivio M and Masella R:
OxLDL induced p53-dependent apoptosis by activating p38MAPK and
PKCδ signaling pathways in J774A.1 macrophage cells. J Mol Cell
Biol. 3:316–318. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yoon JK and Lee JS: Cellular signaling and
biological functions of R-spondins. Cell Signal. 24:369–377. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Han XH, Jin YR, Seto M and Yoon JK: A
WNT/beta-catenin signaling activator, R-spondin, plays positive
regulatory roles during skeletal myogenesis. J Biol Chem.
286:10649–10659. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Boyden LM, Mao J, Belsky J, Mitzner L,
Farhi A, Mitnick MA, Wu D, Insogna K and Lifton RP: High bone
density due to a mutation in LDL-receptor-related protein 5. N Engl
J Med. 346:1513–1521. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chua AW, Ma D, Gan SU, Fu Z, Han HC, Song
C, Sabapathy K and Phan TT: The role of R-spondin2 in keratinocyte
proliferation and epidermal thickening in keloid scarring. J Invest
Dermatol. 131:644–654. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Wu C, Qiu S, Lu L, Zou J, Li WF, Wang O,
Zhao H, Wang H, Tang J, Chen L, et al: RSPO2-LGR5 signaling has
tumour-suppressive activity in colorectal cancer. Nat Commun.
5:31492014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Klauzinska M, Baljinnyam B, Raafat A,
Rodriguez-Canales J, Strizzi L, Greer YE, Rubin JS and Callahan R:
Rspo2/Int7 regulates invasiveness and tumorigenic properties of
mammary epithelial cells. J Cell Physiol. 227:1960–1971. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Longo KA, Kennell JA, Ochocinska MJ, Ross
SE, Wright WS and MacDougald OA: Wnt signaling protects 3T3-L1
preadipocytes from apoptosis through induction of insulin-like
growth factors. J Biol Chem. 277:38239–38244. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Devries-Seimon T, Li Y, Yao PM, Stone E,
Wang Y, Davis RJ, Flavell R and Tabas I: Cholesterol-induced
macrophage apoptosis requires ER stress pathways and engagement of
the type A scavenger receptor. J Cell Biol. 171:61–73. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang S, Sun Z, Zhang X, Li Z, Wu M, Zhao
W, Wang H, Chen T, Yan H and Zhu J: Wnt1 positively regulates CD36
expression via TCF4 and PPAR-γ in macrophages. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 35:1289–1302. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Liu J, Lee J, Salazar Hernandez MA,
Mazitschek R and Ozcan U: Treatment of obesity with celastrol.
Cell. 161:999–1011. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Murphy JE, Tedbury PR, Homer-Vanniasinkam
S, Walker JH and Ponnambalam S: Biochemistry and cell biology of
mammalian scavenger receptors. Atherosclerosis. 182:1–15. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tontonoz P, Nagy L, Alvarez JG, Thomazy VA
and Evans RM: PPARgamma promotes monocyte/macrophage
differentiation and uptake of oxidized LDL. Cell. 93:241–252. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Watson AL, Rahrmann EP, Moriarity BS, Choi
K, Conboy CB, Greeley AD, Halfond AL, Anderson LK, Wahl BR, Keng
VW, et al: Canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling drives human schwann
cell transformation, progression and tumor maintenance. Cancer
Discov. 3:674–689. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chartier C, Raval J, Axelrod F, Bond C,
Cain J, Dee-Hoskins C, Ma S, Fischer MM, Shah J, Wei J, et al:
Therapeutic targeting of tumor-derived R-spondin attenuates
β-catenin signaling and tumorigenesis in multiple cancer types.
Cancer Res. 76:713–723. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hajri T, Han XX, Bonen A and Abumrad NA:
Defective fatty acid uptake modulates insulin responsiveness and
metabolic responses to diet in CD36-null mice. J Clin Invest.
109:1381–1389. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Febbraio M, Podrez EA, Smith JD, Hajjar
DP, Hazen SL, Hoff HF, Sharma K and Silverstein RL: Targeted
disruption of the class B scavenger receptor CD36 protects against
atherosclerotic lesion development in mice. J Clin Invest.
105:1049–1056. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Drover VA, Ajmal M, Nassir F, Davidson NO,
Nauli AM, Sahoo D, Tso P and Abumrad NA: CD36 deficiency impairs
intestinal lipid secretion and clearance of chylomicrons from the
blood. J Clin Invest. 115:1290–1297. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Rać ME, Safranow K and Poncyljusz W:
Molecular basis of human CD36 gene mutations. Mol Med. 13:288–296.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|