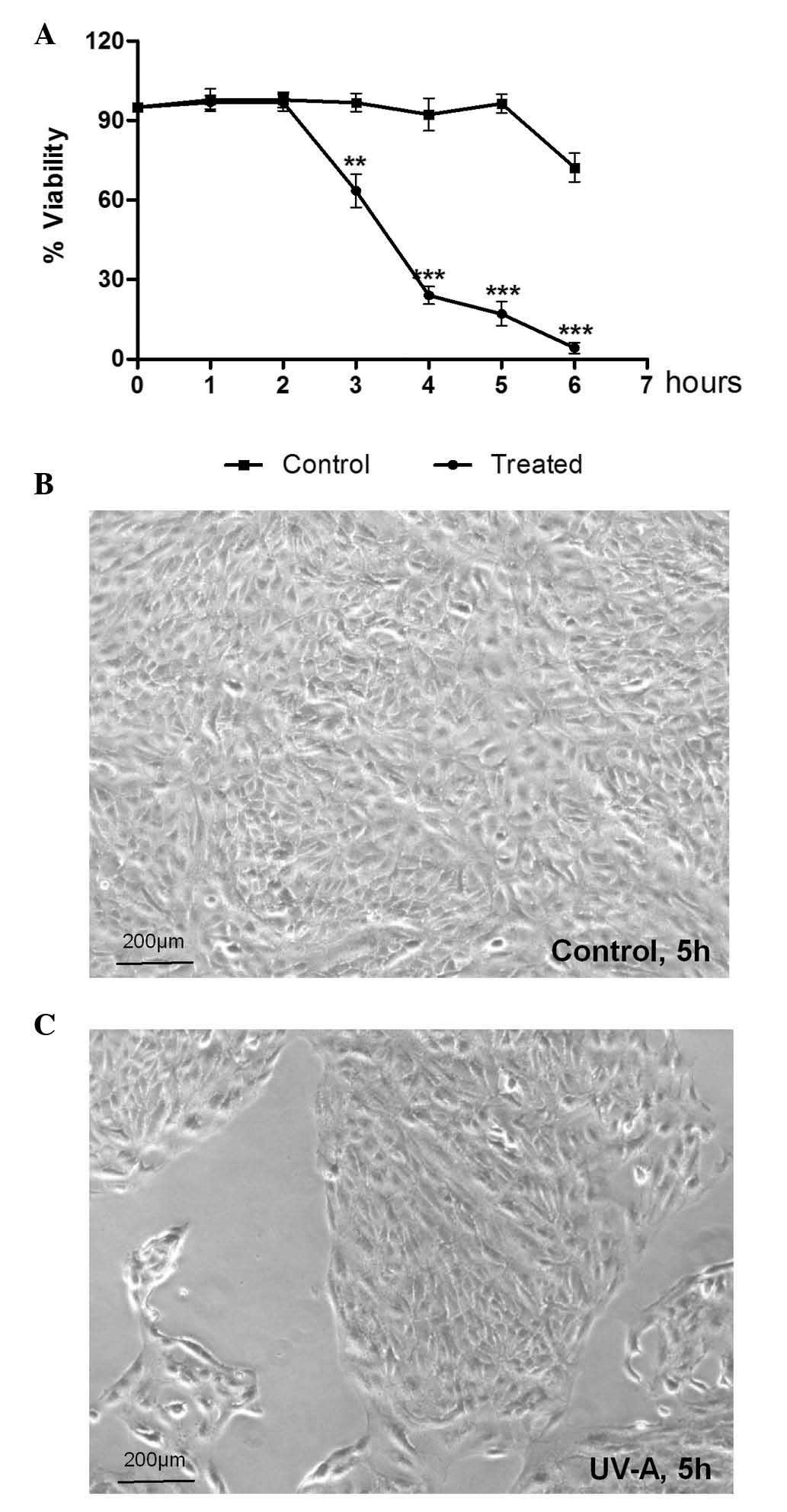
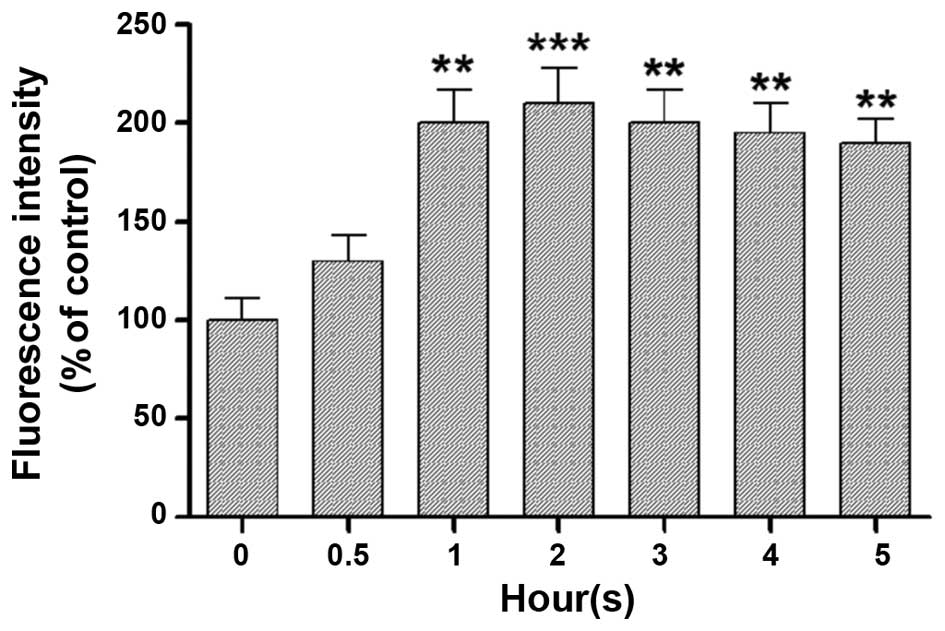
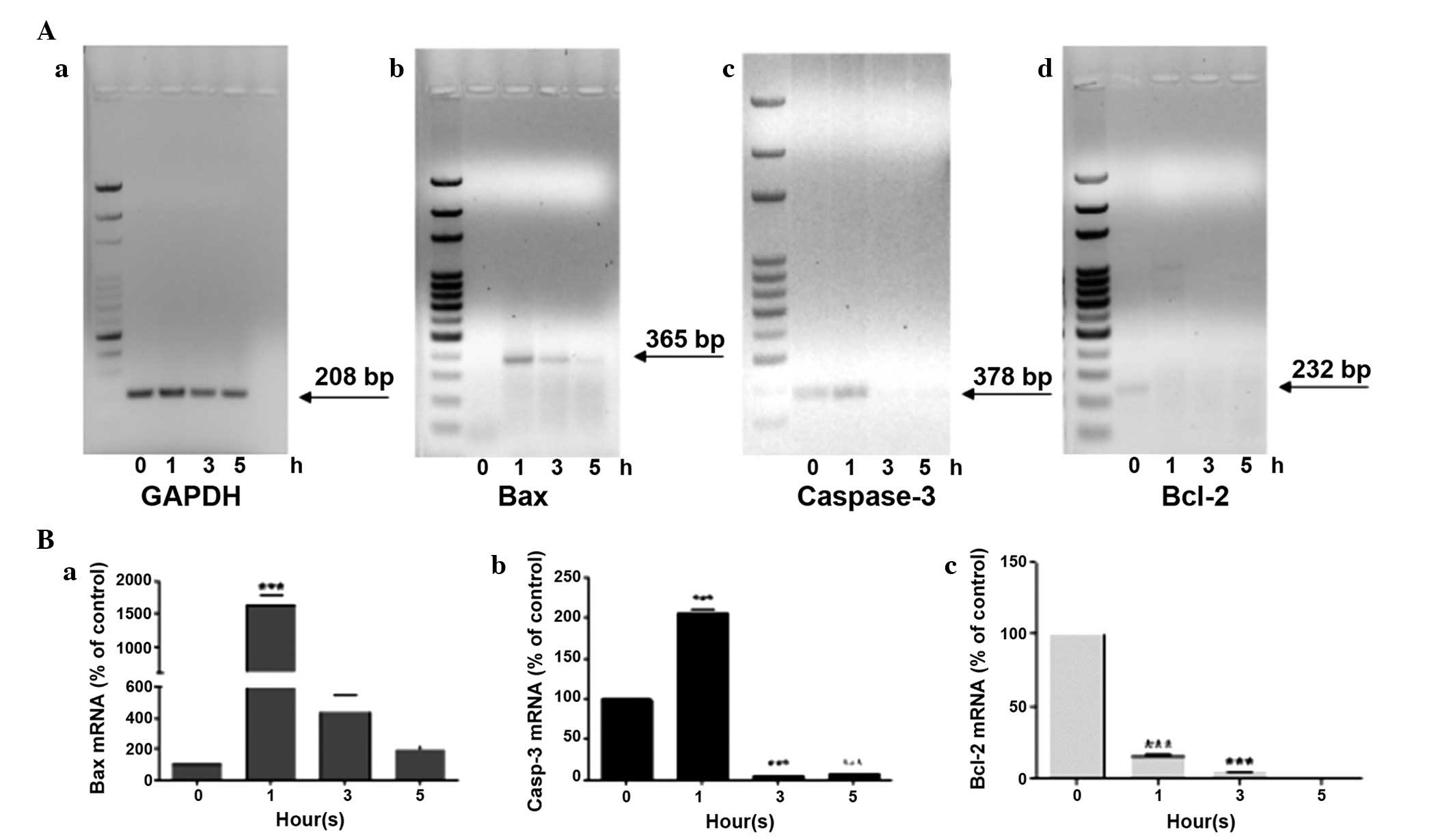
|
1
|
Kuznetsova AV, Kurinov AM and Aleksandrova
MA: Cell models to study regulation of cell transformation in
pathologies of retinal pigment epithelium. J Ophthalmol.
2014:8017872014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rizzolo LJ: Barrier properties of cultured
retinal pigment epithelium. Exp Eye Res. 126:16–26. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Pfeffer BA and Philp NJ: Cell culture of
retinal pigment epithelium: Special Issue. Exp Eye Res. 126:1–4.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Glickman RD: Ultraviolet phototoxicity to
the retina. Eye Contact Lens. 37:196–205. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Blasiak J, Petrovski G, Veréb Z, Facskó A
and Kaarniranta K: Oxidative stress, hypoxia, and autophagy in the
neovascular processes of age-related macular degeneration. Biomed
Res Int. 2014:7680262014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tu G, Zhang YF, Wei W, Li L, Zhang Y, Yang
J and Xing Y: Allicin attenuates H2O2-induced
cytotoxicity in retinal pigmented epithelial cells by regulating
the levels of reactive oxygen species. Mol Med Rep. 13:2320–2326.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Plestina-Borjan I and Klinger-Lasić M:
Long-term exposure to solar ultraviolet radiation as a risk factor
for age-related macular degeneration. Coll Antropol. 31(Suppl 1):
33–38. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li X, Zhao H, Wang Q, Liang H and Jiang X:
Fucoidan protects ARPE-19 cells from oxidative stress via
normalization of reactive oxygen species generation through the
Ca2+-dependent ERK signaling pathway. Mol Med
Rep. 11:3746–3752. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Øsnes-Ringen O, Azqueta AO, Moe MC,
Zetterström C, Røger M, Nicolaissen B and Collins AR: DNA damage in
lens epithelium of cataract patients in vivo and ex vivo. Acta
Ophthalmol. 91:652–656. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Ji Y, Cai L, Zheng T, Ye H, Rong X, Rao J
and Lu Y: The mechanism of UVB irradiation induced-apoptosis in
cataract. Mol Cell Biochem. 401:87–95. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Roduit R and Schorderet DF: MAP kinase
pathways in UV-induced apoptosis of retinal pigment epithelium
ARPE19 cells. Apoptosis. 13:343–353. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hanus J, Zhang H, Wang Z, Liu Q, Zhou Q
and Wang S: Induction of necrotic cell death by oxidative stress in
retinal pigment epithelial cells. Cell Death Dis. 4:e9652013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Shah D, Naciri M, Clee P and Al-Rubeai M:
NucleoCounter-An efficient technique for the determination of cell
number and viability in animal cell culture processes.
Cytotechnology. 51:39–44. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Chan CM, Huang CH, Li HJ, Hsiao CY, Su CC,
Lee PL and Hung CF: Protective effects of resveratrol against
UVA-induced damage in ARPE19 cells. Int J Mol Sci. 16:5789–5802.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Murakami Y, Matsumoto H, Roh M, Giani A,
Kataoka K, Morizane Y, Kayama M, Thanos A, Nakatake S, Notomi S, et
al: Programmed necrosis, not apoptosis, is a key mediator of cell
loss and DAMP-mediated inflammation in dsRNA-induced retinal
degeneration. Cell Death Differ. 21:270–277. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
16
|
Hildeman DA, Mitchell T, Aronow B,
Wojciechowski S, Kappler J and Marrack P: Control of Bcl-2
expression by reactive oxygen species. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
100:15035–15040. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Han S, Lu Q and Wang N: Apr3 accelerates
the senescence of human retinal pigment epithelial cells. Mol Med
Rep. 13:3121–3126. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kannan K and Jain SK: Oxidative stress and
apoptosis. Pathophysiology. 7:153–163. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|