|
1
|
Schwab JM, Zhang Y, Kopp MA, Brommer B and
Popovich PG: The paradox of chronic neuroinflammation, systemic
immune suppression, autoimmunity after traumatic chronic spinal
cord injury. Exp Neurol. 258:121–129. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
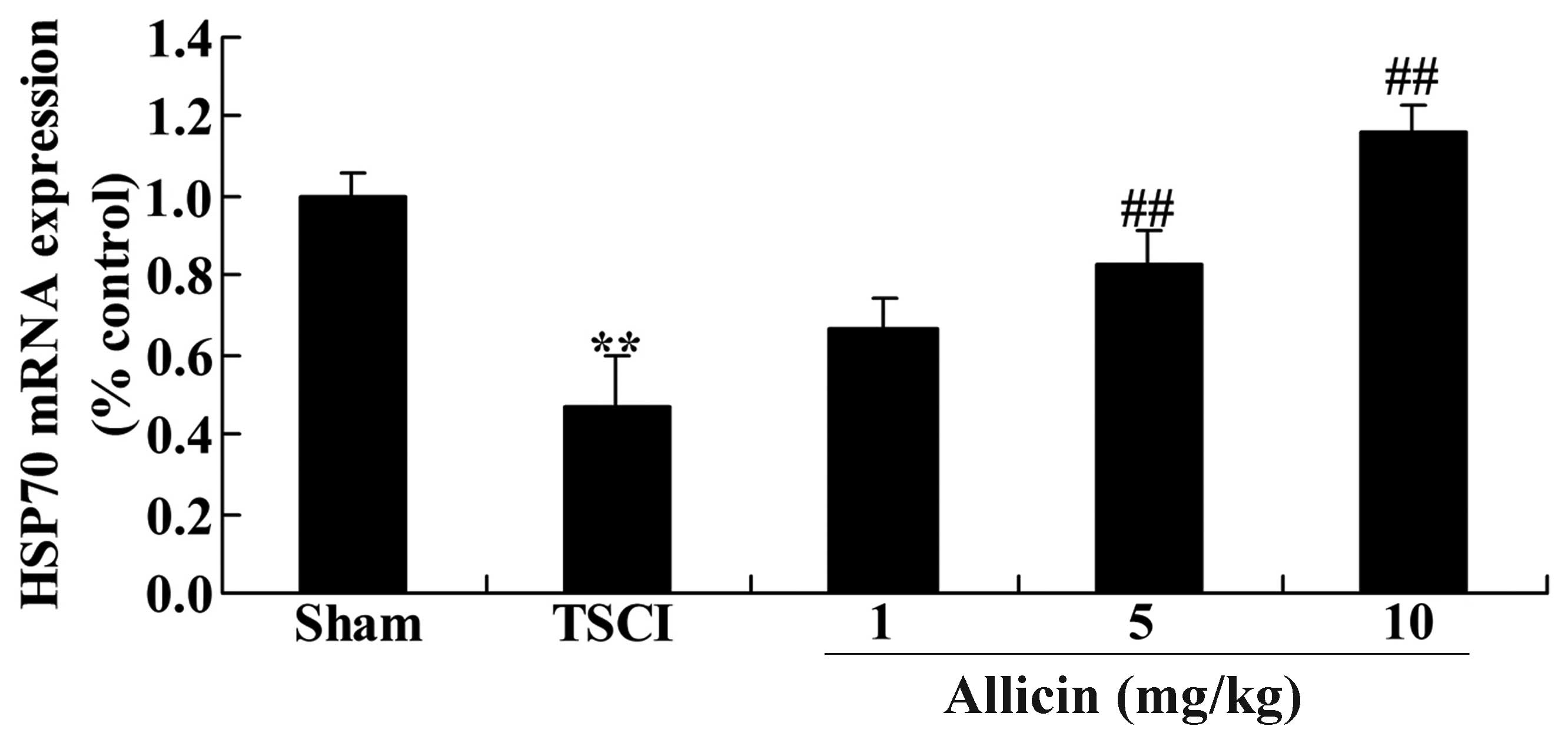
2
|
Konya D, Gercek A, Akakin A, Akakin D,
Tural S, Cetinel S, Ozgen S and Pamir MN: The effects of
inflammatory response associated with traumatic spinal cord injury
in cutaneous wound healing and on expression of transforming growth
factor-beta1 (TGF-beta1) and platelet-derived growth factor
(PDGF)-A at the wound site in rats. Growth Factors. 26:74–79. 2008.
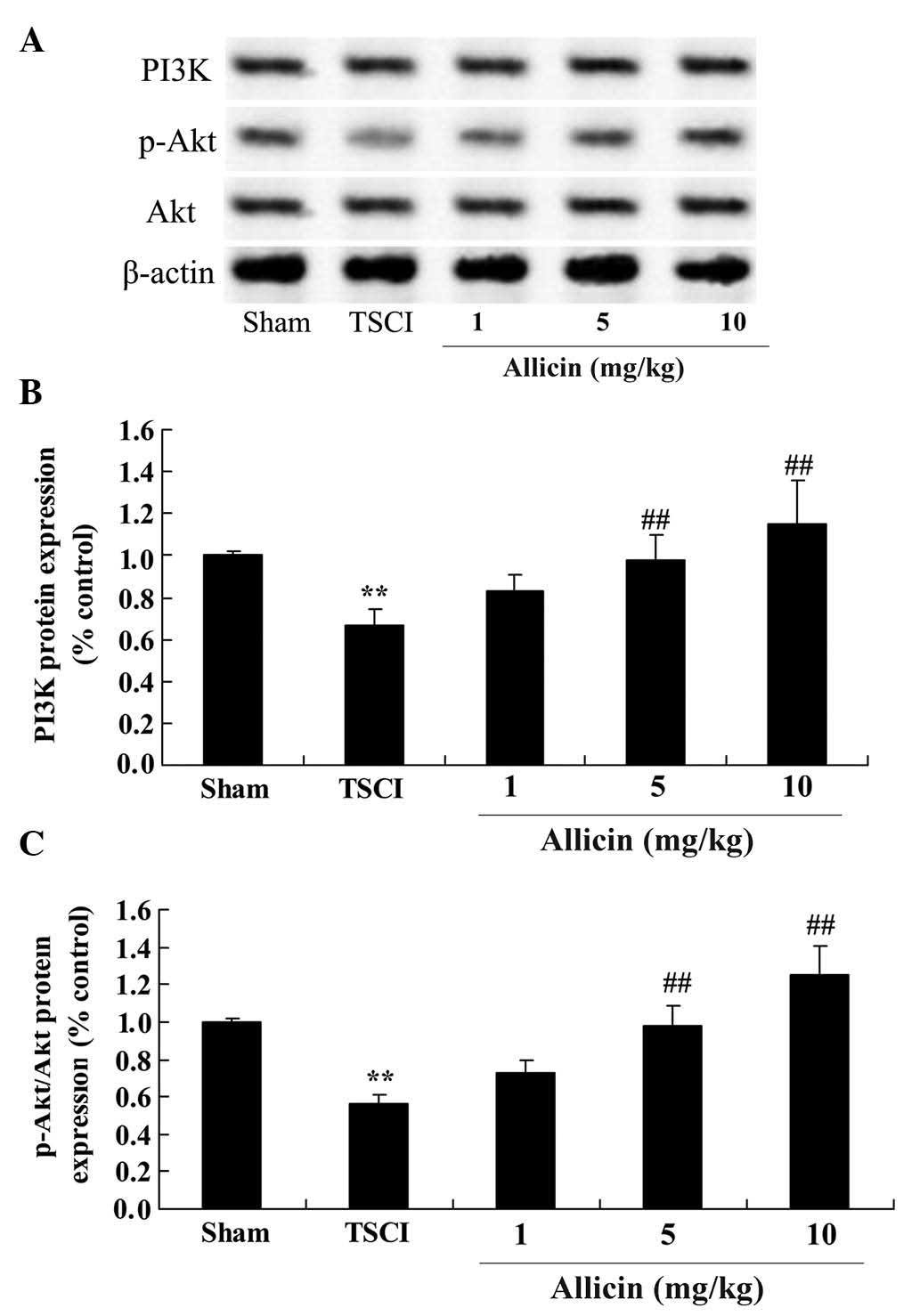
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
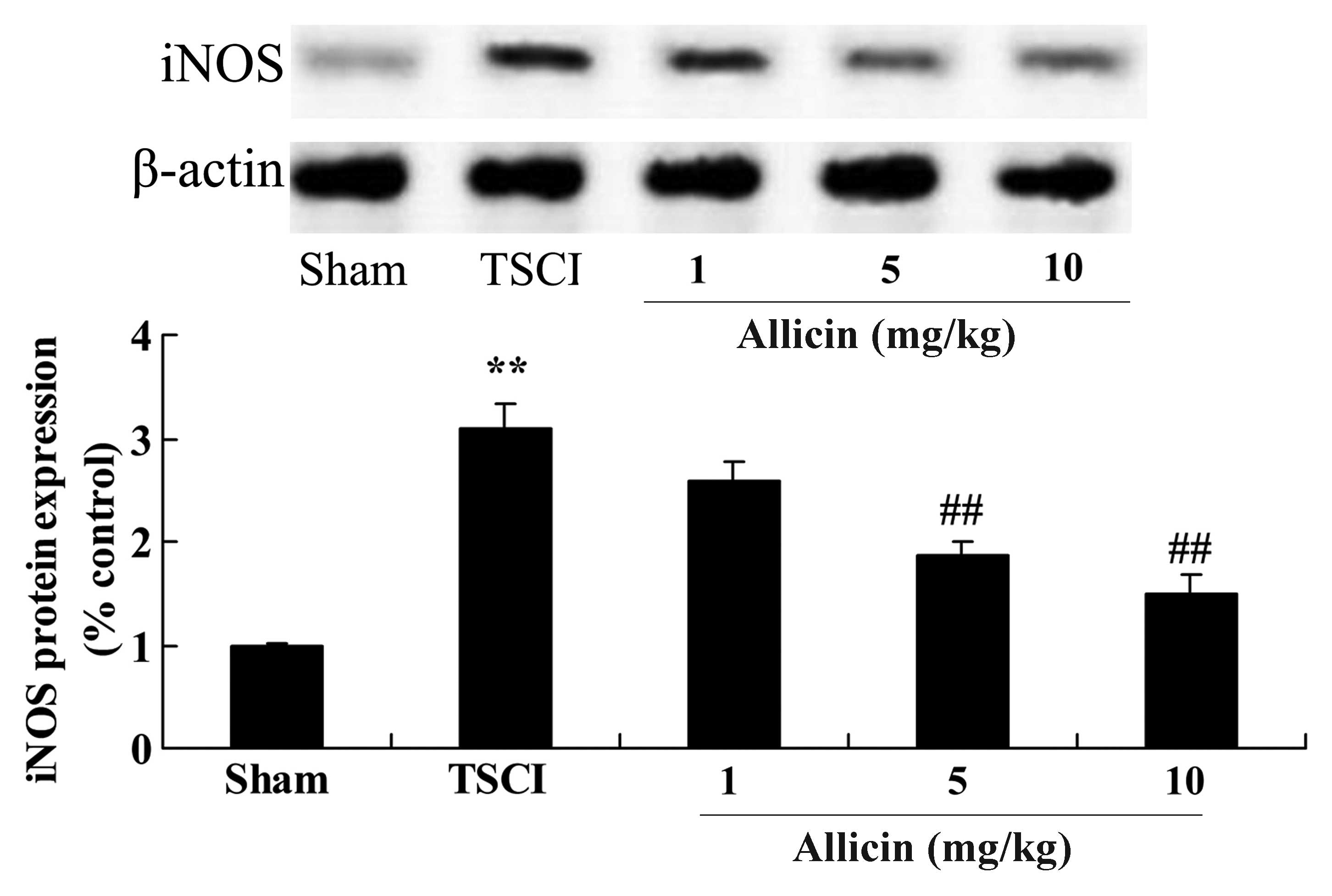
|
Yin KJ, Kim GM, Lee JM, He YY, Xu J and
Hsu CY: JNK activation contributes to DP5 induction and apoptosis
following traumatic spinal cord injury. Neurobiol Dis. 20:881–889.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chan SC and Chan AP: Rehabilitation
outcomes following traumatic spinal cord injury in a tertiary
spinal cord injury centre: A comparison with an international
standard. Spinal Cord. 43:489–498. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Franceschini M, Di Clemente B, Citterio A
and Pagliacci MC: Follow-up in persons with traumatic spinal cord
injury: Questionnaire reliability. Eura Medicophys. 42:211–218.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dobkin BH, Apple D, Barbeau H, Basso M,
Behrman A, Deforge D, Ditunno J, Dudley G, Elashoff R, Fugate L, et
al: Methods for a randomized trial of weight-supported treadmill
training versus conventional training for walking during inpatient
rehabilitation after incomplete traumatic spinal cord injury.
Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 17:153–167. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
van Weert KC, Schouten EJ, Hofstede J, van
de Meent H, Holtslag HR and van den Berg-Emons RJ: Acute phase
complications following traumatic spinal cord injury in Dutch level
1 trauma centres. J Rehabil Med. 46:882–885. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wong AM, Leong CP, Su TY, Yu SW, Tsai WC
and Chen CP: Clinical trial of acupuncture for patients with spinal
cord injuries. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 82:21–27. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
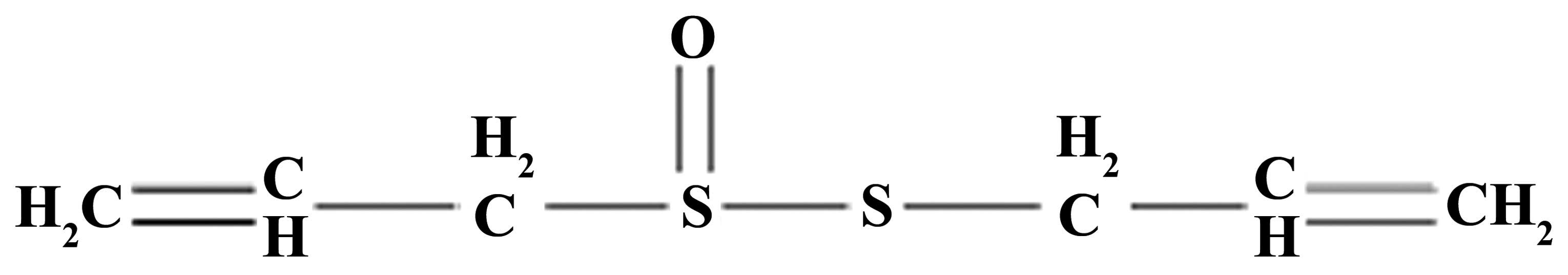
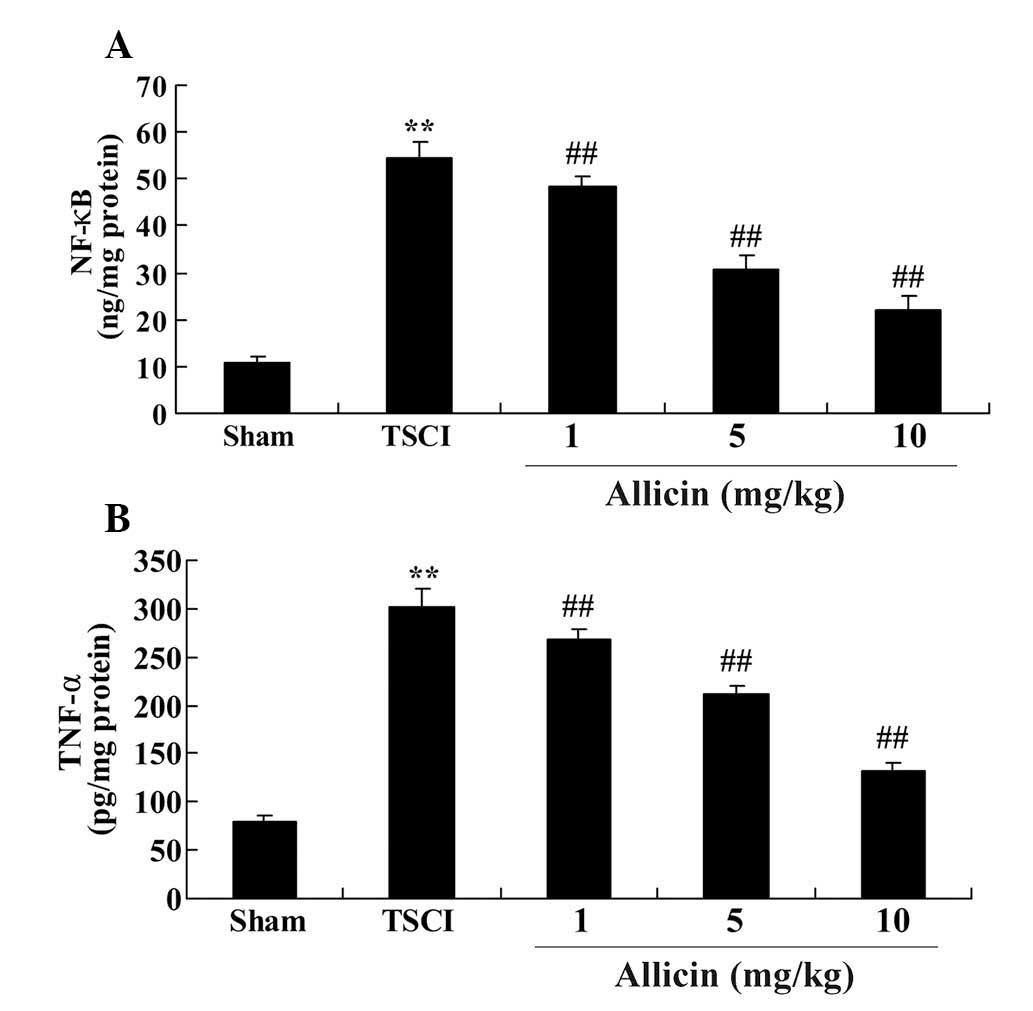
Liu SG, Ren PY, Wang GY, Yao SX and He XJ:
Allicin protects spinal cord neurons from glutamate-induced
oxidative stress through regulating the heat shock protein
70/inducible nitric oxide synthase pathway. Food Funct. 6:321–330.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Adetumbi MA and Lau BH: Allium sativum
(garlic)–a natural antibiotic. Med Hypotheses. 12:227–237. 1983.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Borlinghaus J, Albrecht F, Gruhlke MC,
Nwachukwu ID and Slusarenko AJ: Allicin: Chemistry and biological
properties. Molecules. 19:12591–12618. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Huang W, Wang Y, Cao YG, Qi HP, Li L, Bai
B, Liu Y and Sun HL: Antiarrhythmic effects and ionic mechanisms of
allicin on myocardial injury of diabetic rats induced by
streptozotocin. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 386:697–704.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sieber MW, Claus RA, Witte OW and Frahm C:
Attenuated inflammatory response in aged mice brains following
stroke. PLoS One. 6:e262882011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wu Q, Ning GZ, Li YL, Feng HY and Feng SQ:
Factors affecting the length of stay of patients with traumatic
spinal cord injury in Tianjin, China. J Spinal Cord Med.
36:237–242. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang H, Xiang Q, Li C and Zhou Y:
Epidemiology of traumatic cervical spinal fractures and risk
factors for traumatic cervical spinal cord injury in China. J
Spinal Disord Tech. 26:E306–E313. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li C, Lun W, Zhao X, Lei S, Guo Y, Ma J
and Zhi F: Allicin alleviates inflammation of
trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid-induced rats and suppresses P38 and
JNK pathways in Caco-2 cells. Mediators Inflamm. 2015:4346922015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yu L, Xie J, Xin N and Wang Z: Panax
notoginseng saponins promote wound repair of anterior cruciate
ligament through phosphorylation of PI3K, AKT and ERK. Int J Clin
Exp Pathol. 8:441–449. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yune TY, Park HG, Lee JY and Oh TH:
Estrogen-induced Bcl-2 expression after spinal cord injury is
mediated through phosphoinositide-3-kinase/Akt-dependent CREB
activation. J Neurotrauma. 25:1121–1131. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jung SY, Kim DY, Yune TY, Shin DH, Baek SB
and Kim CJ: Treadmill exercise reduces spinal cord injury-induced
apoptosis by activating the PI3K/Akt pathway in rats. Exp Ther Med.
7:587–593. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu C, Cao F, Tang QZ, Yan L, Dong YG, Zhu
LH, Wang L, Bian ZY and Li H: Allicin protects against cardiac
hypertrophy and fibrosis via attenuating reactive oxygen
species-dependent signaling pathways. J Nutr Biochem. 21:1238–1250.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jiang Y, Gong FL, Zhao GB and Li J:
Chrysin suppressed inflammatory responses and the inducible nitric
oxide synthase pathway after spinal cord injury in rats. Int J Mol
Sci. 15:12270–12279. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Abbasi Habashi S, Sabouni F, Moghimi A and
Ansari Majd S: Modulation of lipopolysaccharide stimulated nuclear
factor kappa B mediated iNOS/NO production by bromelain in rat
primary microglial cells. Iran Biomed J. 20:33–40. 2016.
|
|
23
|
Ren B, Zhang YX, Zhou HX, Sun FW, Zhang
ZF, Wei Z, Zhang CY and Si DW: Tanshinone IIA prevents the loss of
nigrostriatal dopaminergic neurons by inhibiting NADPH oxidase and
iNOS in the MPTP model of Parkinson's disease. J Neurol Sci.
348:142–152. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Chen M, Xia X, Zhu X, Cao J, Xu D, Ni Y,
Liu Y, Yan S, Cheng X, Liu Y and Wang Y: Expression of SGTA
correlates with neuronal apoptosis and reactive gliosis after
spinal cord injury. Cell Tissue Res. 358:277–288. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhou YF, Li WT, Han HC, Gao DK, He XS, Li
L, Song JN and Fei Z: Allicin protects rat cortical neurons against
mechanical trauma injury by regulating nitric oxide synthase
pathways. Brain Res Bull. 100:14–21. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Sharma HS, Olsson Y and Westman J: A
serotonin synthesis inhibitor, p-chlorophenylalanine reduces the
heat shock protein response following trauma to the spinal cord: An
immunohistochemical and ultrastructural study in the rat. Neurosci
Res. 21:241–249. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Iguchi M, Littmann AE, Chang SH, Wester
LA, Knipper JS and Shields RK: Heat stress and cardiovascular,
hormonal, and heat shock proteins in humans. J Athl Train.
47:184–190. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bains M and Hall ED: Antioxidant therapies
in traumatic brain and spinal cord injury. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1822:675–684. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Yeo JE, Kim JH and Kang SK: Selenium
attenuates ROS-mediated apoptotic cell death of injured spinal cord
through prevention of mitochondria dysfunction; in vitro and in
vivo study. Cell Physiol Biochem. 21:225–238. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chan JY, Tsui HT, Chung IY, Chan RY, Kwan
YW and Chan SW: Allicin protects rat cardiomyoblasts (H9c2 cells)
from hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative injury through inhibiting
the generation of intracellular reactive oxygen species. Int J Food
Sci Nutr. 65:868–873. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Jin W, Ming X, Hou X, Zhu T, Yuan B, Wang
J, Ni H, Jiang J, Wang H and Liang W: Protective effects of
erythropoietin in traumatic spinal cord injury by inducing the Nrf2
signaling pathway activation. J Trauma Acute Care Surg.
76:1228–1234. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lee YS, Sindhu RK, Lin CY, Ehdaie A, Lin
VW and Vaziri ND: Effects of nerve graft on nitric oxide synthase,
NAD(P)H oxidase, and antioxidant enzymes in chronic spinal cord
injury. Free Radic Biol Med. 36:330–339. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Rabinkov A, Miron T, Konstantinovski L,
Wilchek M, Mirelman D and Weiner L: The mode of action of allicin:
Trapping of radicals and interaction with thiol containing
proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1379:233–244. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|