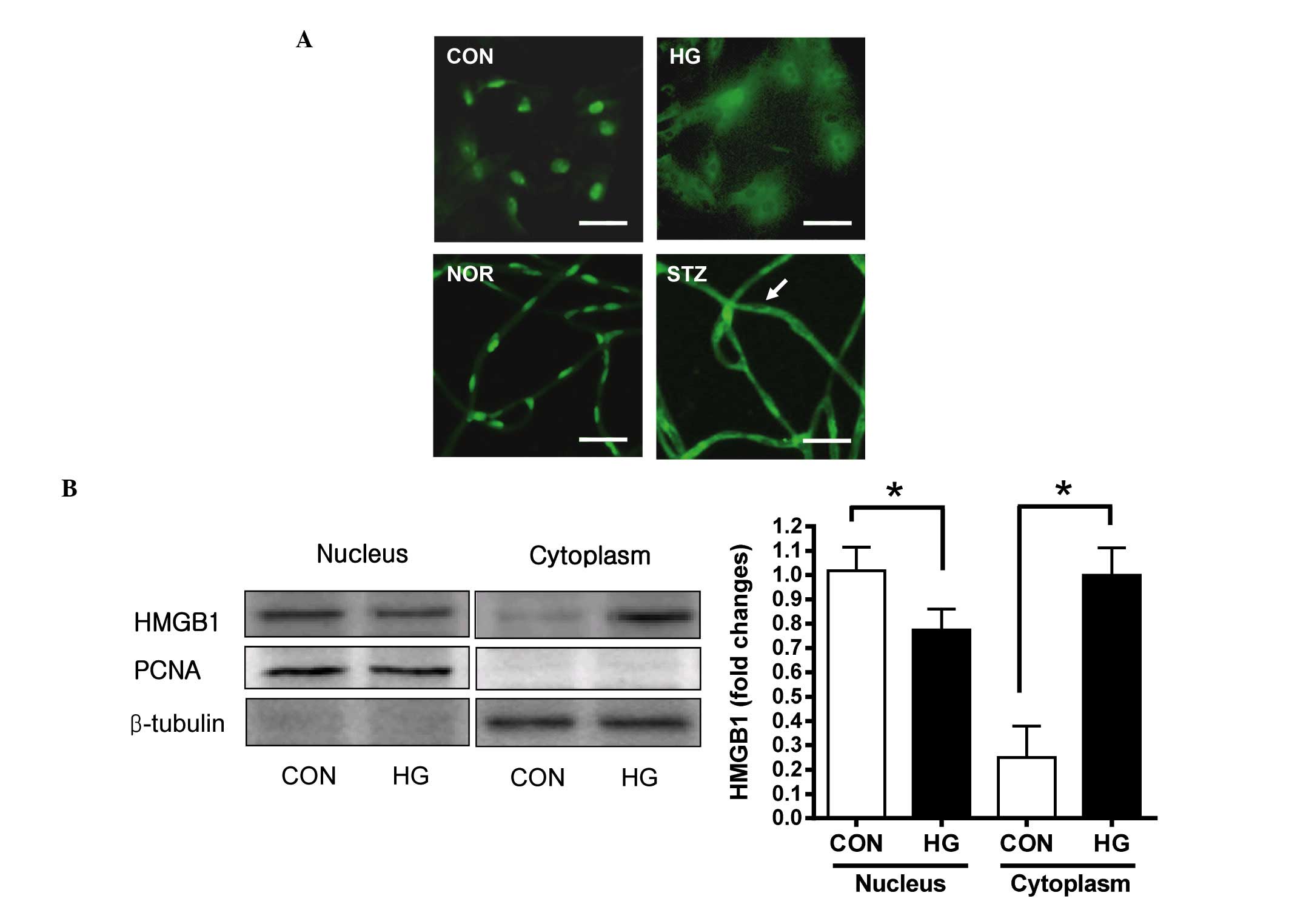
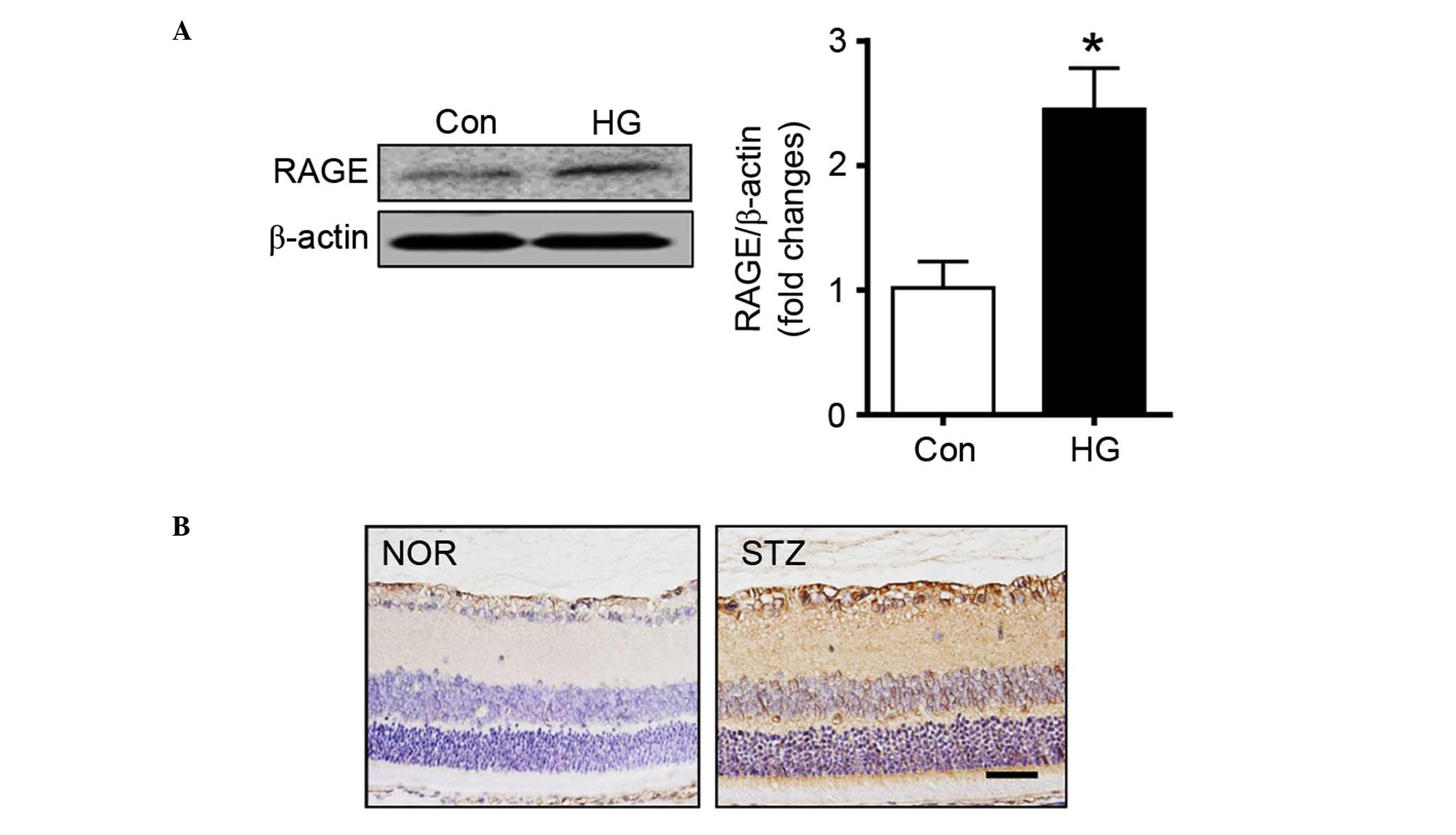
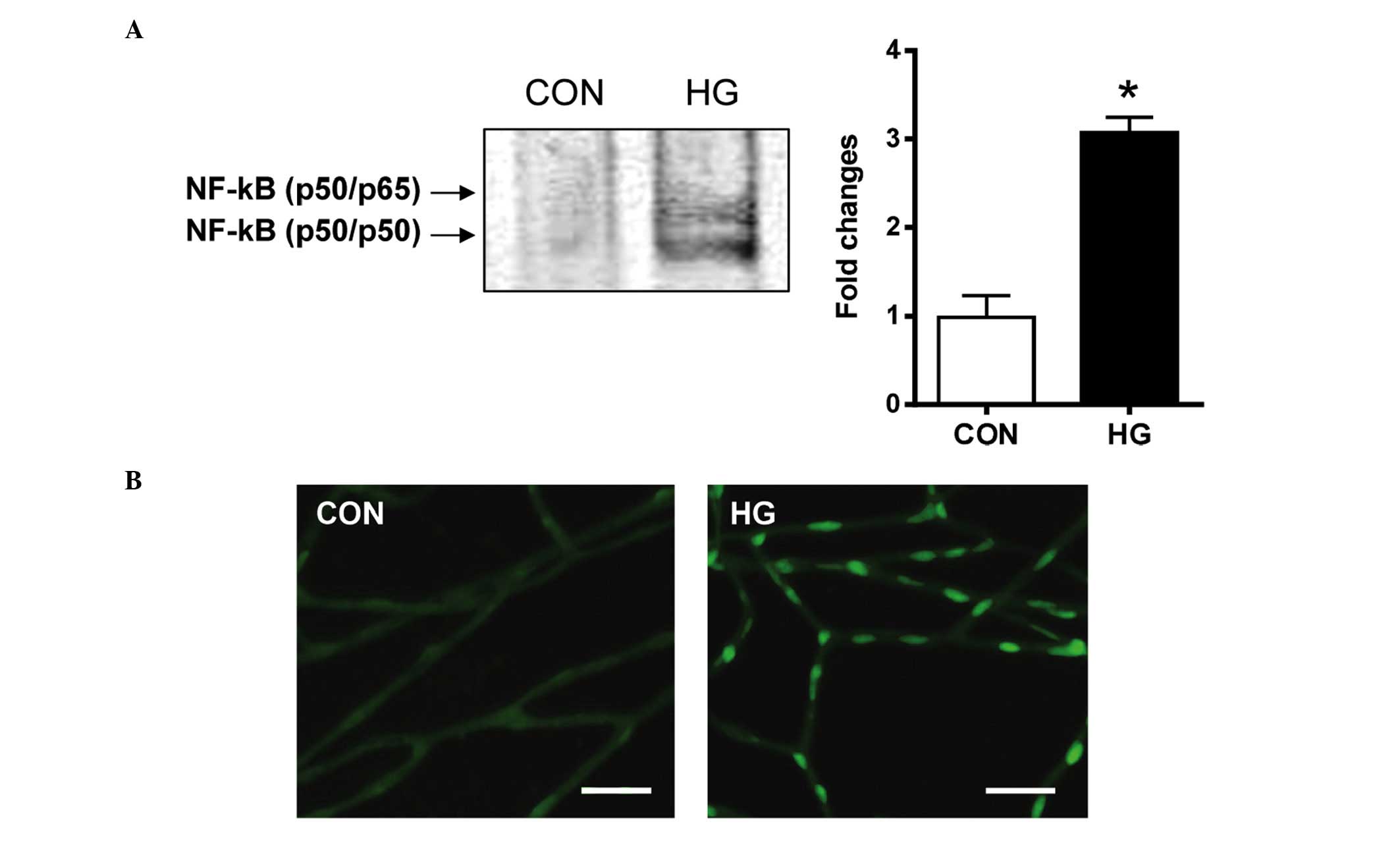
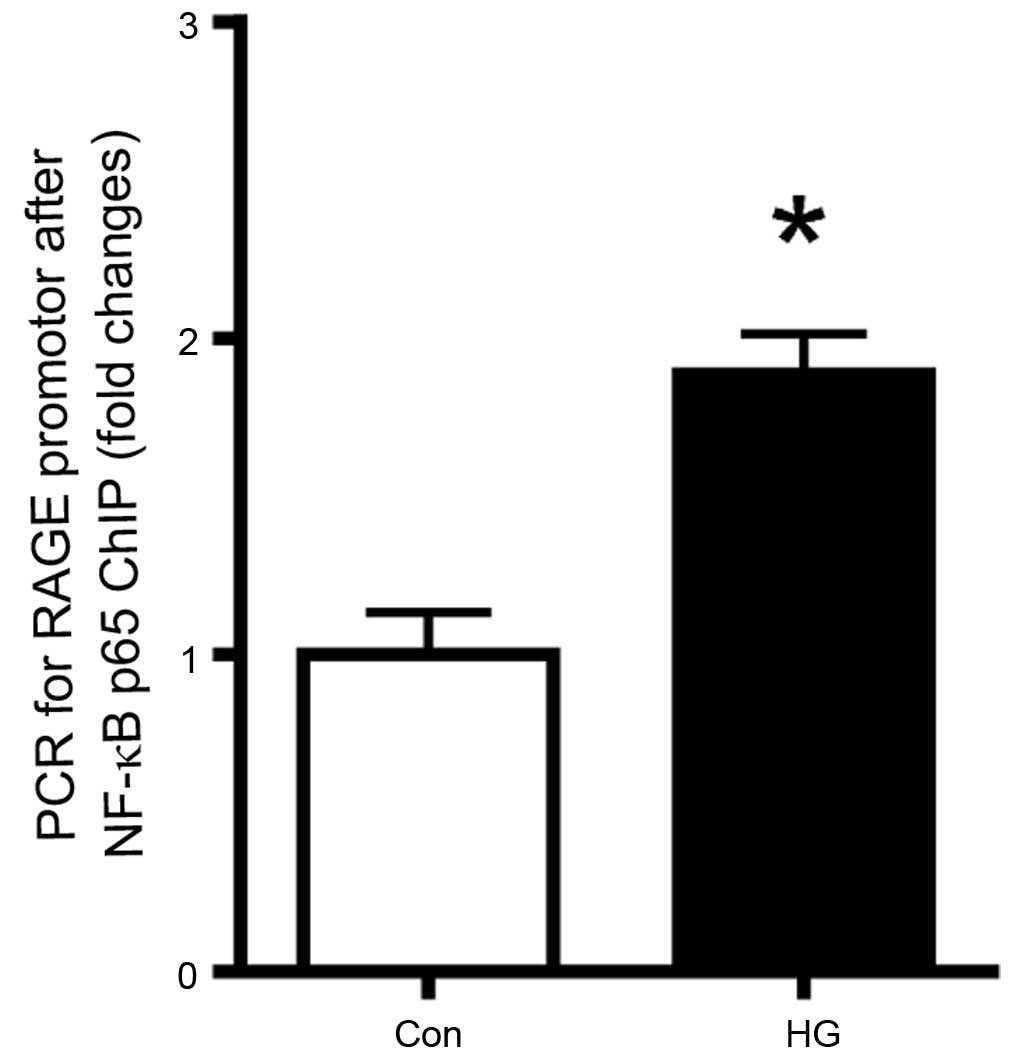
|
1
|
The DCCT Research Group: The effect of
intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression
of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus.
N Engl J Med. 329:977–986. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Joussen AM, Poulaki V, Le ML, Koizumi K,
Esser C, Janicki H, Schraermeyer U, Kociok N, Fauser S, Kirchhof B,
et al: A central role for inflammation in the pathogenesis of
diabetic retinopathy. FASEB J. 18:1450–1452. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
King GL: The role of inflammatory
cytokines in diabetes and its complications. J Periodontol.
79:1527–1534. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Muller S, Ronfani L and Bianchi ME:
Regulated expression and subcellular localization of HMGB1, a
chromatin protein with a cytokine function. J Intern Med.
255:332–343. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bianchi ME: Significant (re)location: How
to use chromatin and/or abundant proteins as messages of life and
death. Trends Cell Biol. 14:287–293. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ulloa L and Messmer D: High-mobility group
box 1 (HMGB1) protein: Friend and foe. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev.
17:189–201. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Scaffidi P, Misteli T and Bianchi ME:
Release of chromatin protein HMGB1 by necrotic cells triggers
inflammation. Nature. 418:191–195. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bianchi ME and Manfredi A: Chromatin and
cell death. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1677:181–186. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lotze MT and Tracey KJ: High-mobility
group box 1 protein (HMGB1): Nuclear weapon in the immune arsenal.
Nat Rev Immunol. 5:331–342. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jiang W, Li J, Gallowitsch-Puerta M,
Tracey KJ and Pisetsky DS: The effects of CpG DNA on HMGB1 release
by murine macrophage cell lines. J Leukoc Biol. 78:930–936. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Riedemann NC, Guo RF and Ward PA: The
enigma of sepsis. J Clin Invest. 112:460–467. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fiuza C, Bustin M, Talwar S, Tropea M,
Gerstenberger E, Shelhamer JH and Suffredini AF:
Inflammation-promoting activity of HMGB1 on human microvascular
endothelial cells. Blood. 101:2652–2660. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Wang H, Bloom O, Zhang M, Vishnubhakat JM,
Ombrellino M, Che J, Frazier A, Yang H, Ivanova S, Borovikova L, et
al: HMG-1 as a late mediator of endotoxin lethality in mice.
Science. 285:248–251. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Taniguchi N, Kawahara K, Yone K,
Hashiguchi T, Yamakuchi M, Goto M, Inoue K, Yamada S, Ijiri K,
Matsunaga S, et al: High mobility group box chromosomal protein 1
plays a role in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis as a novel
cytokine. Arthritis Rheum. 48:971–981. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Inoue K, Kawahara K, Biswas KK, Ando K,
Mitsudo K, Nobuyoshi M and Maruyama I: HMGB1 expression by
activated vascular smooth muscle cells in advanced human
atherosclerosis plaques. Cardiovasc Pathol. 16:136–143. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kalinina N, Agrotis A, Antropova Y,
DiVitto G, Kanellakis P, Kostolias G, Ilyinskaya O, Tararak E and
Bobik A: Increased expression of the DNA-binding cytokine HMGB1 in
human atherosclerotic lesions: Role of activated macrophages and
cytokines. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 24:2320–2325. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yao D and Brownlee M:
Hyperglycemia-induced reactive oxygen species increase expression
of the receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) and RAGE
ligands. Diabetes. 59:249–255. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Lupo G, Motta C, Giurdanella G, Anfuso CD,
Alberghina M, Drago F, Salomone S and Bucolo C: Role of
phospholipases A2 in diabetic retinopathy: In vitro and in vivo
studies. Biochem Pharmacol. 86:1603–1613. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tamura H, Miyamoto K, Kiryu J, Miyahara S,
Katsuta H, Hirose F, Musashi K and Yoshimura N: Intravitreal
injection of corticosteroid attenuates leukostasis and vascular
leakage in experimental diabetic retina. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
46:1440–1444. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jonas JB and Söfker A: Intraocular
injection of crystalline cortisone as adjunctive treatment of
diabetic macular edema. Am J Ophthalmol. 132:425–427. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cai J, Kehoe O, Smith GM, Hykin P and
Boulton ME: The angiopoietin/Tie-2 system regulates pericyte
survival and recruitment in diabetic retinopathy. Invest Ophthalmol
Vis Sci. 49:2163–2171. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Capetandes A and Gerritsen ME: Simplified
methods for consistent and selective culture of bovine retinal
endothelial cells and pericytes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
31:1738–1744. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kondo T, Hosoya K, Hori S, Tomi M, Ohtsuki
S, Takanaga H, Nakashima E, Iizasa H, Asashima T, Ueda M, et al:
Establishment of conditionally immortalized rat retinal pericyte
cell lines (TR-rPCT) and their application in a co-culture system
using retinal capillary endothelial cell line (TR-iBRB2). Cell
Struct Funct. 28:145–153. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang YL, Hui YN, Guo B and Ma JX:
Strengthening tight junctions of retinal microvascular endothelial
cells by pericytes under normoxia and hypoxia involving
angiopoietin-1 signal way. Eye (Lond). 21:1501–1510. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Cacicedo JM, Benjachareowong S, Chou E,
Ruderman NB and Ido Y: Palmitate-induced apoptosis in cultured
bovine retinal pericytes: Roles of NAD (P)H oxidase, oxidant
stress, and ceramide. Diabetes. 54:1838–1845. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Schreiber E, Matthias P, Müller MM and
Schaffner W: Rapid detection of octamer binding proteins with
'mini-extracts', prepared from a small number of cells. Nucleic
Acids Res. 17:64191989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bradford MM: A rapid and sensitive method
for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing
the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 72:248–254.
1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
von Knethen A, Callsen D and Brüne B:
NF-kappaB and AP-1 activation by nitric oxide attenuated apoptotic
cell death in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Mol Biol Cell. 10:361–372.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Vos MD, Ellis CA, Elam C, Ulku AS, Taylor
BJ and Clark GJ: RASSF2 is a novel K-Ras-specific effector and
potential tumor suppressor. J Biol Chem. 278:28045–28051. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hori O, Brett J, Slattery T, Cao R, Zhang
J, Chen JX, Nagashima M, Lundh ER, Vijay S, Nitecki D, et al: The
receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) is a cellular
binding site for amphoterin. Mediation of neurite outgrowth and
co-expression of rage and amphoterin in the developing nervous
system. J Biol Chem. 270:25752–25761. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Clynes R, Moser B, Yan SF, Ramasamy R,
Herold K and Schmidt AM: Receptor for AGE (RAGE): Weaving tangled
webs within the inflammatory response. Curr Mol Med. 7:743–751.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Motiejunaite R and Kazlauskas A: Pericytes
and ocular diseases. Exp Eye Res. 86:171–177. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Kuwabara T and Cogan DG: Retinal vascular
patterns. VII. Acellular change. Invest Ophthalmol. 4:1049–1064.
1965.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Sims DE: Diversity within pericytes. Clin
Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 27:842–846. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Joussen AM, Murata T, Tsujikawa A,
Kirchhof B, Bursell SE and Adamis AP: Leukocyte-mediated
endothelial cell i njury and death in the diabetic retina. Am J
Pathol. 158:147–152. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kern TS: Contributions of inflammatory
processes to the development of the early stages of diabetic
retinopathy. Exp Diabetes Res. 2007:951032007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Hofmann MA, Drury S, Fu C, Qu W, Taguchi
A, Lu Y, Avila C, Kambham N, Bierhaus A, Nawroth P, et al: RAGE
mediates a novel proinflammatory axis: A central cell surface
receptor for S100/calgranulin polypeptides. Cell. 97:889–901. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bierhaus A, Schiekofer S, Schwaninger M,
Andrassy M, Humpert PM, Chen J, Hong M, Luther T, Henle T, Klöting
I, et al: Diabetes-associated sustained activation of the
transcription factor nuclear factor-kappaB. Diabetes. 50:2792–2808.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Thornalley PJ: Dietary AGEs and ALEs and
risk to human health by their interaction with the receptor for
advanced glycation endproducts (RAGE)-an introduction. Mol Nutr
Food Res. 51:1107–1110. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ramasamy R, Yan SF and Schmidt AM: Arguing
for the motion: Yes, RAGE is a receptor for advanced glycation
endproducts. Mol Nutr Food Res. 51:1111–1115. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Heizmann CW: The mechanism by which
dietary AGEs are a risk to human health is via their interaction
with RAGE: Arguing against the motion. Mol Nutr Food Res.
51:1116–1119. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Foell D, Wittkowski H, Vogl T and Roth J:
S100 proteins expressed in phagocytes: A novel group of
damage-associated molecular pattern molecules. J Leukoc Biol.
81:28–37. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Yamagishi S, Takeuchi M, Matsui T,
Nakamura K, Imaizumi T and Inoue H: Angiotensin II augments
advanced glycation end product-induced pericyte apoptosis through
RAGE overexpression. FEBS Lett. 579:4265–4270. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yan SD, Schmidt AM, Anderson GM, Zhang J,
Brett J, Zou YS, Pinsky D and Stern D: Enhanced cellular oxidant
stress by the interaction of advanced glycation end products with
their receptors/binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 269:9889–9897.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Karin M and Ben-Neriah Y: Phosphorylation
meets ubiquitination: The control of NF-[kappa]B activity. Annu Rev
Immunol. 18:621–663. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Kim J, Kim OS, Kim CS, Kim NH and Kim JS:
Cytotoxic role of methylglyoxal in rat retinal pericytes:
Involvement of a nuclear factor-kappaB and inducible nitric oxide
synthase pathway. Chem Biol Interact. 188:86–93. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Kim J, Son JW, Lee JA, Oh YS and Shinn SH:
Methylglyoxal induces apoptosis mediated by reactive oxygen species
in bovine retinal pericytes. J Korean Med Sci. 19:95–100. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Romeo G, Liu WH, Asnaghi V, Kern TS and
Lorenzi M: Activation of nuclear factor-kappaB induced by diabetes
and high glucose regulates a proapoptotic program in retinal
pericytes. Diabetes. 51:2241–2248. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Zhang SX, Wang JJ, Dashti A, Wilson K, Zou
MH, Szweda L, Ma JX and Lyons TJ: Pigment epithelium-derived factor
mitigates inflammation and oxidative stress in retinal pericytes
exposed to oxidized low-density lipoprotein. J Mol Endocrinol.
41:135–143. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|