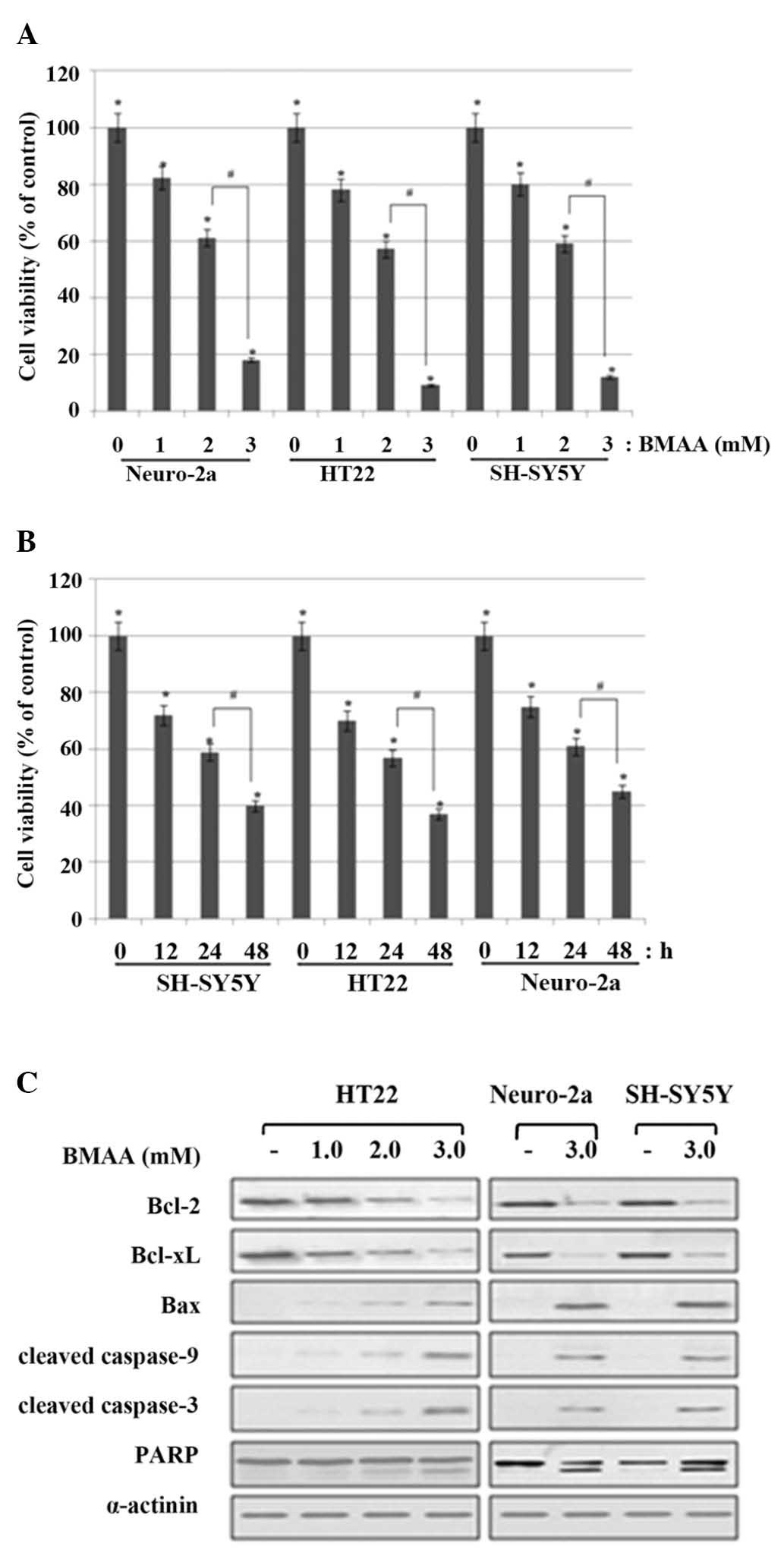
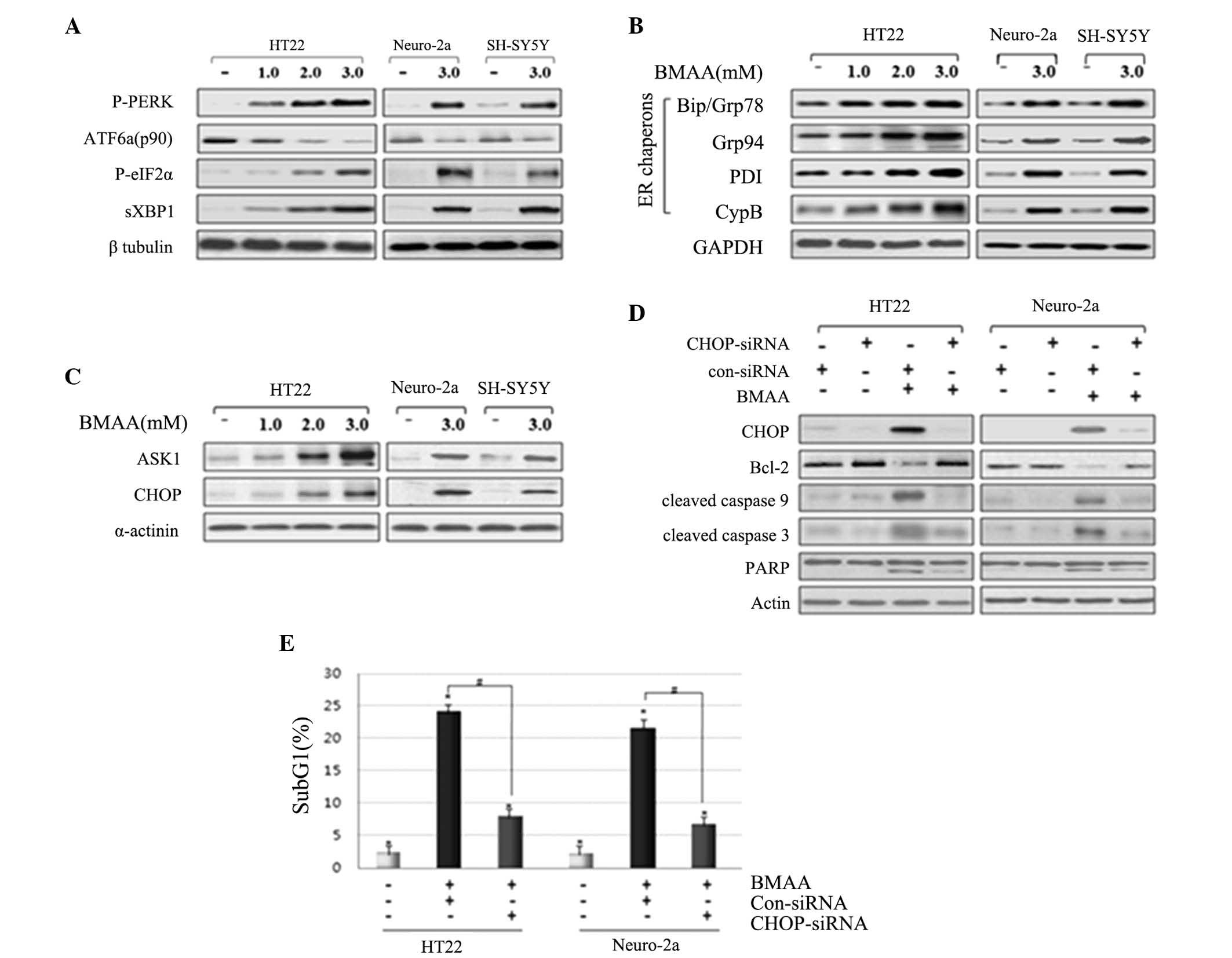
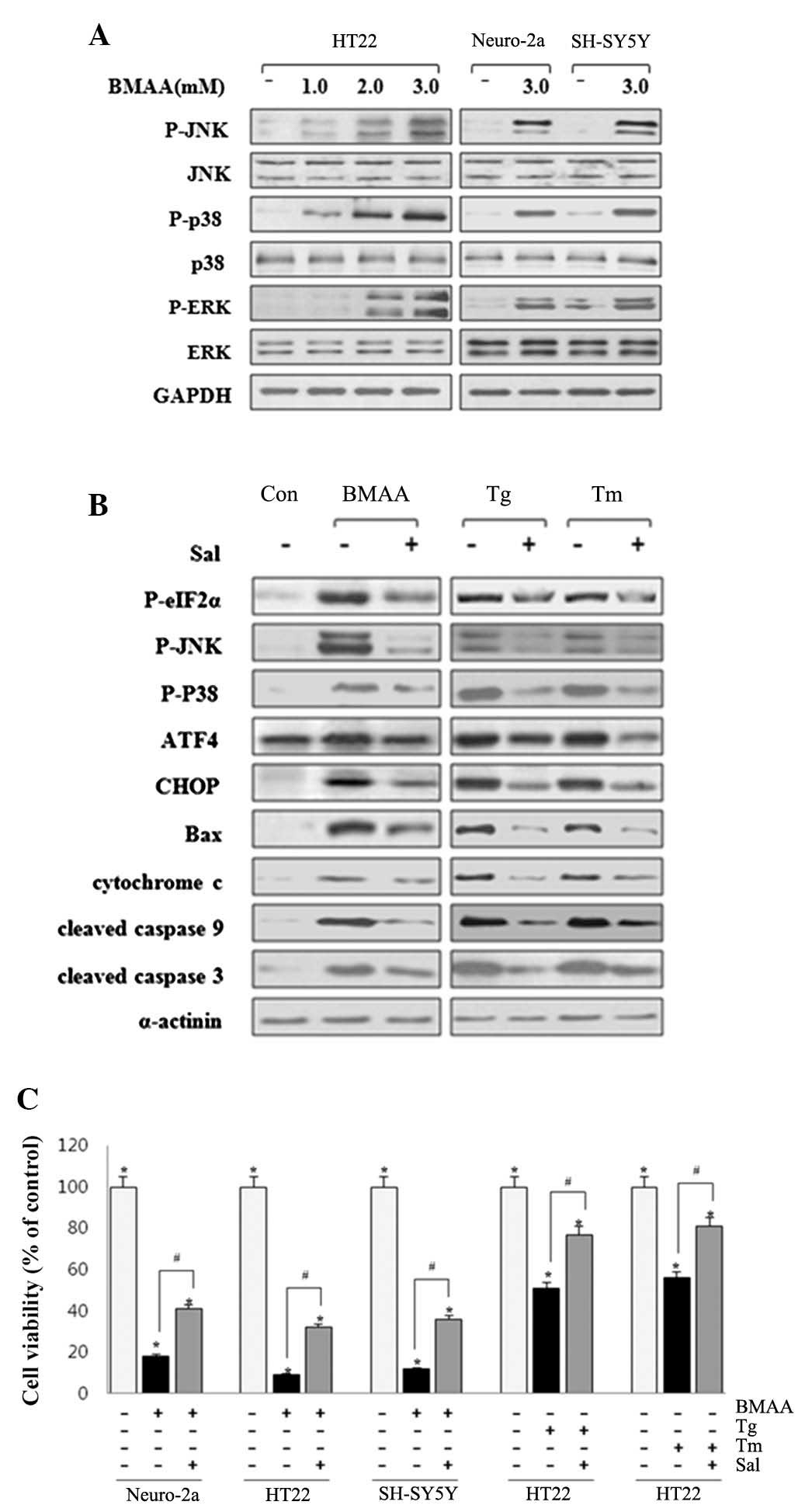
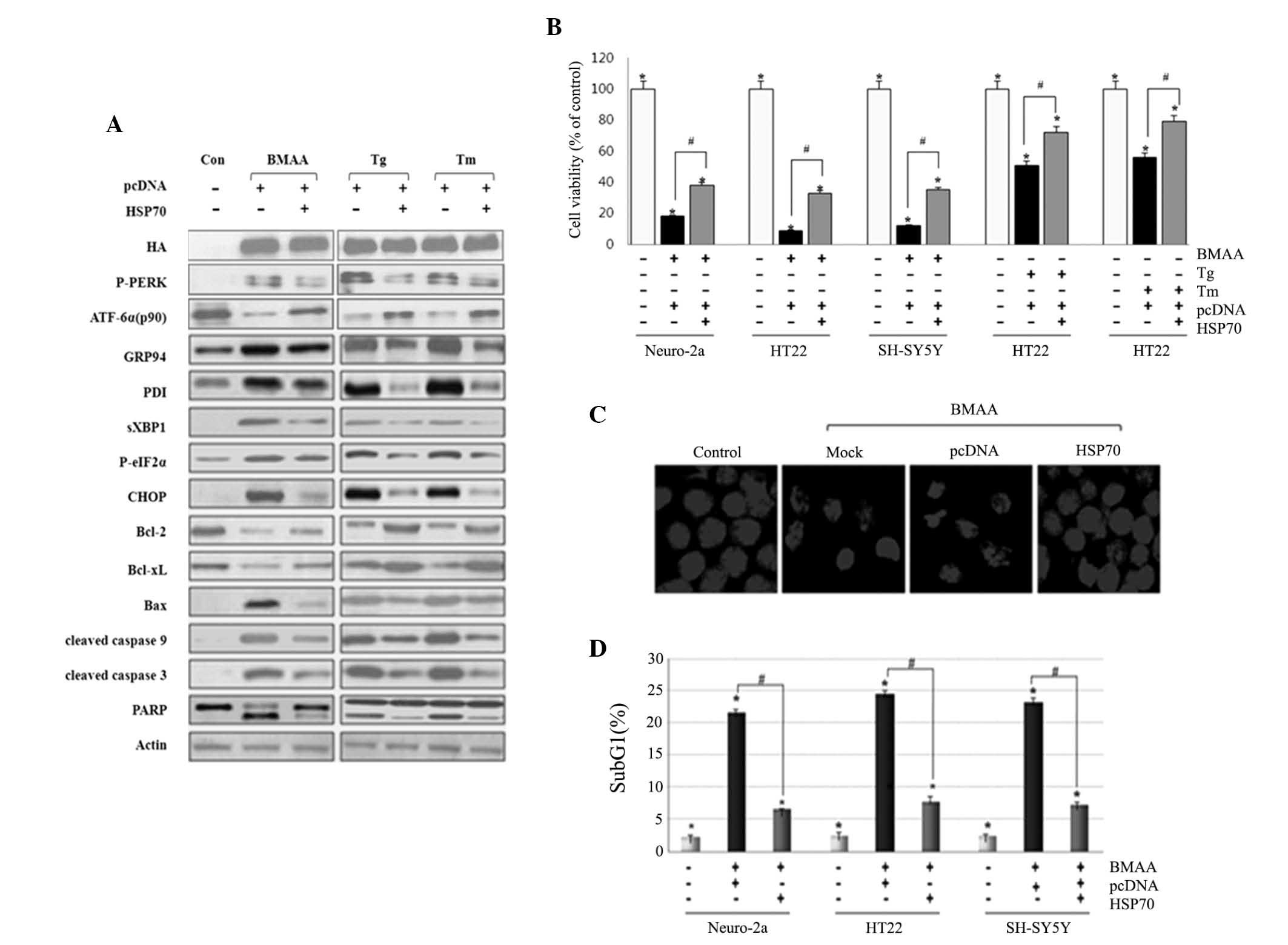
|
1
|
Murch SJ, Cox PA, Banack SA, Steele JC and
Sacks OW: Occurrence of beta-methylamino-l-alanine (BMAA) in
ALS/PDC patients from Guam. Acta Neurol Scand. 110:267–269. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pablo J, Banack SA, Cox PA, Johnson TE,
Papapetropoulos S, Bradley WG, Buck A and Mash DC: Cyanobacterial
neurotoxin BMAA in ALS and Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neurol Scand.
120:216–225. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Banack SA, Johnson HE, Cheng R and Cox PA:
Production of the neurotoxin BMAA by a marine cyanobacterium. Mar
Drugs. 5:180–196. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Banack SA and Cox PA: Biomagnification of
cycad neurotoxins in flying foxes: Implications for ALS-PDC in
Guam. Neurology. 61:387–389. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Smith QR, Nagura H, Takada Y and Duncan
MW: Facilitated transport of the neurotoxin,
beta-N-methylamino-L-alanine, across the blood-brain barrier. J
Neurochem. 58:1330–1337. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Plato CC, Cruz MT and Kurland LT:
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-Parkinsonism dementia complex of
Guam: Further genetic investigations. Am J Hum Genet. 21:133–141.
1969.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Spencer PS, Palmer VS, Herman A and Asmedi
A: Cycad use and motor neurone disease in Irian Jaya. Lancet.
2:1273–1274. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Karamyan VT and Speth RC: Animal models of
BMAA neurotoxicity: A critical review. Life Sci. 82:233–246. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Holtcamp W: The emerging science of BMAA:
Do cyanobacteria contribute to neurodegenerative disease? Environ
Health Perspect. 120:A110–A116. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lindholm D, Wootz H and Korhonen L: ER
stress and neurodegenerative diseases. Cell Death Differ.
13:385–392. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rasheva VI and Domingos PM: Cellular
responses to endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis. Apoptosis.
14:996–1007. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Urano F, Wang X, Bertolotti A, Zhang Y,
Chung P, Harding HP and Ron D: Coupling of stress in the ER to
activation of JNK protein kinases by transmembrane protein kinase
IRE1. Science. 287:664–666. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Boyce M and Yuan J: Cellular response to
endoplasmic reticulum stress: A matter of life or death. Cell Death
Differ. 13:363–373. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Weiss JH and Choi DW:
Beta-N-methylamino-L-alanine neurotoxicity: Requirement for
bicarbonate as a cofactor. Science. 241:973–975. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lobner D, Piana PM, Salous AK and Peoples
RW: Beta-N-methylamino-L-alanine enhances neurotoxicity through
multiple mechanisms. Neurobiol Dis. 25:360–366. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Okle O, Stemmer K, Deschl U and Dietrich
DR: L-BMAA induced ER stress and enhanced caspase 12 cleavage in
human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells at low nonexcitotoxic
concentrations. Toxicol Sci. 131:217–224. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lee AS: The ER chaperone and signaling
regulator GRP78/BiP as a monitor of endoplasmic reticulum stress.
Methods. 35:373–381. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kim I, Xu W and Reed JC: Cell death and
endoplasmic reticulum stress: Disease relevance and therapeutic
opportunities. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 7:1013–1030. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Walker AK, Farg MA, Bye CR, McLean CA,
Horne MK and Atkin JD: Protein disulphide isomerase protects
against protein aggregation and is S-nitrosylated in amyotrophic
lateral sclerosis. Brain. 133:105–116. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Nagai H, Noguchi T, Takeda K and Ichijo H:
Pathophysiological roles of ASK1-MAP kinase signaling pathways. J
Biochem Mol Biol. 40:1–6. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hung JH, Su IJ, Lei HY, Wang HC, Lin WC,
Chang WT, Huang W, Chang WC, Chang YS, Chen CC and Lai MD:
Endoplasmic reticulum stress stimulates the expression of
cyclooxygenase-2 through activation of NF-kappaB and pp38
mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 279:46384–46392.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang XZ and Ron D: Stress-induced
phosphorylation and activation of the transcription factor CHOP
(GADD153) by p38 MAP Kinase. Science. 272:1347–1349. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Boyce M, Bryant KF, Jousse C, Long K,
Harding HP, Scheuner D, Kaufman RJ, Ma D, Coen DM, Ron D and Yuan
J: A selective inhibitor of eIF2alpha dephosphorylation protects
cells from ER stress. Science. 307:935–939. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kim YE, Hipp MS, Bracher A, Hayer-Hartl M
and Hartl FU: Molecular chaperone functions in protein folding and
proteostasis. Annu Rev Biochem. 82:323–355. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mosser DD, Caron AW, Bourget L, Meriin AB,
Sherman MY, Morimoto RI and Massie B: The chaperone function of
hsp70 is required for protection against stress-induced apoptosis.
Mol Cell Biol. 20:7146–7159. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ross CA and Poirier MA: Protein
aggregation and neurodegenerative disease. Nat Med. 10:(Suppl).
S10–S17. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lee JW, Beebe K, Nangle LA, Jang J,
Longo-Guess CM, Cook SA, Davisson MT, Sundberg JP, Schimmel P and
Ackerman SL: Editing-defective tRNA synthetase causes protein
misfolding and neurodegeneration. Nature. 443:50–55. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Dunlop RA, Cox PA, Banack SA and Rodgers
KJ: The non-protein amino acid BMAA is misincorporated into human
proteins in place of L-serine causing protein misfolding and
aggregation. PLoS One. 8:e753762013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Rao SD, Banack SA, Cox PA and Weiss JH:
BMAA selectively injures motor neurons via AMPA/kainate receptor
activation. Exp Neurol. 201:244–252. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cucchiaroni ML, Viscomi MT, Bernardi G,
Molinari M, Guatteo E and Mercuri NB: Metabotropic glutamate
receptor 1 mediates the electrophysiological and toxic actions of
the cycad derivative beta-N-Methylamino-L-alanine on substantia
nigra pars compacta DAergic neurons. J Neurosci. 30:5176–5188.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Brownson DM, Mabry TJ and Leslie SW: The
cycad neurotoxic amino acid, beta-N-methylamino-L-alanine (BMAA),
elevates intracellular calcium levels in dissociated rat brain
cells. J Ethnopharmacol. 82:159–167. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liu X, Rush T, Zapata J and Lobner D:
beta-N-methylamino-l- alanine induces oxidative stress and
glutamate release through action on system Xc(−). Exp Neurol.
217:429–433. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Görlach A, Klappa P and Kietzmann T: The
endoplasmic reticulum: Folding, calcium homeostasis, signaling and
redox control. Antioxid Redox Signal. 8:1391–1418. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Doyle KM, Kennedy D, Gorman AM, Gupta S,
Healy SJ and Samali A: Unfolded proteins and endoplasmic reticulum
stress in neurodegenerative disorders. J Cell Mol Med.
15:2025–2039. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Oyadomari S and Mori M: Roles of
CHOP/GADD153 in endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Death Differ.
11:381–389. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Sokka AL, Putkonen N, Mudo G, Pryazhnikov
E, Reijonen S, Khiroug L, Belluardo N, Lindholm D and Korhonen L:
Endoplasmic reticulum stress inhibition protects against
excitotoxic neuronal injury in the rat brain. J Neurosci.
27:901–908. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chaudhuri TK and Paul S:
Protein-misfolding diseases and chaperone-based therapeutic
approaches. FEBS J. 273:1331–1349. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|