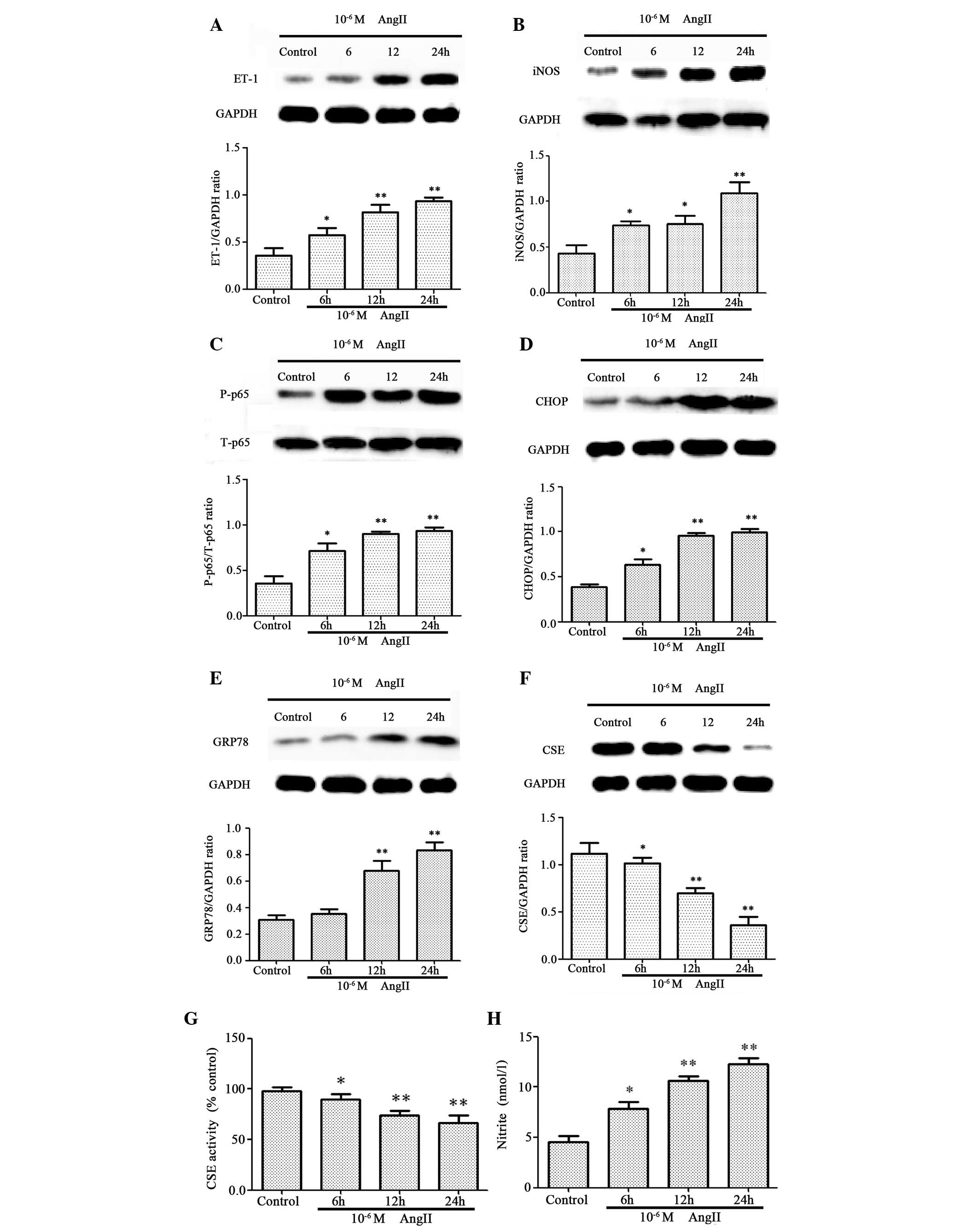
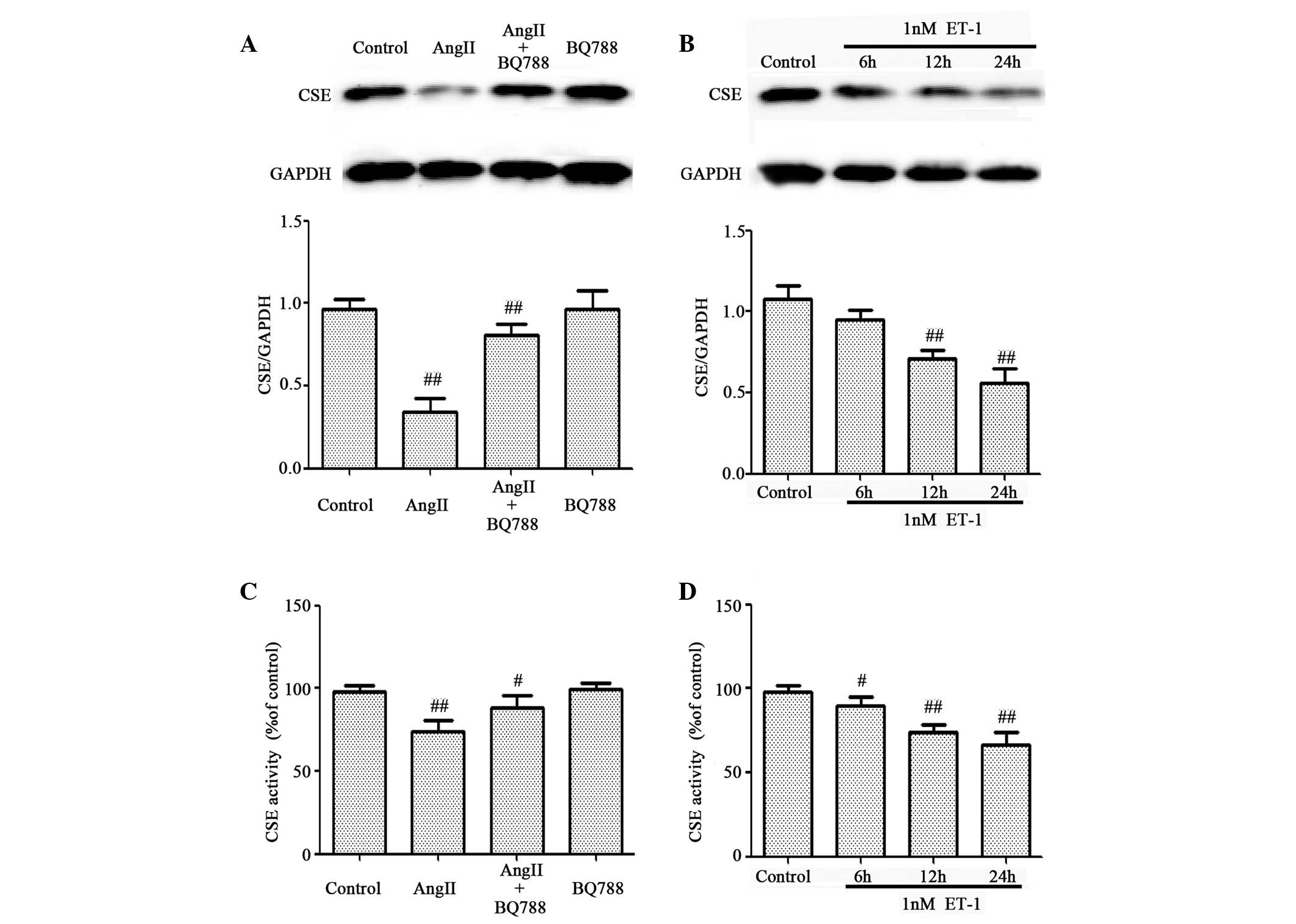
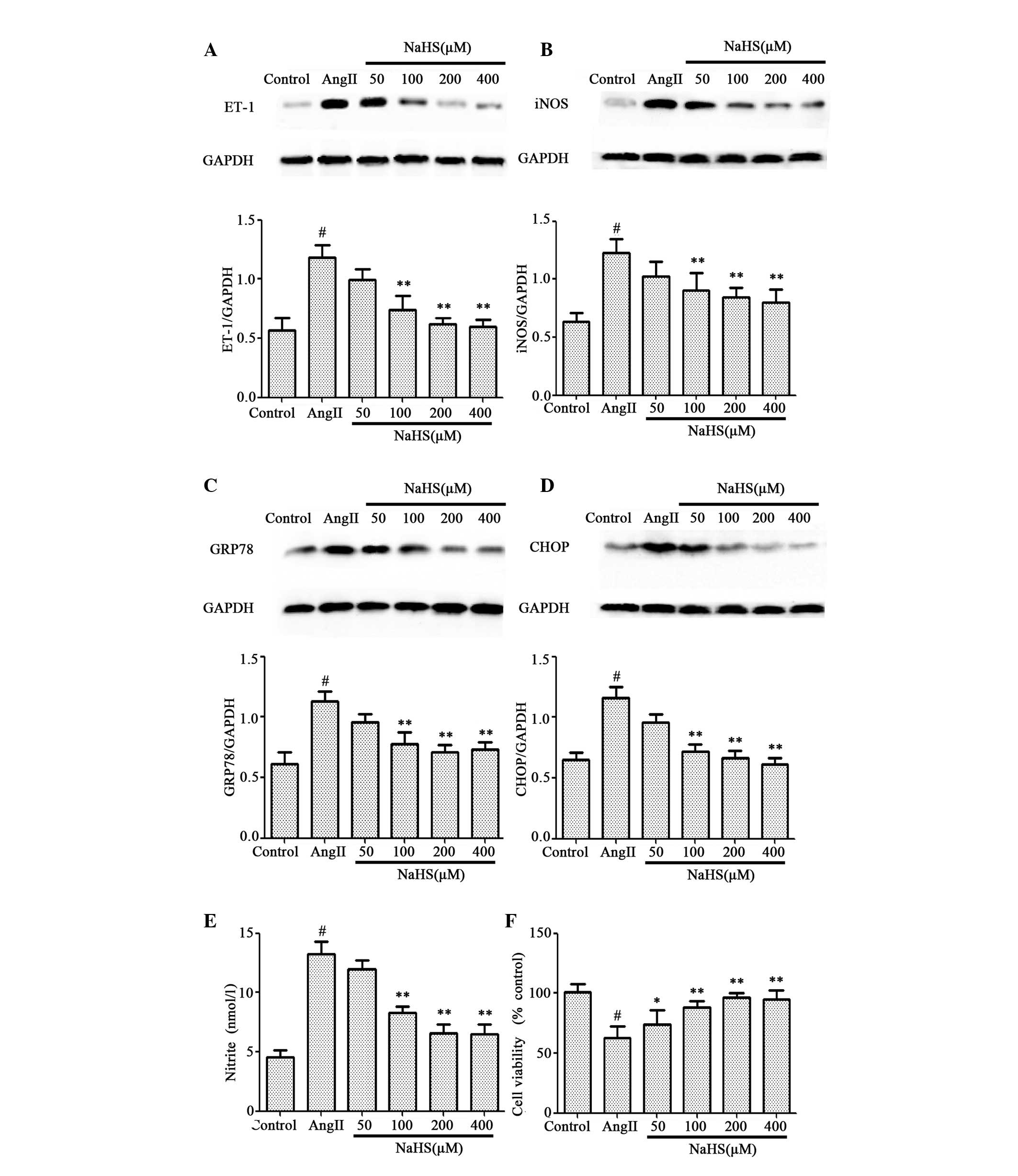
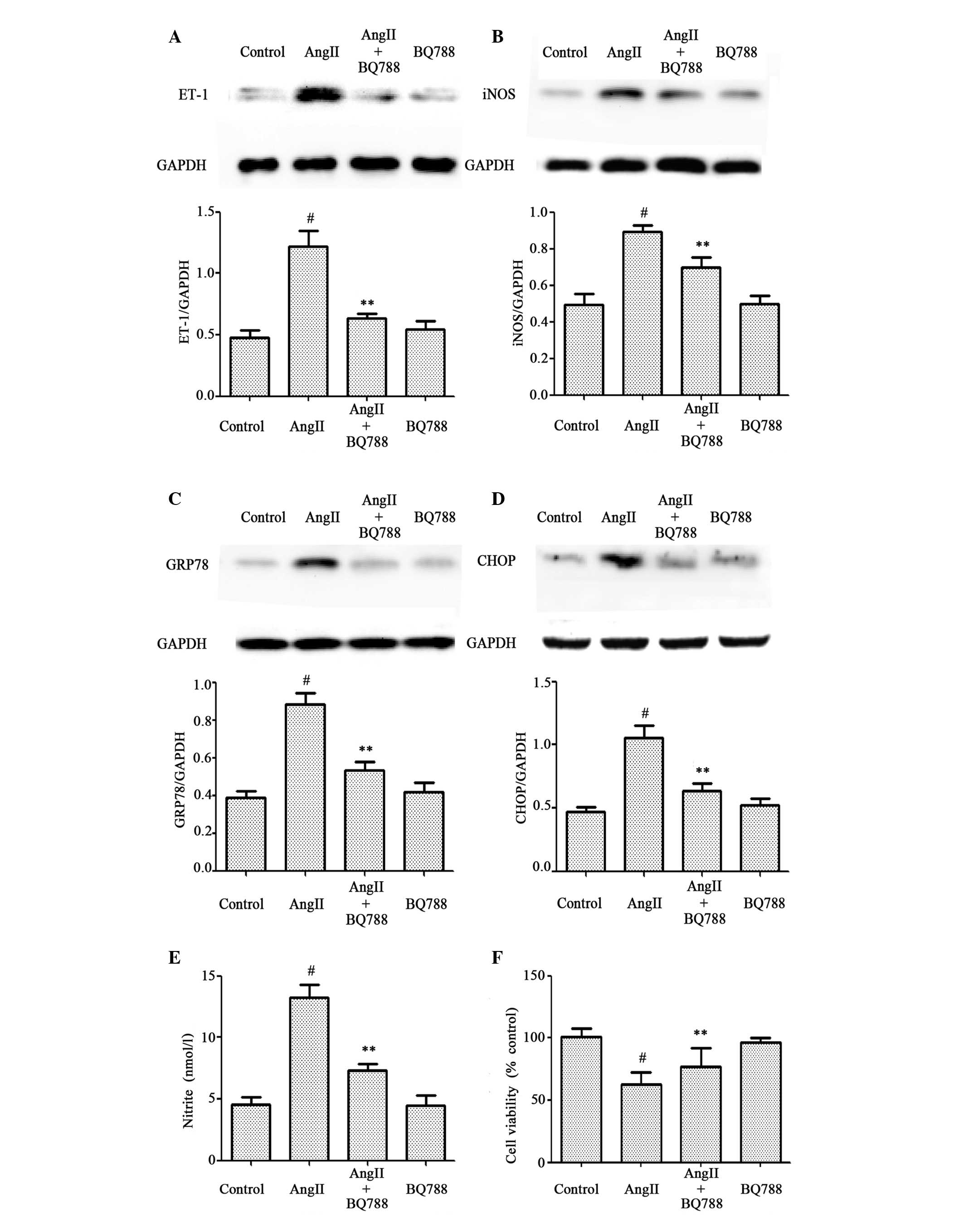
|
1
|
Feinstein M, Ning H, Kang J, Bertoni A,
Carnethon M and Lloyd-Jones DM: Racial differences in risks for
first cardiovascular events and noncardiovascular death: The
atherosclerosis risk in communities study, the cardiovascular
health study, and the multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis.
Circulation. 126:50–59. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Davignon J and Ganz P: Role of endothelial
dysfunction in atherosclerosis. Circulation. 109(23): Suppl 1.
III27–III32. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Loyer X, Potteaux S, Vion AC, Guérin CL,
Boulkroun S, Rautou PE, Ramkhelawon B, Esposito B, Dalloz M, Paul
JL, et al: Inhibition of microRNA-92a prevents endothelial
dysfunction and atherosclerosis in mice. Circ Res. 114:434–443.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Barton M, Haudenschild CC, d'Uscio LV,
Shaw S, Münter K and Luscher TF: Endothelin ETA receptor blockade
restores NO-mediated endothelial function and inhibits
atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 95:14367–14372. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Brunner F, Brás-Silva C, Cerdeira AS and
Leite-Moreira AF: Cardiovascular endothelins: Essential regulators
of cardiovascular homeostasis. Pharmacol Ther. 111:508–531. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kamata K, Kanie N, Matsumoto T and
Kobayashi T: Endothelin-1-induced impairment of
endothelium-dependent relaxation in aortas isolated from controls
and diabetic rats. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1(44): Suppl. S186–S190.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Barton M, Traupe T and Haudenschild CC:
Endothelin, hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerosis. Coron Artery
Dis. 14:477–490. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tummala PE, Chen XL, Sundell CL, Laursen
JB, Hammes CP, Alexander RW, Harrison DG and Medford RM:
Angiotensin II induces vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 expression
in rat vasculature: A potential link between the renin-angiotensin
system and atherosclerosis. Circulation. 100:1223–1229. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Marampon F, Gravina GL, Scarsella L,
Festuccia C, Lovat F, Ciccarelli C, Zani BM, Polidoro L, Grassi D,
Desideri G, et al: Angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibition
counteracts angiotensin II-mediated endothelial cell dysfunction by
modulating the p38/SirT1 axis. J Hypertens. 31:1972–1983. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ayari H: Respective roles of cortisol,
aldosterone and angiotensin II during pathophysiology of
atherosclerosis. Ann Biol Clin (Paris). 71:381–388. 2013.(In
French). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nishida Y, Takahashi Y, Susa N, Kanou N,
Nakayama T and Asai S: Comparative effect of angiotensin II type I
receptor blockers on serum uric acid in hypertensive patients with
type 2 diabetes mellitus: A retrospective observational study.
Cardiovasc Diabetol. 12:1592013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ocaranza MP, Michea L, Chiong M, Lagos CF,
Lavandero S and Jalil JE: Recent insights and therapeutic
perspectives of angiotensin-(1–9) in the cardiovascular system.
Clin Sci (Lond). 127:549–557. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yang HY, Bian YF, Zhang HP, Gao F, Xiao
CS, Liang B, Li J, Zhang NN and Yang ZM: Angiotensin-(1–7)
treatment ameliorates angiotensin II-induced apoptosis of human
umbilical vein endothelial cells. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol.
39:1004–1010. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ron D and Walter P: Signal integration in
the endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 8:519–529. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Uhal BD, Nguyen H, Dang M, Gopallawa I,
Jiang J, Dang V, Ono S and Morimoto K: Abrogation of ER
stress-induced apoptosis of alveolar epithelial cells by
angiotensin 1–7. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 305:L33–L41.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chistiakov DA, Sobenin IA, Orekhov AN and
Bobryshev YV: Role of endoplasmic reticulum stress in
atherosclerosis and diabetic macrovascular complications. Biomed
Res Int. 2014:6101402014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chaudhari N, Talwar P, Parimisetty A,
Lefebvre d'Hellencourt C and Ravanan P: A molecular web:
Endoplasmic reticulum stress, inflammation, and oxidative stress.
Front Cell Neurosci. 8:2132014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Guo RW, Yang LX, Li MQ, Liu B and Wang XM:
Angiotensin II induces NF-kappa B activation in HUVEC via the
p38MAPK pathway. Peptides. 27:3269–3275. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Pushpakumar SB, Kundu S and Sen U:
Endothelial dysfunction: The link between homocysteine and hydrogen
sulfide. Curr Med Chem. 21:3662–3672. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Łowicka E and Beltowski J: Hydrogen
sulfide (H2S)-the third gas of interest for pharmacologists.
Pharmacol Rep. 59:4–24. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yang G, Wu L, Jiang B, Yang W, Qi J, Cao
K, Meng Q, Mustafa AK, Mu W, Zhang S, et al: H2S as a physiologic
vasorelaxant: Hypertension in mice with deletion of cystathionine
gamma-lyase. Science. 322:587–590. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Suo R, Zhao ZZ, Tang ZH, Ren Z, Liu X, Liu
LS, Wang Z, Tang CK, Wei DH and Jiang ZS: Hydrogen sulfide prevents
H2O2-induced senescence in human umbilical vein endothelial cells
through SIRT1 activation. Mol Med Rep. 7:1865–1870. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ng DS, Peh MT, Anwar AB, Atan MSB
Mohammed, Tsai C-Yi, Kumar SD and Moore PK: P27 Changes in the
hydrogen sulfide (H2S) system arising from administration of high
fat diet. Nitric Oxide. 31:(Suppl 2). S46–S47. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Pan LL, Liu XH, Gong QH, Wu D and Zhu YZ:
Hydrogen sulfide attenuated tumor necrosis factor-α-induced
inflammatory signaling and dysfunction in vascular endothelial
cells. PLoS One. 6:e197662011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mani S, Untereiner A, Wu L and Wang R:
Hydrogen sulfide and the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Antioxid
Redox Signal. 20:805–817. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xue H, Yuan P, Ni J, Li C, Shao D, Liu J,
Shen Y, Wang Z, Zhou L, Zhang W, et al: H(2)S inhibits
hyperglycemia-induced intrarenal renin-angiotensin system
activation via attenuation of reactive oxygen species generation.
PLoS One. 8:e743662013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lin YJ, Kwok CF, Juan CC, Hsu YP, Shih KC,
Chen CC and Ho LT: Angiotensin II enhances endothelin-1-induced
vasoconstriction through upregulating endothelin type A receptor.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 451:263–269. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Al-Magableh MR, Kemp-Harper BK and Hart
JL: Hydrogen sulfide treatment reduces blood pressure and oxidative
stress in angiotensin II-induced hypertensive mice. Hypertens Res.
38:13–20. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kossmann S, Hu H, Steven S, Schönfelder T,
Fraccarollo D, Mikhed Y, Brähler M, Knorr M, Brandt M, Karbach SH,
et al: Inflammatory monocytes determine endothelial nitric oxide
synthase uncoupling and nitro-oxidative stress induced by
angiotensin II. J Biol Chem. 289:27540–27550. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Miyata K, Satou R, Shao W, Prieto MC,
Urushihara M, Kobori H and Navar LG: ROCK/NF-κB axis-dependent
augmentation of angiotensinogen by angiotensin II in
primary-cultured preglomerular vascular smooth muscle cells. Am J
Physiol Renal Physiol. 306:F608–F618. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Adiarto S, Heiden S, Vignon-Zellweger N,
Nakayama K, Yagi K, Yanagisawa M and Emoto N: ET-1 from endothelial
cells is required for complete angiotensin II-induced cardiac
fibrosis and hypertrophy. Life Sci. 91:651–657. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Browatzki M, Schmidt J, Kübler W and
Kranzhöfer R: Endothelin-1 induces interleukin-6 release via
activation of the transcriptio n factor NF-kappaB in human vascular
smooth muscle cells. Basic Res Cardiol. 95:98–105. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chen X, Rateri DL, Howatt DA, Balakrishnan
A, Moorleghen JJ, Morris AJ, Charnigo R, Cassis LA and Daugherty A:
Amlodipine reduces AngII-induced aortic aneurysms and
atherosclerosis in hypercholesterolemic mice. PLoS One.
8:e817432013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Murdoch CE, Chaubey S, Zeng L, Yu B,
Ivetic A, Walker SJ, Vanhoutte D, Heymans S, Grieve DJ, Cave AC, et
al: Endothelial NADPH oxidase-2 promotes interstitial cardiac
fibrosis and diastolic dysfunction through proinflammatory effects
and endothelial-mesenchymal transition. J Am Coll Cardiol.
63:2734–2741. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wei LH, Huang XR, Zhang Y, Li YQ, Chen HY,
Heuchel R, Yan BP, Yu CM and Lan HY: Deficiency of Smad7 enhances
cardiac remodeling induced by angiotensin II infusion in a mouse
model of hypertension. PLoS One. 8:e701952013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lin CC, Hsieh HL, Chi PL, Yang CC, Hsiao
LD and Yang CM: Upregulation of COX-2/PGE2 by ET-1 mediated through
Ca2+-dependent signals in mouse brain microvascular endothelial
cells. Mol Neurobiol. 49:1256–1269. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Shiraki A, Oyama J, Komoda H, Asaka M,
Komatsu A, Sakuma M, Kodama K, Sakamoto Y, Kotooka N, Hirase T and
Node K: The glucagon-like peptide 1 analog liraglutide reduces
TNF-α-induced oxidative stress and inflammation in endothelial
cells. Atherosclerosis. 221:375–382. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lee W, Ku SK and Bae JS: Factor Xa
inhibits HMGB1-induced septic responses in human umbilical vein
endothelial cells and in mice. Thromb Haemost. 112:757–769. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Schrader LI, Kinzenbaw DA, Johnson AW,
Faraci FM and Didion SP: IL-6 deficiency protects against
angiotensin II induced endothelial dysfunction and hypertrophy.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 27:2576–2581. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Rojas E, Rodríguez-Molina D, Bolli P,
Israili ZH, Faría J, Fidilio E, Bermúdez V and Velasco M: The role
of adiponectin in endothelial dysfunction and hypertension. Curr
Hypertens Rep. 16:4632014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lamarca B: Endothelial dysfunction. An
important mediator in the pathophysiology of hypertension during
pre-eclampsia. Minerva Ginecol. 64:309–320. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Du J, Huang Y, Yan H, Zhang Q, Zhao M, Zhu
M, Liu J, Chen SX, Bu D, Tang C and Jin H: Hydrogen sulfide
suppresses oxidized low-density lipoprotein (ox-LDL)-stimulated
monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 generation from macrophages via
the nuclear factor kappaB (NF-κB) pathway. J Biol Chem.
289:9741–9753. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Sata M and Fukuda D: Crucial role of
renin-angiotensin system in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. J
Med Invest. 57:12–25. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lynn EG and Austin RC: Hydrogen sulfide in
the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis and its therapeutic potential.
Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 4:97–108. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Liu Z, Han Y, Li L, Lu H, Meng G, Li X,
Shirhan M, Peh MT, Xie L, Zhou S, et al: The hydrogen sulfide
donor, GYY4137, exhibits anti-atherosclerotic activity in high fat
fed apolipoprotein E(−/−) mice. Br J Pharmacol. 169:1795–1809.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Meng G, Zhu J, Xiao Y, Huang Z, Zhang Y,
Tang X, Xie L, Chen Y, Shao Y, Ferro A, et al: Hydrogen sulfide
donor GYY4137 protects against myocardial fibrosis. Oxid Med Cell
Longev. 2015:6910702015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Piechota-Polanczyk A, Kleniewska P and
Goraca A: The influence of ETA and ETB receptor blockers on
LPS-induced oxidative stress and NF-κB signaling pathway in heart.
Gen Physiol Biophys. 31:271–278. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Guo R, Wu K, Chen J, Mo L, Hua X, Zheng D,
Chen P, Chen G, Xu W and Feng J: Exogenous hydrogen sulfide
protects against doxorubicin-induced inflammation and cytotoxicity
by inhibiting p38MAPK/NFκB pathway in H9c2 cardiac cells. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 32:1668–1680. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Qabazard B, Ahmed S, Li L, Arlt VM, Moore
PK and Stürzenbaum SR: C. elegans aging is modulated by hydrogen
sulfide and the sulfhydrylase/cysteine synthase cysl-2. PLoS One.
8:e801352013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Touyz RM, Yao G, Viel E, Amiri F and
Schiffrin EL: Angiotensin II and endothelin-1 regulate MAP kinases
through different redox-dependent mechanisms in human vascular
smooth muscle cells. J Hypertens. 22:1141–1149. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|