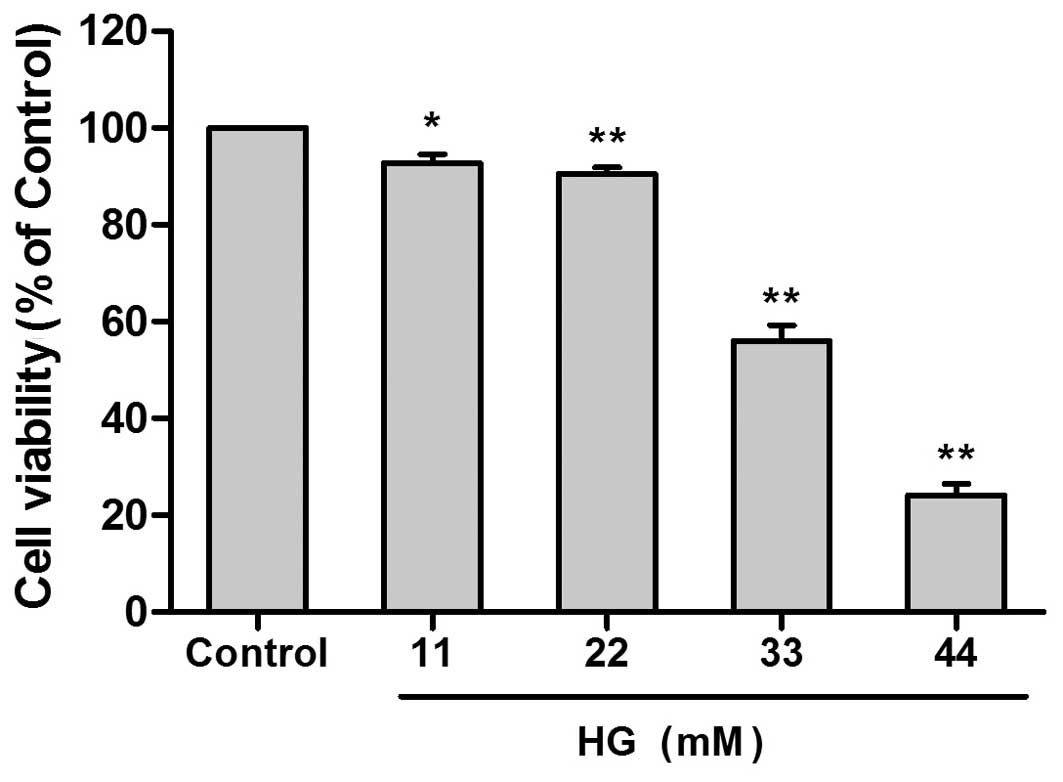
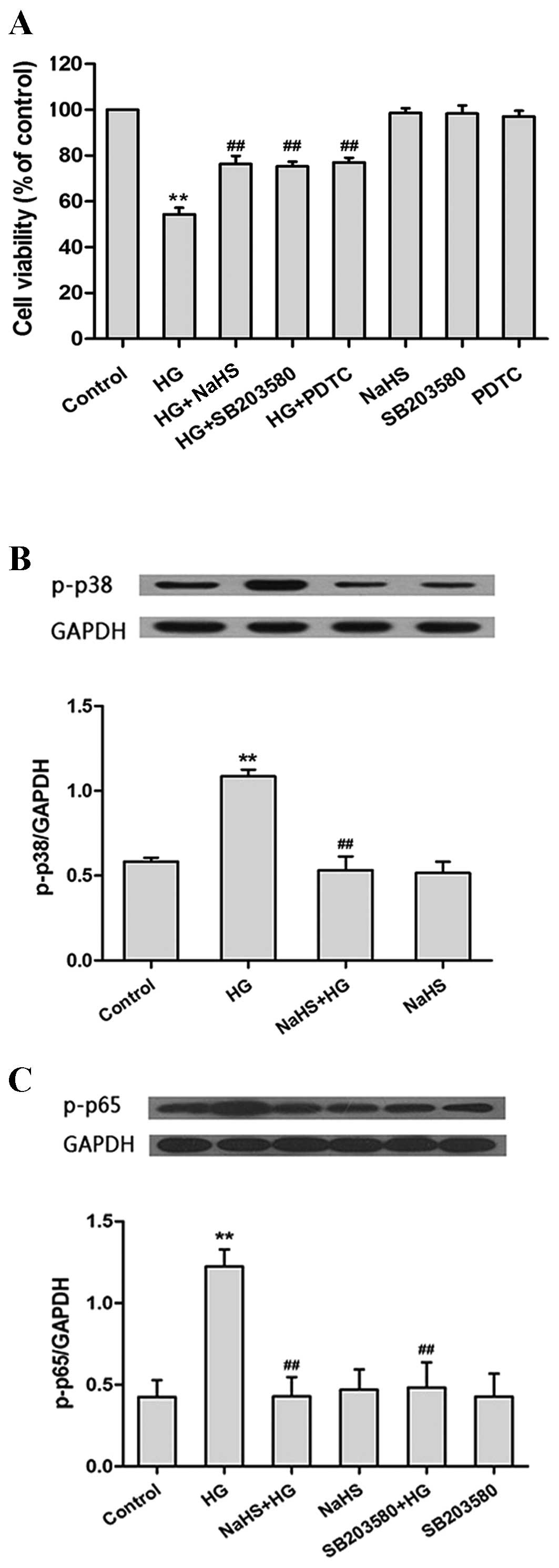
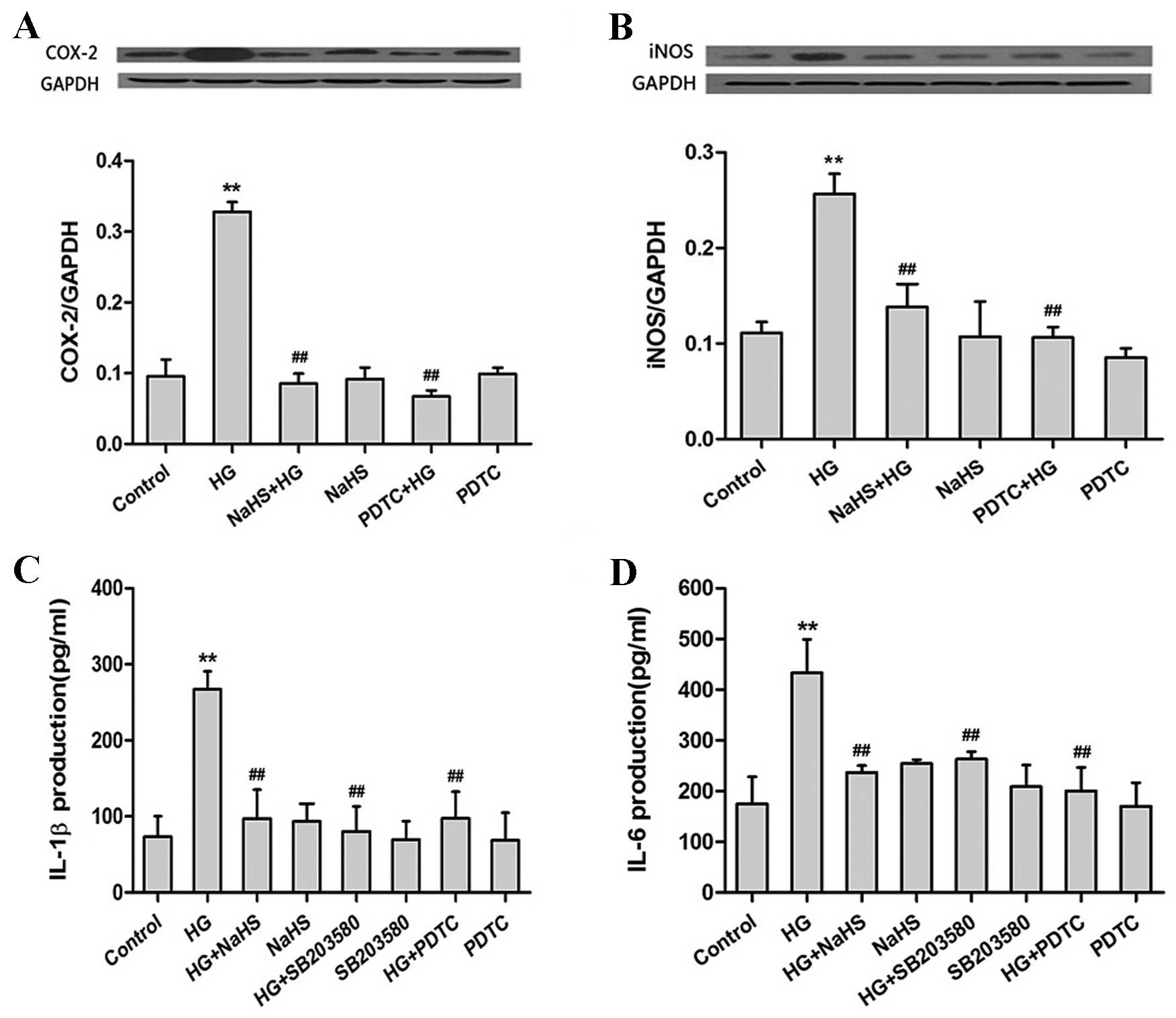
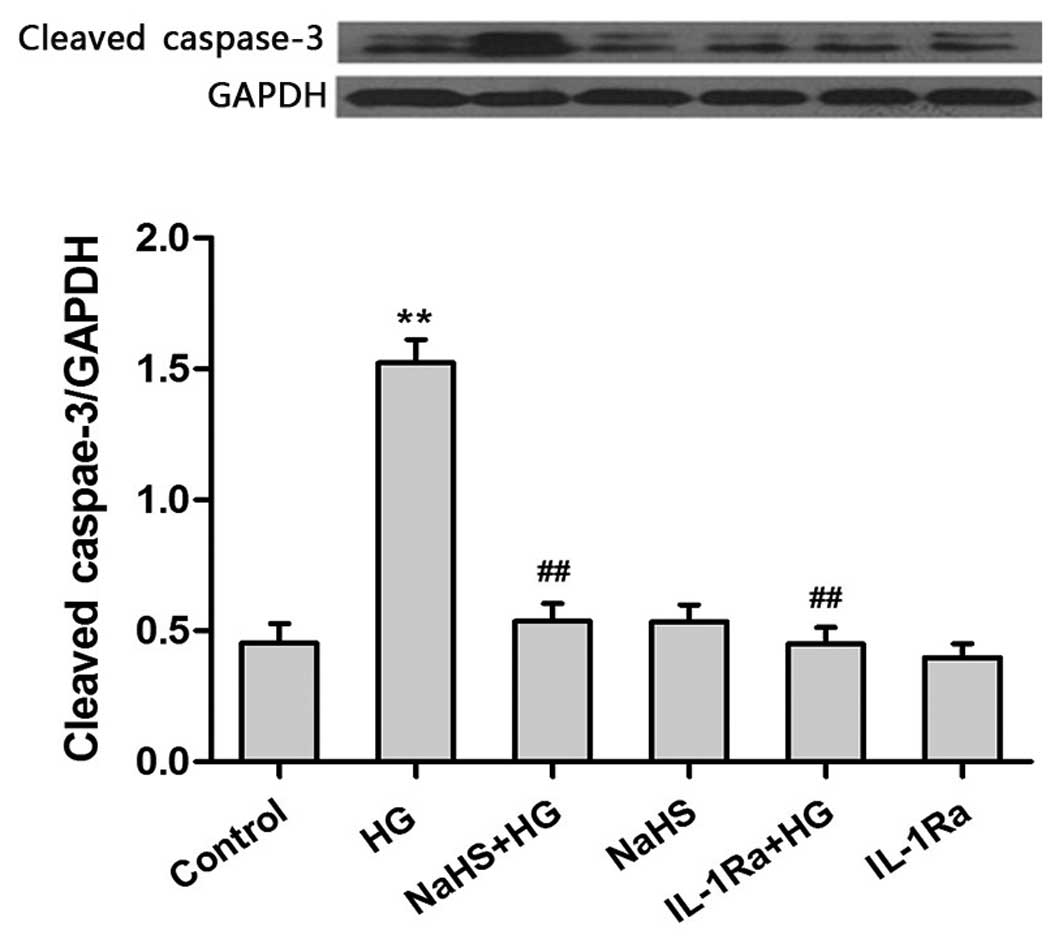
|
1
|
Chen L, Magliano DJ and Zimmet PZ: The
worldwide epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus-present and
future perspectives. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 8:228–236. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Goyal BR and Mehta AA: Diabetic
cardiomyopathy: Pathophysiological mechanisms and cardiac
dysfuntion. Hum Exp Toxicol. 32:571–590. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Poornima IG, Parikh P and Shannon RP:
Diabetic cardiomyopathy: The search for a unifying hypothesis. Circ
Res. 98:596–605. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Shen E, Li Y, Li Y, Shan L, Zhu H, Feng Q,
Arnold JM and Peng T: Rac1 is required for cardiomyocyte apoptosis
during hyperglycemia. Diabetes. 58:2386–2395. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Puthanveetil P, Zhang D, Wang Y, Wang F,
Wan A, Abrahani A and Rodrigues B: Diabetes triggers a PARP1
mediated death pathway in the heart through participation of FoxO1.
J Mol Cell Cardiol. 53:677–686. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Evans JL, Goldfine ID, Maddux BA and
Grodsky GM: Oxidative stress and stress-activated signaling
pathways: A unifying hypothesis of type 2 diabetes. Endocr Rev.
23:599–622. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Igarashi M, Wakasaki H, Takahara N, Ishii
H, Jiang ZY, Yamauchi T, Kuboki K, Meier M, Rhodes CJ and King GL:
Glucose or diabetes activates p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase
via different pathways. J Clin Invest. 103:185–195. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Crowell JA, Steele VE, Sigman CC and Fay
JR: Is inducible nitric oxide synthase a target for
chemoprevention? Mol Cancer Ther. 2:815–823. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cho SY, Park SJ, Kwon MJ, Jeong TS, Bok
SH, Choi WY, Jeong WI, Ryu SY, Do SH, Lee CS, et al: Quercetin
suppresses proinflammatory cytokines production through MAP kinases
and NF-kappaB pathway in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophage.
Mol Cell Biochem. 243:153–160. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Puthanveetil P, Zhang D, Wang Y, Wang F,
Wan A, Abrahani A and Rodrigues B: Diabetes triggers a PARP1
mediated death pathway in the heart through participation of FoxO1.
J Mol Cell Cardiol. 53:677–686. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jenke A, Wilk S, Poller W, Eriksson U,
Valaperti A, Rauch BH, Stroux A, Liu P, Schultheiss HP,
Scheibenbogen C and Skurk C: Adiponectin protects against Toll-like
receptor 4-mediated cardiac inflammation and injury. Cardiovasc
Res. 99:422–431. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Streicher JM, Kamei K, Ishikawa TO,
Herschman H and Wang Y: Compensatory hypertrophy induced by
ventricular cardiomyocyte-specific COX-2 expression in mice. J Mol
Cell Cardiol. 49:88–94. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Soetikno V, Sari FR, Sukumaran V,
Lakshmanan AP, Mito S, Harima M, Thandavarayan RA, Suzuki K, Nagata
M, Takagi R and Watanabe K: Curcumin prevents diabetic
cardiomyopathy in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats: Possible
involvement of PKC-MAPK signaling pathway. Eur J Pharm Sci.
47:604–614. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liu YH, Lu M, Hu LF, Wong PT, Webb GD and
Bian JS: Hydrogen sulfide in the mammalian cardiovascular system.
Antioxid Redox Signal. 17:141–185. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Holwerda KM, Karumanchi SA and Lely AT:
Hydrogen sulfide: Role in vascular physiology and pathology. Curr
Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 24:170–176. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li L, Bhatia M and Moore PK: Hydrogen
sulphide-A novel mediator of inflammation? Curr Opin Pharmacol.
6:125–129. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen SL, Yang CT, Yang ZL, Guo RX, Meng
JL, Cui Y, Lan AP, Chen PX and Feng JQ: Hydrogen sulphide protects
H9c2 cells against chemical hypoxia-induced injury. Clin Exp
Pharmacol Physiol. 37:316–321. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
El-Seweidy MM, Sadik NA and Shaker OG:
Role of sulfurous mineral water and sodium hydrosulfide as potent
inhibitors of fibrosis in the heart of diabetic rats. Arch Biochem
Biophys. 506:48–57. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Guo R, Wu K, Chen J, Mo L, Hua X, Zheng D,
Chen P, Chen G, Xu W and Feng J: Exogenous hydrogen sulfide
protects against doxorubicin-induced inflammation and cytotoxicity
by inhibiting p38MAPK/NFκB pathway in H9c2 cardiac cells. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 32:1668–1680. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xu W, Wu W, Chen J, Guo R, Lin J, Liao X
and Feng J: Exogenous hydrogen sulfide protects H9c2 cardiac cells
against high glucose-induced injury by inhibiting the activities of
the p38 MAPK and ERK1/2 pathways. Int J Mol Med. 32:917–925.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wei WB, Hu X, Zhuang XD, Liao LZ and Li
WD: GYY4137, a novel hydrogen sulfide-releasing molecule, likely
protects against high glucose-induced cytotoxicity by activation of
the AMPK/mTOR signal pathway in H9c2 cells. Mol Cell Biochem.
389:249–256. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhou X and Lu X: Hydrogen sulfide inhibits
high-glucose-induced apoptosis in neonatal rat cardiomyocytes. Exp
Biol Med (Maywood). 238:370–374. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Fulda S: Targeting apoptosis for
anticancer therapy. Semin Cancer Biol. 31:84–88. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mortuza R and Chakrabarti S:
Glucose-induced cell signaling in the pathogenesis of diabetic
cardiomyopathy. Heart Fail Rev. 19:75–86. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Rodrigues B, Cam MC and McNeill JH:
Metabolic disturbances in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Mol Cell
Biochem. 180:53–57. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Cheng Y, Ndisang JF, Tang G, Cao K and
Wang R: Hydrogen sulfide-induced relaxation of resistance
mesenteric artery beds of rats. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
287:H2316–H2323. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ali MY, Ping CY, Mok YY, Ling L, Whiteman
M, Bhatia M and Moore PK: Regulation of vascular nitric oxide in
vitro and in vivo; a new role for endogenous hydrogen sulphide? Br
J Pharmacol. 149:625–634. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hosoki R, Matsuki N and Kimura H: The
possible role of hydrogen sulfide as an endogenous smooth muscle
relaxant in synergy with nitric oxide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
237:527–531. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kiss L, Deitch EA and Szabo C: Hydrogen
sulfide decreases adenosine triphosphate levels in aortic rings and
leads to vasorelaxation via metabolic inhibition. Life Sci.
83:589–594. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lim JJ, Liu YH, Khin ES and Bian JS:
Vasoconstrictive effect of hydrogen sulfide involves downregulation
of cAMP in vascular smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
295:C1261–C1270. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Abe K and Kimura H: The possible role of
hydrogen sulfide as an endogenous neuromodulator. J Neurosci.
16:1066–1071. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hu LF, Wong PT, Moore PK and Bian JS:
Hydrogen sulfide attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation
by inhibition of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in microglia.
J Neurochem. 100:1121–1128. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Li L, Bhatia M and Moore PK: Hydrogen
sulphide-a novel mediator of inflammation? Curr Opin Pharmacol.
6:125–129. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Johansen D, Ytrehus K and Baxter GF:
Exogenous hydrogen sulfide (H2S) protects against regional
myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury-Evidence for a role of K ATP
channels. Basic Res Cardiol. 101:53–60. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Elrod JW, Calvert JW, Morrison J, Doeller
JE, Kraus DW, Tao L, Jiao X, Scalia R, Kiss L, Szabo C, et al:
Hydrogen sulfide attenuates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury
by preservation of mitochondrial function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
104:15560–15565. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Jain SK, Bull R, Rains JL, Bass PF, Levine
SN, Reddy S, McVie R and Bocchini JA: Low levels of hydrogen
sulfide in the blood of diabetes patients and
streptozotocin-treated rats causes vascular inflammation? Antioxid
Redox Signal. 12:1333–1337. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yusuf M, Huat BT Kwong, Hsu A, Whiteman M,
Bhatia M and Moore PK: Streptozotocin-induced diabetes in the rat
is associated with enhanced tissue hydrogen sulfide biosynthesis.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 333:1146–1152. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Du J, Hui Y, Cheung Y, Bin G, Jiang H,
Chen X and Tang C: The possible role of hydrogen sulfide as a
smooth muscle cell proliferation inhibitor in rat cultured cells.
Heart Vessels. 19:75–80. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hu LF, Lu M, Wu ZY, Wong PT and Bian JS:
Hydrogen sulfide inhibits rotenone-induced apoptosis via
preservation of mitochondrial function. Mol Pharmacol. 75:27–34.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Oh GS, Pae HO, Lee BS, Kim BN, Kim JM, Kim
HR, Jeon SB, Jeon WK, Chae HJ and Chung HT: Hydrogen sulfide
inhibits nitric oxide production and nuclear factor-kappaB via heme
oxygenase-1 expression in RAW264.7 macrophages stimulated with
lipopolysaccharide. Free Radic Biol Med. 41:106–119. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Tripatara P, Patel NS, Collino M,
Gallicchio M, Kieswich J, Castiglia S, Benetti E, Stewart KN, Brown
PA, Yaqoob MM, et al: Generation of endogenous hydrogen sulfide by
cystathionine gamma-lyase limits renal ischemia/reperfusion injury
and dysfunction. Lab Invest. 88:1038–1048. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Tamizhselvi R, Moore PK and Bhatia M:
Inhibition of hydrogen sulfide synthesis attenuates chemokine
production and protects mice against acute pancreatitis and
associated lung injury. Pancreas. 36:e24–e31. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Sivarajah A, McDonald MC and Thiemermann
C: The production of hydrogen sulfide limits myocardial ischemia
and reperfusion injury and contributes to the cardioprotective
effects of preconditioning with endotoxin, but not ischemia in the
rat. Shock. 26:154–161. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Boudina S and Abel ED: Diabetic
cardiomyopathy, causes and effects. Rev Endocr Metab Disord.
11:31–39. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zheng X, Zhu S, Chang S, Cao Y, Dong J, Li
J, Long R and Zhou Y: Protective effects of chronic resveratrol
treatment on vascular inflammatory injury in steptozotocin-induced
type 2 diabetic rats: Role of NF-kappaB signaling. Eur J Pharmacol.
720:147–157. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
MacMicking J, Xie QW and Nathan C: Nitric
oxide and macrophage function. Annu Rev Immunol. 15:323–350. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Bardell AL and MacLeod KM: Evidence for
inducible nitric-oxide synthase expression and activity in vascular
smooth muscle of streptozotocin-diabetic rats. J Pharmacol Exp
Ther. 296:252–259. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Alhouayek M and Muccioli GG: COX-2-derived
endocannabinoid metabolites as novel inflammatory mediators. Trends
Pharmacol Sci. 35:284–292. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Zamorano B and Carmona MT:
Prostaglandin-E2 and cyclic adenosine 3′-5′ monophosphate levels in
the hypertrophied rat heart. Biol Res. 25:85–89. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Song ZF, Chen DY, DU B and Ji XP: Poly
(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor reduces heart
ischaemia/reperfusion injury via inflammation and Akt signalling in
rats. Chin Med J (Engl). 126:1913–1917. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Liu ZF, Zheng D, Fan GC, Peng T and Su L:
Heat stress prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced apoptosis in
pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells by blocking calpain/p38
MAPK signalling. Apoptosis. 21:896–904. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Dong Y, Yin S, Song X, Huo Y, Fan L, Ye M
and Hu H: Involvement of ROS-p38-H2AX axis in novel curcumin
analogues-induced apoptosis in breast cancer cells. Mol Carcinog.
55:323–334. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Han OJ, Joe KH, Kim SW, Lee HS, Kwon NS,
Baek KJ and Yun HY: Involvement of p38 mitogen-activated protein
kinase and apoptosis signal-regulating kinase-1 in nitric
oxide-induced cell death in PC12 cells. Neurochem Res. 26:525–532.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|