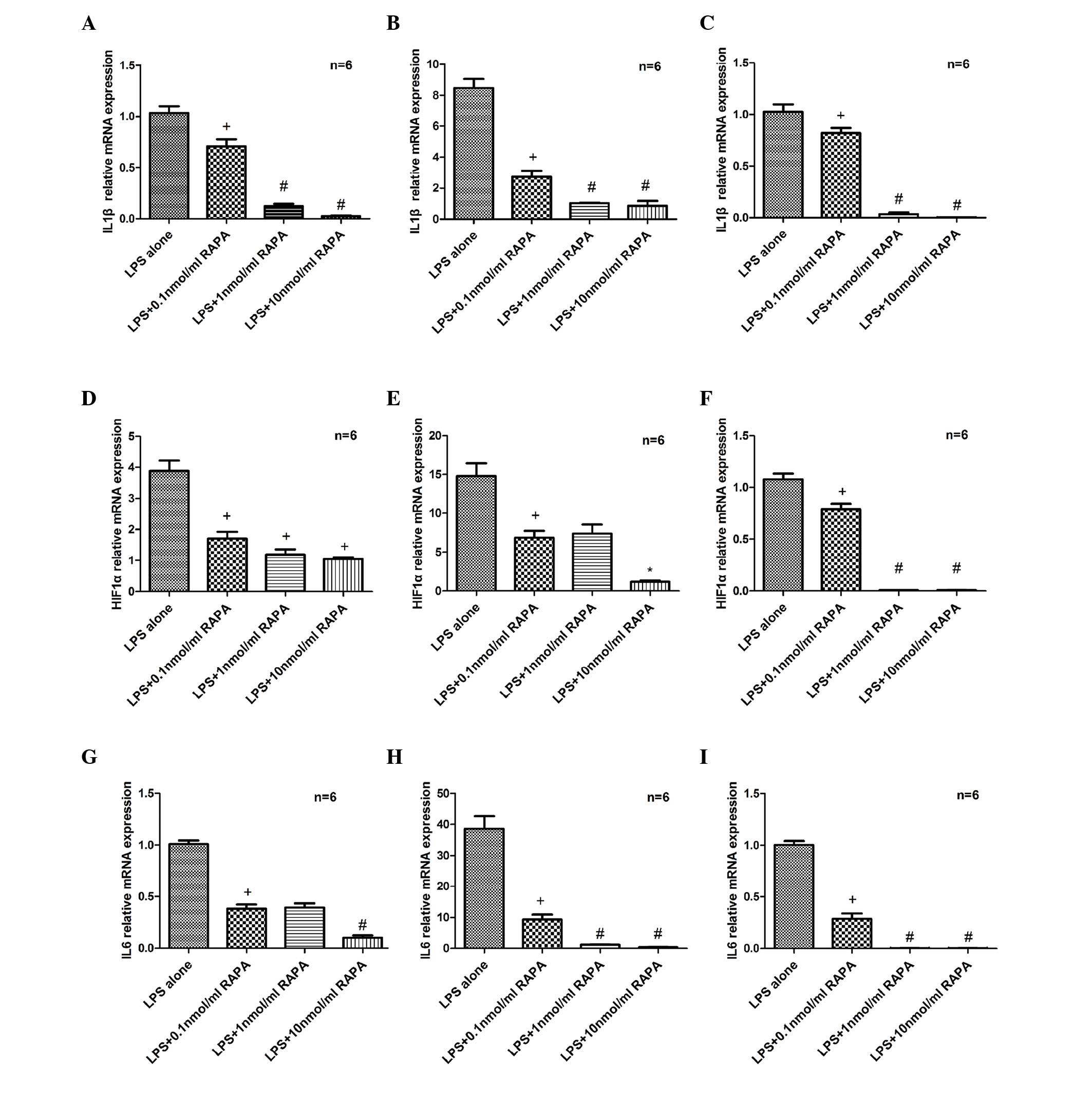
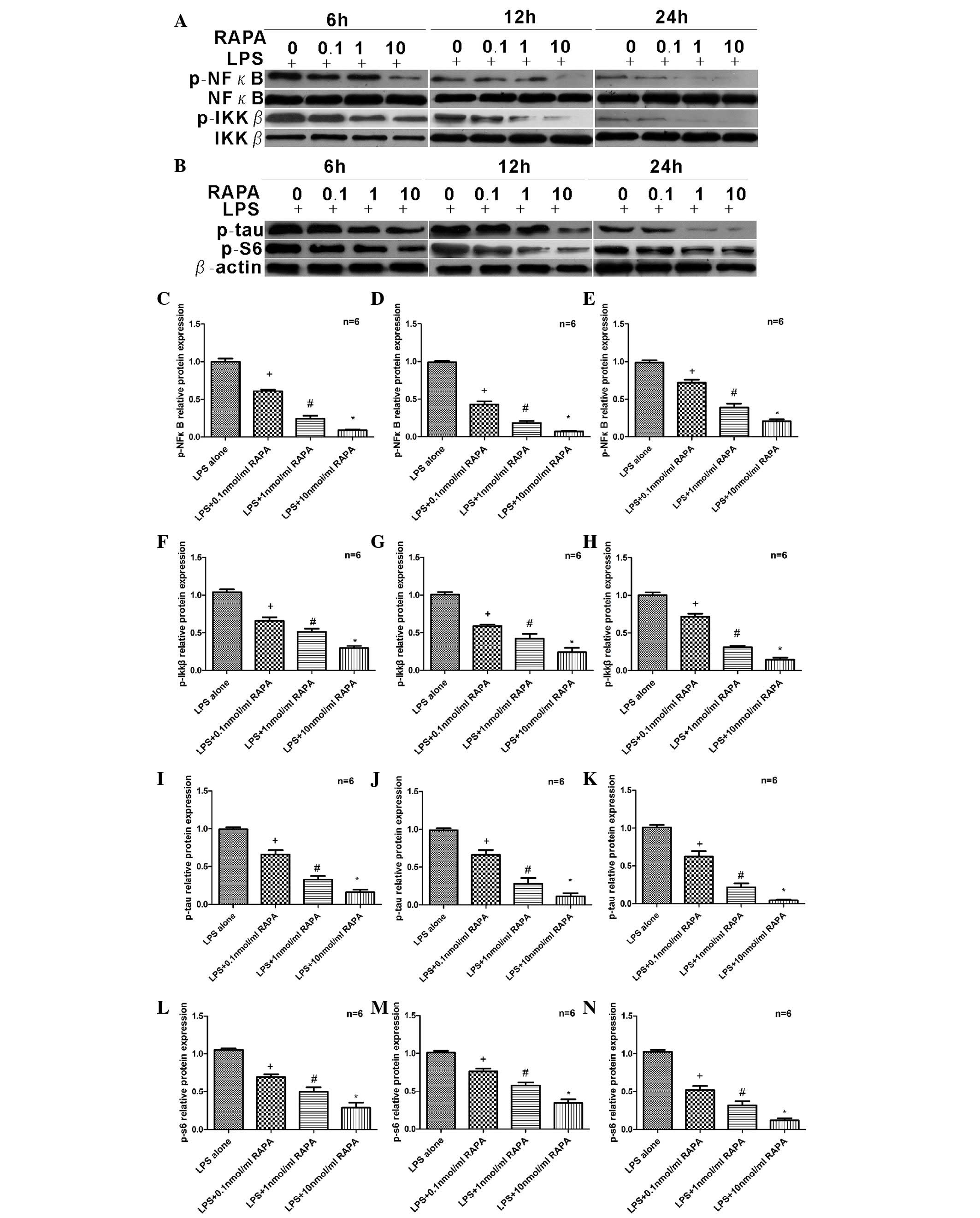
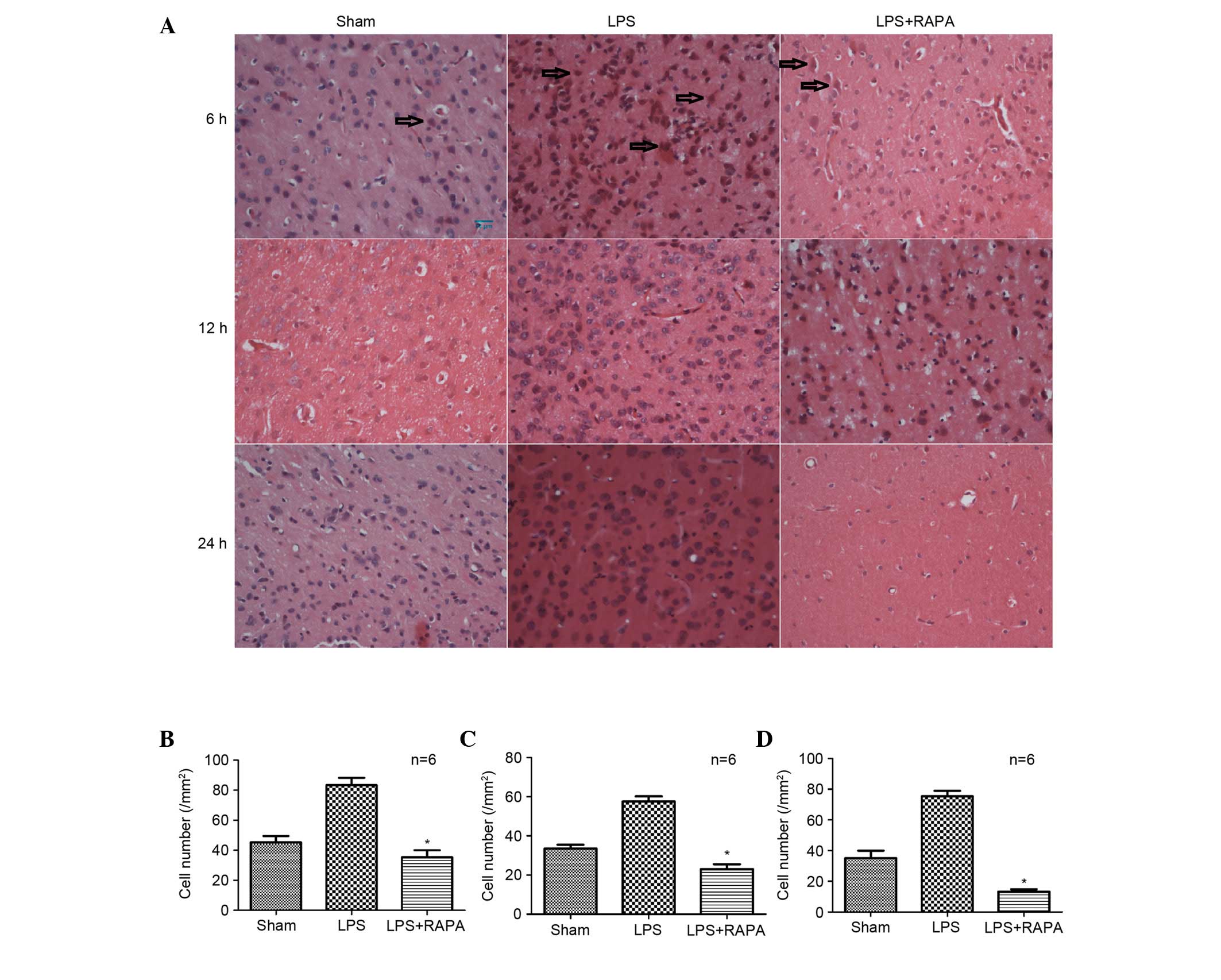
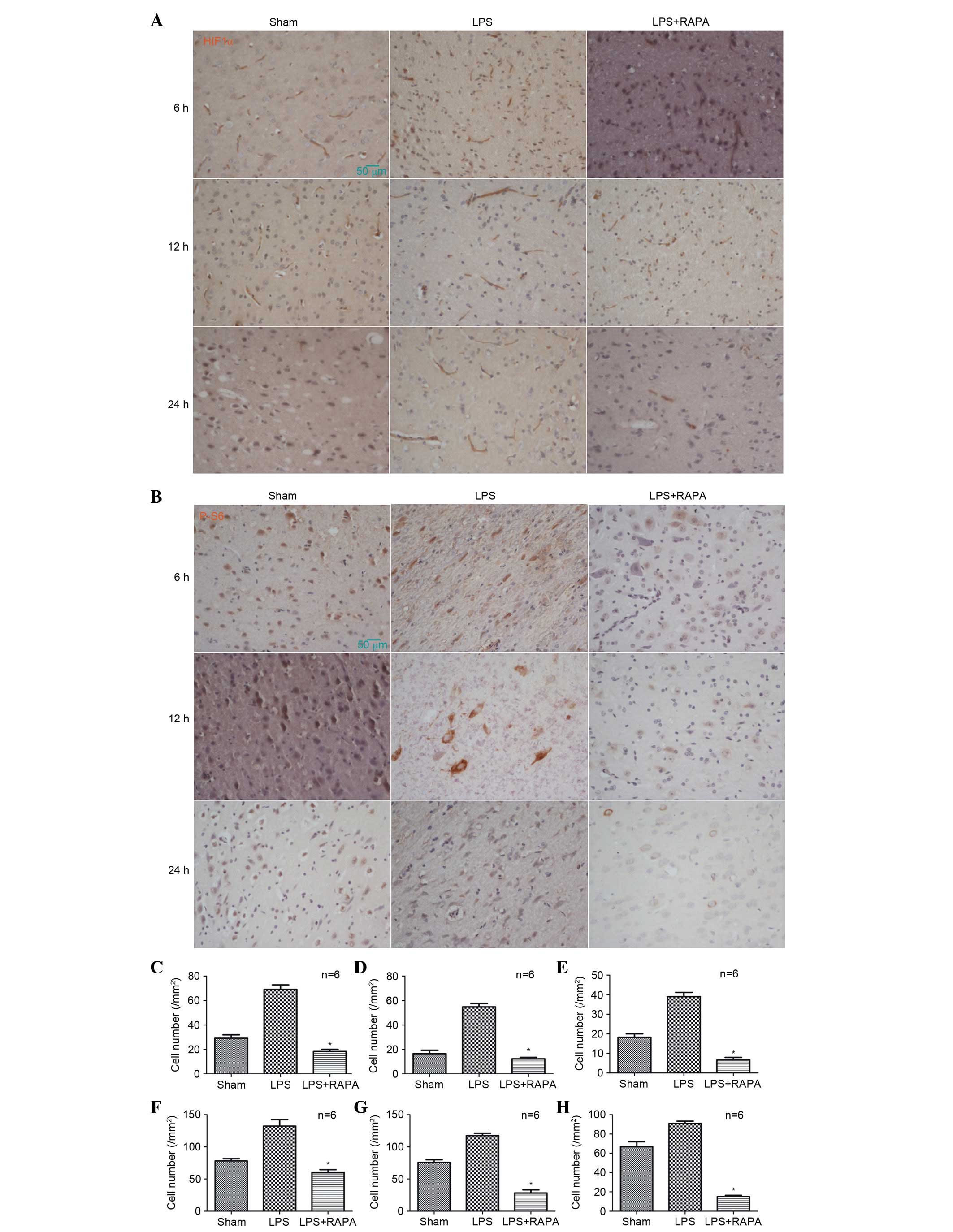
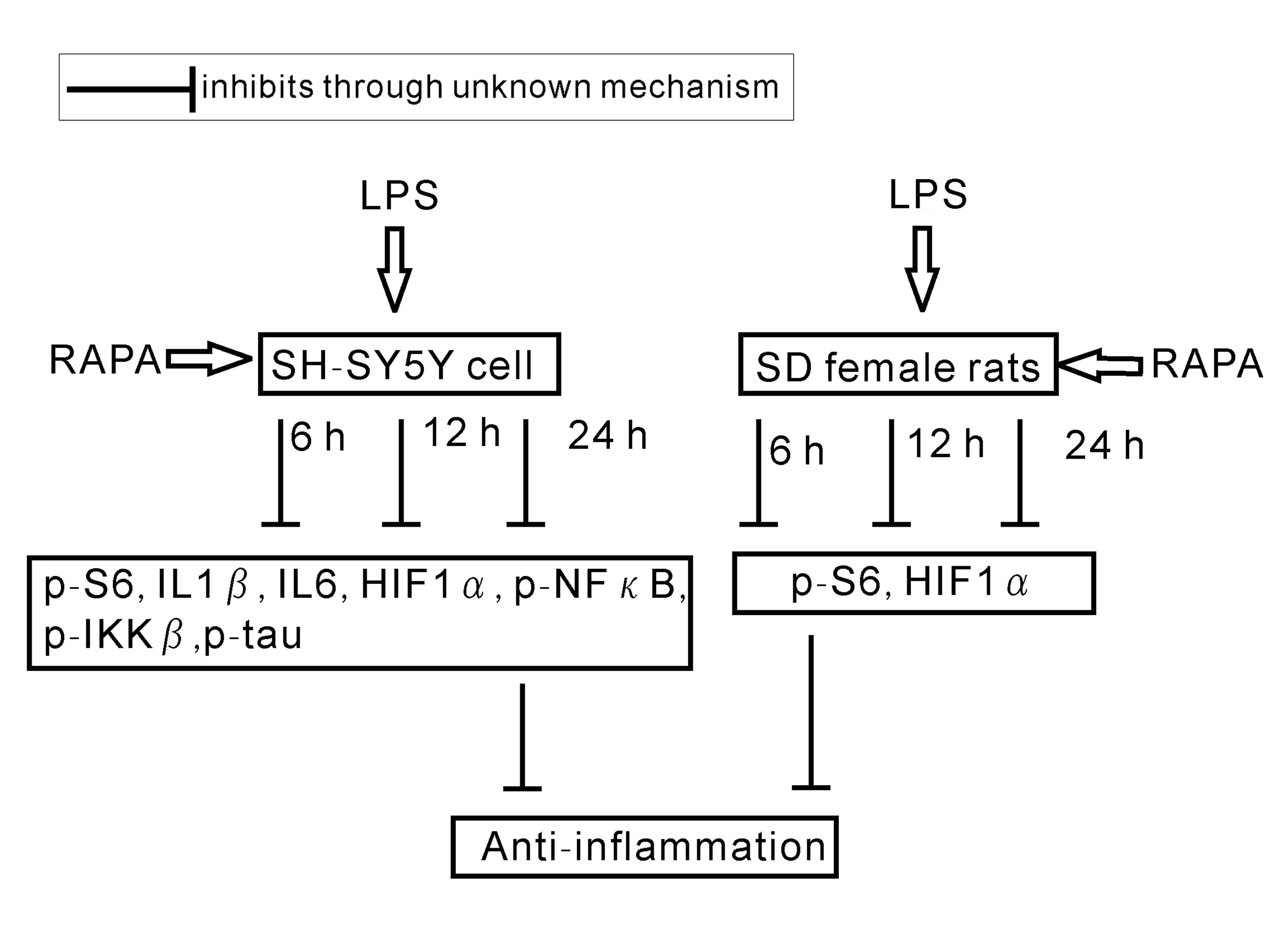
|
1
|
Giulian D: Microglia and the immune
pathology of Alzheimer disease. Am J Hum Genet. 65:13–18. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Alzheimer's Association: 2014 Alzheimer's
disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 10:e47–e92. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Golde TE, Petrucelli L and Lewis J:
Targeting Abeta and tau in Alzheimer's disease, an early interim
report. Exp Neurol. 223:252–266. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Veerhuis R, Janssen I, De Groot CJ, Van
Muiswinkel FL, Hack CE and Eikelenboom P: Cytokines associated with
amyloid plaques in Alzheimer's disease brain stimulate human glial
and neuronal cell cultures to secrete early complement proteins,
but not C1-inhibitor. Exp Neurol. 160:289–299. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Baker H, Sidorowicz A, Sehgal SN and
Vézina C: Rapamycin (AY-22,989), a new antifungal antibiotic. III.
In vitro and in vivo evaluation. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 31:539–545.
1978. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Majumder PK, Febbo PG, Bikoff R, Berger R,
Xue Q, McMahon LM, Manola J, Brugarolas J, McDonnell TJ, Golub TR,
et al: mTOR inhibition reverses Akt-dependent prostate
intraepithelial neoplasia through regulation of apoptotic and
HIF-1-dependent pathways. Nat Med. 10:594–601. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bonow RH, Aïd S, Zhang Y, Becker KG and
Bosetti F: The brain expression of genes involved in inflammatory
response, the ribosome, and learning and memory is altered by
centrally injected lipopolysaccharide in mice. Pharmacogenomics J.
9:116–126. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hauss-Wegrzyniak B, Lukovic L, Bigaud M
and Stoeckel ME: Brain inflammatory response induced by
intracerebroventricular infusion of lipopolysaccharide: An
immunohistochemical study. Brain Res. 794:211–224. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Burguillos MA, Hajji N, Englund E, Persson
A, Cenci AM, Machado A, Cano J, Joseph B and Venero JL:
Apoptosis-inducing factor mediates dopaminergic cell death in
response to LPS-induced inflammatory stimulus: Evidence in
Parkinson's disease patients. Neurobiol Dis. 41:177–188. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Erlich S, Alexandrovich A, Shohami E and
Pinkas-Kramarski R: Rapamycin is a neuroprotective treatment for
traumatic brain injury. Neurobiol Dis. 26:86–93. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL and
Randall RJ: Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J
Biol Chem. 193:265–275. 1951.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Espinosa-Oliva AM, de Pablos RM and
Herrera AJ: Intracranial injection of LPS in rat as animal model of
neuroinflammation. Methods Mol Biol. 1041:295–305. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Vignot S, Faivre S, Aguirre D and Raymond
E: mTOR-targeted therapy of cancer with rapamycin derivatives. Ann
Oncol. 16:525–537. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Akiyama H, Barger S, Barnum S, Bradt B,
Bauer J, Cole GM, Cooper NR, Eikelenboom P, Emmerling M, Fiebich
BL, et al: Inflammation and Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol aging.
21:383–421. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Griffin WS, Sheng JG, Roberts GW and Mrak
RE: Interleukin-1 expression in different plaque types in
Alzheimer's disease: Significance in plaque evolution. J
Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 54:276–281. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Griffin WS, Sheng JG, Royston MC,
Gentleman SM, McKenzie JE, Graham DI, Roberts GW and Mrak RE:
Glial-neuronal interactions in Alzheimer's disease: The potential
role of a ‘cytokine cycle’ in disease progression. Brain Pathol.
8:65–72. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Heinrich PC, Horn F, Graeve L, Dittrich E,
Kerr I, Müller-Newen G, Grötzinger J and Wollmer A: Interleukin-6
and related cytokines: Effect on the acute phase reaction. Z
Ernahrungswiss (37 Suppl 1). 43–49. 1998.
|
|
19
|
Hirano T, Nakajima K and Hibi M: Signaling
mechanisms through gp130: A model of the cytokine system. Cytokine
Growth Factor Rev. 8:241–252. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Campbell IL: Transgenic mice and cytokine
actions in the brain: Bridging the gap between structural and
functional neuropathology. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 26:327–336.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gadient RA and Otten UH: Interleukin-6
(IL-6)-a molecule with both beneficial and destructive potentials.
Prog Neurobiol. 52:379–390. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
März P, Cheng JG, Gadient RA, Patterson
PH, Stoyan T, Otten U and Rose-John S: Sympathetic neurons can
produce and respond to interleukin 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
95:3251–3256. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Rodriguez M, Pavelko KD, McKinney CW and
Leibowitz JL: Recombinant human IL-6 suppresses demyelination in a
viral model of multiple sclerosis. J Immunol. 153:3811–3821.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yang P, Wen H, Ou S, Cui J and Fan D: IL-6
promotes regeneration and functional recovery after cortical spinal
tract injury by reactivating intrinsic growth program of neurons
and enhancing synapse formation. Exp Neurol. 236:19–27. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jeong YJ, Cho HJ, Magae J, Lee IK, Park KG
and Chang YC: Ascofuranone suppresses EGF-induced HIF-1α protein
synthesis by inhibition of the Akt/mTOR/p70S6K pathway in
MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
273:542–550. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Shin JM, Jeong YJ, Cho HJ, Park KK, Chung
IK, Lee IK, Kwak JY, Chang HW, Kim CH, Moon SK, et al: Melittin
suppresses HIF-1α/VEGF expression through inhibition of ERK and
mTOR/p70S6K pathway in human cervical carcinoma cells. PloS one.
8:e693802013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
White NM, Masui O, Newsted D, Scorilas A,
Romaschin AD, Bjarnason GA, Siu KW and Yousef GM: Galectin-1 has
potential prognostic significance and is implicated in clear cell
renal cell carcinoma progression through the HIF/mTOR signaling
axis. Br J Cancer. 110:1250–1259. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Singh N, Sharma G and Mishra V: Hypoxia
inducible factor-1: Its potential role in cerebral ischemia. Cell
Mol Neurobiol. 32:491–507. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Umschweif G, Alexandrovich AG, Trembovler
V, Horowitz M and Shohami E: Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 is
essential for spontaneous recovery from traumatic brain injury and
is a key mediator of heat acclimation induced neuroprotection. J
Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 33:524–531. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Argyriou P, Papageorgiou SG, Panteleon V,
Psyrri A, Bakou V, Pappa V, Spathis A, Economopoulou P,
Papageorgiou E, Economopoulos T and Rontogianni D:
Hypoxia-inducible factors in mantle cell lymphoma: Implication for
an activated mTORC1->HIF-1α pathway. Ann Hematol. 90:315–322.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Weng Q, Zhang J, Cao J, Xia Q, Wang D, Hu
Y, Sheng R, Wu H, Zhu D, Zhu H, et al: Q39, a quinoxaline
1,4-Di-N-oxide derivative, inhibits hypoxia-inducible factor-1α
expression and the Akt/mTOR/4E-BP1 signaling pathway in human
hepatoma cells. Invest New Drugs. 29:1177–1187. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Palazon A, Goldrath AW, Nizet V and
Johnson RS: HIF transcription factors, inflammation, and immunity.
Immunity. 41:518–528. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Cramer T, Yamanishi Y, Clausen BE, Förster
I, Pawlinski R, Mackman N, Haase VH, Jaenisch R, Corr M and Nizet
V: HIF-1alpha is essential for myeloid cell-mediated inflammation.
Cell. 112:645–657. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Laplante M and Sabatini DM: mTOR signaling
at a glance. J Cell Sci. 122:3589–3594. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
An WL, Cowburn RF, Li L, Braak H,
Alafuzoff I, Iqbal K, Iqbal IG, Winblad B and Pei JJ: Up-regulation
of phosphorylated/activated p70 S6 kinase and its relationship to
neurofibrillary pathology in Alzheimer's disease. Am J Pathol.
163:591–607. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chang RC, Wong AK, Ng HK and Hugon J:
Phosphorylation of eukaryotic initiation factor-2alpha (eIF2alpha)
is associated with neuronal degeneration in Alzheimer's disease.
Neuroreport. 13:2429–2432. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Griffin RJ, Moloney A, Kelliher M,
Johnston JA, Ravid R, Dockery P, O'Connor R and O'Neill C:
Activation of Akt/PKB, increased phosphorylation of Akt substrates
and loss and altered distribution of Akt and PTEN are features of
Alzheimer's disease pathology. Journal of Neurochemistry.
93:105–117. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Onuki R, Bando Y, Suyama E, Katayama T,
Kawasaki H, Baba T, Tohyama M and Taira K: An RNA-dependent protein
kinase is involved in tunicamycin-induced apoptosis and Alzheimer's
disease. EMBO J. 23:959–968. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Peel AL and Bredesen DE: Activation of the
cell stress kinase PKR in Alzheimer's disease and human amyloid
precursor protein transgenic mice. Neurobiol Dis. 14:52–62. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Pei JJ, Björkdahl C, Zhang H, Zhou X and
Winblad B: p70 S6 kinase and tau in Alzheimer's disease. J
Alzheimers Dis. 14:385–392. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Pei JJ and Hugon J: mTOR-dependent
signalling in Alzheimer's disease. J Cell Mol Med. 12:2525–2532.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lipton JO and Sahin M: The neurology of
mTOR. Neuron. 84:275–291. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Tan L, Schedl P, Song HJ, Garza D and
Konsolaki M: The Toll->NFkappaB signaling pathway mediates the
neuropathological effects of the human Alzheimer's Abeta42
polypeptide in Drosophila. PloS one. 3:e39662008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Garwood CJ, Cooper JD, Hanger DP and Noble
W: Anti-inflammatory impact of minocycline in a mouse model of
tauopathy. Front Psychiatry. 1:1362010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Walker D and Lue LF: Anti-inflammatory and
immune therapy for Alzheimer's disease: Current status and future
directions. Curr Neuropharmacol. 5:232–243. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Liu B, Gao HM and Hong JS: Parkinson's
disease and exposure to infectious agents and pesticides and the
occurrence of brain injuries: Role of neuroinflammation. Environ
Health Perspect. 111:1065–1073. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|