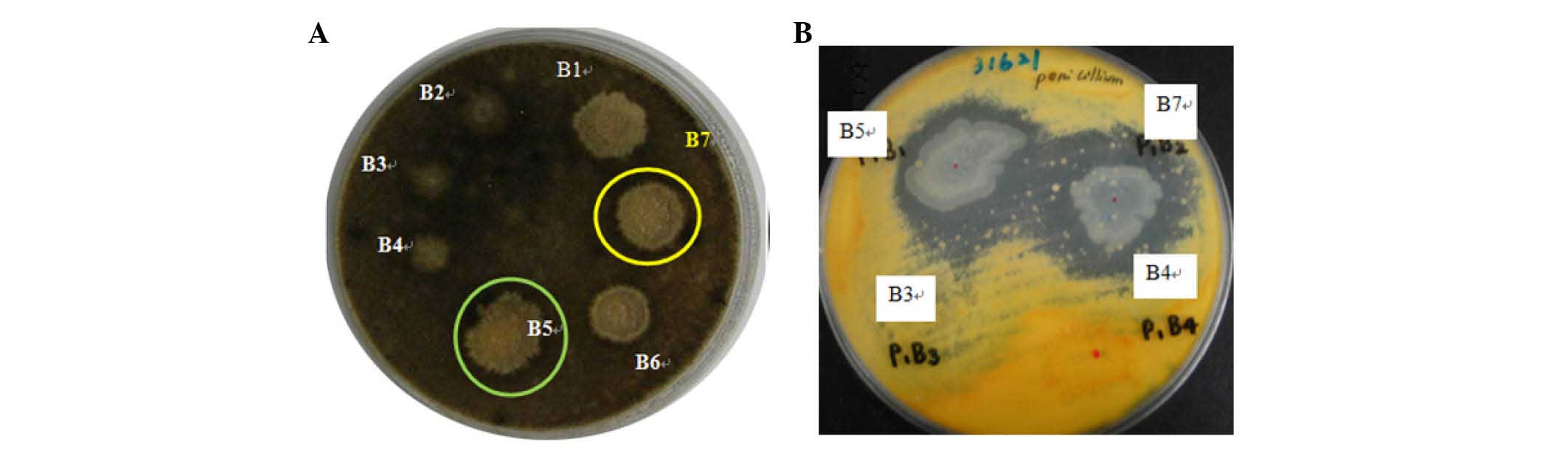
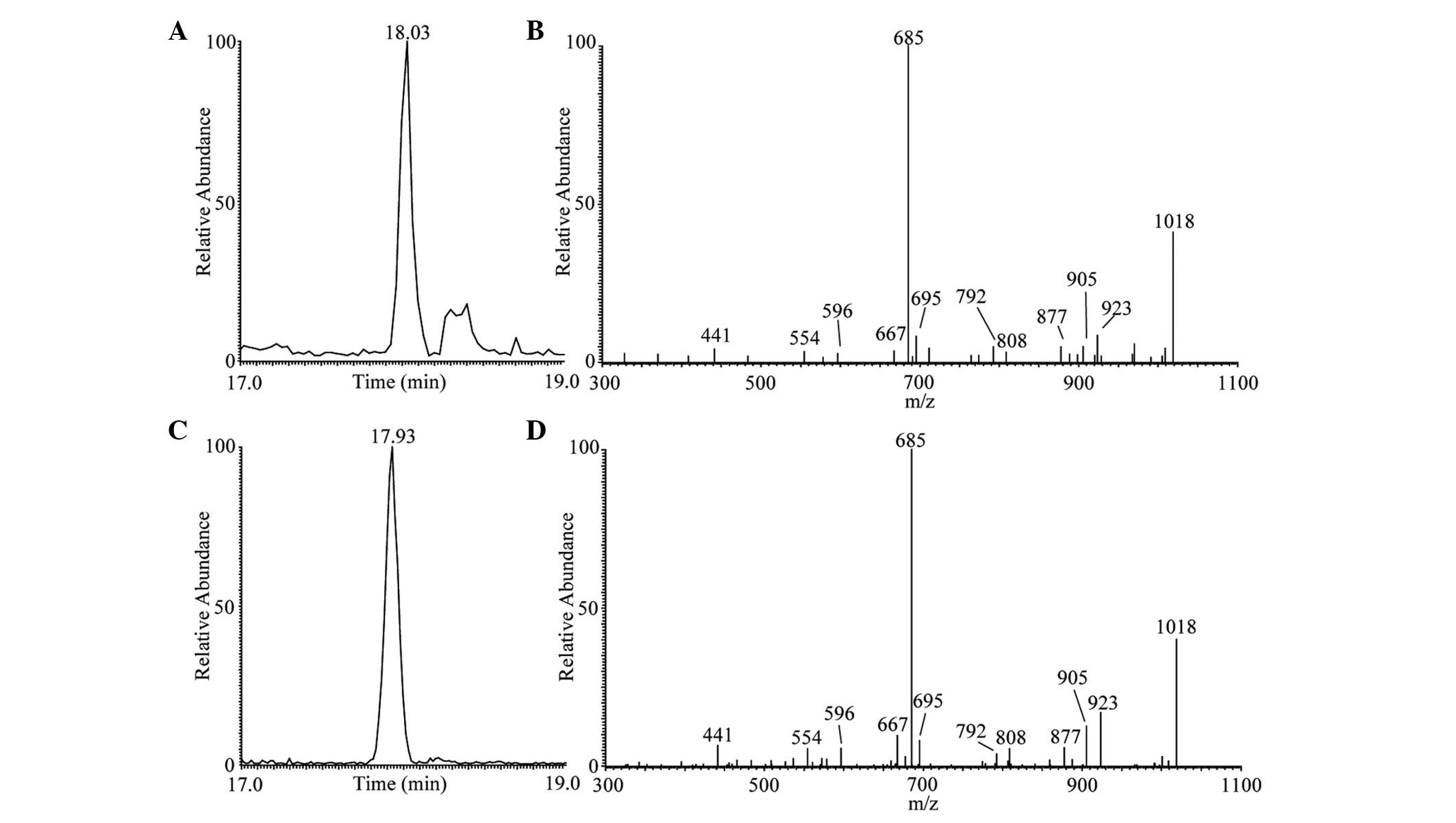
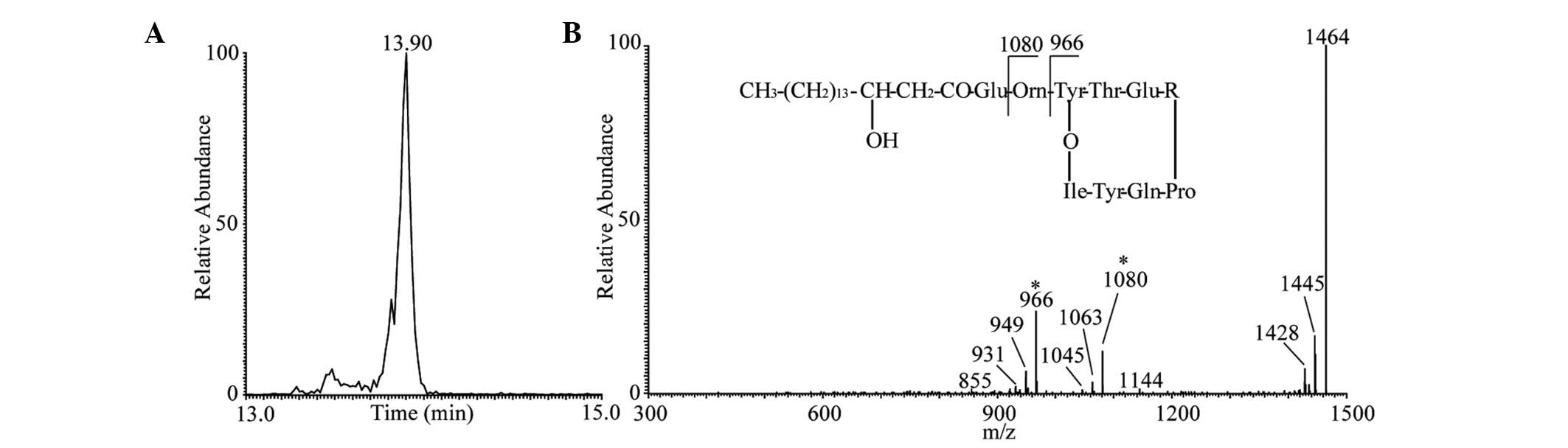
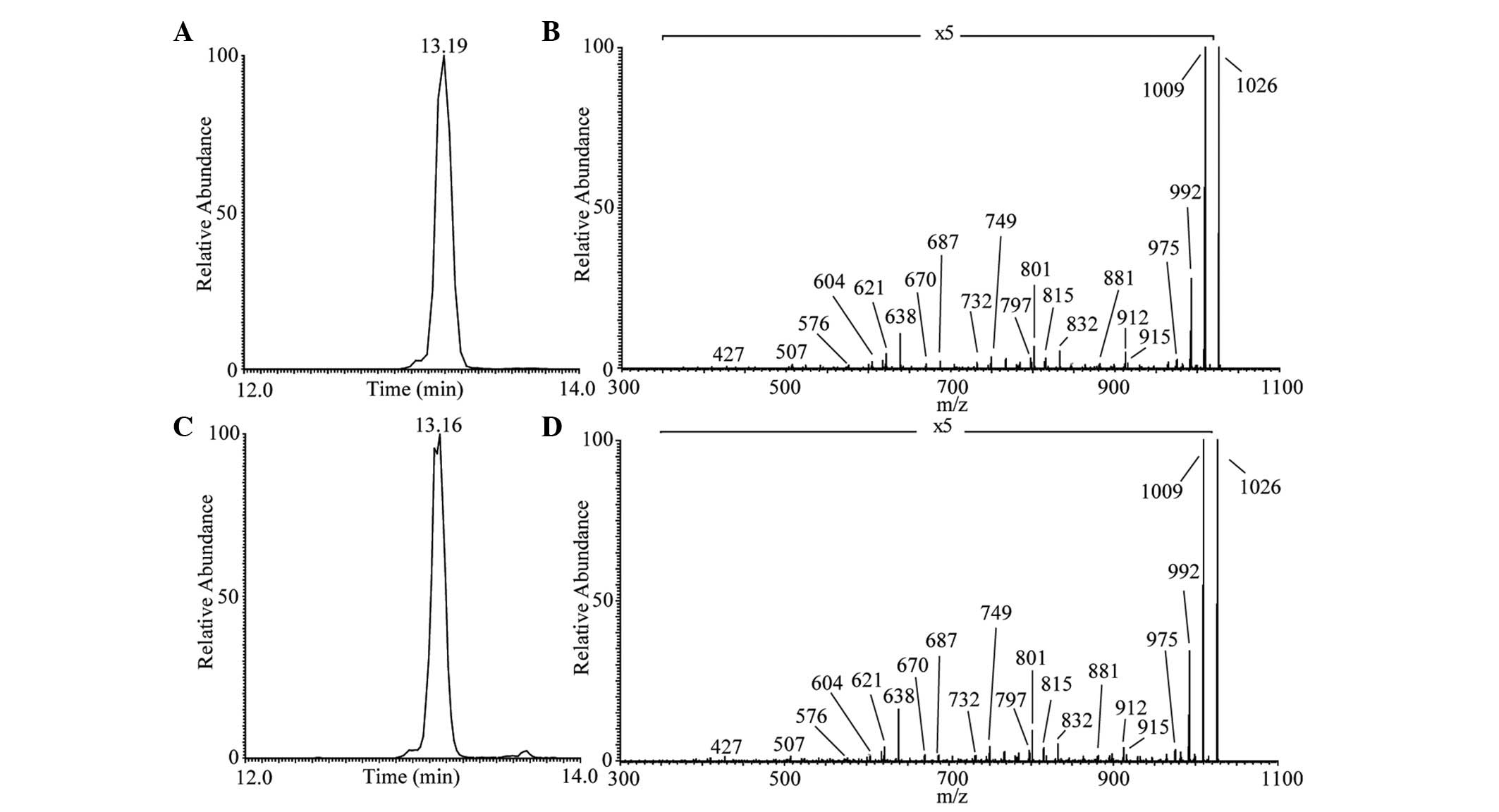
|
1
|
Niazi A, Manzoor S, Bejai S, Meijer J and
Bongcam-Rudloff E: Complete genome sequence of a plant associated
bacterium Bacillus amyloliquefaciens subsp. plantarum UCMB5033.
Stand Genomic Sci. 9:718–725. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cai J, Liu F, Liao X and Zhang R: Complete
genome sequence of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens LFB112 isolated from
Chinese herbs, a strain of a broad inhibitory spectrum against
domestic animal pathogens. J Biotechnol. 175:63–64. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ait Kaki A, Chaouche N Kacem, Dehimat L,
Milet A, Youcef-Ali M, Ongena M and Thonart P: Biocontrol and plant
growth promotion characterization of Bacillus species isolated from
calendula officinalis rhizosphere. Indian J Microbiol. 53:447–452.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Geetha I, Aruna R and Manonmani AM:
Mosquitocidal Bacillus amyloliquefaciens: Dynamics of growth &
production of novel pupicidal biosurfactant. Indian J Med Res.
140:427–434. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Han JH, Shim H, Shin JH and Kim KS:
Antagonistic activities of Bacillus spp. strains isolated from
tidal flat sediment towards anthracnose pathogens Colletotrichum
acutatum and C. gloeosporioides in South Korea. Plant Pathol J.
31:165–175. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Xu HM, Rong YJ, Zhao MX, Song B and Chi
ZM: Antibacterial activity of the lipopetides produced by Bacillus
amyloliquefaciens M1 against multidrug-resistant Vibrio spp.
isolated from diseased marine animals. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol.
98:127–136. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ruckert C, Blom J, Chen X, Reva O and
Borriss R: Genome sequence of B. amyloliquefaciens type strain
DSM7(T) reveals differences to plant-associated B.
amyloliquefaciens FZB42. J Biotechnol. 155:78–85. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xu Z, Shao J, Li B, Yan X, Shen Q and
Zhang R: Contribution of bacillomycin D in Bacillus
amyloliquefaciens SQR9 to antifungal activity and biofilm
formation. Appl Environ Microbiol. 79:808–815. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yuan J, Raza W, Huang Q and Shen Q: The
ultrasound-assisted extraction and identification of antifungal
substances from B. amyloliquefaciens strain NJN-6 suppressing
Fusarium oxysporum. J Basic Microbiol. 52:721–730. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhao P, Quan C, Jin L, Wang L, Wang J and
Fan S: Effects of critical medium components on the production of
antifungal lipopeptides from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Q-426
exhibiting excellent biosurfactant properties. World J Microbiol
Biotechnol. 29:401–409. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chi Z, Rong YJ, Li Y, Tang MJ and Chi ZM:
Biosurfactins production by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens R3 and their
antibacterial activity against multi-drug resistant pathogenic E.
coli. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng. 38:853–861. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kadaikunnan S, Rejiniemon T, Khaled JM,
Alharbi NS and Mothana R: In-vitro antibacterial, antifungal,
antioxidant and functional properties of Bacillus
amyloliquefaciens. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 14:92015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cao H, He S, Wei R, Diong M and Lu L:
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens G1: A potential antagonistic bacterium
against eel-pathogenic aeromonas hydrophila. Evid Based Complement
Alternat Med. 2011:8241042011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ma Z, Hu J, Wang X and Wang S: NMR
spectroscopic and MS/MS spectrometric characterization of a new
lipopeptide antibiotic bacillopeptin B1 produced by a marine
sediment-derived Bacillus amyloliquefaciens SH-B74. J Antibiot
(Tokyo). 67:175–178. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mora I, Cabrefiga J and Montesinos E:
Cyclic lipopeptide biosynthetic genes and products, and inhibitory
activity of plant-associated Bacillus against phytopathogenic
bacteria. PLoS One. 10:e01277382015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nihorimbere V, Cawoy H, Seyer A, Brunelle
A, Thonart P and Ongena M: Impact of rhizosphere factors on cyclic
lipopeptide signature from the plant beneficial strain Bacillus
amyloliquefaciens S499. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 79:176–191. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Arrebola E, Jacobs R and Korsten L: Iturin
A is the principal inhibitor in the biocontrol activity of Bacillus
amyloliquefaciens PPCB004 against postharvest fungal pathogens. J
Appl Microbiol. 108:386–395. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Arguelles-Arias A, Ongena M, Halimi B,
Lara Y, Brans A, Joris B and Fickers P: Bacillus amyloliquefaciens
GA1 as a source of potent antibiotics and other secondary
metabolites for biocontrol of plant pathogens. Microb Cell Fact.
8:632009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Vágvölgyi C, Sajben-Nagy E, Bóka B, Vörös
M, Berki A, Palágyi A, Krisch J, Skrbić B, Durišić-Mladenović N and
Manczinger L: Isolation and characterization of antagonistic
Bacillus strains capable to degrade ethylenethiourea. Curr
Microbiol. 66:243–250. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kim PI, Bai H, Bai D, Chae H, Chung S, Kim
Y, Park R and Chi YT: Purification and characterization of a
lipopeptide produced by Bacillus thuringiensis CMB26. J Appl
Microbiol. 97:942–949. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Maget-Dana R and Peypoux F: Iturins, a
special class of pore-forming lipopeptides: Biological and
physicochemical properties. Toxicology. 87:151–174. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Stein T: Bacillus subtilis antibiotics:
Structures, syntheses and specific functions. Mol Microbiol.
56:845–857. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yoshida S, Hiradate S, Tsukamoto T,
Hatakeda K and Shirata A: Antimicrobial activity of culture
filtrate of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens RC-2 isolated from mulberry
leaves. Phytopathology. 91:181–187. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Benitez L, Correa A, Daroit D and
Brandelli A: Antimicrobial activity of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens
LBM 5006 is enhanced in the presence of Escherichia coli. Curr
Microbiol. 62:1017–1022. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Arias A Arguelles, Ongena M, Devreese B,
Terrak M, Joris B and Fickers P: Characterization of amylolysin, a
novel lantibiotic from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens GA1. PLoS One.
8:e830372013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Salazar JK, Wu Z, McMullen PD, Luo Q,
Freitag NE, Tortorello ML, Hu S and Zhang W: PrfA-like
transcription factor gene lmo0753 contributes to L-rhamnose
utilization in Listeriamonocytogenes strains associated with human
food-borne infections. Appl Environ Microbiol. 79:5584–5592. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shalaby MA, Mohamed MS, Mansour MA and Abd
El-Haffiz AS: Comparison of polymerase chain reaction and
conventional methods for diagnosis of Listeria monocytogenes
isolated from different clinical specimens and food stuffs. Clin
Lab. 57:919–924. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Neetoo H, Ye M and Chen H: Potential
antimicrobials to control Listeria monocytogenes in vacuum-packaged
cold-smoked salmon pâté and fillets. Int J Food Microbiol.
123:220–227. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Pérez-Rodriguez F, van Asselt ED,
Garcia-Gimeno RM, Zurera G and Zwietering MH: Extracting additional
risk managers information from a risk assessment of Listeria
monocytogenes in deli meats. J Food Prot. 70:1137–1152. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Althaus D, Lehner A, Brisse S, Maury M,
Tasara T and Stephan R: Characterization of Listeria monocytogenes
strains isolated during 2011–2013 from human infections in
Switzerland. Foodborne Pathog Dis. 11:753–758. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Pontello M, Guaita A, Sala G, Cipolla M,
Gattuso A, Sonnessa M and Gianfranceschi MV: Listeria monocytogenes
serotypes in human infections (Italy, 2000–2010). Ann Ist Super
Sanita. 48:146–150. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lisboa MP, Bonatto D, Bizani D, Henriques
JA and Brandelli A: Characterization of a bacteriocin-like
substance produced by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens isolated from the
Brazilian Atlantic forest. Int Microbiol. 9:111–118.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sağdiç O, Ozkan G, Ozcan M and Ozçelik S:
A study on inhibitory effects of Siğla tree (Liquidambar orientalis
Mill. var. orientalis) storax against several bacteria. Phytother
Res. 19:549–551. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Agarwal A and Aggarwal AN: Bone and joint
infections in children: Acute hematogenous osteomyelitis. Indian J
Pediatr. 2015.
|
|
35
|
Christiansen JG, Jensen HE, Johansen LK,
Kochl J, Koch J, Aalbaek B, Nielsen OL and Leifsson PS: Porcine
models of non-bacterial thrombotic endocarditis (NBTE) and
infective endocarditis (IE) caused by Staphylococcus aureus: A
preliminary study. J Heart Valve Dis. 22:368–376. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Vos FJ, Kullberg BJ, Sturm PD, Krabbe PF,
van Dijk AP, Wanten GJ, Oyen WJ and Bleeker-Rovers CP: Metastatic
infectious disease and clinical outcome in Staphylococcus aureus
and Streptococcus species bacteremia. Medicine (Baltimore).
91:86–94. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hasanvand A, Ghafourian S, Taherikalani M,
Jalilian FA, Sadeghifard N and Pakzad I: Antiseptic resistance in
methicillin sensitive and methicillin resistant Staphylococcus
aureus isolates from some major hospitals, Iran. Recent Pat
Antiinfect Drug Discov. 10:105–112. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kaur DC and Chate SS: Study of antibiotic
resistance pattern in methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus
with special reference to newer antibiotic. J Glob Infect Dis.
7:78–84. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
McMaster J, Booth MG, Smith A and Hamilton
K: Meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in the intensive care
unit: Its effect on outcome and risk factors for acquisition. J
Hosp Infect. 90:327–332. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Dancer SJ: Controlling hospital-acquired
infection: Focus on the role of the environment and new
technologies for decontamination. Clin Microbiol Rev. 27:665–690.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lima ET, Filho RL Andreatti, Okamoto AS,
Noujaim JC, Barros MR and Crocci AJ: Evaluation in vitro of the
antagonistic substances produced by Lactobacillus spp. isolated
from chickens. Can J Vet Res. 71:103–107. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chen H, Wang L, Su CX, Gong GH, Wang P and
Yu ZL: Isolation and characterization of lipopeptide antibiotics
produced by Bacillus subtilis. Lett Appl Microbiol. 47:180–186.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Østensvik Ø, From C, Heidenreich B,
O'Sullivan K and Granum PE: Cytotoxic Bacillus spp. belonging to
the B. cereus and B. subtilis groups in Norwegian surface waters. J
Appl Microbiol. 96:987–993. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zaghloul TI, Al-Bahra M and Al-Azmeh H:
Isolation, identification, and keratinolytic activity of several
feather-degrading bacterial isolates. Appl Biochem Biotechnol
70–72. 207–213. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Marroki A, Zúñiga M, Kihal M and
Pérez-Martinez G: Characterization of lactobacillus from algerian
goat's milk based on phenotypic, 16S rDNA sequencing and their
technological properties. Braz J Microbiol. 42:158–171. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Tajbakhsh M, Nayer BN, Motavaze K,
Kharaziha P, Chiani M, Zali MR and Klena JD: Phylogenetic
relationship of Salmonella enterica strains in Tehran, Iran, using
16S rRNA and gyrB gene sequences. J Infect Dev Ctries. 5:465–472.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wang LT, Lee FL, Tai CJ and Kasai H:
Comparison of gyrB gene sequences, 16S rRNA gene sequences and
DNA-DNA hybridization in the Bacillus subtilis group. Int J Syst
Evol Microbiol. 57:1846–1850. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schäffer AA, Zhang
J, Zhang Z, Miller W and Lipman DJ: Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A
new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids
Res. 25:3389–3402. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Tsuge K, Akiyama T and Shoda M: Cloning,
sequencing, and characterization of the iturin A operon. J
Bacteriol. 183:6265–6273. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Razafindralambo H, Paquot M, Hbid C,
Jacques P, Destain J and Thonart P: Purification of antifungal
lipopeptides by reversed-phase high-performance liquid
chromatography. J Chromatogr. 639:81–85. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Perea Vélez M, Hermans K, Verhoeven TL,
Lebeer SE, Vanderleyden J and De Keersmaecker SC: Identification
and characterization of starter lactic acid bacteria and probiotics
from Columbian dairyproducts. J Appl Microbiol. 103:666–674. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Zeriouh H, de Vicente A, Pérez-Garcia A
and Romero D: Surfactin triggers biofilm formation of Bacillus
subtilis in melon phylloplane and contributes to the biocontrol
activity. Environ Microbiol. 16:2196–2211. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Zhao X, Han Y, Tan XQ, Wang J and Zhou ZJ:
Optimization of antifungal lipopeptide production from Bacillus sp.
BH072 by response surface methodology. J Microbiol. 52:324–332.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Wang J, Liu J, Wang X, Yao J and Yu Z:
Application of electrospray ionization mass spectrometry in rapid
typing of fengycin homologues produced by Bacillus subtilis. Lett
Appl Microbiol. 39:98–102. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Tagg JR and McGiven AR: Assay system for
bacteriocins. Appl Microbiol. 21:9431971.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Pecci Y, Rivardo F, Martinotti MG and
Allegrone G: LC/ESI-MS/MS characterisation of lipopeptide
biosurfactants produced by the Bacillus licheniformis V9T14 strain.
J Mass Spectrom. 45:772–778. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Vanittanakom N, Loeffler W, Koch U and
Jung G: Fengycin-a novel antifungal lipopeptide antibiotic produced
by Bacillus subtilis F-29-3. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 39:888–901. 1986.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Zhao P, Quan C, Wang Y, Wang J and Fan S:
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Q-426 as a potential biocontrol agent
against Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. spinaciae. J Basic Microbiol.
54:448–456. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Yuan B, Wang Z, Qin S, Zhao GH, Feng YJ,
Wei LH and Jiang JH: Study of the anti-sapstain fungus activity of
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens CGMCC 5569 associated with Ginkgo biloba
and identification of its active components. Bioresour Technol.
114:536–541. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Kröber M, Wibberg D, Grosch R, Eikmeyer F,
Verwaaijen B, Chowdhury SP, Hartmann A, Pühler A and Schlüter A:
Effect of the strain Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42 on the
microbial community in the rhizosphere of lettuce under field
conditions analyzed by whole metagenome sequencing. Front
Microbiol. 5:2522014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Huang J, Wei Z, Tan S, Mei X, Shen Q and
Xu Y: Suppression of bacterial wilt of tomato by bioorganic
fertilizer made from the antibacterial compound producing strain
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens HR62. J Agric Food Chem. 62:10708–10716.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Yuan J, Zhang F, Wu Y, Zhang J, Raza W,
Shen Q and Huang Q: Recovery of several cell pellet-associated
antibiotics produced by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens NJN-6. Lett Appl
Microbiol. 59:169–176. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
He P, Hao K, Blom J, Rückert C, Vater J,
Mao Z, Wu Y, Hou M, He P, He Y and Borriss R: Genome sequence of
the plant growth promoting strain Bacillus amyloliquefaciens subsp.
plantarum B9601-Y2 and expression of mersacidin and other secondary
metabolites. J Biotechnol. 164:281–291. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Compaoré CS, Nielsen DS, Sawadogo-Lingani
H, Berner TS, Nielsen KF, Adimpong DB, Diawara B, Ouédraogo GA,
Jakobsen M and Thorsen L: Bacillus amyloliquefaciens ssp. plantarum
strains as potential protective starter cultures for the production
of Bikalga, an alkaline fermented food. J Appl Microbiol.
115:133–146. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Hajji S, Ghorbel-Bellaaj O, Younes I,
Jellouli K and Nasri M: Chitin extraction from crab shells by
Bacillus bacteria. Biological activities of fermented crab
supernatants. Int J Biol Macromol. 79:167–173. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Alvarez F, Castro M, Principe A, Borioli
G, Fischer S, Mori G and Jofré E: The plant-associated Bacillus
amyloliquefaciens strains MEP2 18 and ARP2 3 capable of producing
the cyclic lipopeptides iturin or surfactin and fengycin are
effective in biocontrol of sclerotinia stem rot disease. J Appl
Microbiol. 112:159–174. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Hsieh FC, Lin TC, Meng M and Kao SS:
Comparing methods for identifying Bacillus strains capable of
producing the antifungal lipopeptide iturin A. Curr Microbiol.
56:1–5. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Wang SL, Shih IL, Liang TW and Wang CH:
Purification and characterization of two antifungal chitinases
extracellularly produced by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens V656 in a
shrimp and crab shell powder medium. J Agric Food Chem.
50:2241–2248. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Ongena M and Jacques P: Bacillus
lipopeptides: Versatile weapons for plant disease biocontrol.
Trends Microbiol. 16:115–125. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|