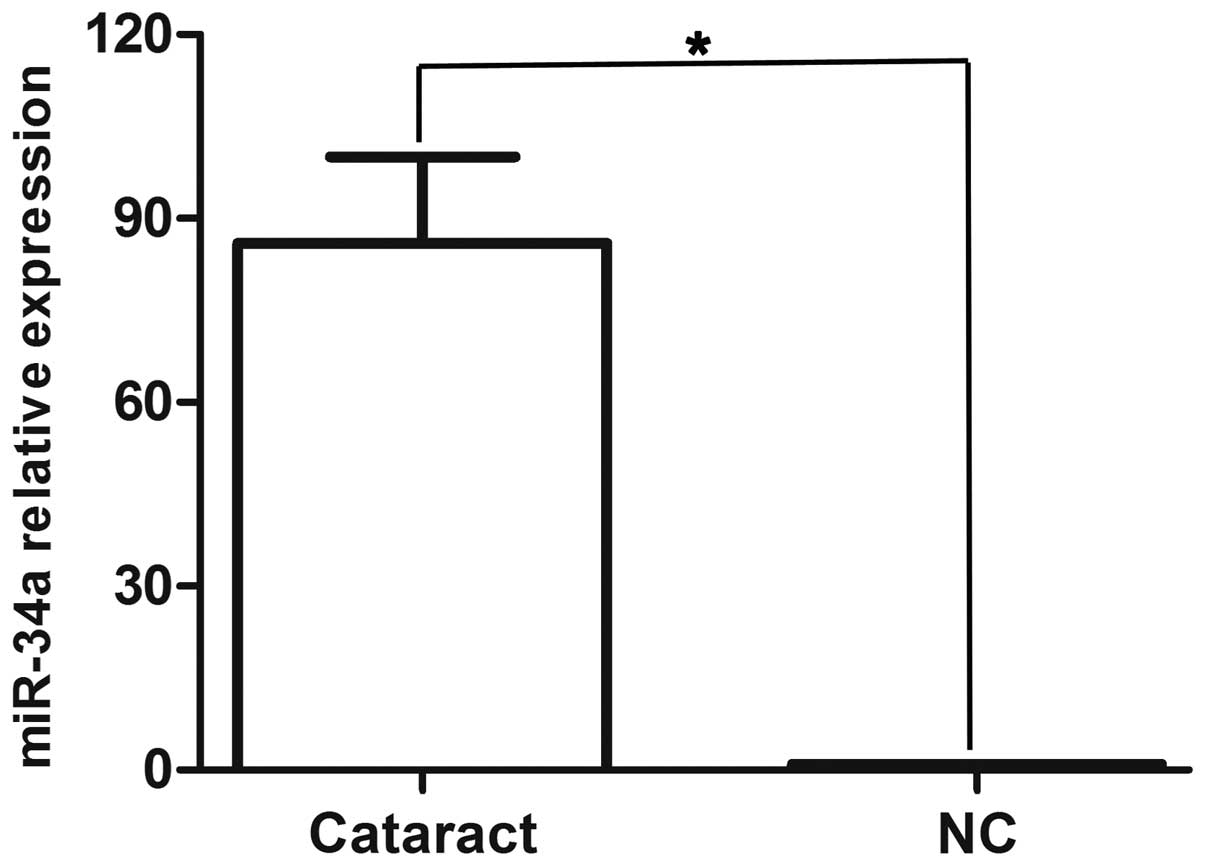
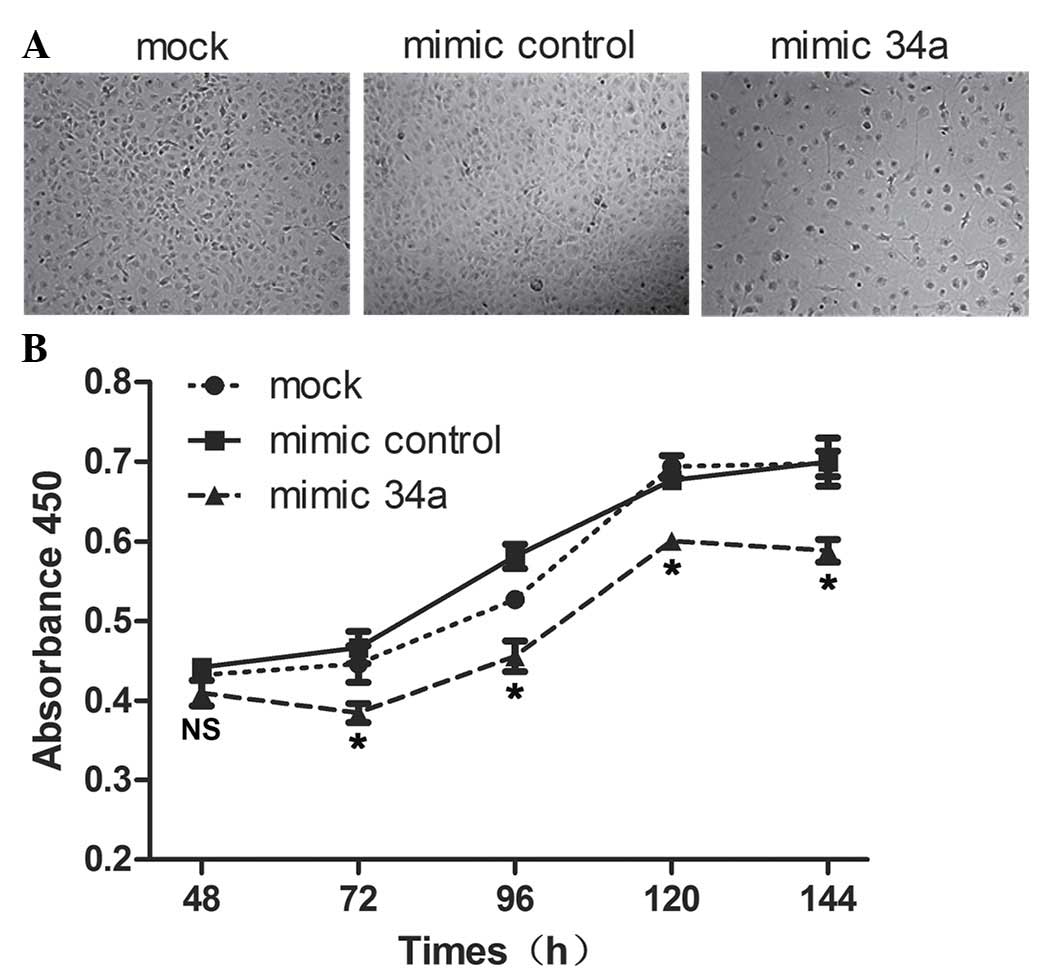
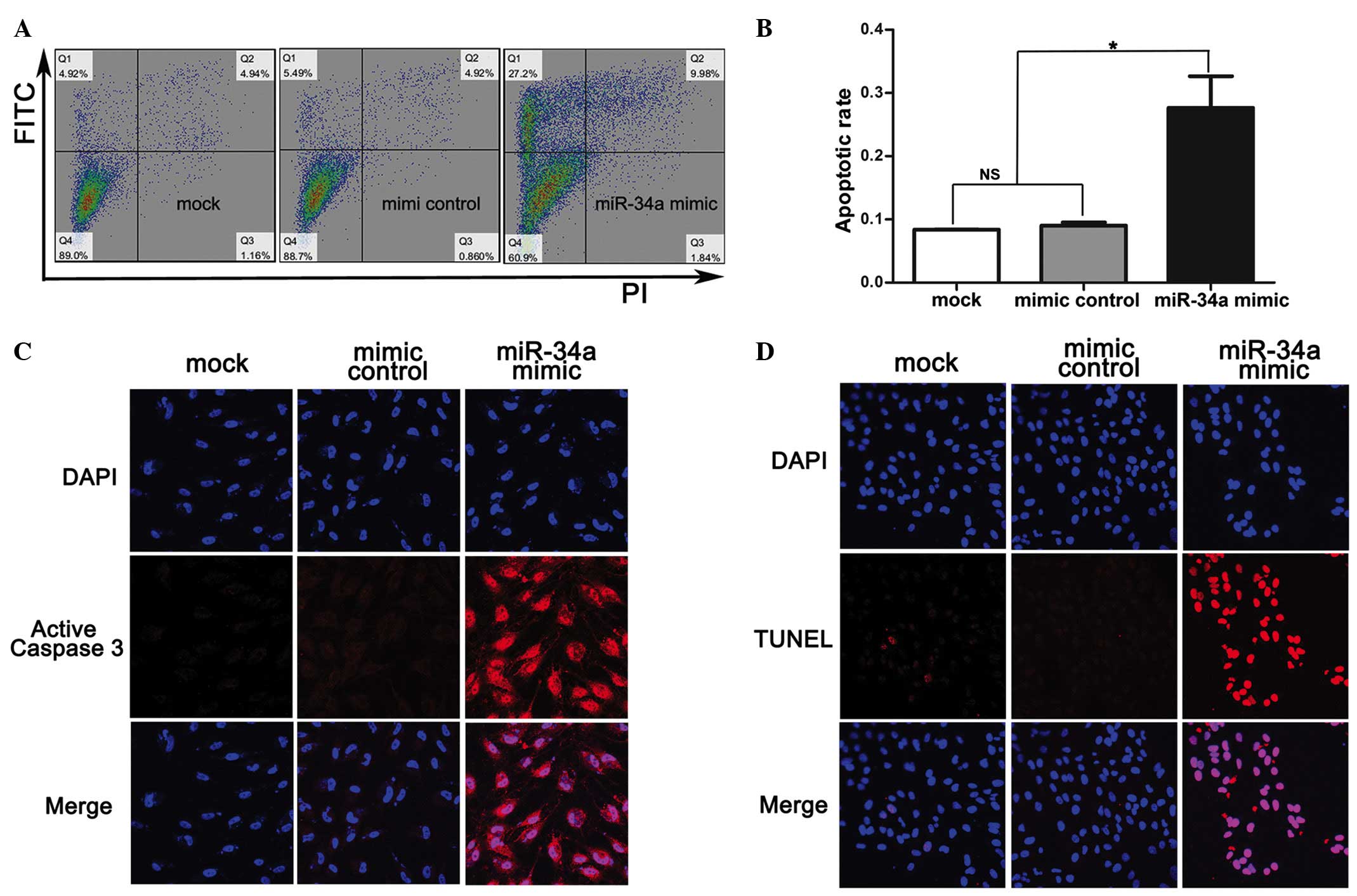
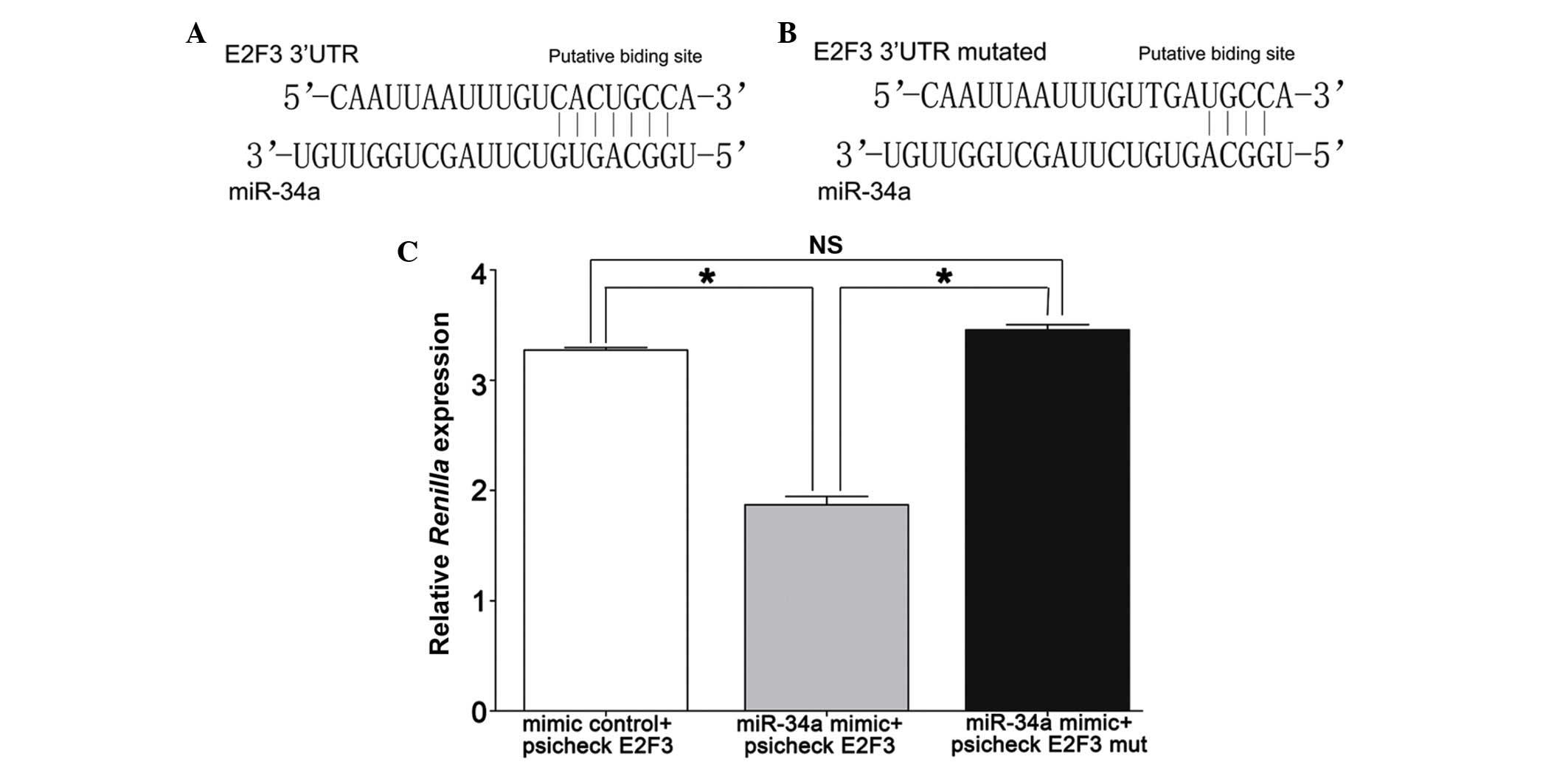
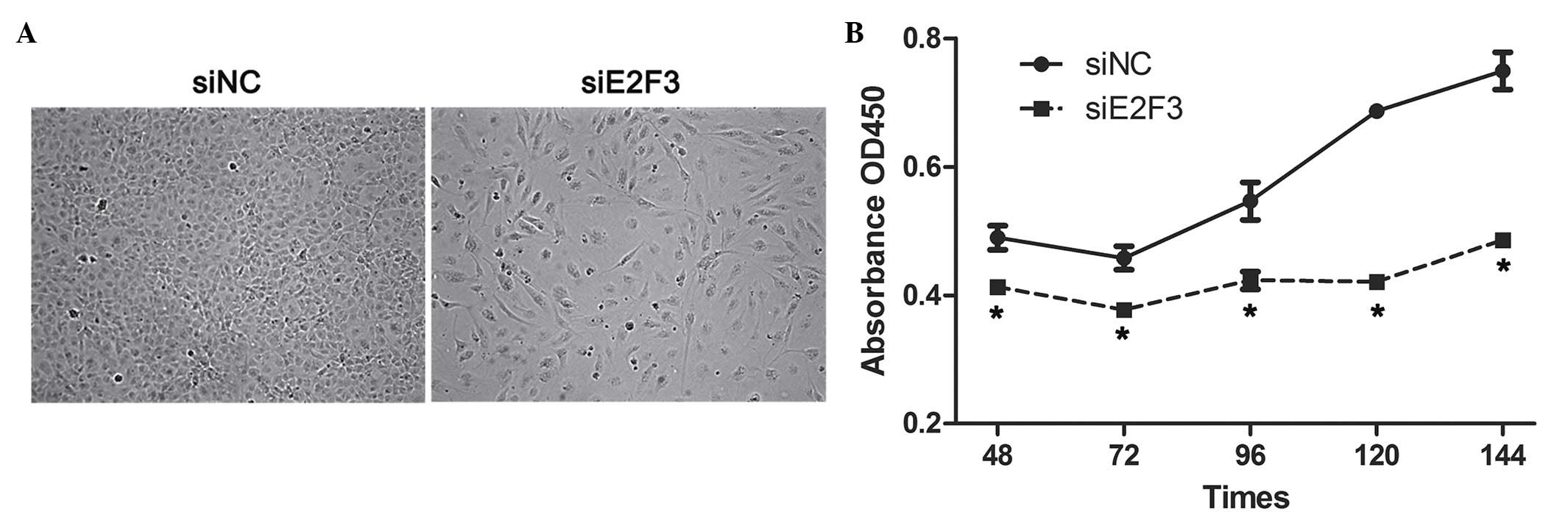
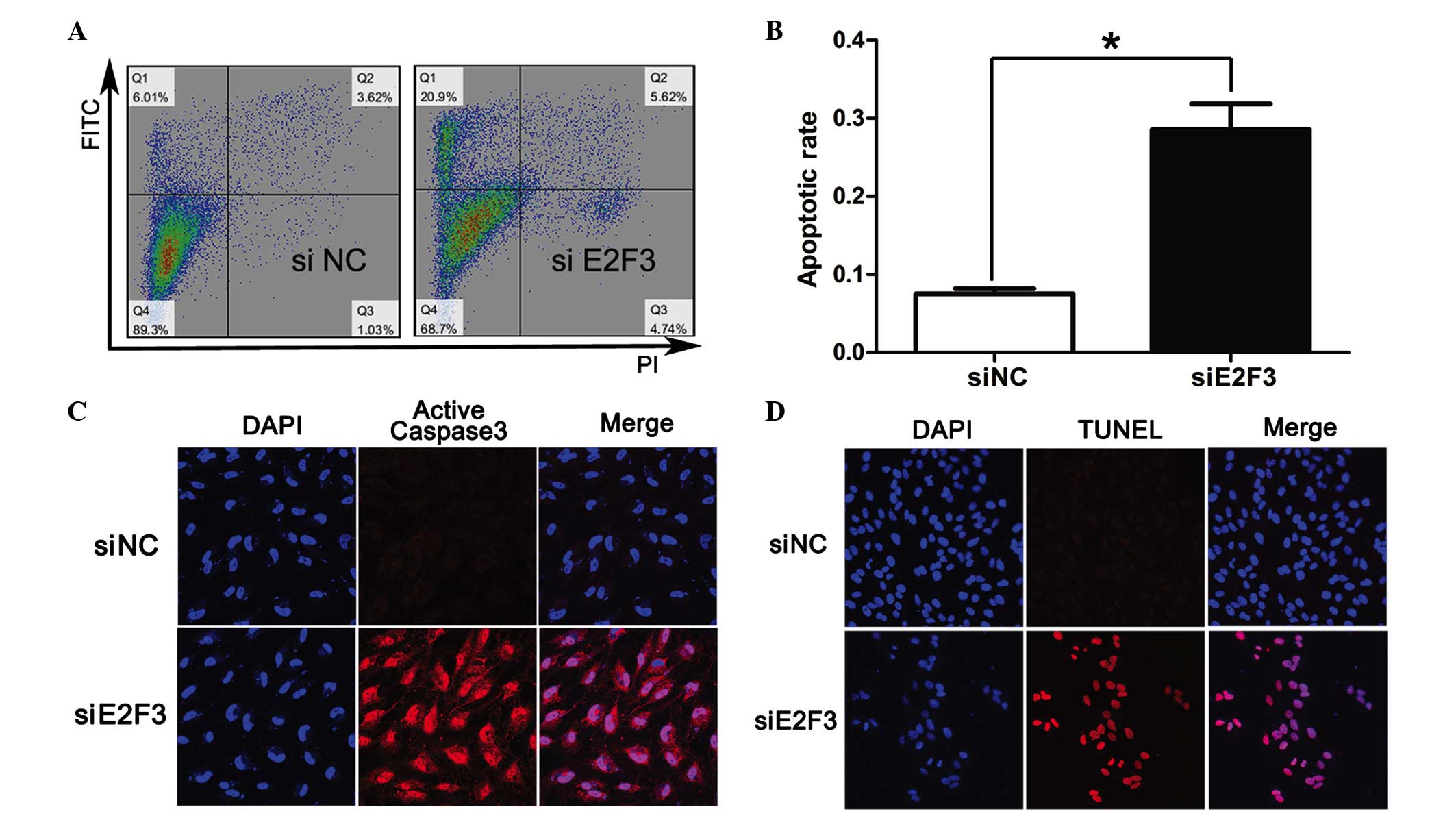
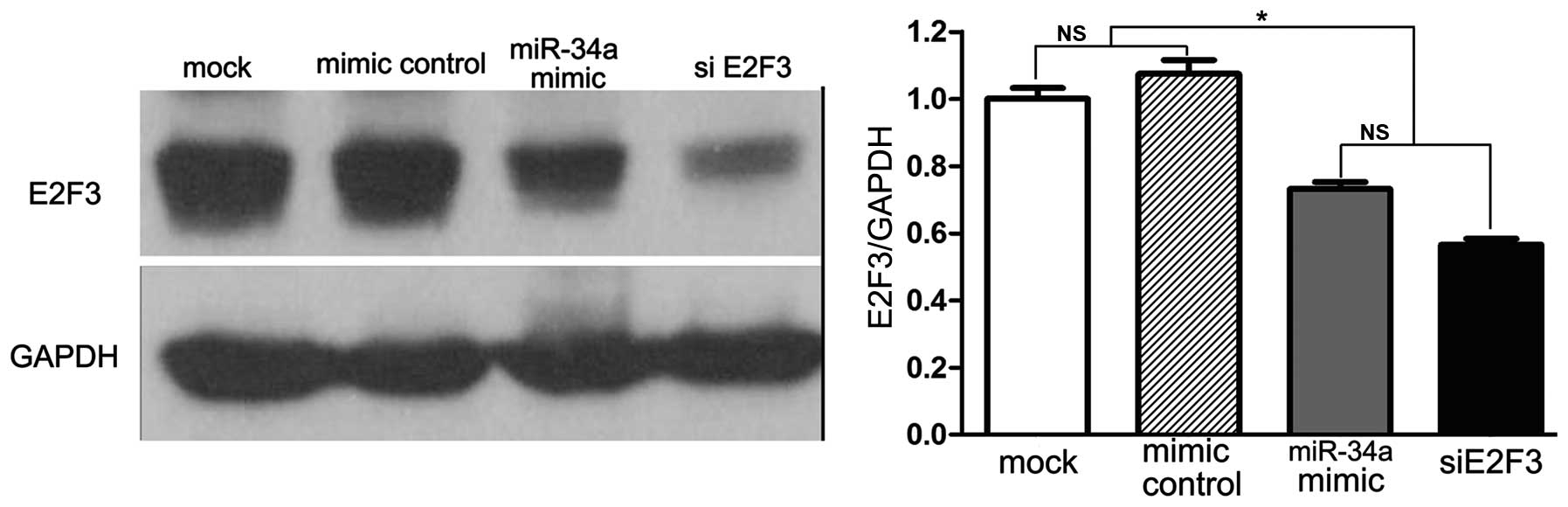
|
1
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wu C, Lin H, Wang Q, Chen W, Luo H, Chen W
and Zhang H: Discrepant expression of microRNAs in transparent and
cataractous human lenses. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 53:3906–3912.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Christoffersen NR, Shalgi R, Frankel LB,
Leucci E, Lees M, Klausen M, Pilpel Y, Nielsen FC, Oren M and Lund
AH: p53-independent upregulation of miR-34a during oncogene-induced
senescence represses MYC. Cell Death Differ. 17:236–245. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
He L, He X, Lim LP, de Stanchina E, Xuan
Z, Liang Y, Xue W, Zender L, Magnus J, Ridzon D, et al: A microRNA
component of the p53 tumour suppressor network. Nature.
447:1130–1134. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hermeking H: MicroRNAs in the p53 network:
Micromanagement of tumour suppression. Nat Rev Cancer. 12:613–626.
2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wenzel PL, Chong JL, Sáenz-Robles MT,
Ferrey A, Hagan JP, Gomez YM, Rajmohan R, Sharma N, Chen HZ, Pipas
JM, et al: Cell proliferation in the absence of E2F1-3. Dev Biol.
351:35–45. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chen Q, Liang D, Yang T, Leone G and
Overbeek PA: Distinct capacities of individual E2Fs to induce cell
cycle re-entry in postmitotic lens fiber cells of transgenic mice.
Dev Neurosci. 26:435–445. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chong JL, Tsai SY, Sharma N, Opavsky R,
Price R, Wu L, Fernandez SA and Leone G: E2f3a and E2f3b contribute
to the control of cell proliferation and mouse development. Mol
Cell Biol. 29:414–424. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yan Q, Liu JP and Li DW: Apoptosis in lens
development and pathology. Differentiation. 74:195–211. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ayala M, Strid H, Jacobsson U and
Söderberg PG: p53 expression and apoptosis in the lens after
ultraviolet radiation exposure. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
48:4187–4191. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Galichanin K, Löfgren S, Bergmanson J and
Söderberg P: Evolution of damage in the lens after in vivo close to
threshold exposure to UV-B radiation: Cytomorphological study of
apoptosis. Exp Eye Res. 91:369–377. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tamada Y, Fukiage C, Nakamura Y, Azuma M,
Kim YH and Shearer TR: Evidence for apoptosis in the selenite rat
model of cataract. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 275:300–306. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Murata M, Ohta N, Sakurai S, Alam S, Tsai
J, Kador PF and Sato S: The role of aldose reductase in sugar
cataract formation: Aldose reductase plays a key role in lens
epithelial cell death (apoptosis). Chem Biol Interact 130–132.
617–625. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Takamura Y, Kubo E, Tsuzuki S and Akagi Y:
Apoptotic cell death in the lens epithelium of rat sugar cataract.
Exp Eye Res. 77:51–57. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yoshizawa K, Oishi Y, Nambu H, Yamamoto D,
Yang J, Senzaki H, Miki H and Tsubura A: Cataractogenesis in
neonatal Sprague-Dawley rats by N-methyl-N-nitrosourea. Toxicol
Pathol. 28:555–564. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Pandya U, Saini MK, Jin GF, Awasthi S,
Godley BF and Awasthi YC: Dietary curcumin prevents ocular toxicity
of naphthalene in rats. Toxicol Lett. 115:195–204. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Nakajima Y, Nakamura T, Enomoto T and
Murata Y: Loss of one allele of the p53 gene in the lens epithelial
tumor in transgenic mice suppresses apoptosis induced by a
topoisomerase I inhibitor (CPT-11). Cancer Lett. 179:165–173. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Durand G, Hubert MF, Kuno H, Cook WO,
Boussiquet-Leroux C, Owen R, Fujimaki Y, Kemi M, Virat M and van
Zwieten MJ: Muscarinic receptor antagonist-induced lenticular
opacity in rats. Toxicol Sci. 66:166–172. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lewis BP, Burge CB and Bartel DP:
Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that
thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 120:15–20.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Harries LW: MicroRNAs as mediators of the
ageing process. Genes (Basel). 5:656–670. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tazawa H, Tsuchiya N, Izumiya M and
Nakagama H: Tumor-suppressive miR-34a induces senescence-like
growth arrest through modulation of the E2F pathway in human colon
cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:15472–15477. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Welch C, Chen Y and Stallings RL:
MicroRNA-34a functions as a potential tumor suppressor by inducing
apoptosis in neuroblastoma cells. Oncogene. 26:5017–5022. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Maiti B, Li J, de Bruin A, Gordon F,
Timmers C, Opavsky R, Patil K, Tuttle J, Cleghorn W and Leone G:
Cloning and characterization of mouse E2F8, a novel mammalian E2F
family member capable of blocking cellular proliferation. J Biol
Chem. 280:18211–18220. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Brodeur GM: Neuroblastoma: Biological
insights into a clinical enigma. Nat Rev Cancer. 3:203–216. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bagchi A and Mills AA: The quest for the
1p36 tumor suppressor. Cancer Res. 68:2551–2556. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Boon RA, Iekushi K, Lechner S, Seeger T,
Fischer A, Heydt S, Kaluza D, Tréguer K, Carmona G, Bonauer A, et
al: MicroRNA-34a regulates cardiac ageing and function. Nature.
495:107–110. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ito T, Yagi S and Yamakuchi M:
MicroRNA-34a regulation of endothelial senescence. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 398:735–740. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chien KH, Chen SJ, Liu JH, Chang HM, Woung
LC, Liang CM, Chen JT, Lin TJ, Chiou SH and Peng CH: Correlation
between microRNA-34a levels and lens opacity severity in
age-related cataracts. Eye (Lond). 27:883–888. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tarasov V, Jung P, Verdoodt B, Lodygin D,
Epanchintsev A, Menssen A, Meister G and Hermeking H: Differential
regulation of microRNAs by p53 revealed by massively parallel
sequencing: miR-34a is a p53 target that induces apoptosis and
G1-arrest. Cell Cycle. 6:1586–1593. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Maes OC, Sarojini H and Wang E: Stepwise
up-regulation of microRNA expression levels from replicating to
reversible and irreversible growth arrest states in WI-38 human
fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol. 221:109–119. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Fujita K, Mondal AM, Horikawa I, Nguyen
GH, Kumamoto K, Sohn JJ, Bowman ED, Mathe EA, Schetter AJ, Pine SR,
et al: p53 isoforms Delta133p53 and p53beta are endogenous
regulators of replicative cellular senescence. Nat Cell Biol.
11:1135–1142. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhao T, Li J and Chen AF: MicroRNA-34a
induces endothelial progenitor cell senescence and impedes its
angiogenesis via suppressing silent information regulator 1. Am J
Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 299:E110–E116. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kinoshita JH: Mechanisms initiating
cataract formation. Proctor Lecture. Invest Ophthalmol. 13:713–724.
1974.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Piatigorsky J: Lens differentiation in
vertebrates. A review of cellular and molecular features.
Differentiation. 19:134–153. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Li WC, Kuszak JR, Wang GM, Wu ZQ and
Spector A: Calcimycin-induced lens epithelial cell apoptosis
contributes to cataract formation. Exp Eye Res. 61:91–98. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Li DW and Spector A: Hydrogen
peroxide-induced expression of the proto-oncogenes, c-jun, c-fos
and c-myc in rabbit lens epithelial cells. Mol Cell Biochem.
173:59–69. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li WC, Kuszak JR, Dunn K, Wang RR, Ma W,
Wang GM, Spector A, Leib M, Cotliar AM, Weiss M, et al: Lens
epithelial cell apoptosis appears to be a common cellular basis for
non-congenital cataract development in humans and animals. J Cell
Biol. 130:169–181. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Guggenmoos-Holzmann I, Engel B, Henke V
and Naumann GO: Cell density of human lens epithelium in women
higher than in men. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 30:330–332.
1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Balaram M, Tung WH, Kuszak JR, Ayaki M,
Shinohara T and Chylack LJ Jr: Noncontact specular microscopy of
human lens epithelium. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 41:474–481.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhang L, Yan Q, Liu JP, Zou LJ, Liu J, Sun
S, Deng M, Gong L, Ji WK and Li DW: Apoptosis: Its functions and
control in the ocular lens. Curr Mol Med. 10:864–875. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Humbert PO, Verona R, Trimarchi JM, Rogers
C, Dandapani S and Lees JA: E2f3 is critical for normal cellular
proliferation. Genes Dev. 14:690–703. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wu L, Timmers C, Maiti B, Saavedra HI,
Sang L, Chong GT, Nuckolls F, Giangrande P, Wright FA, Field SJ, et
al: The E2F1-3 transcription factors are essential for cellular
proliferation. Nature. 414:457–462. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|