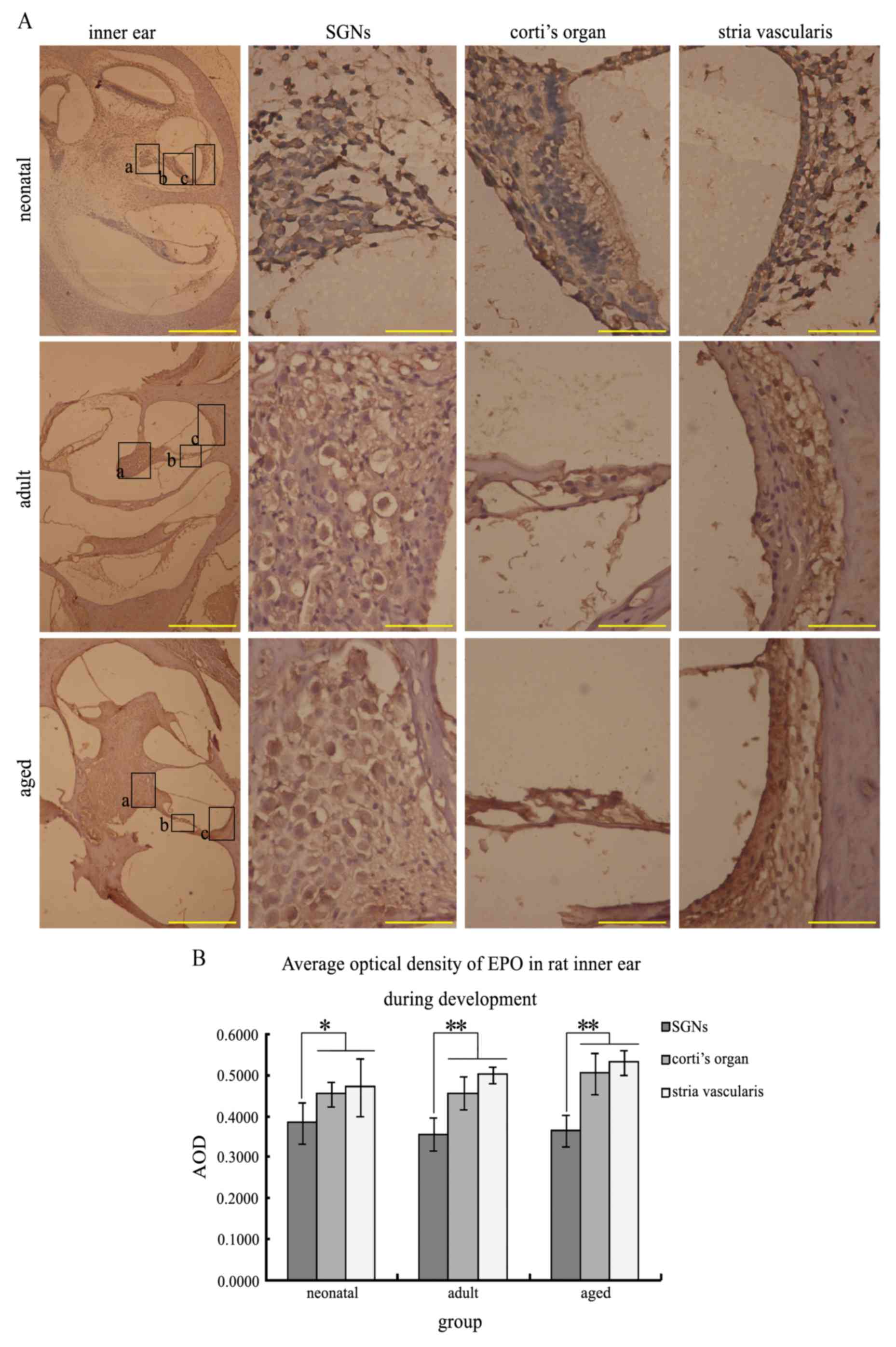
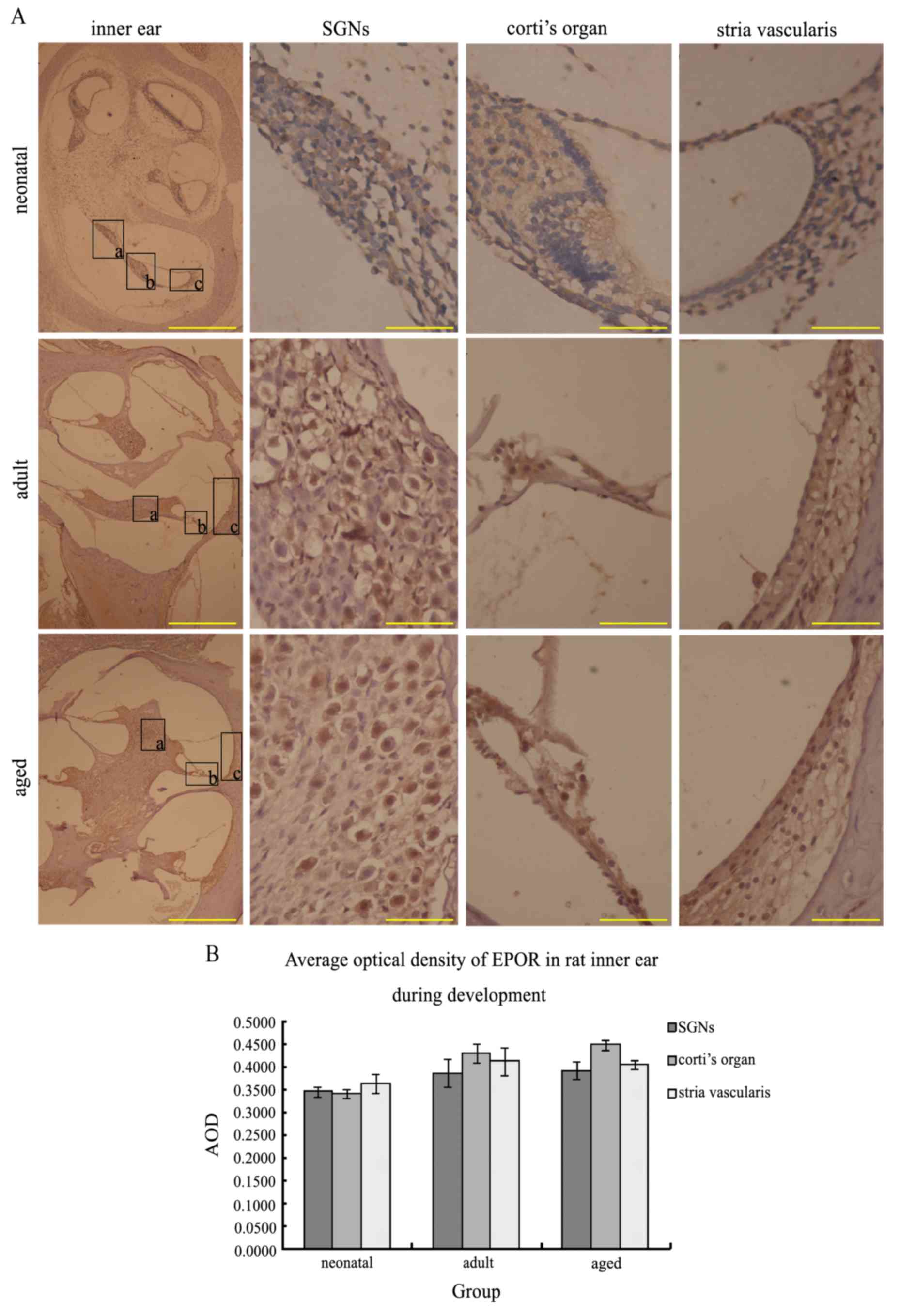
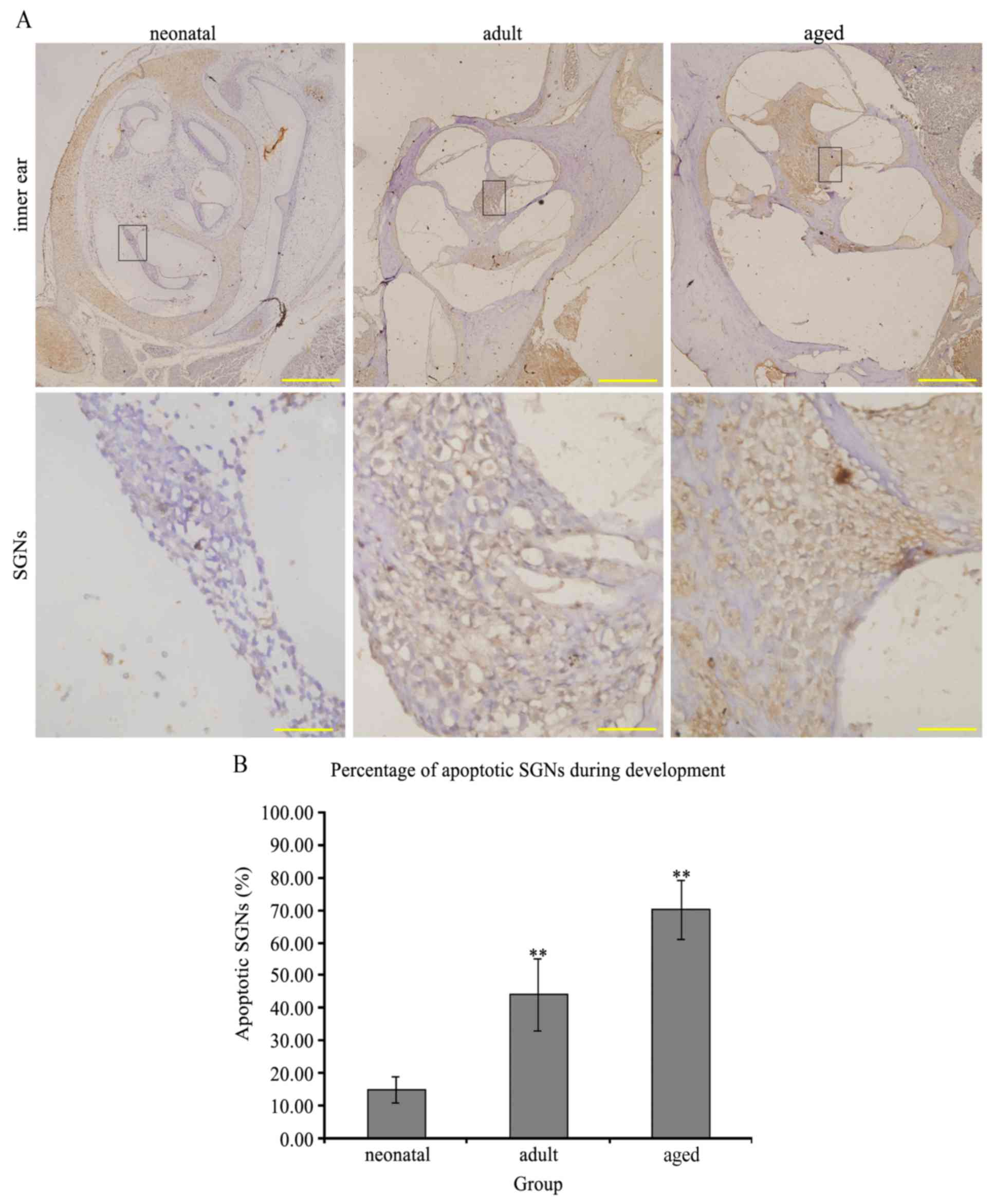
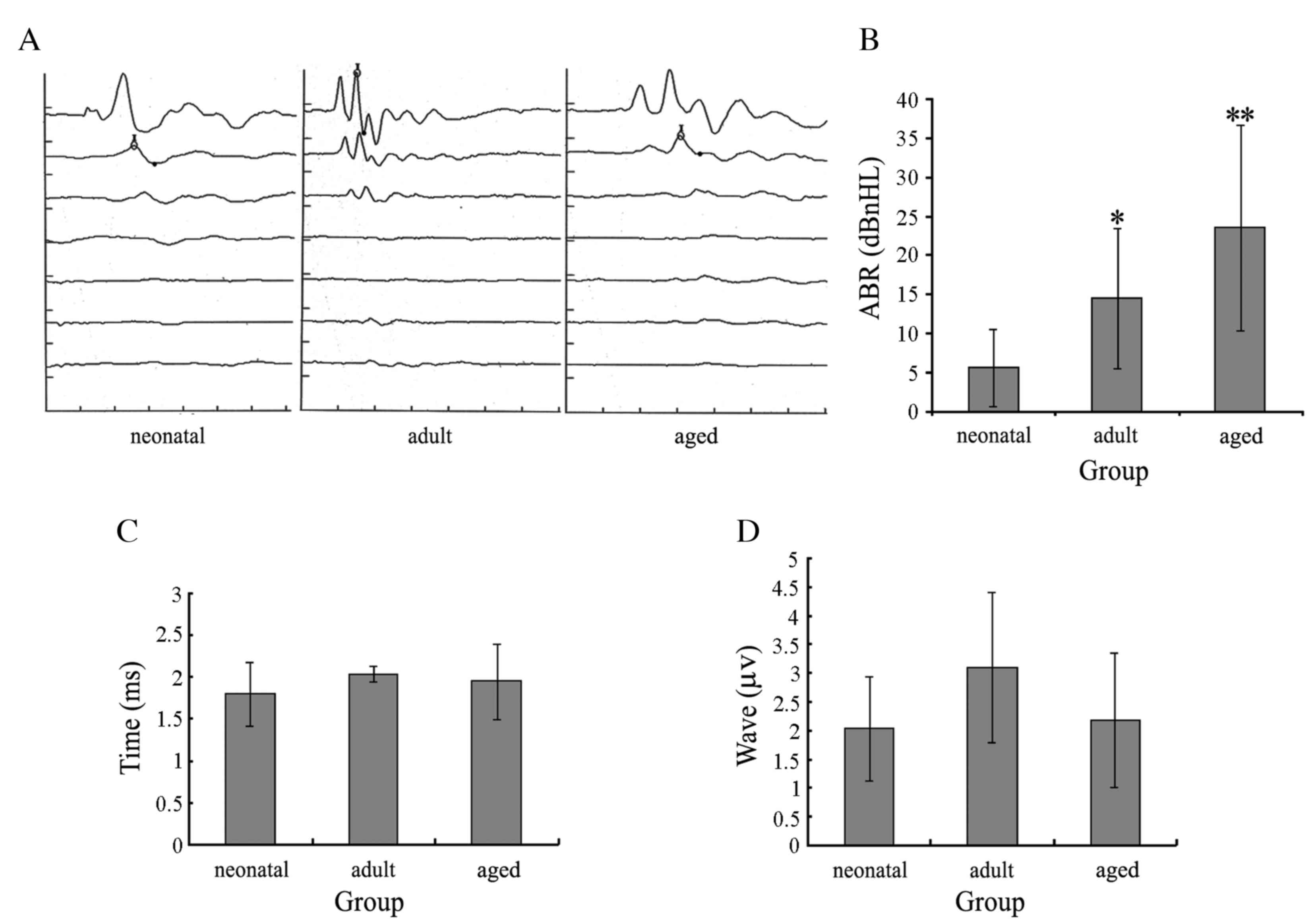
|
1
|
Monini S, Filippi C, Baldini R and Barbara
M: Perceived disability from hearing and voice changes in the
elderly. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 15:147–155. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yamasoba T, Lin FR, Someya S, Kashio A,
Sakamoto T and Kondo K: Current concepts in age-related hearing
loss: Epidemiology and mechanistic pathways. Hear Res. 303:30–38.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bao J and Ohlemiller KK: Age-related loss
of spiral ganglion neurons. Hear Res. 264:93–97. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Byts N and Sirén AL: Erythropoietin: A
multimodal neuroprotective agent. Exp Transl Stroke Med. 1:42009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Brines M and Cerami A: Discovering
erythropoietin's extra-hematopoietic functions: Biology and
clinical promise. Kidney Int. 70:246–250. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cayé-Thomasen P, Wagner N, Frederiksen B
Lidegaard, Asal K and Thomsen J: Erythropoietin and erythropoietin
receptor expression in the guinea pig inner ear. Hear Res.
203:21–27. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Berkingali N, Warnecke A, Gomes P, Paasche
G, Tack J, Lenarz T and Stöver T: Neurite outgrowth on cultured
spiral ganglion neurons induced by erythropoietin. Hear Res.
243:121–126. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Naldi A Monge, Gassmann M and Bodmer D:
Erythropoietin but not VEGF has a protective effect on auditory
hair cells in the inner ear. Cell Mol Life Sci. 66:3595–3599. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Panza F, Solfrizzi V and Logroscino G:
Age-related hearing impairment-a risk factor and frailty marker for
dementia and AD. Nat Rev Neurol. 11:166–175. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jewett DL and Williston JS:
Auditory-evoked far fields averaged from the scalp of humans.
Brain. 94:681–696. 1971. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Malherbe TK, Hanekom T and Hanekom JJ: Can
subject-specific single-fibreelectrically evoked auditory brainstem
response data be predicted from a model? Med Eng Phys. 35:926–936.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rattay F and Danner SM: Peak I of the
human auditory brainstem response results from the somatic regions
of type I spiral ganglion cells: Evidence from computer modeling.
Hear Res. 315:67–79. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Brown DJ and Patuzzi RB: Evidence that the
compound action potential (CAP) from the auditory nerve is a
stationary potential generated across dura mater. Hear Res.
267:12–26. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chong ZZ and Maiese K: Erythropoietin
involves the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway, 14-4-4 protein
and FOXO3a nuclear traffic-king to preserve endothelia cell
integrity. Br J Pharmacol. 150:839–850. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sims B, Clarke M, Njah W, Hopkins ES and
Sontheimer H: Erythropoietin-induced neuroprotection requires
cystine glutamate exchanger activity. Brain Res. 1321:88–95. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gross J, Moller R, Amarjargal N, Machulik
A, Fuchs J, Ungethüm U, Kuban RJ, Henke W, Haupt H and Mazurek B:
Expression of erythropoietin and angiogenic growth factors
following inner ear injury of newborn rats. Prague Med Rep.
110:310–331. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kaiser O, Paasche G, Stöver T, Ernst S,
Lenarz T, Kral A and Warnecke A: TGF-beta superfamily member
activin A acts with BDNF and erythropoietin to improve survival of
spiral ganglion neurons in vitro. Neuropharma. 75:416–425. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Juul SE, Stallings SA and Christensen RD:
Erythropoieti n in the cerebrospinal fluid of neonates who
sustained CNS injury. Pediatr Res. 46:543–547. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Saunders NR, Habgood MD and Dziegielewska
KM: Barrier mechanisms in the brain, II. Immature brain. Clin Exp
Pharmacol Physiol. 26:85–91. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Banks WA, Jumbe NL, Farrell CL, Niehoff ML
and Heatherington AC: Passage of erythropoietic agents across the
blood-brain barrier: A comparison of human and murine
erythropoietin and the analog darbepoetin alfa. Eur J Pharmacol.
505:93–101. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Frederiksen BL, Cayé-Thomasen P, Lund SP,
Wagner N, Asal K, Olsen NV and Thomsen J: Does erythropoietin
augment noise induced hearing loss? Hear Res. 223:129–137. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Maiese K, Chong ZZ, Li F and Shang YC:
Erythropoietin: Elucidating new cellular targets that broaden
therapeutic strategies. Prog Neurobiol. 85:194–213. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|