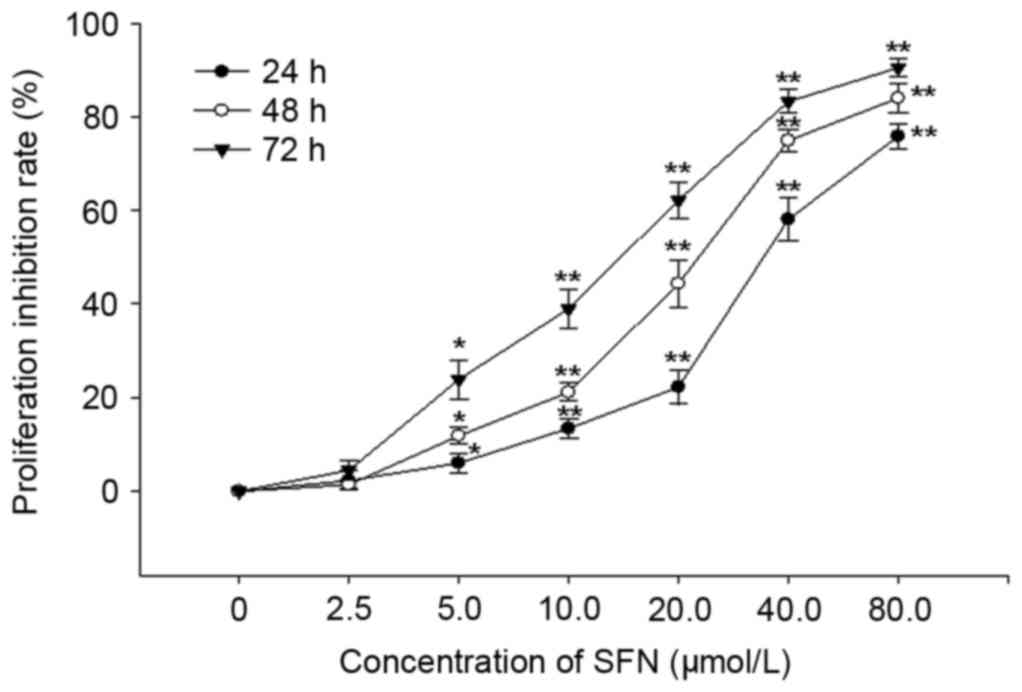
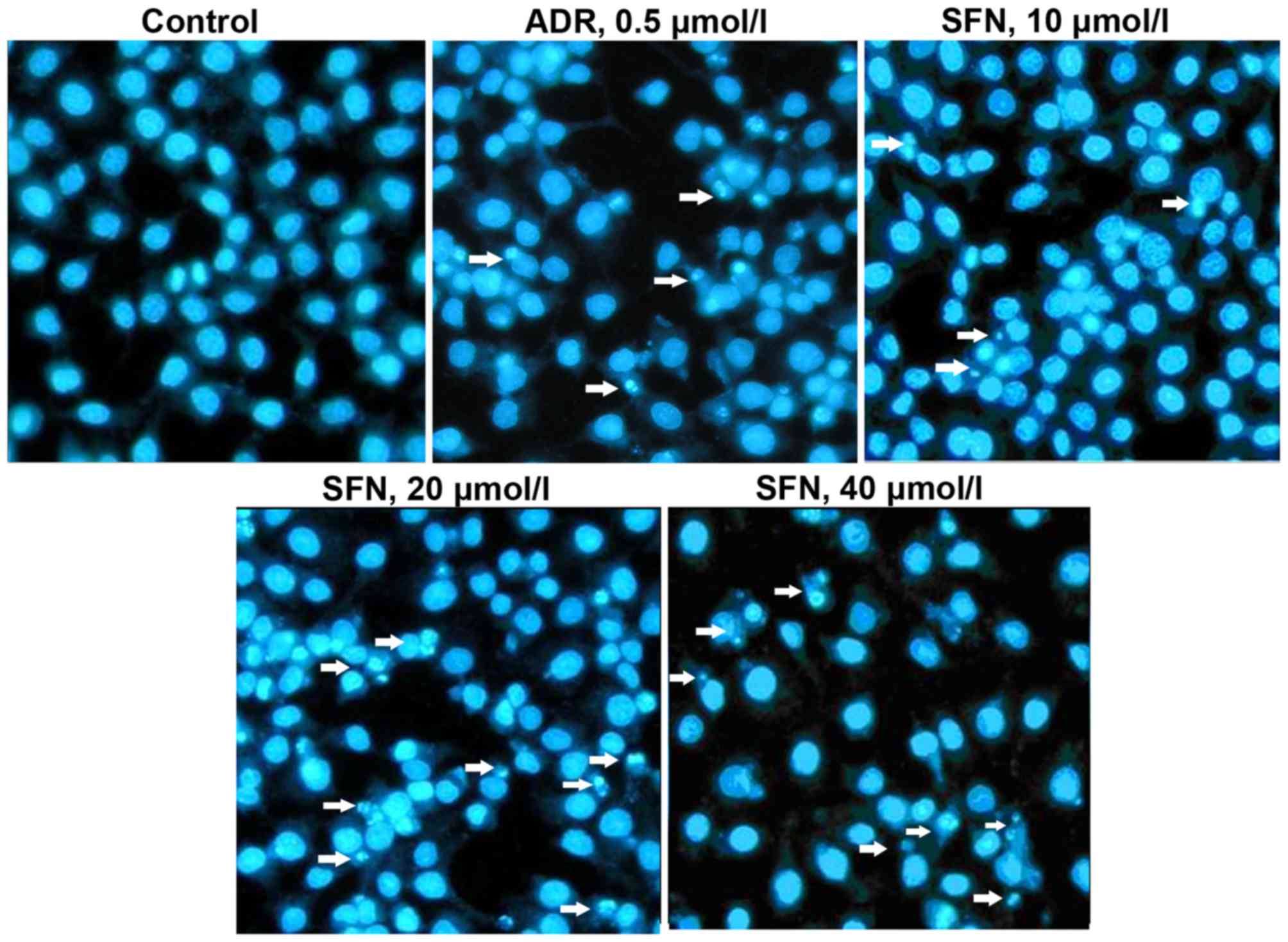
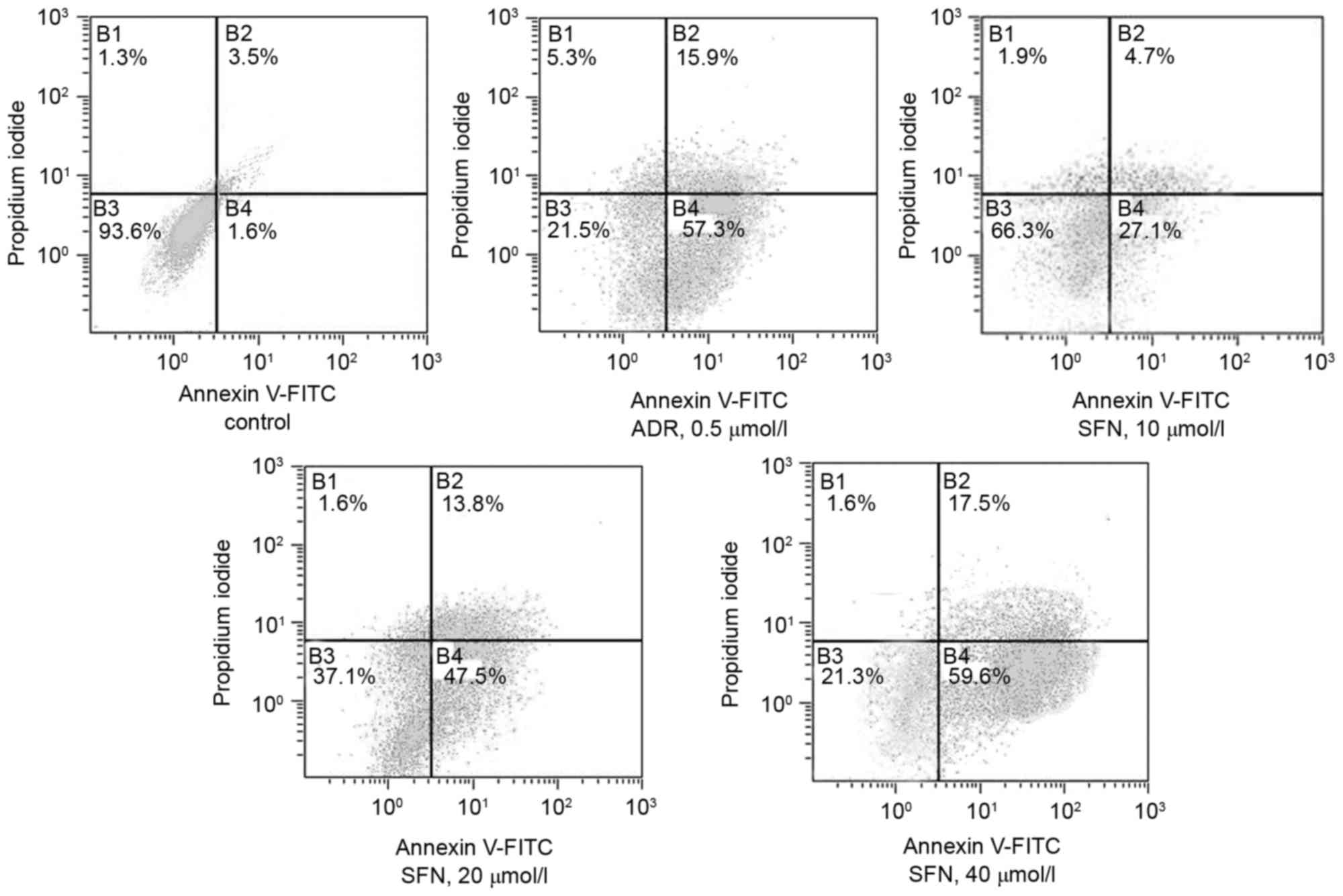
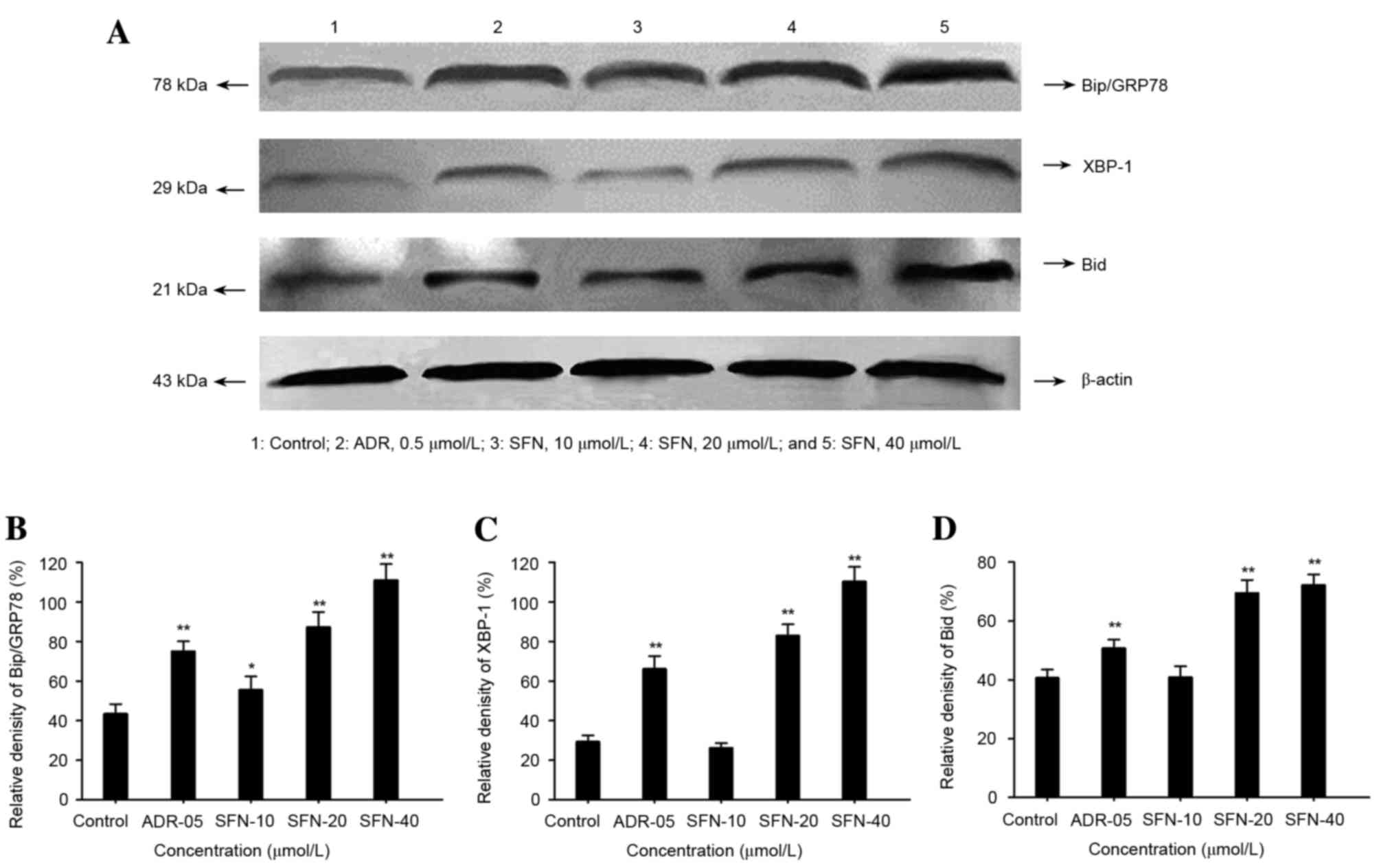
|
1
|
Wei KR, Yu X, Zheng RS, Peng XB, Zhang SW,
Ji MF, Liang ZH, Ou ZX and Chen WQ: Incidence and mortality of
liver cancer in China, 2010. Chin J Cancer. 33:388–394.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bernard WS and Chrstopher PW: World cancer
report 2014. IARC; Lyon: 2014
|
|
3
|
Fan YG, Wang JB, Jiang Y, Li P, Xiao HJ,
Chen WQ, Qiao YL and Boffetta P: Attributable causes of lung cancer
mortality and incidence in China. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
14:7251–7256. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ji YB, Qu ZY and Zou X: Juglone-induced
apoptosis in human gastric cancer SGC-7901 cells via the
mitochondrial pathway. Exp Toxicol Pathol. 63:69–78. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Traka MH, Melchini A and Mithen RF:
Sulforaphane and prostate cancer interception. Drug Discov Today.
19:1488–1492. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Abdull Razis AF and Noor NM: Sulforaphane
is superior to glucoraphanin in modulating carcinogen-metabolising
enzymes in Hep G2 cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 14:4235–4238.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sawai Y, Murata H, Horii M, Koto K, Matsui
T, Horie N, Tsuji Y, Ashihara E, Maekawa T, Kubo T and Fushiki S:
Effectiveness of sulforaphane as a radiosensitizer for murine
osteosarcoma cells. Oncol Rep. 29:941–945. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li SH, Fu J, Watkins DN, Srivastava RK and
Shankar S: Sulforaphane regulates self-renewal of pancreatic cancer
stem cells through the modulation of Sonic hedgehog-GLI pathway.
Mol Cell Biochem. 373:217–227. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sharma C, Sadrieh L, Priyani A, Ahmed M,
Hassan AH and Hussain A: Anti-carcinogenic effects of sulforaphane
in association with its apoptosis-inducing and anti-inflammatory
properties in human cervical cancer cells. Cancer Epidemiol.
35:272–278. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chang CC, Hung CM, Yang YR, Lee MJ and Hsu
YC: Sulforaphane induced cell cycle arrest in the G2/M phase via
the blockade of cyclin B1/CDC2 in human ovarian cancer cells. J
Ovarian Res. 6:412013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Choi S, Lew KL, Xiao H, Herman-Antosiewicz
A, Xiao D, Brown CK and Singh SV: D,L-Sulforaphane-induced cell
death in human prostate cancer cells is regulated by inhibitor of
apoptosis family proteins and Apaf-1. Carcinogenesis. 28:151–162.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jo GH, Kim GY, Kim WJ, Park KY and Choi
YH: Sulforaphane induces apoptosis in T24 human urinary bladder
cancer cells through a reactive oxygen species-mediated
mitochondrial pathway: The involvement of endoplasmic reticulum
stress and the Nrf2 signaling pathway. Int J Oncol. 45:1497–1506.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Suppipat K, Park CS, Shen Y, Zhu X and
Lacorazza HD: Sulforaphane induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis
in acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. PLoS One. 7:e512512012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Singh SV, Herman-Antosiewicz A, Singh AV,
Lew KL, Srivastava SK, Kamarh R, Brown KD, Zhang L and Baskaran R:
Sulforaphane-induced G2/M phase cell cycle arrest involves
checkpoint kinase 2-mediated phosphorylation of cell division cycle
25C. J Biol Chem. 279:25813–25822. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bryant CS, Kumar S, Chamala S, Shah J, Pal
J, Seward S, Qazi AM, Morris R, Semaan A, Shammas MA, et al:
Sulforaphane induces cell cycle arrest by protecting RB-E2F-1
complex in epithelial ovarian cancer cells. Mol Cancer. 9:472010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zou X, Qu ZY and Ji YB: Study on JNK
pathway in human hapetocelluar carcinoma HepG-2 cells apoptosis
induced by sulforaphane. Journal of Harbin University of Commerce
Natural Sciences Edition. 27:532–535. 2011.
|
|
17
|
Zou X, Qu ZY, Gao P, Sun SN and Ji Yb:
Effects of sulforaphane on G_2/M phase arrest in HepG-2 cells and
the expression of Cdk1 and CyclinB1. Acta Chinese Medicine and
Pharmacology. 38:8–10. 2010.
|
|
18
|
Yeh CT and Yen GC: Effect of sulforaphane
on metallothionein expression and induction of apoptosis in human
hepatoma HepG2 cells. Carcinogenesis. 26:2138–2148. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jeon YK, Yoo DR, Jang YH, Jang SY and Nam
MJ: Sulforaphane induces apoptosis in human hepatic cancer cells
through inhibition of
6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-biphosphatase4, mediated by
hypoxia inducible factor-1-dependent pathway. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1814:1340–1348. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zou X, Qu ZY, Gao P and Ji YB: Effects of
sulforaphane on gene transcription and protein expression of Bcl-2
and Bax in HepG-2 Cell. Acta Universitatis Traditionis Medicalis
Sinensis Pharmacologiaeque Shanghai. 24:76–80. 2010.
|
|
21
|
Herr I, Lozanovski V, Houben P, Schemmer P
and Büchler MW: Sulforaphane and related mustard oils in focus of
cancer prevention and therapy. Wien Med Wochenschr. 163:80–88.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Juge N, Mithen RF and Traka M: Molecular
basis for chemoprevention by sulforaphane: A comprehensive review.
Cell Mol Life Sci. 64:1105–1127. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Xiao D, Powolny AA, Antosiewicz J, Hahm
ER, Bommareddy A, Zeng Y, Desai D, Amin S, Herman-Antosiewicz A and
Singh SV: Cellular responses to cancer chemopreventive agent
D,L-sulforaphane in human prostate cancer cells are initiated by
mitochondrial reactive oxygen species. Pharm Res. 26:1729–1738.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang L, Tian Z, Yang Q, Li H, Guan H, Shi
B, Hou P and Ji M: Sulforaphane inhibits thyroid cancer cell growth
and invasiveness through the reactive oxygen species-dependent
pathway. Oncotarget. 6:25917–25931. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mondal A, Biswas R, Rhee YH, Kim J and Ahn
JC: Sulforaphene promotes Bax/Bcl2, MAPK-dependent human gastric
cancer AGS cells apoptosis and inhibits migration via EGFR,
p-ERK1/2 down-regulation. Gen Physiol Biophys. 35:25–34.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Park SY, Kim GY, Bae SJ, Yoo YH and Choi
YH: Induction of apoptosis by isothiocyanate sulforaphane in human
cervical carcinoma HeLa and hepatocarcinoma HepG2 cells through
activation of caspase-3. Oncol Rep. 18:181–187. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zou X, Qu ZY, Bai J and Ji YB: Effect of
sulforaphane on protein expression of ERK and pathway in human
hapetocelluar carcinoma HepG-2 cells. Journal of Harbin University
of Commerce (Natural Sciences Edition). 27257–258. (266)2011.
|
|
28
|
Franceschelli S, Moltedo O, Amodio G,
Tajana G and Remondelli P: In the Huh7 hepatoma cells diclofenac
and indomethacin activate differently the unfolded protein response
and induce ER stress apoptosis. Open Biochem J. 5:45–51. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhou Y, Lee J, Reno CM, Sun C, Chung J,
Lee J, Fisher SJ, White MF, Biddinger SB and Ozcan U: Regulation of
glucose homeostasis through a XBP-1-FoxO1 interaction. Nat Med.
17:356–365. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chen X, Fu XS, Li CP and Zhao HX: ER
stress and ER stress-induced apoptosis are activated in gastric
SMCs in diabetic rats. World J Gastroenterol. 20:8260–8267. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Harshberger CA, Harper AJ, Carro GW, Spath
WE, Hui WC, Lawton JM and Brockstein BE: Outcomes of computerized
physician order entry in an electronic health record after
implementation in an outpatient oncology setting. J Oncol Pract.
7:233–237. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Uchibayashi R, Tsuruma K, Inokuchi Y,
Shimazawa M and Hara H: Involvement of Bid and caspase-2 in
endoplasmic reticulum stress- and oxidative stress-induced retinal
ganglion cell death. J Neurosci Res. 89:1783–1794. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|