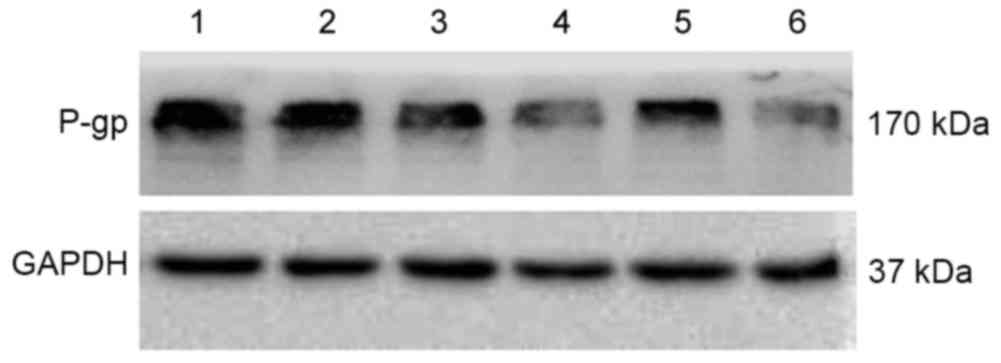
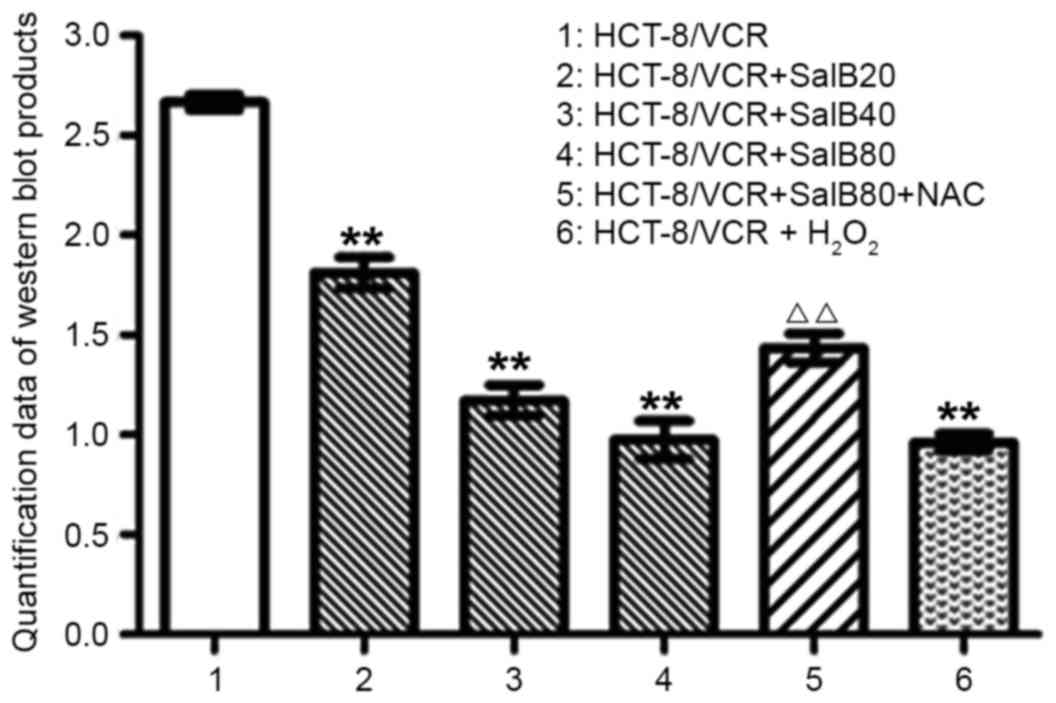
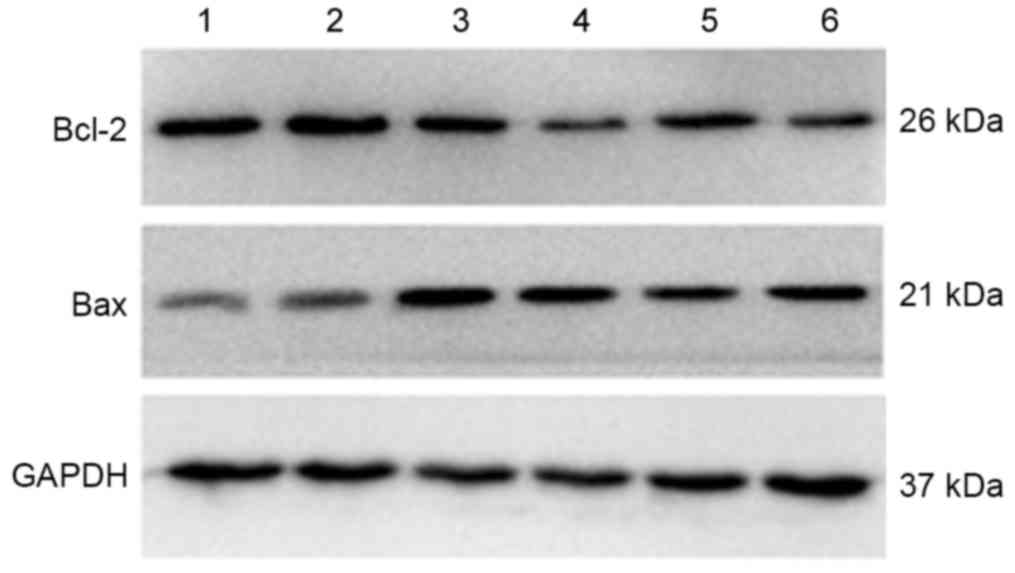
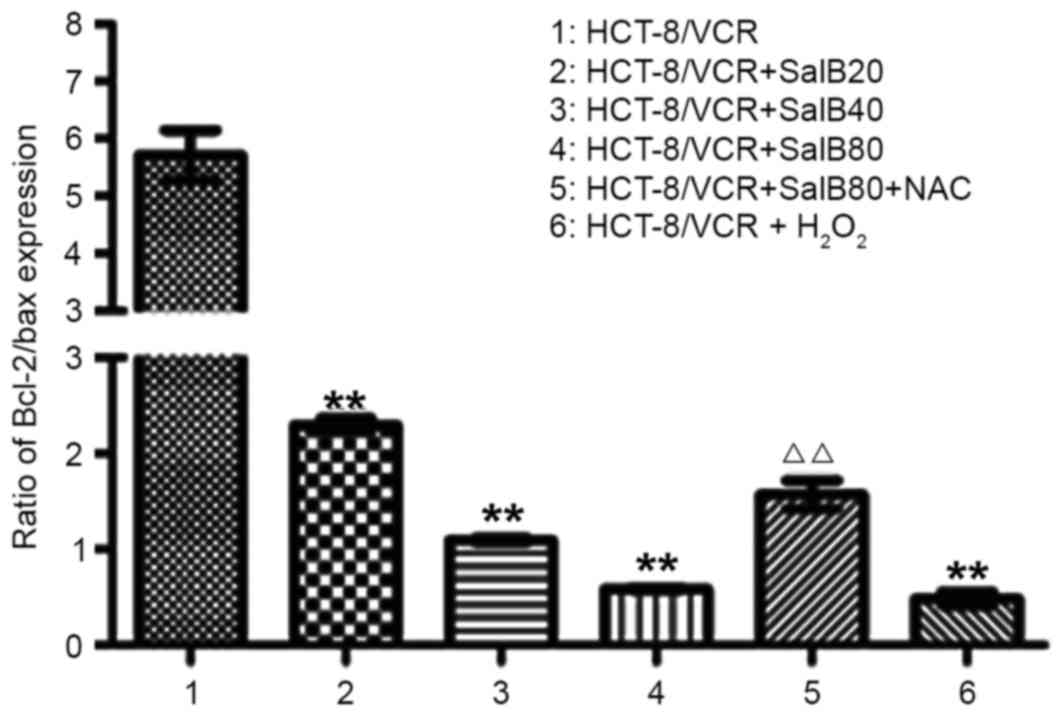
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:7–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Maiti AK: Genetic determinants of
oxidative stress-mediated sensitization of drug-resistant cancer
cells. Int J Cancer. 130:1–9. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dahdouh F, Raane M, Thévenod F and Lee WK:
Nickel-induced cell death and survival pathways in cultured renal
proximal tubule cells: Roles of reactive oxygen species, ceramide
and ABCB1. Arch Toxicol. 88:881–892. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lo YL and Tu WC: Co-encapsulation of
chrysophsin-1 and epirubicin in PEGylated liposomes circumvents
multidrug resistance in HeLa cells. Chem Biol Interact. 242:13–23.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Brahimi-Horn MC, Giuliano S, Saland E,
Lacas-Gervais S, Sheiko T, Pelletier J, Bourget I, Bost F, Féral C,
Boulter E, et al: Knockout of Vdac1 activates hypoxia-inducible
factor through reactive oxygen species generation and induces tumor
growth by promoting metabolic reprogramming and inflammation.
Cancer Metab. 3:82015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Singh KK: Mitochondrial dysfunction is a
common phenotype in aging and cancer. Ann N Y Acad Sci.
1019:260–264. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sinicrope FA, Hart J, Brasitus TA,
Michelassi F, Lee JJ and Safa AR: Relationship of P-glycoprotein
and carcinombryonic antigen expression in human colon carcinoma to
local invasion. DNA ploidy, and disease relapse. Caner.
74:2908–2917. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Salphati L, Plise EG and Li G: Expression
and activity of the efflux transporters ABCB1, ABCC2 and ABCG2 in
the human colorectal carcinoma cell line LS513. Eur J Pharm Sci.
37:463–468. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang M, Sun G, Wu P, Chen R, Yao F, Qin M,
Luo Y, Sun H, Zhang Q, Dong X and Sun X: Salvianolic Acid B
prevents arsenic trioxide-induced cardiotoxicity in vivo and
enhances its anticancer activity in vitro. Evid Based Complement
Alternat Med. 2013:7594832013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhao Y, Hao Y, Ji H, Fang Y, Guo Y, Sha W,
Zhou Y, Pang X, Southerland WM, Califano JA and Gu X: Combination
effects of salvianolic acid B with low-dose celecoxib on inhibition
of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma growth in vitro and in
vivo. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 3:787–796. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Shen A, Chen H, Chen Y, Lin J, Lin W, Liu
L, Sferra TJ and Peng J: Pien Tze Huang Overcomes Multidrug
Resistance and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Human
Colorectal Carcinoma Cells via Suppression of TGF-β Pathway. Evid
Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014:6794362014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ravindranath AK, Kaur S, Wernyj RP,
Kumaran MN, Miletti-Gonzalez KE, Chan R, Lim E, Madura K and
Rodriguez-Rodriguez L: CD44 promotes multi-drug resistance by
protecting P-glycoprotein from FBXO21-mediated ubiquitination.
Oncotarget. 6:26308–26321. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Katayama K, Noguchi K and Sugimoto Y:
FBXO15 regulates P-glycoprotein/ABCB1 expression through the
ubiquitin-proteasome pathway in cancer cells. Cancer Sci.
104:694–702. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sui H, Liu X, Jin BH, Pan SF, Zhou LH, Yu
NA, Wu J, Cai JF, Fan ZZ, Zhu HR and Li Q: Zuo Jin Wan, a
Traditional Chinese Herbal Formula, Reverses P-gp-Mediated MDR In
Vitro and In Vivo. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2013:9570782013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sun H, Liu XD, Liu Q, Wang FP, Bao XQ and
Zhang D: Reversal of P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance
by the novel tetrandrine derivative W6. J Asian Nat Prod Res.
17:638–648. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jin Y, Zhang Z, Zhao T, Liu X and Jian L:
Mixed micelles of doxorubicin overcome multidrug resistance by
inhibiting the expression of P-Glycoprotein. J Biomed Nanotechnol.
11:1330–1338. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Beeran AA, Maliyakkal N, Rao CM and Udupa
N: The enriched fraction of Elephantopus scaber Triggers apoptosis
and inhibits multi-drug resistance transporters in human epithelial
cancer cells. Pharmacogn Mag. 11:257–268. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Agarwal A, Ayaz A, Samanta L, Sharma R,
Assidi M, Abuzenadah AM and Sabanegh E: Comparative proteomic
network signatures in seminal plasma of infertile men as a function
of reactive oxygen species. Clin Proteomics. 12:232015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lo YL, Wang W and Ho CT:
7,3′,4′-Trihydroxyisoflavone modulates multidrug resistance
transporters and induces apoptosis via production of reactive
oxygen species. Toxicology. 302:221–232. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pandey V, Chaube B and Bhat MK:
Hyperglycemia regulates MDR-1, drug accumulation and ROS levels
causing increased toxicity of carboplatin and 5-fluorouracil in
MCF-7 cells. J Cell Biochem. 112:2942–2952. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wei N, Liu GT, Chen XG, Liu Q, Wang FP and
Sun H: H1, a derivative of Tetrandrine, exerts anti-MDR activity by
initiating intrinsic apoptosis pathway and inhibiting the
activation of Erk1/2 and Akt1/2. Biochem Pharmacol. 82:1593–1603.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Singer E, Judkins J, Salomonis N, Matlaf
L, Soteropoulos P, McAllister S and Soroceanu L: Reactive oxygen
species-mediated therapeutic response and resistance in
glioblastoma. Cell Death Dis. 6:e16012015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Brozovic A, Ambriović-Ristov A and Osmak
M: The relationship between cisplatin-induced reactive oxygen
species, glutathione, and BCL-2 and resistance to cisplatin. Crit
Rev Toxicol. 40:347–359. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Okon IS and Zou MH: Mitochondrial ROS and
cancer drug resistance: Implications for therapy. Pharmacol Res.
100:170–174. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Okon IS, Coughlan KA, Zhang M, Wang Q and
Zou MH: Gefitinib-mediated reactive oxygen specie (ROS) instigates
mitochondrial dysfunction and drug resistance in lung cancer cells.
J Biol Chem. 290:9101–9110. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Su Z, Chen M, Xiao Y, Sun M, Zong L,
Asghar S, Dong M, Li H, Ping Q and Zhang C: ROS-triggered and
regenerating anticancer nanosystem: An effective strategy to subdue
tumor's multidrug resistance. J Control Release. 196:370–383. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hao Y, Lin C, Fan H, Yu Y, Li N and Chen
S: Proteomic analysis of Cucumis sativus cotyledons after
glucohexaose treatment as a part of ROS accumulation related
resistance mechanism. Proteome Sci. 12:342014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|