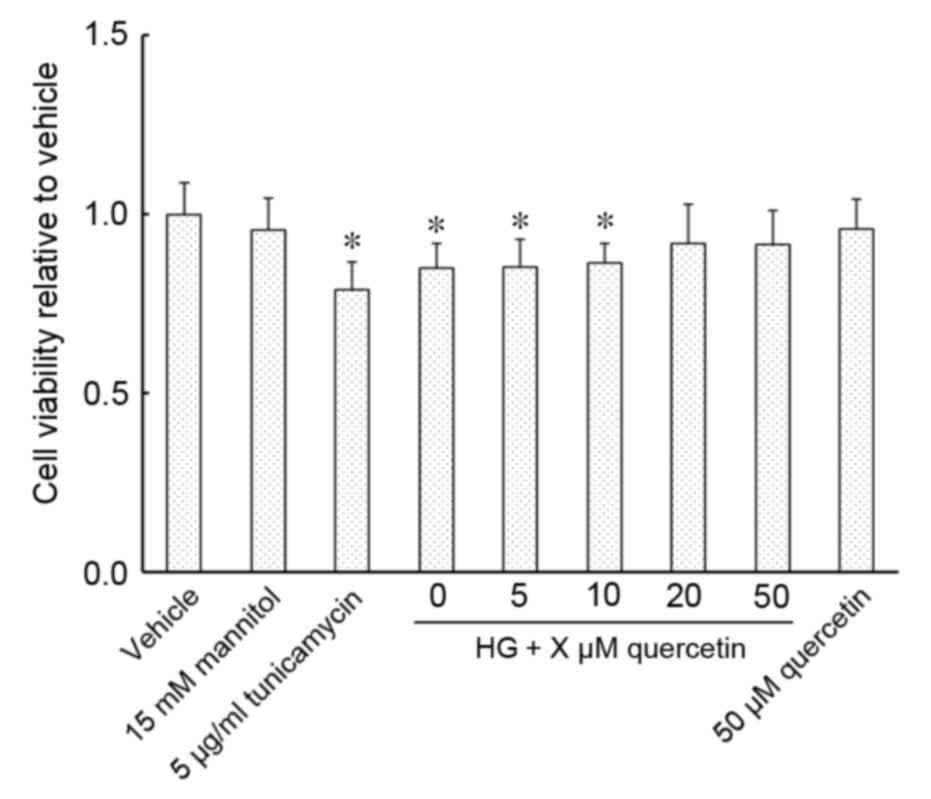
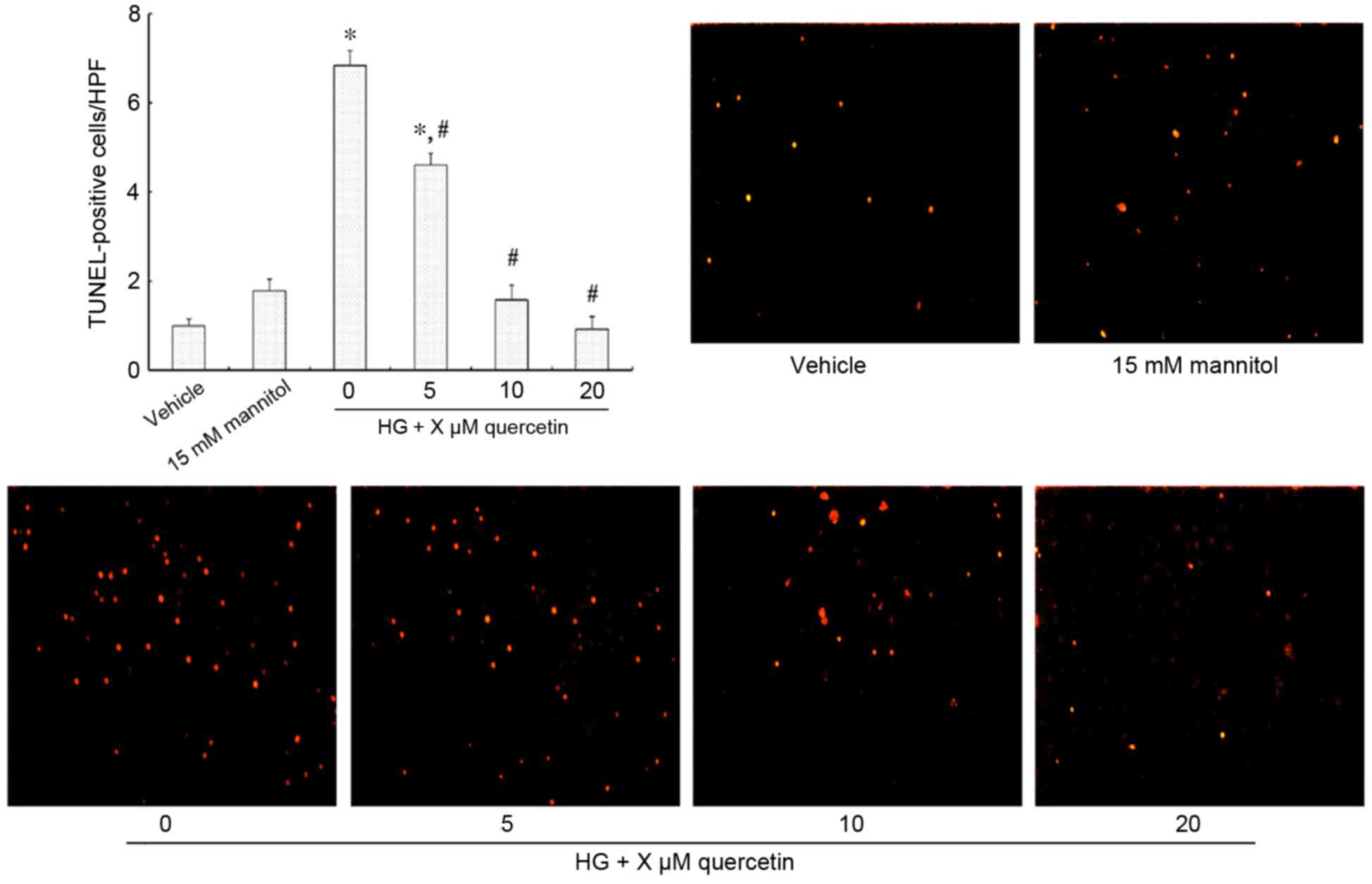
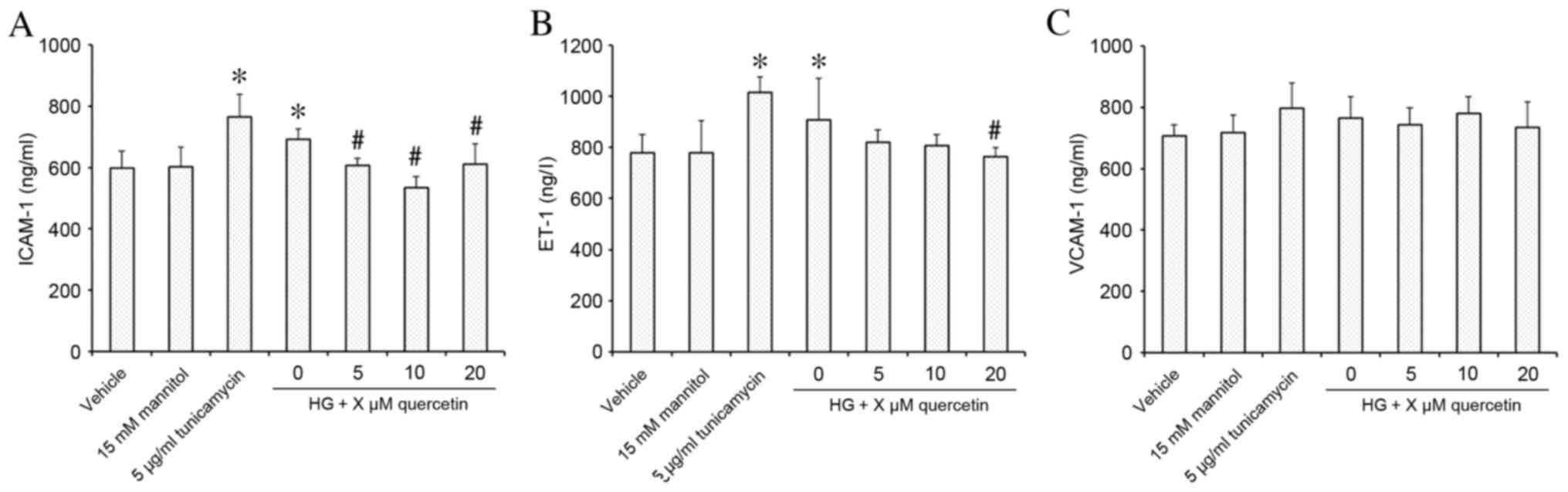
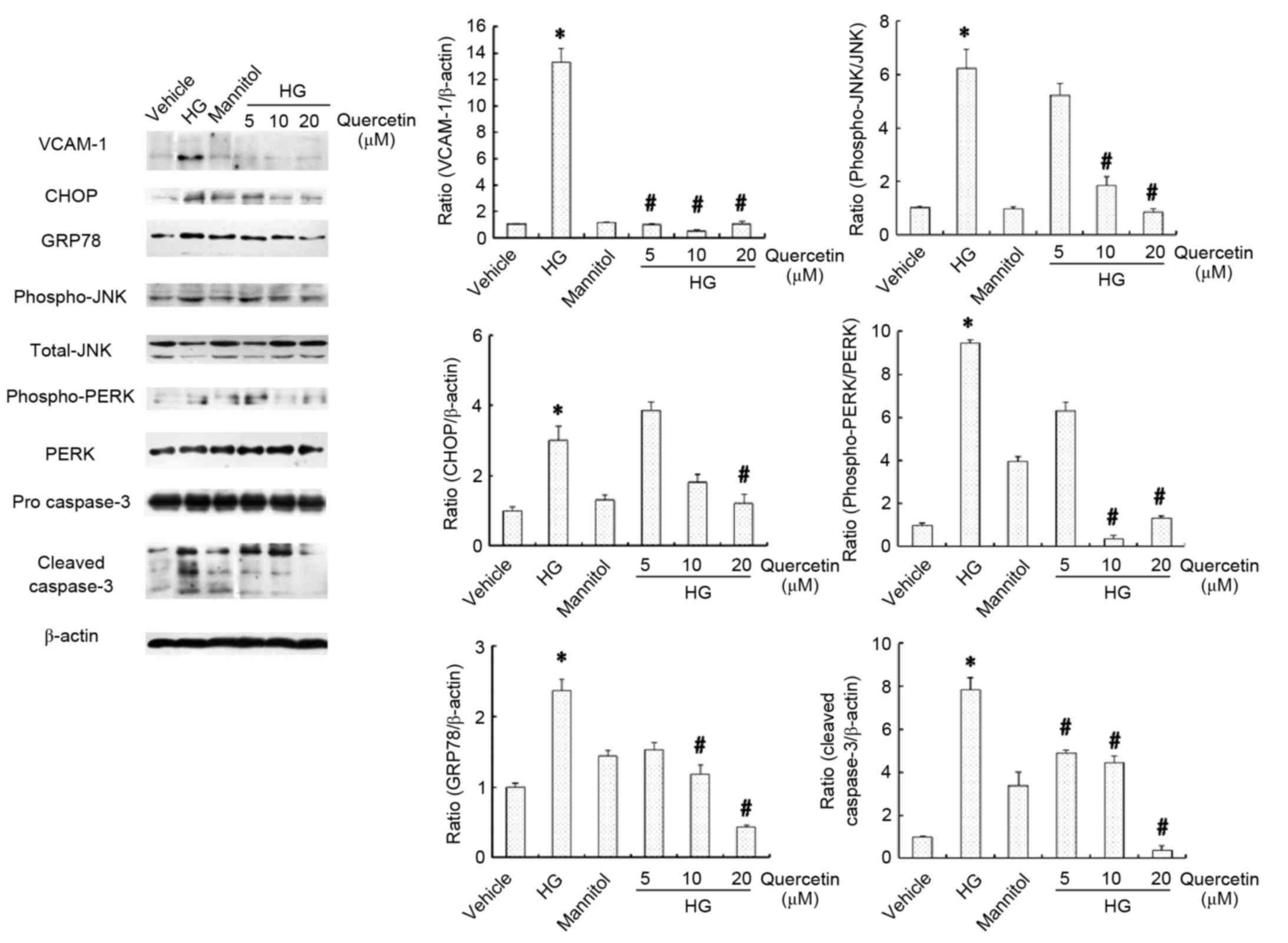
|
1
|
Juutilainen A, Lehto S, Rönnemaa T,
Pyörälä K and Laakso M: Type 2 diabetes as a ‘coronary heart
disease equivalent’: An 18-year prospective population-based study
in Finnish subjects. Diabetes Care. 28:2901–2907. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Haffner SM, Lehto S, Rönnemaa T, Pyörälä K
and Laakso M: Mortality from coronary heart disease in subjects
with type 2 diabetes and in nondiabetic subjects with and without
prior myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 339:229–234. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Han S, Liang CP, DeVries-Seimon T,
Ranalletta M, Welch CL, Collins-Fletcher K, Accili D, Tabas I and
Tall AR: Macrophage insulin receptor deficiency increases ER
stressinduced apoptosis and necrotic core formation in advanced
atherosclerotic lesions. Cell Metab. 3:257–266. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Werstuck GH, Khan MI, Femia G, Kim AJ,
Tedesco V, Trigatti B and Shi Y: Glucosamine-induced endoplasmic
reticulum dysfunction is associated with accelerated
atherosclerosis in a hyperglycemic mouse model. Diabetes.
55:93–101. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Marciniak SJ and Ron D: Endoplasmic
reticulum stress signaling in disease. Physiol Rev. 86:1133–1149.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hotamisligil GS: Endoplasmic reticulum
stress and atherosclerosis. Nat Med. 16:396–399. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Khan MI, Pichna BA, Shi Y, Bowes AJ and
Werstuck GH: Evidence supporting a role for endoplasmic reticulum
stress in the development of atherosclerosis in a hyperglycaemic
mouse model. Antioxid Redox Signal. 11:2289–2298. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhou J, Lhoták S, Hilditch BA and Austin
RC: Activation of the unfolded protein response occurs at all
stages of atherosclerotic lesion development in apolipoprotein
E-deficient mice. Circulation. 111:1814–1821. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kim AJ, Shi Y, Austin RC and Werstuck GH:
Valproate protects cells from ER stress-induced lipid accumulation
and apoptosis by inhibiting glycogen synthase kinase-3. J Cell Sci.
118:89–99. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chen H, Ing BL, Robinson KA, Feagin AC,
Buse MG and Quon MJ: Effects of overexpression of glutamine:
Fructose-6-phosphate amidotransferase (GFAT) and glucosamine
treatment on translocation of GLUT4 in rat adipose cells. Mol Cell
Endocrinol. 135:67–77. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Defronzo RA: Insulin resistance,
lipotoxicity, type 2 diabetes and atherosclerosis: The missing
links. The Claude Bernard Lecture 2009. Diabetologi. 53:1270–1287.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Largo R, Martínez-Calatrava MJ,
Sánchez-Pernaute O, Marcos ME, Moreno-Rubio J, Aparicio C, Egido J
and Herrero-Beaumont G: Effect of a high dose of glucosamine on
systemic and tissue inflammation in an experimental model of
atherosclerosis aggravated by chronic arthritis. Am J Physiol Heart
Circ Physiol. 297:H268–H276. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rajapakse AG, Ming XF, Carvas JM and Yang
Z: O-linked beta-N-acetylglucosamine during hyperglycemia exerts
both anti-inflammatory and pro-oxidative properties in the
endothelial system. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2:172–175. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bao L, Cai X, Zhang Z and Li Y: Grape seed
procyanidin B2 ameliorates mitochondrial dysfunction and inhibits
apoptosis via the AMP-activated protein kinase-silent mating type
information regulation 2 homologue 1-PPARγ co-activator-1α axis in
rat mesangial cells under high-dose glucosamine. Br J Nutr.
113:35–44. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tabas I and Ron D: Integrating the
mechanisms of apoptosis induced by endoplasmic reticulum stress.
Nat Cell Biol. 13:184–190. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sano R and Reed JC: ER stress-induced cell
death mechanisms. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1833:3460–3470. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bahar E, Kim H and Yoon H: ER
stress-mediated signaling: Action potential and Ca(2+) as key
players. Int J Mol Sci. 17:E15582016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Garg R, Tripathy D and Dandona P: Insulin
resistance as a proinflammatory state: Mechanisms, mediators, and
therapeutic interventions. Curr Drug Targets. 4:487–492. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang K and Kaufman RJ: From
endoplasmic-reticulum stress to the inflammatory response. Nature.
454:455–462. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ozcan U, Yilmaz E, Ozcan L, Furuhashi M,
Vaillancourt E, Smith RO, Görgün CZ and Hotamisligil GS: Chemical
chaperones reduce ER stress and restore glucose homeostasis in a
mouse model of type 2 diabetes. Science. 313:1137–1140. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Russo M, Spagnuolo C, Tedesco I, Bilotto S
and Russo GL: The flavonoid quercetin in disease prevention and
therapy: Facts and fancies. Biochem Pharmacol. 83:6–15. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hertog MG, Kromhout D, Aravanis C,
Blackburn H, Buzina R, Fidanza F, Giampaoli S, Jansen A, Menotti A,
Nedeljkovic S, et al: Flavonoid intake and long-term risk of
coronary heart disease and cancer in the seven countries study.
Arch Intern Med. 155:381–386. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Egert S, Bosy-Westphal A, Seiberl J,
Kürbitz C, Settler U, Plachta-Danielzik S, Wagner AE, Frank J,
Schrezenmeir J, Rimbach G, et al: Quercetin reduces systolic blood
pressure and plasma oxidised low-density lipoprotein concentrations
in overweight subjects with a high-cardiovascular disease risk
phenotype: A double-blinded, placebo-controlled cross-over study.
Br J Nutr. 102:1065–1074. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Egert S, Boesch-Saadatmandi C, Wolffram S,
Rimbach G and Müller MJ: Serum lipid and blood pressure responses
to quercetin vary in overweight patients by apolipoprotein E
genotype. J Nutr. 140:278–284. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Duarte J, Pérez-Palencia R, Vargas F,
Ocete MA, Pérez-Vizcaino F, Zarzuelo A and Tamargo J:
Antihypertensive effects of the flavonoid quercetin in
spontaneously hypertensive rats. Br J Pharmacol. 133:117–124. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Juźwiak S, Wójcicki J, Mokrzycki K,
Marchlewicz M, Białecka M, Wenda-Rózewicka L, Gawrońska-Szklarz B
and Droździk M: Effect of quercetin on experimental hyperlipidemia
and atherosclerosis in rabbits. Pharmacol Rep. 57:604–609.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Motoyama K, Koyama H, Moriwaki M, Emura K,
Okuyama S, Sato E, Inoue M, Shioi A and Nishizawa Y:
Atheroprotective and plaque-stabilizing effects of enzymatically
modified isoquercitrin in atherogenic apoE-deficient mice.
Nutrition. 25:421–427. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chuang CC, Martinez K, Xie G, Kennedy A,
Bumrungpert A, Overman A, Jia W and McIntosh MK: Quercetin is
equally or more effective than resveratrol in attenuating tumor
necrosis factor-{alpha}-mediated inflammation and insulin
resistance in primary human adipocytes. Am J Clin Nutr.
92:1511–1521. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ortega MG, Saragusti AC, Cabrera JL and
Chiabrando GA: Quercetin tetraacetyl derivative inhibits
LPS-induced nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) expression in J774A.1
cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 498:105–110. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lara-Guzman OJ, Tabares-Guevara JH,
Leon-Varela YM, Álvarez RM, Roldan M, Sierra JA, Londoño-Londoño JA
and Ramirez-Pineda JR: Proatherogenic macrophage activities are
targeted by the flavonoid quercetin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther.
343:296–306. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kleemann R, Verschuren L, Morrison M,
Zadelaar S, van Erk MJ, Wielinga PY and Kooistra T:
Anti-inflammatory, anti-proliferative and anti-atherosclerotic
effects of quercetin in human in vitro and in vivo models.
Atherosclerosis. 218:44–52. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li YQ, Zhou FC, Gao F, Bian JS and Shan F:
Comparative evaluation of quercetin, isoquercetin and rutin as
inhibitors of alpha-glucosidase. J Agric Food Chem. 57:11463–11468.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Dai X, Ding Y, Zhang Z, Cai X, Bao L and
Li Y: Quercetin but not quercitrin ameliorates tumor necrosis
factor-alpha-induced insulin resistance in C2C12 skeletal muscle
cells. Biol Pharm Bull. 36:788–795. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Suganya N, Bhakkiyalakshmi E,
Suriyanarayanan S, Paulmurugan R and Ramkumar KM: Quercetin
ameliorates tunicamycin-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress in
endothelial cells. Cell Prolif. 47:231–240. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chao CL, Hou YC, Chao PD, Weng CS and Ho
FM: The antioxidant effects of quercetin metabolites on the
prevention of high glucose-induced apoptosis of human umbilical
vein endothelial cells. Br J Nutr. 101:1165–1170. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhao B, Zhang Y, Liu B, Nawroth P and
Dierichs R: Endothelial cells injured by oxidized low density
lipoprotein. Am J Hematol. 49:250–252. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yao S, Sang H, Song G, Yang N, Liu Q,
Zhang Y, Jiao P, Zong C and Qin S: Quercetin protects macrophages
from oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced apoptosis by
inhibiting the endoplasmic reticulum stress-C/EBP homologous
protein pathway. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 237:822–831. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Larson A, Witman MA, Guo Y, Ives S,
Richardson RS, Bruno RS, Jalili T and Symons JD: Acute,
quercetin-induced reductions in blood pressure in hypertensive
individuals are not secondary to lower plasma
angiotensin-converting enzyme activity or endothelin-1: Nitric
oxide. Nutr Res. 32:557–564. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ding Y, Zhang ZF, Dai XQ and Li Y:
Myricetin protects against cytokine- induced cell death in RIN-m5f
β cells. J Med Food. 15:733–740. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Siawaya JF Djoba, Roberts T, Babb C, Black
G, Golakai HJ, Stanley K, Bapela NB, Hoal E, Parida S, van Helden P
and Walzl G: An evaluation of commercial fluorescent bead-based
luminex cytokine assays. PLoS One. 3:e25352008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Matěj R, Smětáková M, Vašáková M, Nováková
J, Sterclová M, Kukal J, Olejár Tětáková M, Vašáková M, Nováková J,
Sterclová M, Kukal J and Olejár TT: PAR-2, IL-4R, TGF-β and TNF-α
in bronchoalveolar lavage distinguishes extrinsic allergic
alveolitis from sarcoidosis. Exp Ther Med. 8:533–538.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kelly GS: Pantothenic acid. Monograph.
Altern Med Rev. 16:263–274. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Azuma K, Ippoushi K, Ito H, Horie H and
Terao J: Enhancing effect of lipids and emulsifiers on the
accumulation of quercetin metabolites in blood plasma after the
short-term ingestion of onion by rats. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem.
67:2548–2555. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Walle T, Walle UK and Halushka PV: Carbon
dioxide is the major metabolite of quercetin in humans. J Nutr.
131:2648–2652. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Fiorentino TV, Procopio T, Mancuso E,
Arcidiacono GP, Andreozzi F, Arturi F, Sciacqua A, Perticone F,
Hribal ML and Sesti G: SRT1720 counteracts glucosamine-induced
endoplasmic reticulum stress and endothelial dysfunction.
Cardiovasc Res. 107:295–306. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Gouze JN, Gouze E, Popp MP, Bush ML,
Dacanay EA, Kay JD, Levings PP, Patel KR, Saran JP, Watson RS and
Ghivizzani SC: Exogenous glucosamine globally protects chondrocytes
from the arthritogenic effects of IL-1beta. Arthritis Res Ther.
8:R1732006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ross R: Atherosclerosis-an inflammatory
disease. N Engl J Med. 340:115–126. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Lusis AJ: Atherosclerosis. Nature.
407:233–241. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Altannavch TS, Roubalová K, Kucera P and
Andel M: Effect of high glucose concentrations on expression of
ELAM-1, VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 in HUVEC with and without cytokine
activation. Physiol Res. 53:77–82. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Azcutia V, Abu-Taha M, Romacho T,
Vázquez-Bella M, Matesanz N, Luscinskas FW, Rodríguez-Mañas L, Sanz
MJ, Sánchez-Ferrer CF and Peiró C: Inflammation determines the
pro-adhesive properties of high extracellular d-glucose in human
endothelial cells in vitro and rat microvessels in vivo. PLoS One.
5:e100912010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Panicker SR, Sreenivas P, Babu MS,
Karunagaran D and Kartha CC: Quercetin attenuates Monocyte
Chemoattractant Protein-1 gene expression in glucose primed aortic
endothelial cells through NF-kappaB and AP-1. Pharmacol Res.
62:328–336. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Wu Z, Xiong Y, Gajanayake T, Ming XF and
Yang Z: p38 Mitogen-activated protein kinase is required for
glucosamine-induced endothelial nitric oxide synthase uncoupling
and plasminogen-activator inhibitor expression. Circ J.
76:2015–2022. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Lima VV, Giachini FR, Carneiro FS,
Carvalho MH, Fortes ZB, Webb RC and Tostes RC: O-GlcNAcylation
contributes to the vascular effects of ET-1 via activation of the
RhoA/Rho-kinase pathway. Cardiovasc Res. 89:614–622. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Wu-Wong JR, Berg CE and Dayton BD:
Endothelin-stimulated glucose uptake: Effects of intracellular
Ca(2+), cAMP and glucosamine. Clin Sci (Lond). 103:418S–423S. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Qiu W, Su Q, Rutledge AC, Zhang J and
Adeli K: Glucosamine-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress
attenuates apolipoprotein B100 synthesis via PERK signaling. J
Lipid Res. 50:1814–1823. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Urano F, Wang X, Bertolotti A, Zhang Y,
Chung P, Harding HP and Ron D: Coupling of stress in the ER to
activation of JNK protein kinases by transmembrane protein kinase
IRE1. Science. 287:664–666. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Xu C, Bailly-Maitre B and Reed JC:
Endoplasmic reticulum stress: Cell life and death decisions. J Clin
Invest. 115:2656–2664. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|