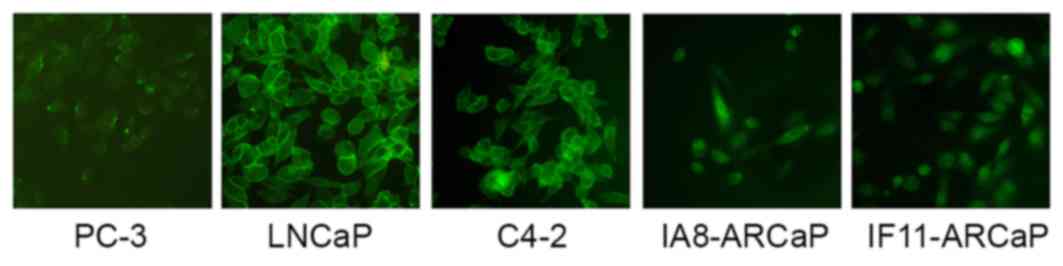
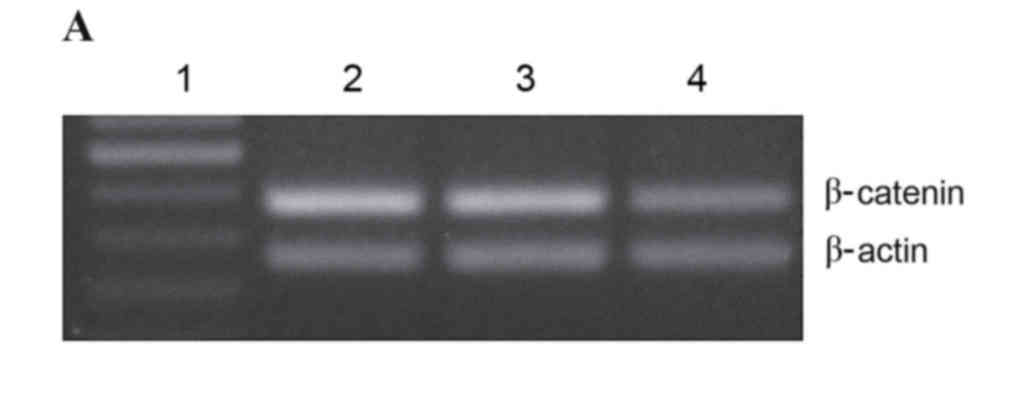
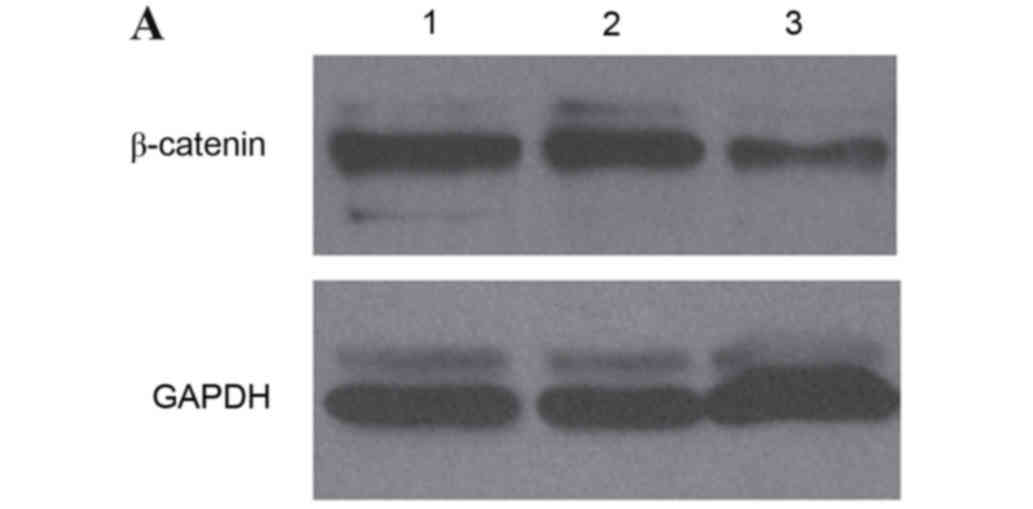
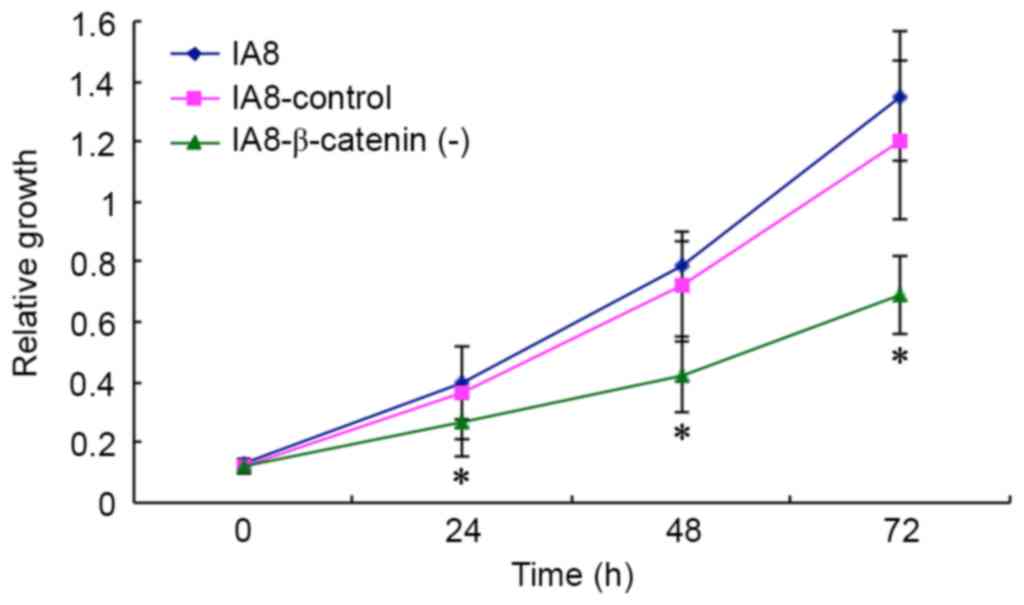
|
1
|
Keller ET, Zhang J, Cooper CR, Smith PC,
McCauley LK, Pienta KJ and Taichman RS: Prostate carcinoma skeletal
metastases: Cross-talk between tumor and bone. Cancer Metastasis
Rev. 20:333–349. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fodde R and Brabletz T: Wnt/beta-catenin
signaling in cancer stemness and malignant behavior. Curr Opin Cell
Biol. 19:150–158. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Guturi KK, Mandal T, Chatterjee A, Sarkar
M, Bhattacharya S, Chatterjee U and Ghosh MK: Mechanism of
β-catenin-mediated transcriptional regulation of epidermal growth
factor receptor expression in glycogen synthase kinase 3
β-inactivated prostate cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 287:18287–18296.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chen G, Shukeir N, Potti A, Sircar K,
Aprikian A, Goltzman D and Rabbani SA: Up-regulation of Wnt-1 and
beta-catenin production in patients with advanced metastatic
prostate carcinoma: Potential pathogenetic and prognostic
implications. Cancer. 101:1345–1356. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Luo Y, He DL, Ning L, Shen SL, Li L and Li
X: Hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha induces the
epithelial-mesenchymal transition of human prostatecancer cells.
Chin Med J (Engl). 119:713–718. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhao JH, Luo Y, Jiang YG, He DL and Wu CT:
Knockdown of β-catenin through shRNA cause a reversal of EMT and
metastatic phenotypes induced by HIF-1α. Cancer Invest. 29:377–382.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jiang YG, Luo Y, He DL, Li X, Zhang LL,
Peng T, Li MC and Lin YH: Role of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling
pathway in epithelial-mesenchymal transition of human prostate
cancer induced by hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha. Int J Urol.
14:1034–1039. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Schmalhofer O, Brabletz S and Brabletz T:
E-cadherin, beta-catenin, and ZEB1 in malignant progression of
cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 28:151–166. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gilbert-Sirieix M, Makoukji J, Kimura S,
Talbot M, Caillou B, Massaad C and Massaad-Massade L: Wnt/β-catenin
signaling pathway is a direct enhancer of thyroid transcription
factor-1 in human papillary thyroid carcinoma cells. PLoS One.
6:e222802011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xu WH, Liu ZB, Yang C, Qin W and Shao ZM:
Expression of dickkopf-1 and beta-catenin related to the prognosis
of breast cancer patients with triple negative phenotype. PLoS One.
7:e376242012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cai C and Zhu X: The Wnt/β-catenin pathway
regulates self-renewal of cancer stem-like cells in human gastric
cancer. Mol Med Report. 5:1191–1196. 2012.
|
|
12
|
Cui J, Jiang W, Wang S, Wang L and Xie K:
Role of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in drug resistance of pancreatic
cancer. Curr Pharm Des. 18:2464–2471. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hall CL, Bafico A, Dai J, Aaronson SA and
Keller ET: Prostate cancer cells promote osteoblastic bone
metastases through Wnts. Cancer Res. 65:7554–7560. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhau HE, Odero-Marah V, Lue HW, Nomura T,
Wang R, Chu G, Liu ZR, Zhou BP, Huang WC and Chung LW: Epithelial
to mesenchymal transition (EMT) in human prostate cancer: Lessons
learned from ARCaP model. Clin Exp Metastasis. 25:601–610. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Fire A, Xu S, Montgomery MK, Kostas SA,
Driver SE and Mello CC: Potent and specific genetic interference by
double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 391:806–811.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Elbashir SM, Harborth J, Lendeckel W,
Yalcin A, Weber K and Tuschl T: Duplexes of 21-nucleotide RNAs
mediate RNA interference in cultured mammalian cells. Nature.
411:494–498. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|