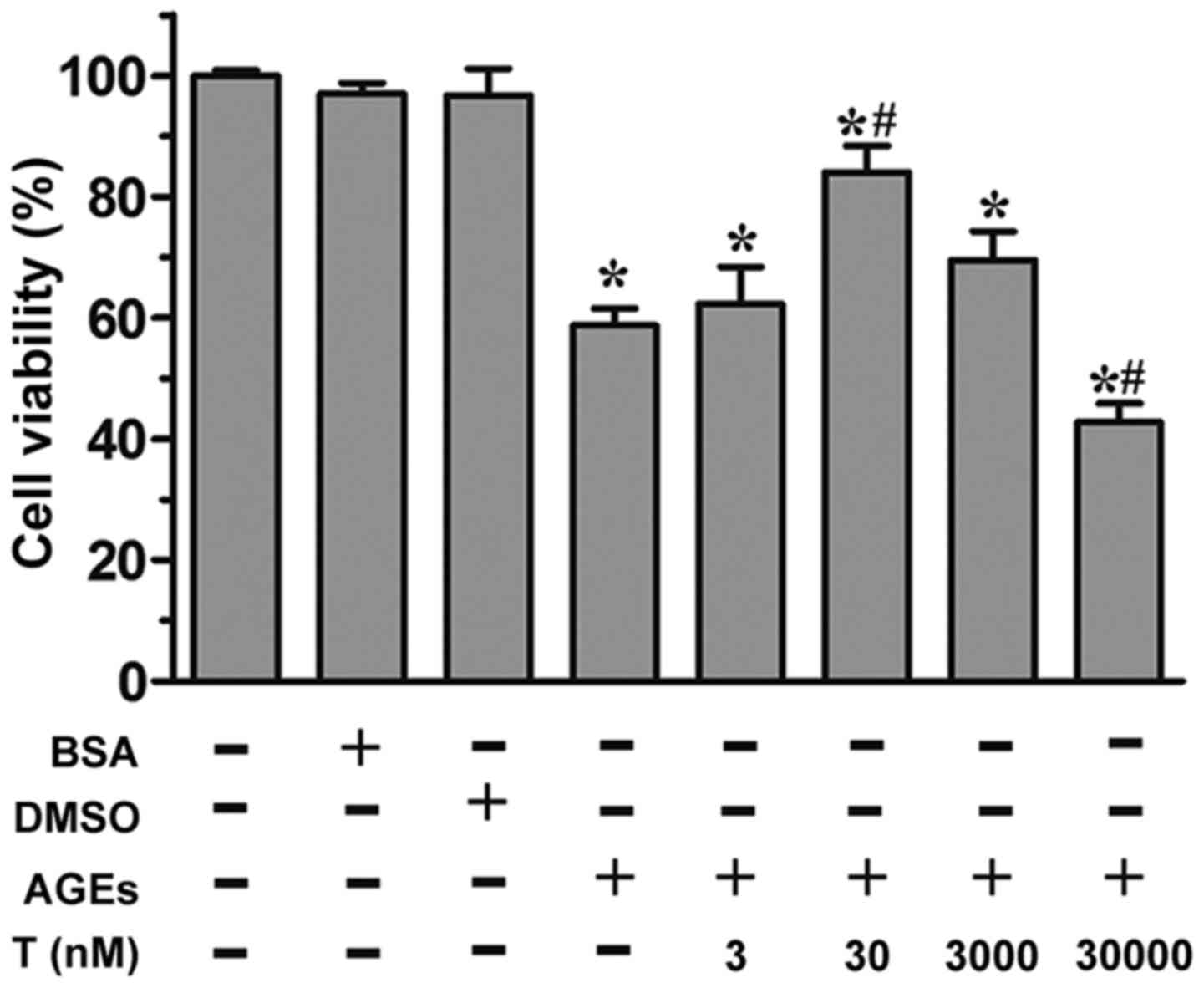
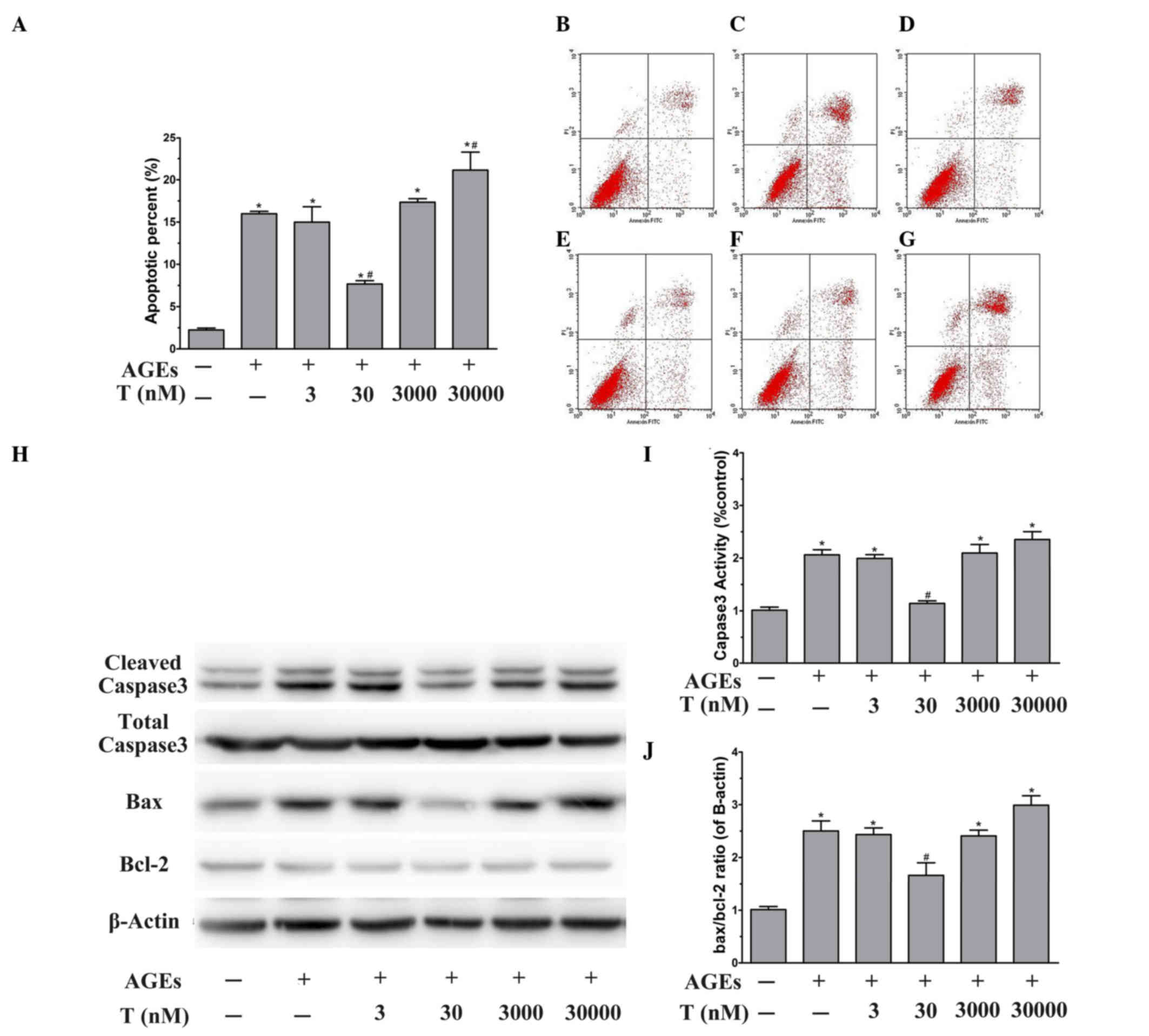
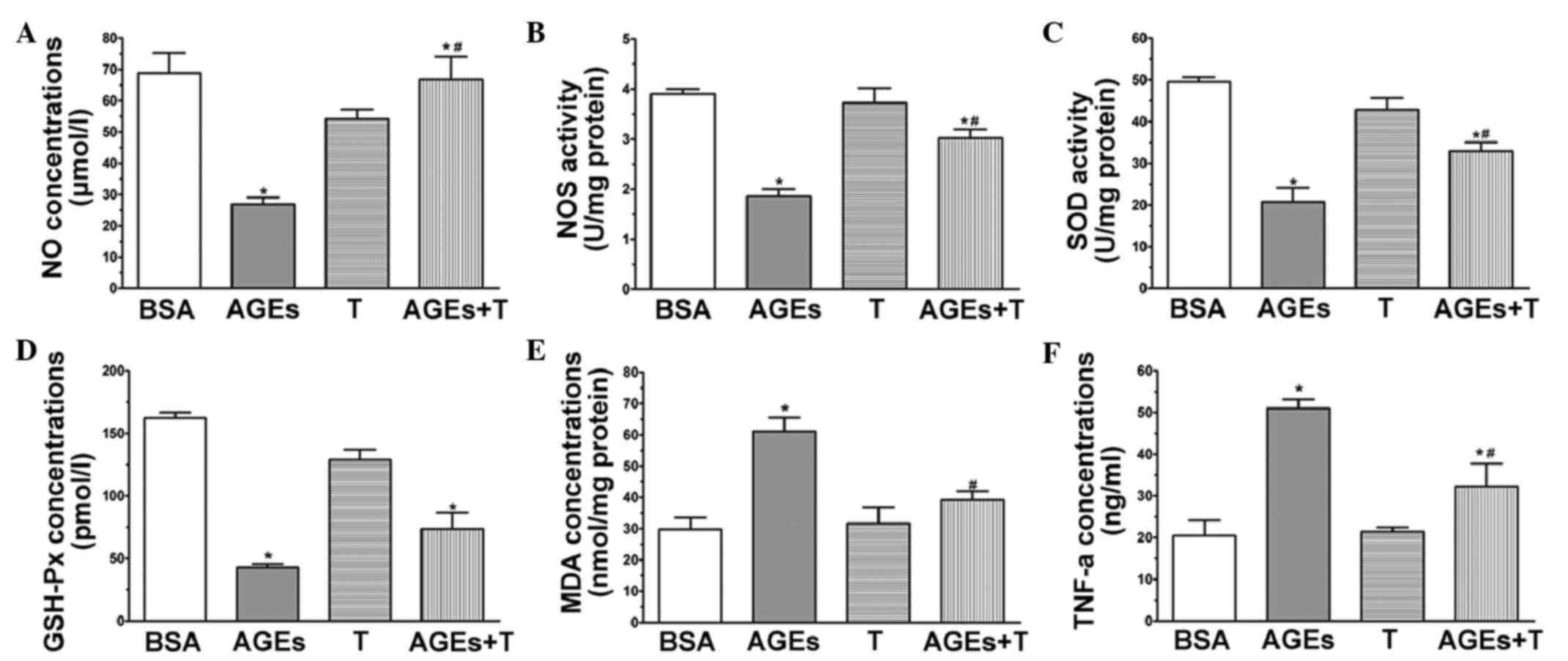
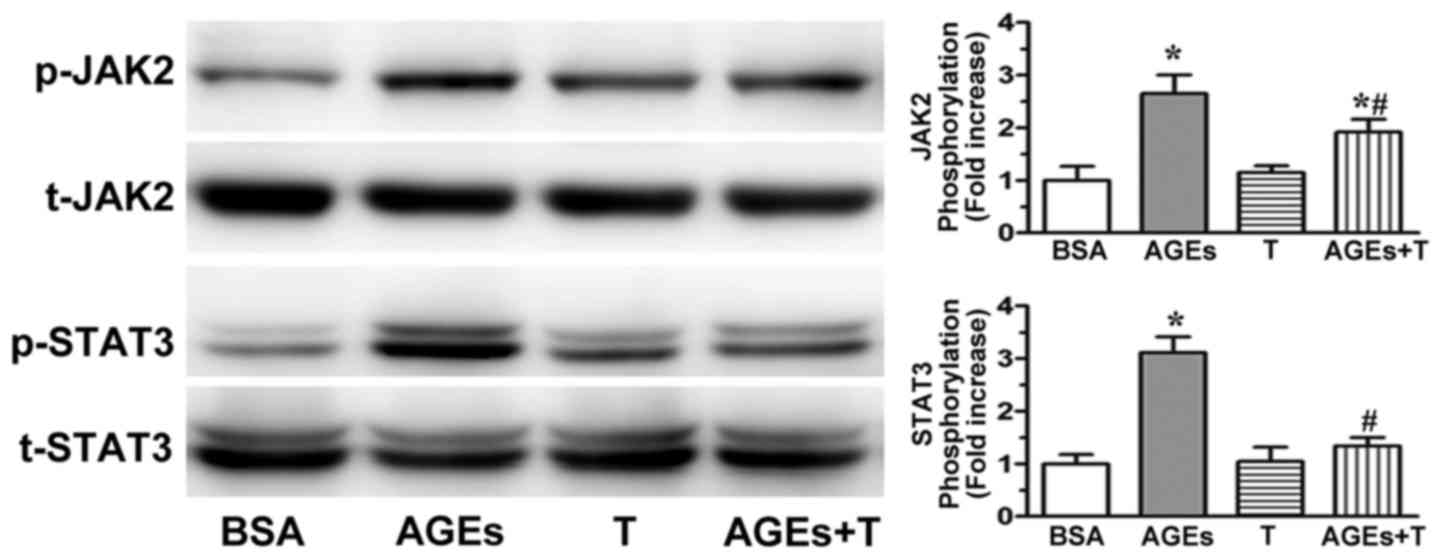
|
1
|
Rahman S, Rahman T, Ismail AA and Rashid
AR: Diabetes-associated macrovasculopathy: Pathophysiology and
pathogenesis. Diabetes Obes Metab. 9:767–780. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cooper ME, Bonnet F, Oldfield M and
Jandeleit-Dahm K: Mechanisms of diabetic vasculopathy: An overview.
Am J Hypertens. 14:475–486. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Neves D: Advanced glycation end-products:
A common pathway in diabetes and age-related erectile dysfunction.
Free Radic Res 47 Suppl. 1:49–69. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Prasad A, Bekker P and Tsimikas S:
Advanced glycation end products and diabetic cardiovascular
disease. Cardiol Rev. 20:177–183. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Basta G, Schmidt AM and De Caterina R:
Advanced glycation end products and vascular inflammation:
Implications for accelerated atherosclerosis in diabetes.
Cardiovasc Res. 63:582–592. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Goldin A, Beckman JA, Schmidt AM and
Creager MA: Advanced glycation end products: Sparking the
development of diabetic vascular injury. Circulation. 114:597–605.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Min C, Kang E, Yu SH, Shinn SH and Kim YS:
Advanced glycation end products induce apoptosis and procoagulant
activity in cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells.
Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 46:197–202. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mendelsohn ME and Karas RH: The protective
effects of estrogen on the cardiovascular system. N Engl J Med.
340:1801–1811. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bagatell CJ and Bremner WJ: Androgens in
men-uses and abuses. N Engl J Med. 334:707–714. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sullivan ML, Martinez CM, Gennis P and
Gallagher EJ: The cardiac toxicity of anabolic steroids. Prog
Cardiovasc Dis. 41:1–15. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jones RD, Nettleship JE, Kapoor D, Jones
HT and Channer KS: Testosterone and atherosclerosis in aging men:
Purported association and clinical implications. Am J Cardiovasc
Drugs. 5:141–154. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Choi BG and McLaughlin MA: Why men's
hearts break: Cardiovascular effects of sex steroids. Endocrinol
Metab Clin North Am. 36:365–377. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Smith AM, English KM, Malkin CJ, Jones RD,
Jones TH and Channer KS: Testosterone does not adversely affect
fibrinogen or tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) and plasminogen
activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) levels in 46 men with chronic stable
angina. Eur J Endocrinol. 152:285–291. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Adams MR, Williams JK and Kaplan JR:
Effects of androgens on coronary artery atherosclerosis and
atherosclerosis-related impairment of vascular responsiveness.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 15:562–570. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Nathan L, Shi W, Dinh H, Mukherjee TK,
Wang X, Lusis AJ and Chaudhuri G: Testosterone inhibits early
atherogenesis by conversion to estradiol: Critical role of
aromatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:3589–3593. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
English KM, Mandour O, Steeds RP, Diver
MJ, Jones TH and Channer KS: Men with coronary artery disease have
lower levels of androgens than men with normal coronary angiograms.
Eur Heart J. 21:890–894. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Jin H, Lin J, Fu L, Mei YF, Peng G, Tan X,
Wang DM, Wang W and Li YG: Physiological testosterone stimulates
tissue plasminogen activator and tissue factor pathway inhibitor
and inhibits plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 release in
endothelial cells. Biochem Cell Biol. 85:246–251. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jin H, Wang DY, Mei YF, Qiu WB, Zhou Y,
Wang DM, Tan XR and Li YG: Mitogen-activated protein kinases
pathway is involved in physiological testosterone-induced tissue
factor pathway inhibitor expression in endothelial cells. Blood
Coagul Fibrinolysis. 21:420–424. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cai J, Hong Y, Weng C, Tan C,
Imperato-McGinley J and Zhu YS: Androgen stimulates endothelial
cell proliferation via an androgen receptor/VEGF/cyclin A-mediated
mechanism. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 300:H1210–H1221. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yu J, Akishita M, Eto M, Ogawa S, Son BK,
Kato S, Ouchi Y and Okabe T: Androgen receptor-dependent activation
of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in vascular endothelial cells:
Role of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/akt pathway. Endocrinology.
151:1822–1828. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xu Y, Feng L, Wang S, Zhu Q, Zheng Z,
Xiang P, He B and Tang D: Calycosin protects HUVECs from advanced
glycation end products-induced macrophage infiltration. J
Ethnopharmacol. 137:359–370. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhuang X, Pang X, Zhang W, Wu W, Zhao J,
Yang H and Qu W: Effects of zinc and manganese on advanced
glycation end products (AGEs) formation and AGEs-mediated
endothelial cell dysfunction. Life Sci. 90:131–139. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Rashid G, Benchetrit S, Fishman D and
Bernheim J: Effect of advanced glycation end-products on gene
expression and synthesis of TNF-alpha and endothelial nitric oxide
synthase by endothelial cells. Kidney Int. 66:1099–1106. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Grimm S, Ott C, Horlacher M, Weber D, Hohn
A and Grune T: Advanced-glycation-end-product-induced formation of
immunoproteasomes: Involvement of RAGE and Jak2/STAT1. Biochem J.
448:127–139. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nedić O, Rattan SI, Grune T and Trougakos
IP: Molecular effects of advanced glycation end products on cell
signalling pathways, ageing and pathophysiology. Free Radic Res.
47:(Suppl 1). S28–S38. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Rodiño-Janeiro BK, González-Peteiro M,
Ucieda-Somoza R, González-Juanatey JR and Alvarez E: Glycated
albumin, a precursor of advanced glycation end-products,
up-regulates NADPH oxidase and enhances oxidative stress in human
endothelial cells: Molecular correlate of diabetic vasculopathy.
Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 26:550–558. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Orasanu G and Plutzky J: The pathologic
continuum of diabetic vascular disease. J Am Coll Cardiol.
53:(Suppl 5). S35–S42. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Méndez JD, Xie J, Aguilar-Hernández M and
Méndez-Valenzuela V: Trends in advanced glycation end products
research in diabetes mellitus and its complications. Mol Cell
Biochem. 341:33–41. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sang HQ, Gu JF, Yuan JR, Zhang MH, Jia XB
and Feng L: The protective effect of Smilax glabra extract
on advanced glycation end products-induced endothelial dysfunction
in HUVECs via RAGE-ERK1/2-NF-κB pathway. J Ethnopharmacol.
155:785–795. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Alexandersen P, Haarbo J, Byrjalsen I,
Lawaetz H and Christiansen C: Natural androgens inhibit male
atherosclerosis: A study in castrated, cholesterol-fed rabbits.
Circ Res. 84:813–819. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Nettleship JE, Jones TH, Channer KS and
Jones RD: Physiological testosterone replacement therapy attenuates
fatty streak formation and improves high-density lipoprotein
cholesterol in the Tfm mouse: An effect that is independent of the
classic androgen receptor. Circulation. 116:2427–2434. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hulsmans M and Holvoet P: The vicious
circle between oxidative stress and inflammation in
atherosclerosis. J Cell Mol Med. 14:70–78. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ho E, Galougahi Karimi K, Liu CC, Bhindi R
and Figtree GA: Biological markers of oxidative stress:
Applications to cardiovascular research and practice. Redox Biol.
1:483–491. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Allen JD, Giordano T and Kevil CG: Nitrite
and nitric oxide metabolism in peripheral artery disease. Nitric
Oxide. 26:217–222. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Huang JS, Guh JY, Hung WC, Yang ML, Lai
YH, Chen HC and Chuang LY: Role of the Janus kinase (JAK)/signal
transducters and activators of transcription (STAT) cascade in
advanced glycation end-product-induced cellular mitogenesis in
NRK-49F cells. Biochem J. 342:231–238. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|