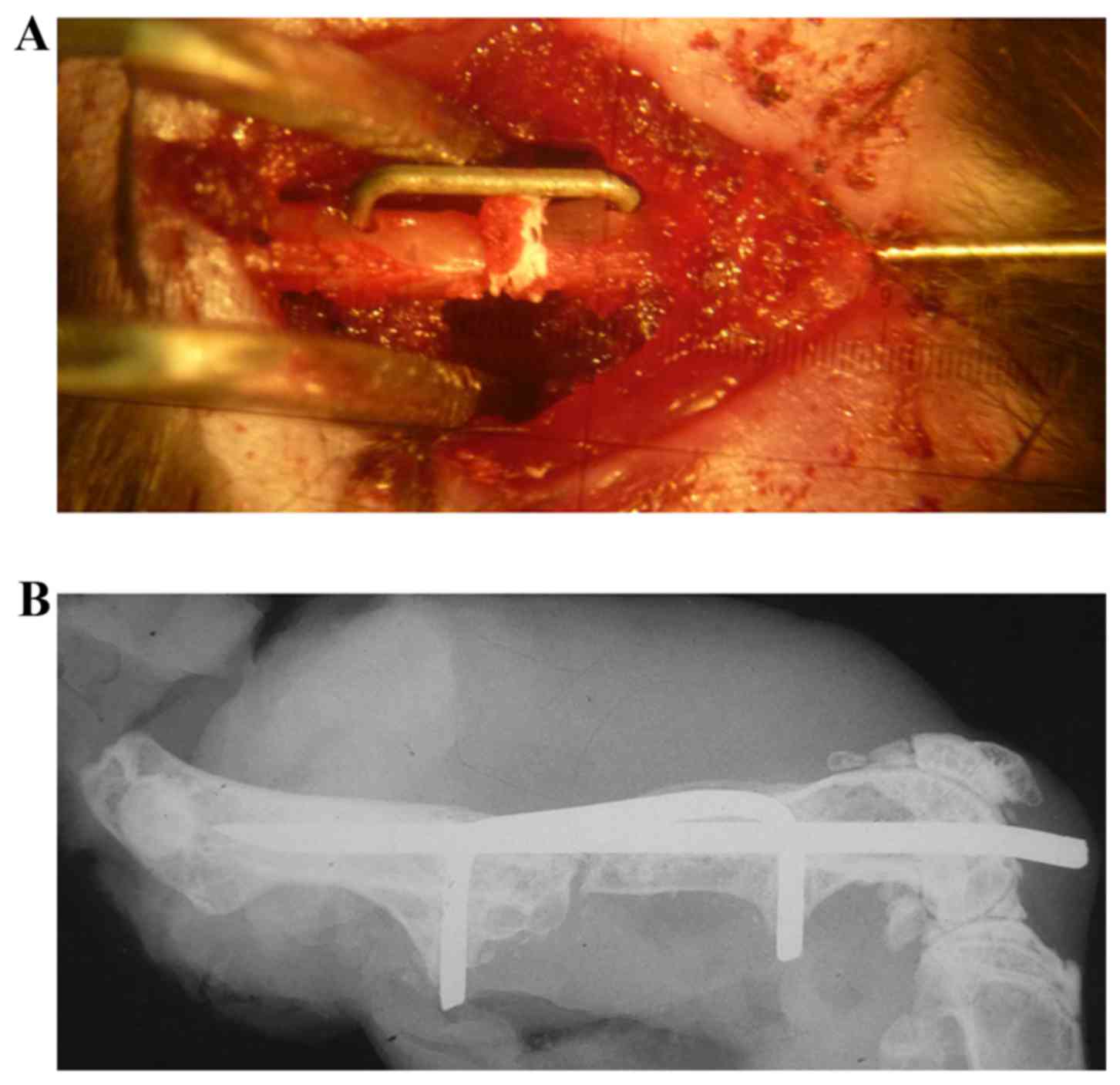
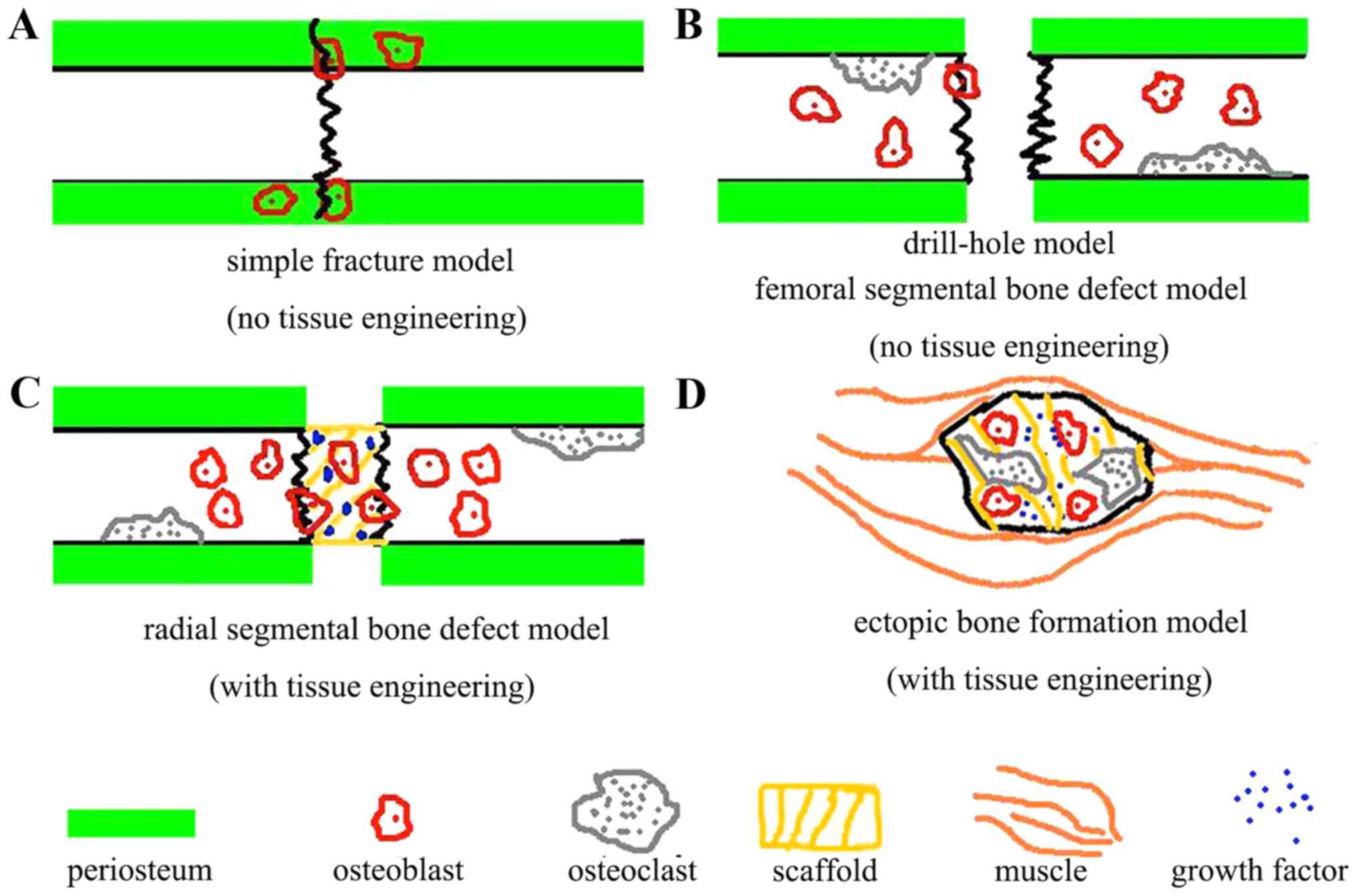
|
1
|
Gomes PS and Fernandes MH: Rodent models
in bone-related research: The relevance of calvarial defects in the
assessment of bone regeneration strategies. Lab Anim. 45:14–24.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hobby B and Lee MA: Managing atrophic
nonunion in the geriatric population: Incidence, distribution and
causes. Orthop Clin North Am. 44:251–256. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Edwards BJ, Bunta AD, Lane J, Odvina C,
Rao DS, Raisch DW, McKoy JM, Omar I, Belknap SM, Garg V, et al:
Bisphosphonates and nonhealing femoral fractures: Analysis of the
FDA adverse event reporting system (FAERS) and international safety
efforts: A systematic review from the research on adverse drug
events and reports (RADAR) project. J Bone Joint Surg Am.
95:297–307. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kleinschmidt K, Ploeger F, Nickel J,
Glockenmeier J, Kunz P and Richter W: Enhanced reconstruction of
long bone architecture by a growth factor mutant combining positive
features of GDF-5 and BMP-2. Biomaterials. 34:5926–5936. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhang X, Zara J, Siu RK, Ting K and Soo C:
The role of NELL-1, a growth factor associated with
craniosynostosis, in promoting bone regeneration. J Dent Res.
89:865–878. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhao YP, Tian QY and Liu CJ: Progranulin
deficiency exaggerates, whereas progranulin-derived Atsttrin
attenuates, severity of dermatitis in mice. FEBS Lett.
587:1805–1810. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Szpalski C, Barr J, Wetterau M, Saadeh PB
and Warren SM: Cranial bone defects: Current and future strategies.
Neurosurgical Focus. 29:E82010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wahl EC, Aronson J, Liu L, Skinner RA,
Ronis MJ and Lumpkin CK Jr: Distraction osteogenesis in TNF
receptor 1 deficient mice is protected from chronic ethanol
exposure. Alcohol. 46:133–138. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang X, Péault B, Chen W, Li W, Corselli
M, James AW, Lee M, Siu RK, Shen P, Zheng Z, et al: The Nell-1
growth factor stimulates bone formation by purified human
perivascular cells. Tissue Eng Part A. 17:2497–2509. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mashiba T, Iwata K, Komatsubara S and
Manabe T: Animal models for bone and joint disease. Animal fracture
model and fracture healing process. Clin calcium. 21:235–241.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Burg KJ, Porter S and Kellam JF:
Biomaterial developments for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials.
21:2347–2359. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Giannoudis PV and Pountos I: Tissue
regeneration. The past, the present and the future. Injury.
36:(Suppl 4). S2–S5. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Maes C, Carmeliet G and Schipani E:
Hypoxia-driven pathways in bone development, regeneration and
disease. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 8:358–366. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rosen V: BMP2 signaling in bone
development and repair. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 20:475–480.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cheng L, Ye F, Yang R, Lu X, Shi Y, Li L,
Fan H and Bu H: Osteoinduction of hydroxyapatite/beta-tricalcium
phosphate bioceramics in mice with a fractured fibula. Acta
Biomater. 6:1569–1574. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kayal RA, Siqueira M, Alblowi J, McLean J,
Krothapalli N, Faibish D, Einhorn TA, Gerstenfeld LC and Graves DT:
TNF-alpha mediates diabetes-enhanced chondrocyte apoptosis during
fracture healing and stimulates chondrocyte apoptosis through
FOXO1. J Bone Miner Res. 25:1604–1615. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Holstein JH, Karabin-Kehl B, Scheuer C,
Garcia P, Histing T, Meier C, Benninger E, Menger MD and Pohlemann
T: Endostatin inhibits Callus remodeling during fracture healing in
mice. J Orthop Res. 31:1579–1584. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Holstein JH, Matthys R, Histing T, Becker
SC, Fiedler M, Garcia P, Meier C, Pohlemann T and Menger MD:
Development of a stable closed femoral fracture model in mice. J
Surg Res. 153:71–75. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
O'Neill KR, Stutz CM, Mignemi NA, Burns
MC, Murry MR, Nyman JS and Schoenecker JG: Micro-computed
tomography assessment of the progression of fracture healing in
mice. Bone. 50:1357–1367. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Einhorn TA: Enhancement of
fracture-healing. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 77:940–956. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kellum E, Starr H, Arounleut P, Immel D,
Fulzele S, Wenger K and Hamrick MW: Myostatin (GDF-8) deficiency
increases fracture callus size, Sox-5 expression, and callus bone
volume. Bone. 44:17–23. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wigner NA, Kulkarni N, Yakavonis M, Young
M, Tinsley B, Meeks B, Einhorn TA and Gerstenfeld LC: Urine matrix
metalloproteinases (MMPs) as biomarkers for the progression of
fracture healing. Injury. 43:274–278. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gerstenfeld LC, Cho TJ, Kon T, Aizawa T,
Tsay A, Fitch J, Barnes GL, Graves DT and Einhorn TA: Impaired
fracture healing in the absence of TNF-alpha signaling: The role of
TNF-alpha in endochondral cartilage resorption. J Bone Miner Res.
18:1584–1592. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Haddock NT, Wapner K and Levin LS:
Vascular bone transfer options in the foot and ankle: A
retrospective review and update on strategies. Plast Reconstr Surg.
132:685–693. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhao YP, Tian QY, Frenkel S and Liu CJ:
The promotion of bone healing by progranulin, a downstream molecule
of BMP-2, through interacting with TNF/TNFR signaling.
Biomaterials. 34:6412–6421. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ben-David D, Srouji S, Shapira-Schweitzer
K, Kossover O, Ivanir E, Kuhn G, Müller R, Seliktar D and Livne E:
Low dose BMP-2 treatment for bone repair using a PEGylated
fibrinogen hydrogel matrix. Biomaterials. 34:2902–2910. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Annibali S, Cicconetti A, Cristalli MP,
Giordano G, Trisi P, Pilloni A and Ottolenghi L: A comparative
morphometric analysis of biodegradable scaffolds as carriers for
dental pulp and periosteal stem cells in a model of bone
regeneration. J Craniofac Surg. 24:866–871. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yang F, Wang J, Hou J, Guo H and Liu C:
Bone regeneration using cell-mediated responsive degradable
PEG-based scaffolds incorporating with rhBMP-2. Biomaterials.
34:1514–1528. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang H and Xing L: Ubiquitin e3 ligase
itch negatively regulates osteoblast differentiation from
mesenchymal progenitor cells. Stem cells. 31:1574–1583. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Fricain JC, Schlaubitz S, Le Visage C,
Arnault I, Derkaoui SM, Siadous R, Catros S, Lalande C, Bareille R,
Renard M, et al: A nano-hydroxyapatite-pullulan/dextran
polysaccharide composite macroporous material for bone tissue
engineering. Biomaterials. 34:2947–2959. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gao X, Usas A, Lu A, Tang Y, Wang B, Chen
CW, Li H, Tebbets JC, Cummins JH and Huard J: BMP2 is superior to
BMP4 for promoting human muscle-derived stem cell-mediated bone
regeneration in a critical-sized calvarial defect model. Cell
transplantat. 22:2393–2408. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Tanaka K, Tanaka S, Sakai A, Ninomiya T,
Arai Y and Nakamura T: Deficiency of vitamin A delays bone healing
process in association with reduced BMP2 expression after
drill-hole injury in mice. Bone. 47:1006–1012. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Katae Y, Tanaka S, Sakai A, Nagashima M,
Hirasawa H and Nakamura T: Elcatonin injections suppress systemic
bone resorption without affecting cortical bone regeneration after
drill-hole injuries in mice. J Orthop Res. 27:1652–1658. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Behr B, Leucht P, Longaker MT and Quarto
N: Fgf-9 is required for angiogenesis and osteogenesis in long bone
repair. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:11853–11858. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Tang N, Song WX, Luo J, Luo X, Chen J,
Sharff KA, Bi Y, He BC, Huang JY, Zhu GH, et al: BMP-9-induced
osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal progenitors requires
functional canonical Wnt/beta-catenin signalling. J Cell Mol Med.
13:2448–2464. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
He YX, Zhang G, Pan XH, Liu Z, Zheng LZ,
Chan CW, Lee KM, Cao YP, Li G, Wei L, et al: Impaired bone healing
pattern in mice with ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis: A drill-hole
defect model. Bone. 48:1388–1400. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Jawad MU, Fritton KE, Ma T, Ren PG,
Goodman SB, Ke HZ, Babij P and Genovese MC: Effects of sclerostin
antibody on healing of a non-critical size femoral bone defect. J
Orthop Res. 31:155–163. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Meszaros LB, Usas A, Cooper GM and Huard
J: Effect of host sex and sex hormones on muscle-derived stem
cell-mediated bone formation and defect healing. Tissue Eng Part A.
18:1751–1759. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Behr B, Sorkin M, Lehnhardt M, Renda A,
Longaker MT and Quarto N: A comparative analysis of the osteogenic
effects of BMP-2, FGF-2, and VEGFA in a calvarial defect model.
Tissue Eng Part A. 18:1079–1086. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Liu K, Li D, Huang X, Lv K, Ongodia D, Zhu
L, Zhou L and Li Z: A murine femoral segmental defect model for
bone tissue engineering using a novel rigid internal fixation
system. J Surg Res. 183:493–502. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Manassero M, Viateau V, Matthys R,
Deschepper M, Vallefuoco R, Bensidhoum M and Petite H: A novel
murine femoral segmental critical-sized defect model stabilized by
plate osteosynthesis for bone tissue engineering purposes. Tissue
Eng Part C Methods. 19:271–280. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Krebsbach PH, Mankani MH, Satomura K,
Kuznetsov SA and Robey PG: Repair of craniotomy defects using bone
marrow stromal cells. Transplantation. 66:1272–1278. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lee JY, Musgrave D, Pelinkovic D,
Fukushima K, Cummins J, Usas A, Robbins P, Fu FH and Huard J:
Effect of bone morphogenetic protein-2-expressing muscle-derived
cells on healing of critical-sized bone defects in mice. J Bone
Joint Surg Am. 83-A:1032–1039. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Wang D, Gilbert JR, Cray JJ Jr, Kubala AA,
Shaw MA, Billiar TR and Cooper GM: Accelerated calvarial healing in
mice lacking Toll-like receptor 4. PLoS One. 7:e469452012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Levi B, Hyun JS, Montoro DT, Lo DD, Chan
CK, Hu S, Sun N, Lee M, Grova M, Connolly AJ, et al: In vivo
directed differentiation of pluripotent stem cells for skeletal
regeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:20379–20384. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Lo DD, Mackanos MA, Chung MT, Hyun JS,
Montoro DT, Grova M, Liu C, Wang J, Palanker D, Connolly AJ, et al:
Femtosecond plasma mediated laser ablation has advantages over
mechanical osteotomy of cranial bone. Lasers Surg Med. 44:805–814.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Garcia P, Holstein JH, Maier S,
Schaumlöffel H, Al-Marrawi F, Hannig M, Pohlemann T and Menger MD:
Development of a reliable non-union model in mice. J Surg Res.
147:84–91. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zwingenberger S, Niederlohmann E, Vater C,
Rammelt S, Matthys R, Bernhardt R, Valladares RD, Goodman SB and
Stiehler M: Establishment of a femoral critical-size bone defect
model in immunodeficient mice. J Surg Res. 181:e7–e14. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Lin EA, Liu CJ, Monroy A, Khurana S and
Egol KA: Prevention of atrophic nonunion by the systemic
administration of parathyroid hormone (PTH 1–34) in an experimental
animal model. J Orthop Trauma. 26:719–723. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Holstein JH, Orth M, Scheuer C, Tami A,
Becker SC, Garcia P, Histing T, Mörsdorf P, Klein M, Pohlemann T
and Menger MD: Erythropoietin stimulates bone formation, cell
proliferation, and angiogenesis in a femoral segmental defect model
in mice. Bone. 49:1037–1045. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Kimelman-Bleich N, Pelled G, Sheyn D,
Kallai I, Zilberman Y, Mizrahi O, Tal Y, Tawackoli W, Gazit Z and
Gazit D: The use of a synthetic oxygen carrier-enriched hydrogel to
enhance mesenchymal stem cell-based bone formation in vivo.
Biomaterials. 30:4639–4648. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Moutsatsos IK, Turgeman G, Zhou S,
Kurkalli BG, Pelled G, Tzur L, Kelley P, Stumm N, Mi S, Müller R,
et al: Exogenously regulated stem cell-mediated gene therapy for
bone regeneration. Mol Ther. 3:449–461. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Kimelman-Bleich N, Pelled G, Zilberman Y,
Kallai I, Mizrahi O, Tawackoli W, Gazit Z and Gazit D: Targeted
gene-and-host progenitor cell therapy for nonunion bone fracture
repair. Mol Ther. 19:53–59. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Tai K, Pelled G, Sheyn D, Bershteyn A, Han
L, Kallai I, Zilberman Y, Ortiz C and Gazit D: Nanobiomechanics of
repair bone regenerated by genetically modified mesenchymal stem
cells. Tissue Eng Part A. 14:1709–1720. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Bergeron E, Leblanc E, Drevelle O, Giguère
R, Beauvais S, Grenier G and Faucheux N: The evaluation of ectopic
bone formation induced by delivery systems for bone morphogenetic
protein-9 or its derived peptide. Tissue Eng Part A. 18:342–352.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Kamiya N: The role of BMPs in bone
anabolism and their potential targets SOST and DKK1. Curr Mol
Pharmacol. 5:153–163. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Chen L, Jiang W, Huang J, He BC, Zuo GW,
Zhang W, Luo Q, Shi Q, Zhang BQ and Wagner ER: Insulin-like growth
factor 2 (IGF-2) potentiates BMP-9-induced osteogenic
differentiation and bone formation. J Bone Miner Res. 25:2447–2459.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Wagner-Ecker M, Voltz P, Egermann M and
Richter W: The collagen component of biological bone graft
substitutes promotes ectopic bone formation by human mesenchymal
stem cells. Acta Biomater. 9:7298–7307. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Frescaline G, Bouderlique T, Mansoor L,
Carpentier G, Baroukh B, Sineriz F, Trouillas M, Saffar JL, Courty
J, Lataillade JJ, et al: Glycosaminoglycan mimetic associated to
human mesenchymal stem cell-based scaffolds inhibit ectopic bone
formation, but induce angiogenesis in vivo. Tissue Eng Part A.
19:1641–1653. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Hasharoni A, Zilberman Y, Turgeman G, Helm
GA, Liebergall M and Gazit D: Murine spinal fusion induced by
engineered mesenchymal stem cells that conditionally express bone
morphogenetic protein-2. J Neurosurg Spine. 3:47–52. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Sheyn D, Pelled G, Zilberman Y, Talasazan
F, Frank JM, Gazit D and Gazit Z: Nonvirally engineered porcine
adipose tissue-derived stem cells: Use in posterior spinal fusion.
Stem cells. 26:1056–1064. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Medici D, Shore EM, Lounev VY, Kaplan FS,
Kalluri R and Olsen BR: Conversion of vascular endothelial cells
into multipotent stem-like cells. Nat Med. 16:1400–1406. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Shimono K, Tung WE, Macolino C, Chi AH,
Didizian JH, Mundy C, Chandraratna RA, Mishina Y, Enomoto-Iwamoto
M, Pacifici M and Iwamoto M: Potent inhibition of heterotopic
ossification by nuclear retinoic acid receptor-γ agonists. Nat Med.
17:454–460. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Eyckmans J, Roberts SJ, Bolander J,
Schrooten J, Chen CS and Luyten FP: Mapping calcium phosphate
activated gene networks as a strategy for targeted osteoinduction
of human progenitors. Biomaterials. 34:4612–4621. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Aalami OO, Nacamuli RP, Lenton KA, Cowan
CM, Fang TD, Fong KD, Shi YY, Song HM, Sahar DE and Longaker MT:
Applications of a mouse model of calvarial healing: Differences in
regenerative abilities of juveniles and adults. Plast Reconstr
Surg. 114:713–720. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Zhang T, Yu H, Gong W, Zhang L, Jia T,
Wooley PH and Yang SY: The effect of osteoprotegerin gene
modification on wear debris-induced osteolysis in a murine model of
knee prosthesis failure. Biomaterials. 30:6102–6108. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Baron R and Kneissel M: WNT signaling in
bone homeostasis and disease: From human mutations to treatments.
Nat Med. 19:179–192. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Seto J, Busse B, Gupta HS, Schäfer C,
Krauss S, Dunlop JW, Masic A, Kerschnitzki M, Zaslansky P, Boesecke
P, et al: Accelerated growth plate mineralization and foreshortened
proximal limb bones in fetuin-A knockout mice. PLoS One.
7:e473382012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Xie C, Xue M, Wang Q, Schwarz EM, O'Keefe
RJ and Zhang X: Tamoxifen-inducible CreER-mediated gene targeting
in periosteum via bone-graft transplantation. J Bone Joint Surg Am.
90:(Suppl 1). S9–S13. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Bockamp E, Maringer M, Spangenberg C, Fees
S, Fraser S, Eshkind L, Oesch F and Zabel B: Of mice and models:
Improved animal models for biomedical research. Physiol Genomics.
11:115–132. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Matsushita Y, Sakamoto K, Tamamura Y,
Shibata Y, Minamizato T, Kihara T, Ito M, Katsube K, Hiraoka S,
Koseki H, et al: CCN3 protein participates in bone regeneration as
an inhibitory factor. J Biol Chem. 288:19973–19985. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Gualeni B, de Vernejoul MC, Marty-Morieux
C, De Leonardis F, Franchi M, Monti L, Forlino A, Houillier P,
Rossi A and Geoffroy V: Alteration of proteoglycan sulfation
affects bone growth and remodeling. Bone. 54:83–91. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
do Soung Y, Gentile MA, le Duong T and
Drissi H: Effects of pharmacological inhibition of cathepsin K on
fracture repair in mice. Bone. 55:248–255. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Colnot C, Zhang X and Tate Knothe ML:
Current insights on the regenerative potential of the periosteum:
Molecular, cellular, and endogenous engineering approaches. J
Orthop Res. 30:1869–1878. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Yu YY, Bahney C, Hu D, Marcucio RS and
Miclau T III: Creating rigidly stabilized fractures for assessing
intramembranous ossification, distraction osteogenesis, or healing
of critical sized defects. J Vis Exp pii. 35522012.
|
|
76
|
Bose S, Roy M and Bandyopadhyay A: Recent
advances in bone tissue engineering scaffolds. Trends Biotechnol.
30:546–554. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Yun YR, Jang JH, Jeon E, Kang W, Lee S,
Won JE, Kim HW and Wall I: Administration of growth factors for
bone regeneration. Regen Med. 7:369–385. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Zhao YP, Tian QY, Liu B, Cuellar J,
Richbourgh B, Jia TH and Liu CJ: Progranulin knockout accelerates
intervertebral disc degeneration in aging mice. Sci Rep.
5:91022015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|