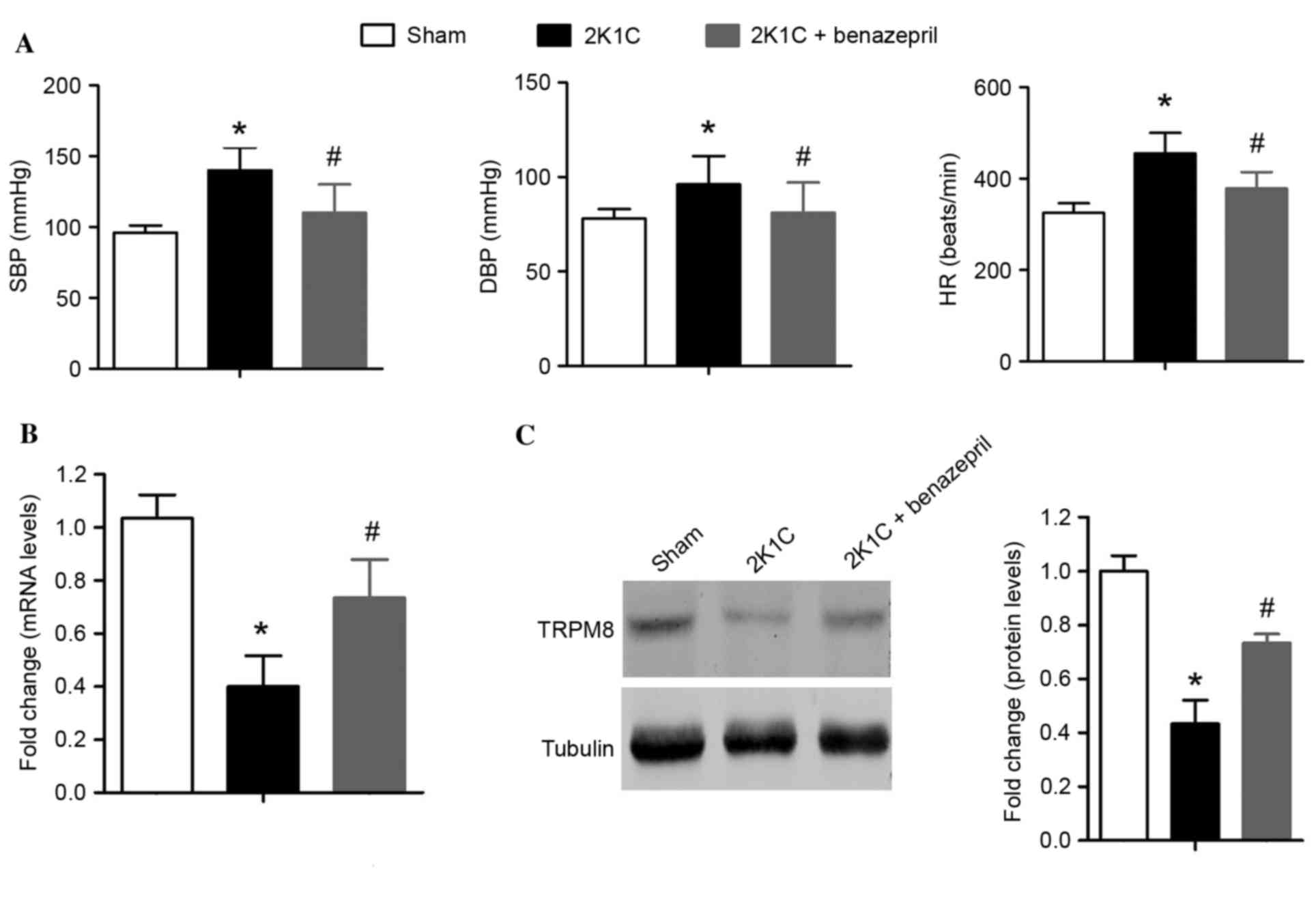
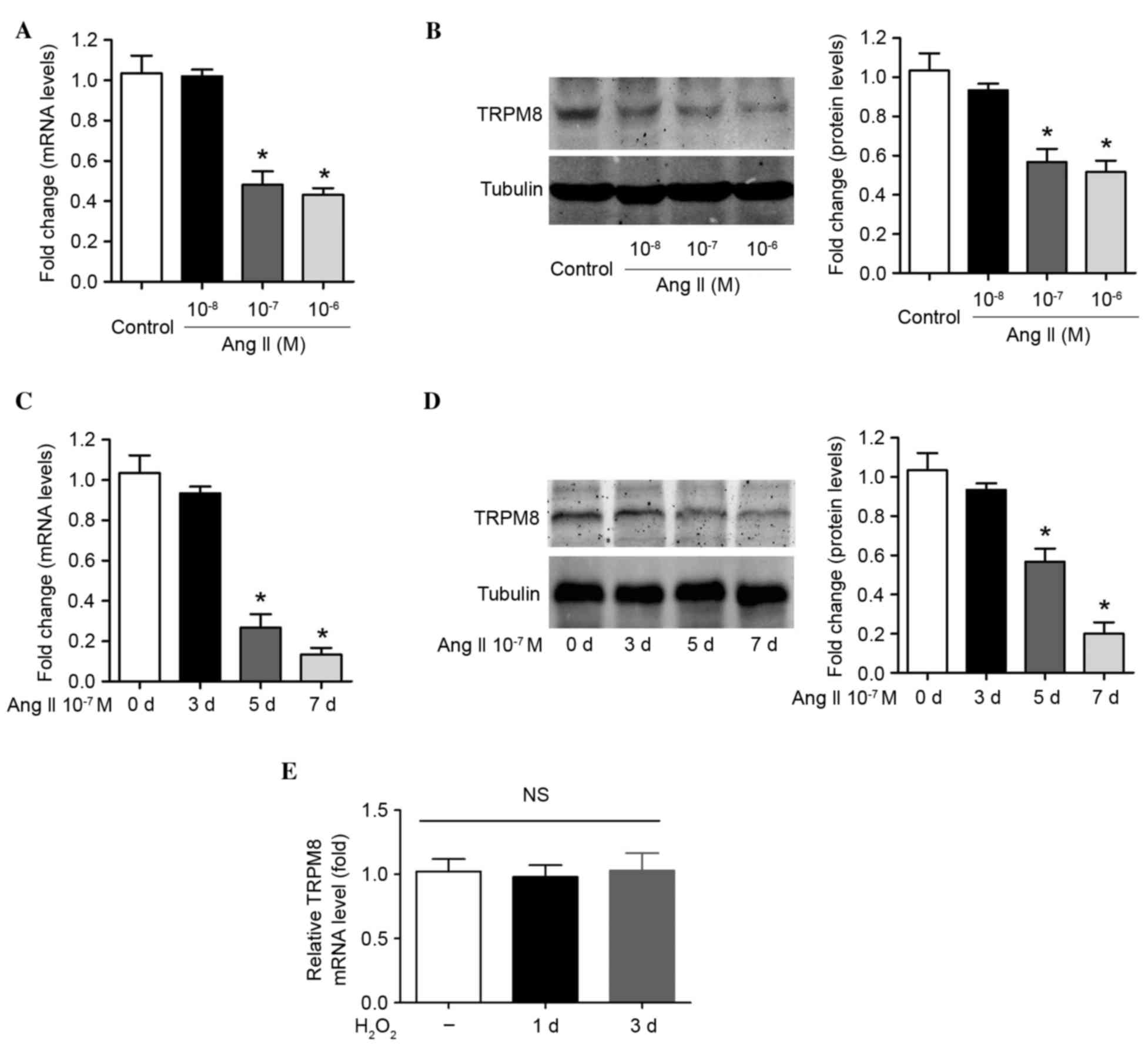
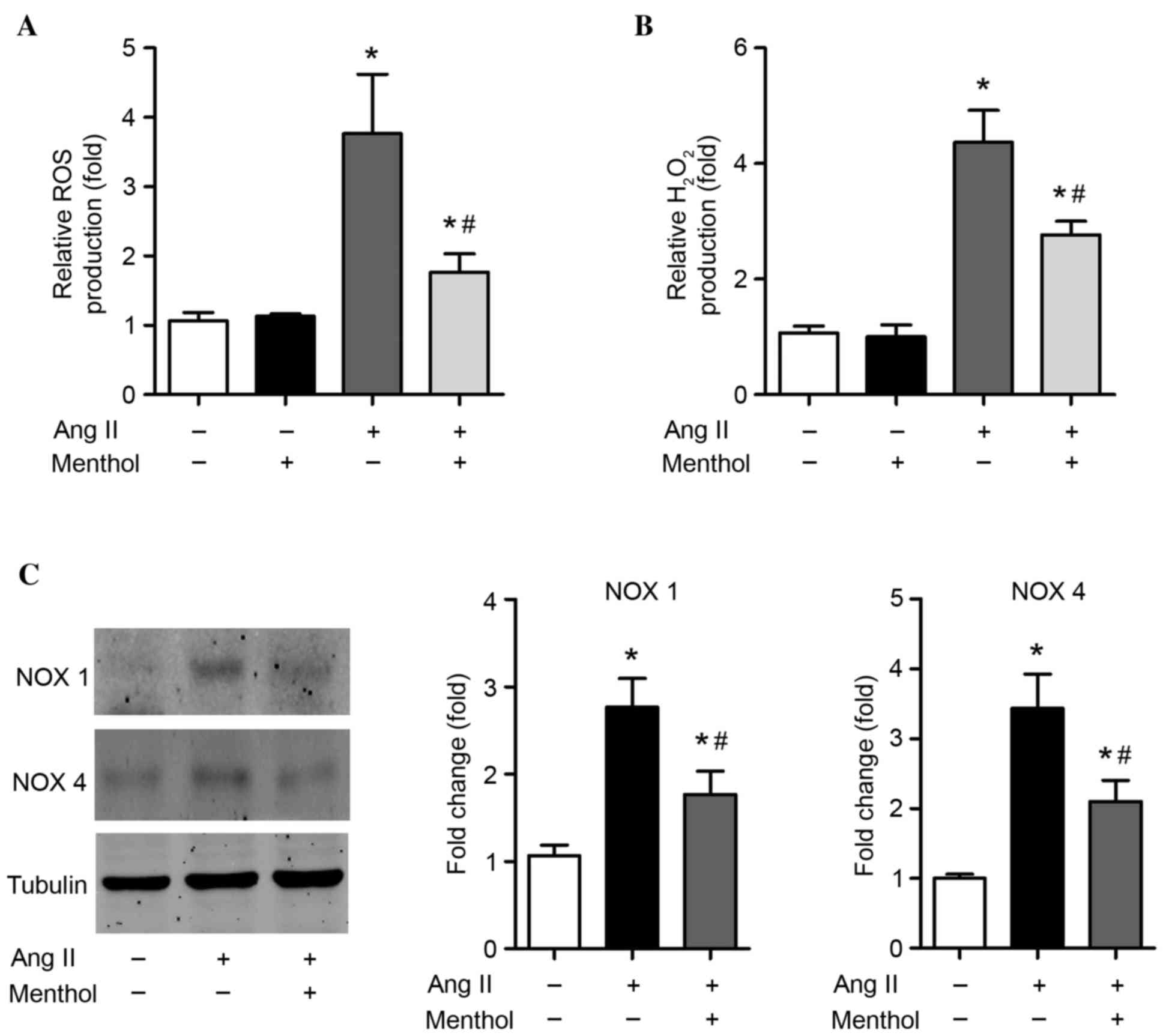
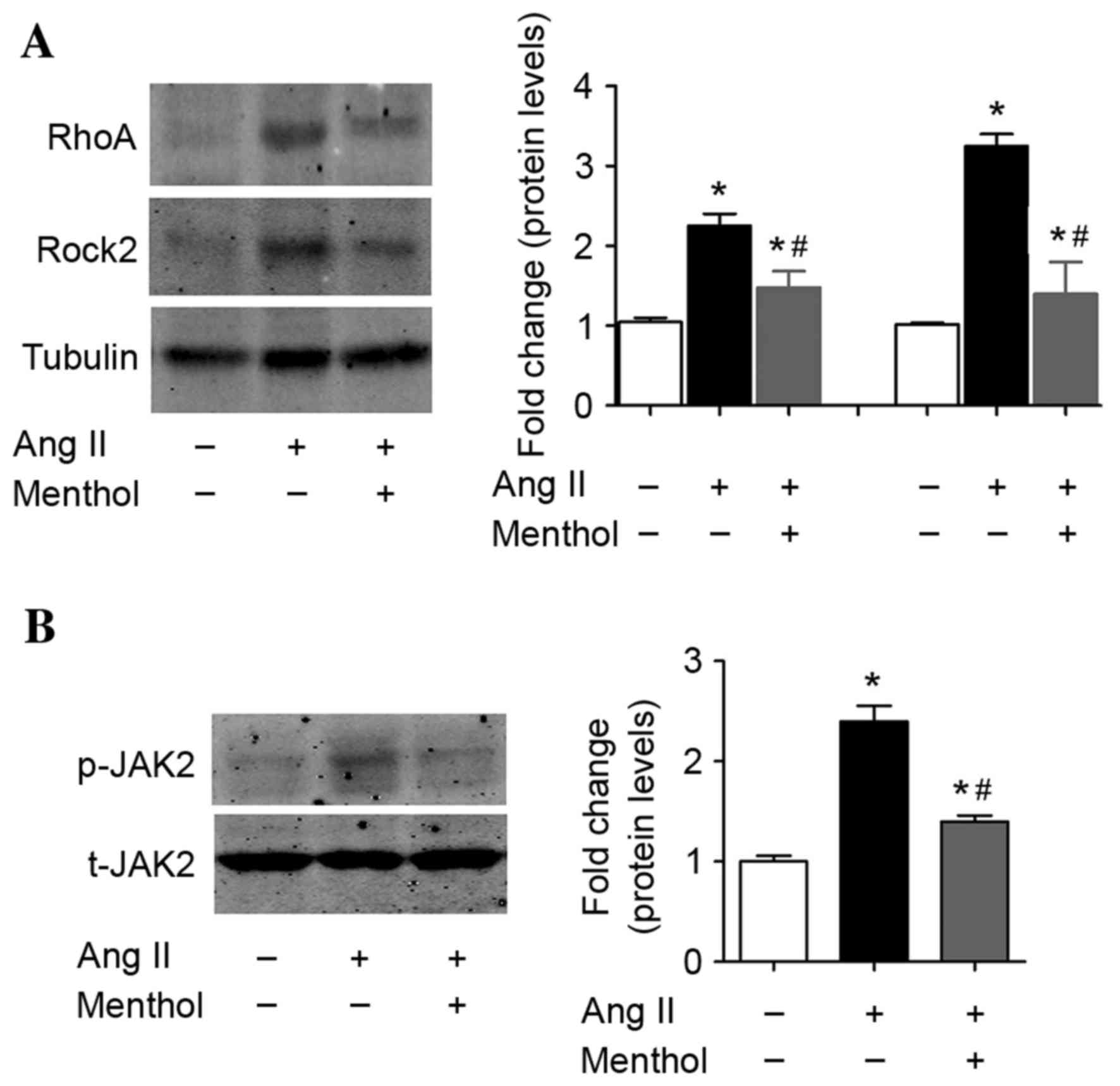
|
1
|
Poulter NR, Prabhakaran D and Caulfield M:
Hypertension. Lancet. 386:801–812. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
He D, Fu M, Miao S, Hotta K, Chandak GR
and Xi B: FTO gene variant and risk of hypertension: A
meta-analysis of 57,464 hypertensive cases and 41,256 controls.
Metabolism. 63:633–639. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wu YL, Hu CY, Lu SS, Gong FF, Feng F, Qian
ZZ, Ding XX, Yang HY and Sun YH: Association between
methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) C677T/A1298C
polymorphisms and essential hypertension: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Metabolism. 63:1503–1511. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Rocha NG, Templeton DL, Greiner JJ,
Stauffer BL and DeSouza CA: Metabolic syndrome and endothelin-1
mediated vasoconstrictor tone in overweight/obese adults.
Metabolism. 63:951–956. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ait Aissa K, Lagrange J, Mohamadi A, Louis
H, Houppert B, Challande P, Wahl D, Lacolley P and Regnault V:
Vascular smooth muscle cells are responsible for a prothrombotic
phenotype of spontaneously hypertensive rat arteries. Arterioscler
Thromb Vasc Biol. 35:930–937. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang C, Li Y, Wang C, Wu Y, Cui W, Miwa
T, Sato S, Li H, Song WC and Du J: Complement 5a receptor mediates
angiotensin II-induced cardiac inflammation and remodeling.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 34:1240–1248. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Xia Y, Jin X, Yan J, Entman ML and Wang Y:
CXCR6 plays a critical role in angiotensin II-induced renal injury
and fibrosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 34:1422–1428. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Usui F, Shirasuna K, Kimura H, Tatsumi K,
Kawashima A, Karasawa T, Yoshimura K, Aoki H, Tsutsui H, Noda T, et
al: Inflammasome activation by mitochondrial oxidative stress in
macrophages leads to the development of angiotensin II-induced
aortic aneurysm. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 35:127–136. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kigawa Y, Miyazaki T, Lei XF, Nakamachi T,
Oguchi T, Kim-Kaneyama JR, Taniyama M, Tsunawaki S, Shioda S and
Miyazaki A: NADPH oxidase deficiency exacerbates angiotensin
II-induced abdominal aortic aneurysms in mice. Arterioscler Thromb
Vasc Biol. 34:2413–2420. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Krishna SM, Seto SW, Jose RJ, Biros E,
Moran CS, Wang Y, Clancy P and Golledge J: A peptide antagonist of
thrombospondin-1 promotes abdominal aortic aneurysm progression in
the angiotensin II-infused apolipoprotein-E-deficient mouse.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 35:389–398. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Davis FM, Rateri DL, Balakrishnan A,
Howatt DA, Strickland DK, Muratoglu SC, Haggerty CM, Fornwalt BK,
Cassis LA and Daugherty A: Smooth muscle cell deletion of
low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 augments
angiotensin II-induced superior mesenteric arterial and ascending
aortic aneurysms. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 35:155–162. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zreikat HH, Harpe SE, Slattum PW, Mays DP,
Essah PA and Cheang KI: Effect of Renin-Angiotensin system
inhibition on cardiovascular events in older hypertensive patients
with metabolic syndrome. Metabolism. 63:392–399. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kristensen KE, Torp-Pedersen C, Gislason
GH, Egfjord M, Rasmussen HB and Hansen PR: Angiotensin-converting
enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers in patients
with abdominal aortic aneurysms: Nation-wide cohort study.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 35:733–740. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pruthi D, McCurley A, Aronovitz M, Galayda
C, Karumanchi SA and Jaffe IZ: Aldosterone promotes vascular
remodeling by direct effects on smooth muscle cell
mineralocorticoid receptors. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
34:355–364. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Alias S, Redwan B, Panzenböck A, Winter
MP, Schubert U, Voswinckel R, Frey MK, Jakowitsch J, Alimohammadi
A, Hobohm L, et al: Defective angiogenesis delays thrombus
resolution: A potential pathogenetic mechanism underlying chronic
thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc
Biol. 34:810–819. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Manka D, Chatterjee TK, Stoll LL, Basford
JE, Konaniah ES, Srinivasan R, Bogdanov VY, Tang Y, Blomkalns AL,
Hui DY and Weintraub NL: Transplanted perivascular adipose tissue
accelerates injury-induced neointimal hyperplasia: Role of monocyte
chemoattractant protein-1. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
34:1723–1730. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Demer LL and Tintut Y: Inflammatory,
metabolic, and genetic mechanisms of vascular calcification.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 34:715–723. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Peier AM, Moqrich A, Hergarden AC, Reeve
AJ, Andersson DA, Story GM, Earley TJ, Dragoni I, McIntyre P, Bevan
S and Patapoutian A: A TRP channel that senses cold stimuli and
menthol. Cell. 108:705–715. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
McKemy DD, Neuhausser WM and Julius D:
Identification of a cold receptor reveals a general role for TRP
channels in thermosensation. Nature. 416:52–58. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Almeida MC, Hew-Butler T, Soriano RN, Rao
S, Wang W, Wang J, Tamayo N, Oliveira DL, Nucci TB, Aryal P, et al:
Pharmacological blockade of the cold receptor TRPM8 attenuates
autonomic and behavioral cold defenses and decreases deep body
temperature. J Neurosci. 32:2086–2099. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Knowlton WM, Daniels RL, Palkar R, McCoy
DD and McKemy DD: Pharmacological blockade of TRPM8 ion channels
alters cold and cold pain responses in mice. PLoS One.
6:e258942011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Morenilla-Palao C, Luis E, Fernández-Peña
C, Quintero E, Weaver JL, Bayliss DA and Viana F: Ion channel
profile of TRPM8 cold receptors reveals a role of TASK-3 potassium
channels in thermosensation. Cell Rep. 8:1571–1582. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Borrelli F, Pagano E, Romano B, Panzera S,
Maiello F, Coppola D, De Petrocellis L, Buono L, Orlando P and Izzo
AA: Colon carcinogenesis is inhibited by the TRPM8 antagonist
cannabigerol, a Cannabis-derived non-psychotropic cannabinoid.
Carcinogenesis. 35:2787–2797. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Patel R, Gonçalves L, Leveridge M, Mack
SR, Hendrick A, Brice NL and Dickenson AH: Anti-hyperalgesic
effects of a novel TRPM8 agonist in neuropathic rats: A comparison
with topical menthol. Pain. 155:2097–2107. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ramachandran R, Hyun E, Zhao L, Lapointe
TK, Chapman K, Hirota CL, Ghosh S, McKemy DD, Vergnolle N, Beck PL,
et al: TRPM8 activation attenuates inflammatory responses in mouse
models of colitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 110:7476–7481. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ma S, Yu H, Zhao Z, Luo Z, Chen J, Ni Y,
Jin R, Ma L, Wang P, Zhu Z, et al: Activation of the cold-sensing
TRPM8 channel triggers UCP1-dependent thermogenesis and prevents
obesity. J Mol Cell Biol. 4:88–96. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Asuthkar S, Elustondo PA, Demirkhanyan L,
Sun X, Baskaran P, Velpula KK, Thyagarajan B, Pavlov EV and
Zakharian E: The TRPM8 protein is a testosterone receptor: I.
Biochemical evidence for direct TRPM8-testosterone interactions. J
Biol Chem. 290:2659–2669. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Quallo T, Vastani N, Horridge E, Gentry C,
Parra A, Moss S, Viana F, Belmonte C, Andersson DA and Bevan S:
TRPM8 is a neuronal osmosensor that regulates eye blinking in mice.
Nat Commun. 6:71502015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Johnson CD, Melanaphy D, Purse A,
Stokesberry SA, Dickson P and Zholos AV: Transient receptor
potential melastatin 8 channel involvement in the regulation of
vascular tone. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 296:H1868–H1877.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sun J, Yang T, Wang P, Ma S and Zhu Z, Pu
Y, Li L, Zhao Y, Xiong S, Liu D and Zhu Z: Activation of
cold-sensing transient receptor potential melastatin subtype 8
antagonizes vasoconstriction and hypertension through attenuating
RhoA/Rho kinase pathway. Hypertension. 63:1354–1363. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chen JK, Zhao T, Ni M, Li DJ, Tao X and
Shen FM: Downregulation of alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor
in two-kidney one-clip hypertensive rats. BMC Cardiovasc Disord.
12:382012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kato Y, Yokoyama U, Yanai C, Ishige R,
Kurotaki D, Umemura M, Fujita T, Kubota T, Okumura S, Sata M, et
al: Epac1 deficiency attenuated vascular smooth muscle cell
migration and neointimal formation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
35:2617–2625. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Weise-Cross L, Taylor JM and Mack CP:
Inhibition of diaphanous formin signaling in vivo impairs
cardiovascular development and alters smooth muscle cell phenotype.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 35:2374–2383. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Fernandez I, Martin-Garrido A, Zhou DW,
Clempus RE, Seidel-Rogol B, Valdivia A, Lassègue B, García AJ,
Griendling KK and San Martin A: Hic-5 mediates TGFβ-induced
adhesion in vascular smooth muscle cells by a Nox4-dependent
mechanism. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 35:1198–1206. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Song J, Li J, Hou F, Wang X and Liu B:
Mangiferin inhibits endoplasmic reticulum stress-associated
thioredoxin-interacting protein/NLRP3 inflammasome activation with
regulation of AMPK in endothelial cells. Metabolism. 64:428–437.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Omodei D, Pucino V, Labruna G, Procaccini
C, Galgani M, Perna F, Pirozzi D, De Caprio C, Marone G, Fontana L,
et al: Immune-metabolic profiling of anorexic patients reveals an
anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory phenotype. Metabolism.
64:396–405. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hwang HJ, Jung TW, Hong HC, Seo JA, Kim
SG, Kim NH, Choi KM, Choi DS, Baik SH and Yoo HJ: LECT2 induces
atherosclerotic inflammatory reaction via CD209 receptor-mediated
JNK phosphorylation in human endothelial cells. Metabolism.
64:1175–1182. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kurano M, Hara M, Satoh H and Tsukamoto K:
Hepatic NPC1L1 overexpression ameliorates glucose metabolism in
diabetic mice via suppression of gluconeogenesis. Metabolism.
64:588–596. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhou XB, Feng YX, Sun Q, Lukowski R, Qiu
Y, Spiger K, Li Z, Ruth P, Korth M, Skolnik EY, et al: Nucleoside
diphosphate kinase B-activated intermediate conductance potassium
channels are critical for neointima formation in mouse carotid
arteries. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 35:1852–1861. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lee MJ, Kim EH, Lee SA, Kang YM, Jung CH,
Yoon HK, Seol SM, Lee YL, Lee WJ and Park JY:
Dehydroepiandrosterone prevents linoleic acid-induced endothelial
cell senescence by increasing autophagy. Metabolism. 64:1134–1145.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ray Hamidie RD, Yamada T, Ishizawa R,
Saito Y and Masuda K: Curcumin treatment enhances the effect of
exercise on mitochondrial biogenesis in skeletal muscle by
increasing cAMP levels. Metabolism. 64:1334–1347. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kadota Y, Toyoda T, Hayashi-Kato M,
Kitaura Y and Shimomura Y: Octanoic acid promotes branched-chain
amino acid catabolisms via the inhibition of hepatic branched-chain
alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase kinase in rats. Metabolism.
64:1157–1164. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Fu L, Bruckbauer A, Li F, Cao Q, Cui X, Wu
R, Shi H, Zemel MB and Xue B: Leucine amplifies the effects of
metformin on insulin sensitivity and glycemic control in
diet-induced obese mice. Metabolism. 64:845–856. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Soe NN, Sowden M, Baskaran P, Smolock EM,
Kim Y, Nigro P and Berk BC: Cyclophilin A is required for
angiotensin II-induced p47phox translocation to caveolae in
vascular smooth muscle cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
33:2147–2153. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Wu YJ, Guo X, Li CJ, Li DQ, Zhang J, Yang
Y, Kong Y, Guo H, Liu DM and Chen LM: Dipeptidyl peptidase-4
inhibitor, vildagliptin, inhibits pancreatic beta cell apoptosis in
association with its effects suppressing endoplasmic reticulum
stress in db/db mice. Metabolism. 64:226–235. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Seshiah PN, Weber DS, Rocic P, Valppu L,
Taniyama Y and Griendling KK: Angiotensin II stimulation of NAD
(P)H oxidase activity: Upstream mediators. Circ Res. 91:406–413.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Lasségue B, San M, artín A and Griendling
KK: Biochemistry, physiology, and pathophysiology of NADPH oxidases
in the cardiovascular system. Circ Res. 110:1364–1390. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Kirabo A, Kearns PN, Jarajapu YP, Sasser
JM, Oh SP, Grant MB, Kasahara H, Cardounel AJ, Baylis C, Wagner KU
and Sayeski PP: Vascular smooth muscle Jak2 mediates angiotensin
II-induced hypertension via increased levels of reactive oxygen
species. Cardiovasc Res. 91:171–179. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Montezano AC, Callera GE, Yogi A, He Y,
Tostes RC, He G, Schiffrin EL and Touyz RM: Aldosterone and
angiotensin II synergistically stimulate migration in vascular
smooth muscle cells through c-Src-regulated redox-sensitive RhoA
pathways. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 28:1511–1518. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Clapham DE, Runnels LW and Strübing C: The
trp ion channel family. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2:387–396. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Touyz RM, He Y, Montezano AC, Yao G,
Chubanov V, Gudermann T and Callera GE: Differential regulation of
transient receptor potential melastatin 6 and 7 cation channels by
Ang II in vascular smooth muscle cells from spontaneously
hypertensive rats. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol.
290:R73–R78. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Yogi A, Callera GE, Tostes R and Touyz RM:
Bradykinin regulates calpain and proinflammatory signaling through
TRPM7-sensitive pathways in vascular smooth muscle cells. Am J
Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 296:R201–R207. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Callera GE, He Y, Yogi A, Montezano AC,
Paravicini T, Yao G and Touyz RM: Regulation of the novel Mg2+
transporter transient receptor potential melastatin 7 (TRPM7)
cation channel by bradykinin in vascular smooth muscle cells. J
Hypertens. 27:155–166. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
He Y, Yao G, Savoia C and Touyz RM:
Transient receptor potential melastatin 7 ion channels regulate
magnesium homeostasis in vascular smooth muscle cells: Role of
angiotensin II. Circ Res. 96:207–215. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Montezano AC, Zimmerman D, Yusuf H, Burger
D, Chignalia AZ, Wadhera V, van Leeuwen FN and Touyz RM: Vascular
smooth muscle cell differentiation to an osteogenic phenotype
involves TRPM7 modulation by magnesium. Hypertension. 56:453–462.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Zhang Z, Wang M, Fan XH, Chen JH, Guan YY
and Tang YB: Upregulation of TRPM7 channels by angiotensin II
triggers phenotypic switching of vascular smooth muscle cells of
ascending aorta. Circ Res. 111:1137–1146. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Yang XR, Lin MJ, McIntosh LS and Sham JS:
Functional expression of transient receptor potential melastatin-
and vanilloid-related channels in pulmonary arterial and aortic
smooth muscle. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 290:L1267–L1276.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Ikeda S, Satoh K, Kikuchi N, Miyata S,
Suzuki K, Omura J, Shimizu T, Kobayashi K, Kobayashi K, Fukumoto Y,
et al: Crucial role of rho-kinase in pressure overload-induced
right ventricular hypertrophy and dysfunction in mice. Arterioscler
Thromb Vasc Biol. 34:1260–1271. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Gadang V, Konaniah E, Hui DY and Jaeschke
A: Mixed-lineage kinase 3 deficiency promotes neointima formation
through increased activation of the RhoA pathway in vascular smooth
muscle cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 34:1429–1436. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Ellawindy A, Satoh K, Sunamura S, Kikuchi
N, Suzuki K, Minami T, Ikeda S, Tanaka S, Shimizu T, Enkhjargal B,
et al: Rho-Kinase inhibition during early cardiac development
causes arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy in mice.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 35:2172–2184. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Shimokawa H and Satoh K: 2015 ATVB Plenary
Lecture: Translational research on rho-kinase in cardiovascular
medicine. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 35:1756–1769. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Liu XR, Liu Q, Chen GY, Hu Y, Sham JS and
Lin MJ: Down-regulation of TRPM8 in pulmonary arteries of pulmonary
hypertensive rats. Cell Physiol Biochem. 31:892–904. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Greenberg S: Vascular responses of the
perfused intestine to vasoactive agents during the development of
two-kidney, one-clip Goldblatt hypertension in dogs. Circ Res.
48:895–906. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Morishita R, Higaki J, Miyazaki M and
Ogihara T: Possible role of the vascular renin-angiotensin system
in hypertension and vascular hypertrophy. Hypertension. 19 Suppl
2:II62–II67. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Cervenka L, Horácek V, Vanecková I,
Hubácek JA, Oliverio MI, Coffman TM and Navar LG: Essential role of
AT1A receptor in the development of 2K1C hypertension.
Hypertension. 40:735–741. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Xie QY, Sun M, Yang TL and Sun ZL:
Losartan reduces monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 expression in
aortic tissues of 2K1C hypertensive rats. Int J Cardiol. 110:60–66.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Maxwell MH, Lupu AN, Viskoper RJ, Aravena
LA and Waks UA: Mechanisms of hypertension during the acute and
intermediate phases of the one-clip, two-kidney model in the dog.
Circ Res. 40(5 Suppl 1): I24–I28. 1977.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Li DJ, Evans RG, Yang ZW, Song SW, Wang P,
Ma XJ, Liu C, Xi T, Su DF and Shen FM: Dysfunction of the
cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway mediates organ damage in
hypertension. Hypertension. 57:298–307. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Jamerson K, Weber MA, Bakris GL, Dahlöf B,
Pitt B, Shi V, Hester A, Gupte J, Gatlin M and Velazquez EJ:
ACCOMPLISH Trial Investigators: Benazepril plus amlodipine or
hydrochlorothiazide for hypertension in high-risk patients. N Engl
J Med. 359:2417–2428. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Jamerson KA, Devereux R, Bakris GL, Dahlöf
B, Pitt B, Velazquez EJ, Weir M, Kelly RY, Hua TA, Hester A and
Weber MA: Efficacy and duration of benazepril plus amlodipine or
hydrochlorothiazide on 24-h ambulatory systolic blood pressure
control. Hypertension. 57:174–179. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Valvo E, Casagrande P, Bedogna V, Antiga
L, Alberti D, Zamboni M, Perobelli L, Dal Santo F and Maschio G:
Systemic and renal effects of a new angiotensin converting enzyme
inhibitor, benazepril, in essential hypertension. J Hypertens.
8:991–995. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Balfour JA and Goa KL: Benazepril. A
review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties, and
therapeutic efficacy in hypertension and congestive heart failure.
Drugs. 42:511–539. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Mochel JP, Fink M, Peyrou M, Soubret A,
Giraudel JM and Danhof M: Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic modeling
of renin-angiotensin aldosterone biomarkers following
angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibition therapy with
benazepril in dogs. Pharm Res. 32:1931–1946. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Dikalov SI, Nazarewicz RR, Bikineyeva A,
Hilenski L, Lassègue B, Griendling KK, Harrison DG and Dikalova AE:
Nox2-induced production of mitochondrial superoxide in angiotensin
II-mediated endothelial oxidative stress and hypertension. Antioxid
Redox Signal. 20:281–294. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Lu S, Xiang L, Clemmer JS, Mittwede PN and
Hester RL: Oxidative stress increases pulmonary vascular
permeability in diabetic rats through activation of transient
receptor potential melastatin 2 channels. Microcirculation.
21:754–760. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Palanivel R, Ganguly R, Turdi S, Xu A and
Sweeney G: Adiponectin stimulates Rho-mediated actin cytoskeleton
remodeling and glucose uptake via APPL1 in primary cardiomyocytes.
Metabolism. 63:1363–1373. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Diaz MB, Herzig S and Vegiopoulos A:
Thermogenic adipocytes: From cells to physiology and medicine.
Metabolism. 63:1238–1249. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Sun L and Trajkovski M: MiR-27
orchestrates the transcriptional regulation of brown adipogenesis.
Metabolism. 63:272–282. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Hondares E, Gallego-Escuredo JM, Flachs P,
Frontini A, Cereijo R, Goday A, Perugini J, Kopecky P, Giralt M,
Cinti S, et al: Fibroblast growth factor-21 is expressed in
neonatal and pheochromocytoma-induced adult human brown adipose
tissue. Metabolism. 63:312–317. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Boström PA, Fernández-Real JM and
Mantzoros C: Irisin in humans: Recent advances and questions for
future research. Metabolism. 63:178–180. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Tsuchiya Y, Ando D, Takamatsu K and Goto
K: Resistance exercise induces a greater irisin response than
endurance exercise. Metabolism. 64:1042–1050. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Sharma AM, Janke J, Gorzelniak K, Engeli S
and Luft FC: Angiotensin blockade prevents type 2 diabetes by
formation of fat cells. Hypertension. 40:609–611. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Santos SH, Braga JF, Mario EG, Pôrto LC,
Rodrigues-Machado Mda G, Murari A, Botion LM, Alenina N, Bader M
and Santos RA: Improved lipid and glucose metabolism in transgenic
rats with increased circulating angiotensin-(1–7). Arterioscler
Thromb Vasc Biol. 30:953–961. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|