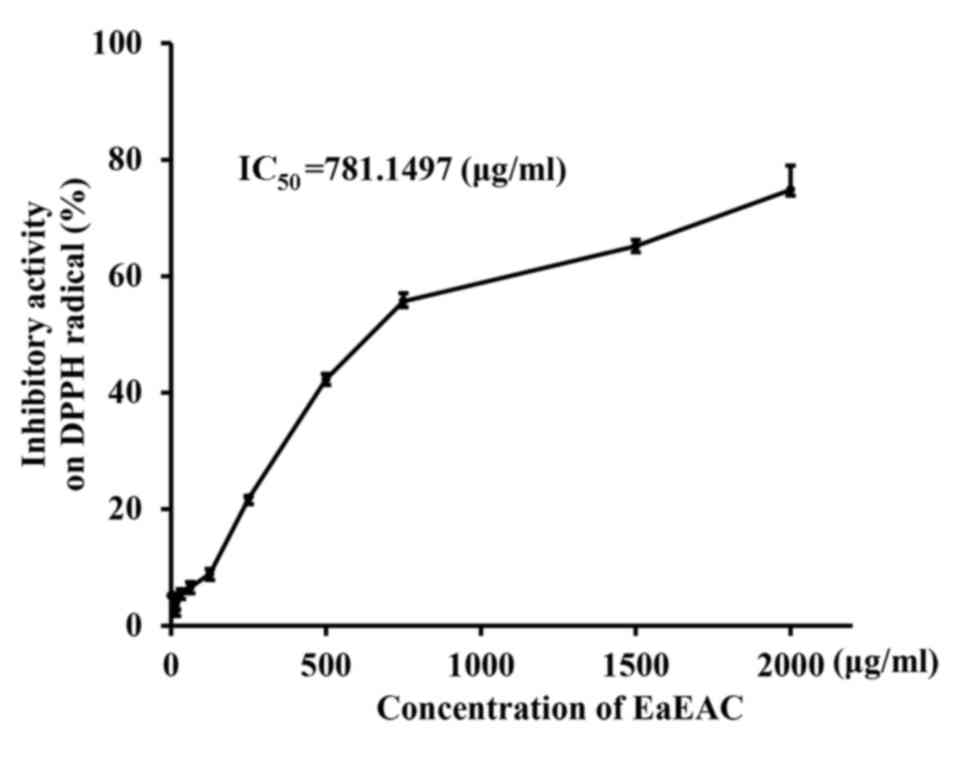
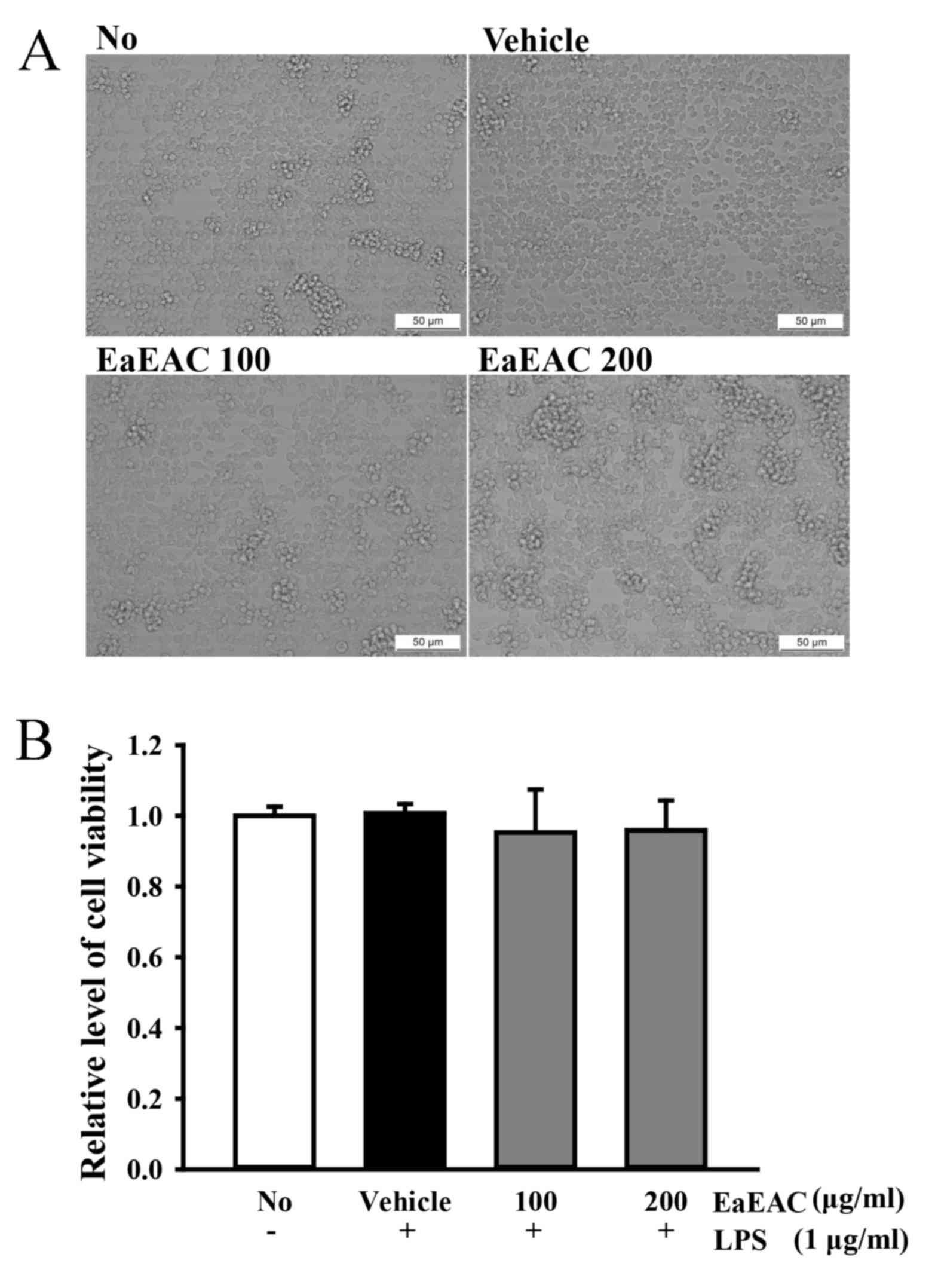
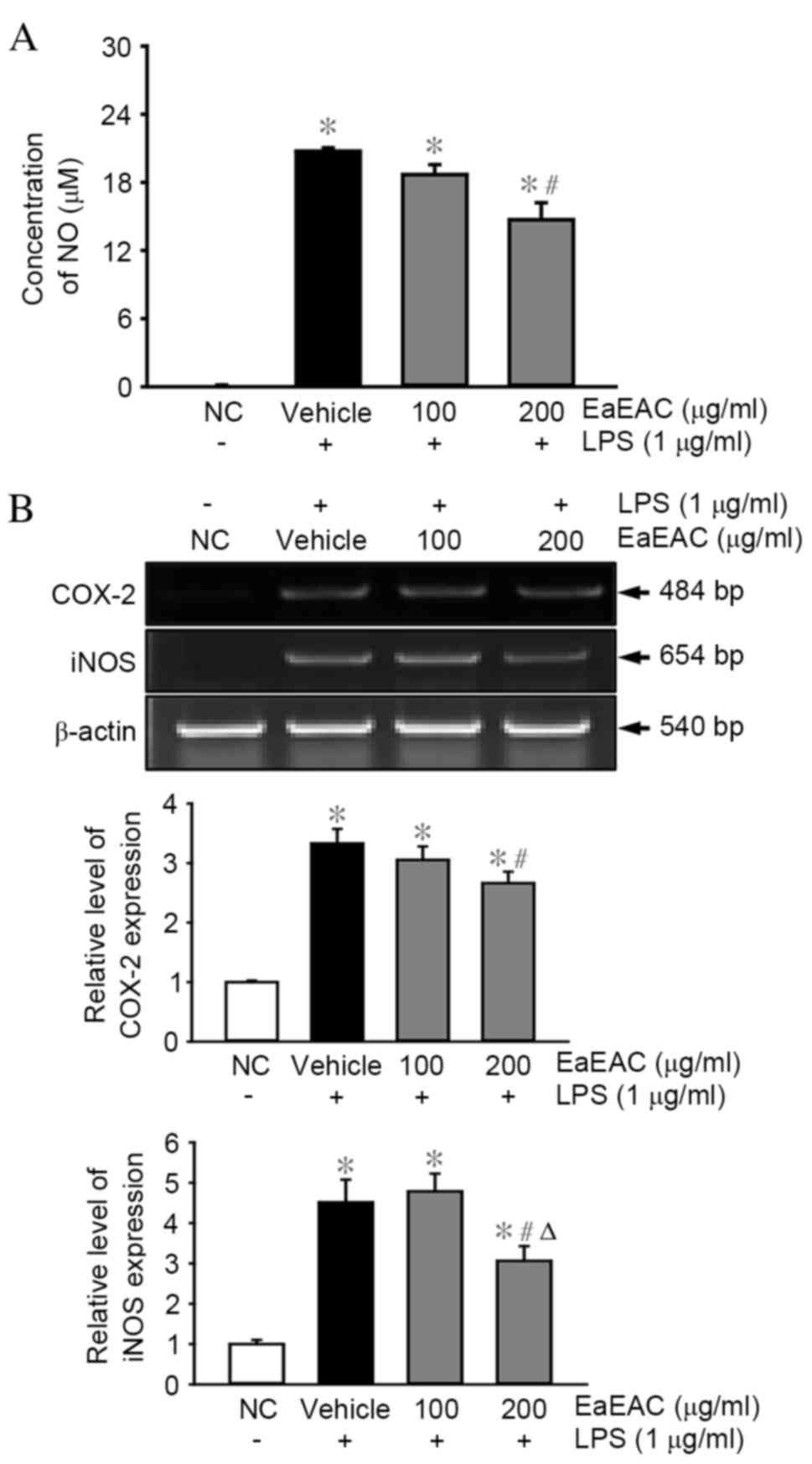
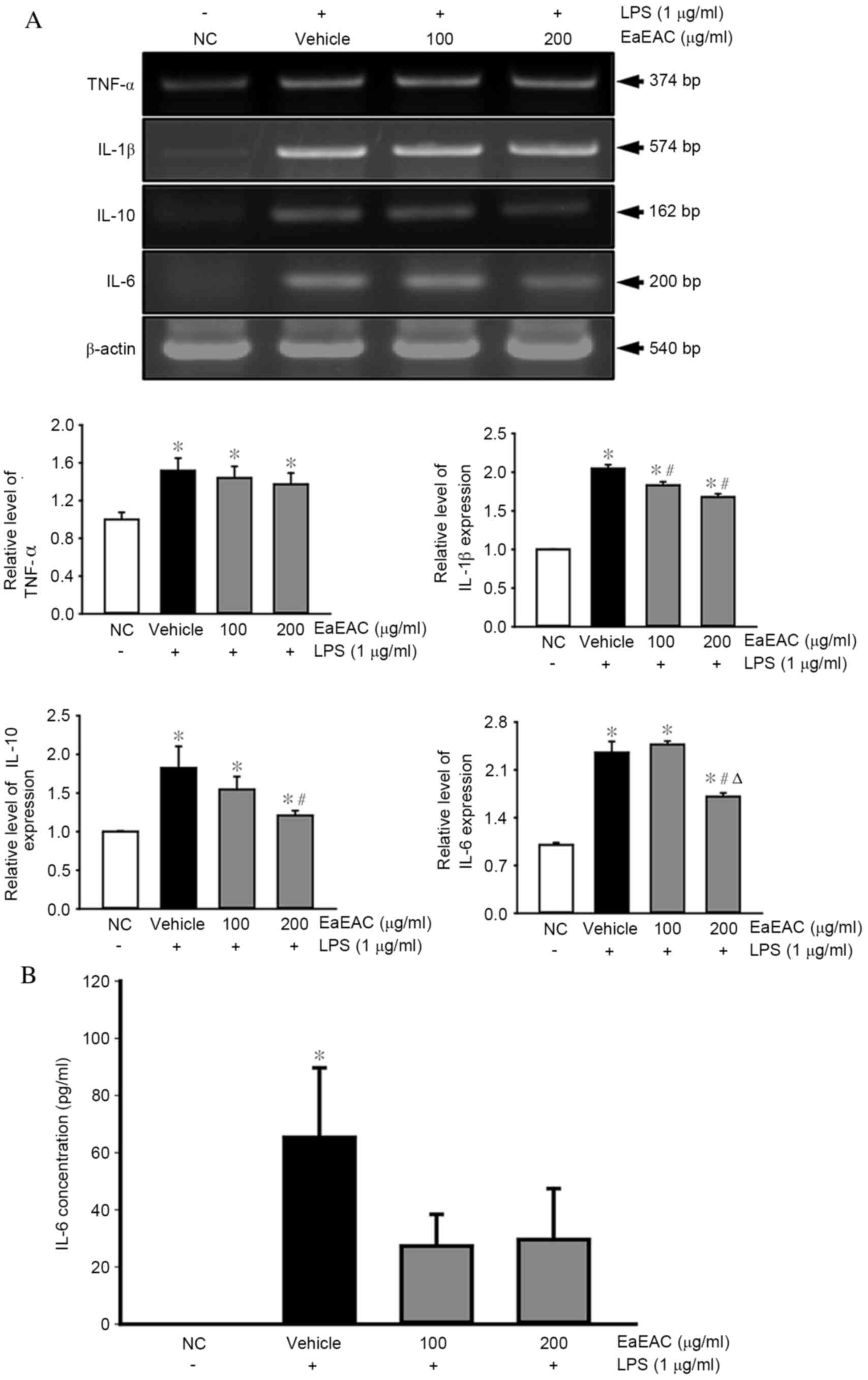
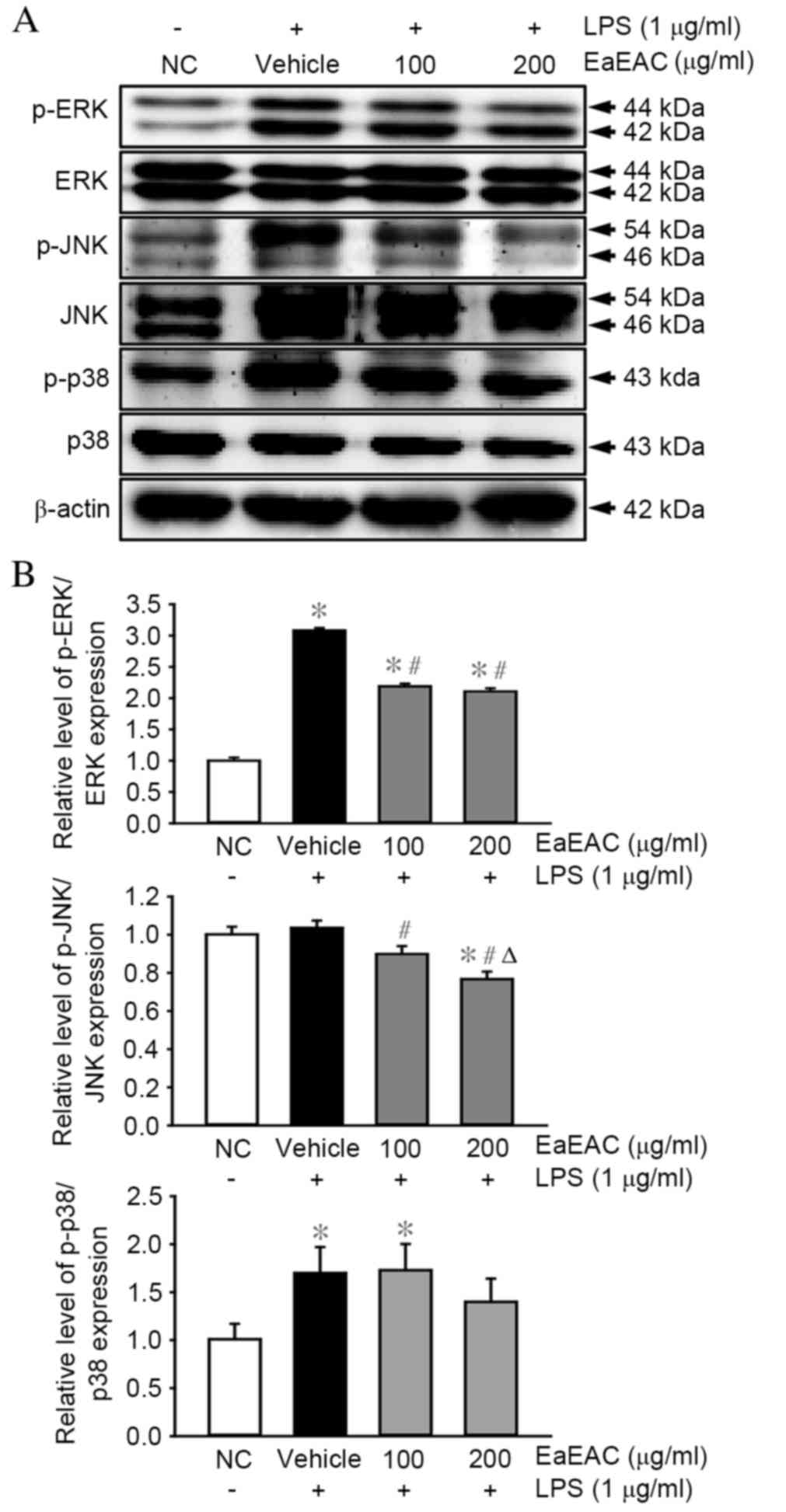
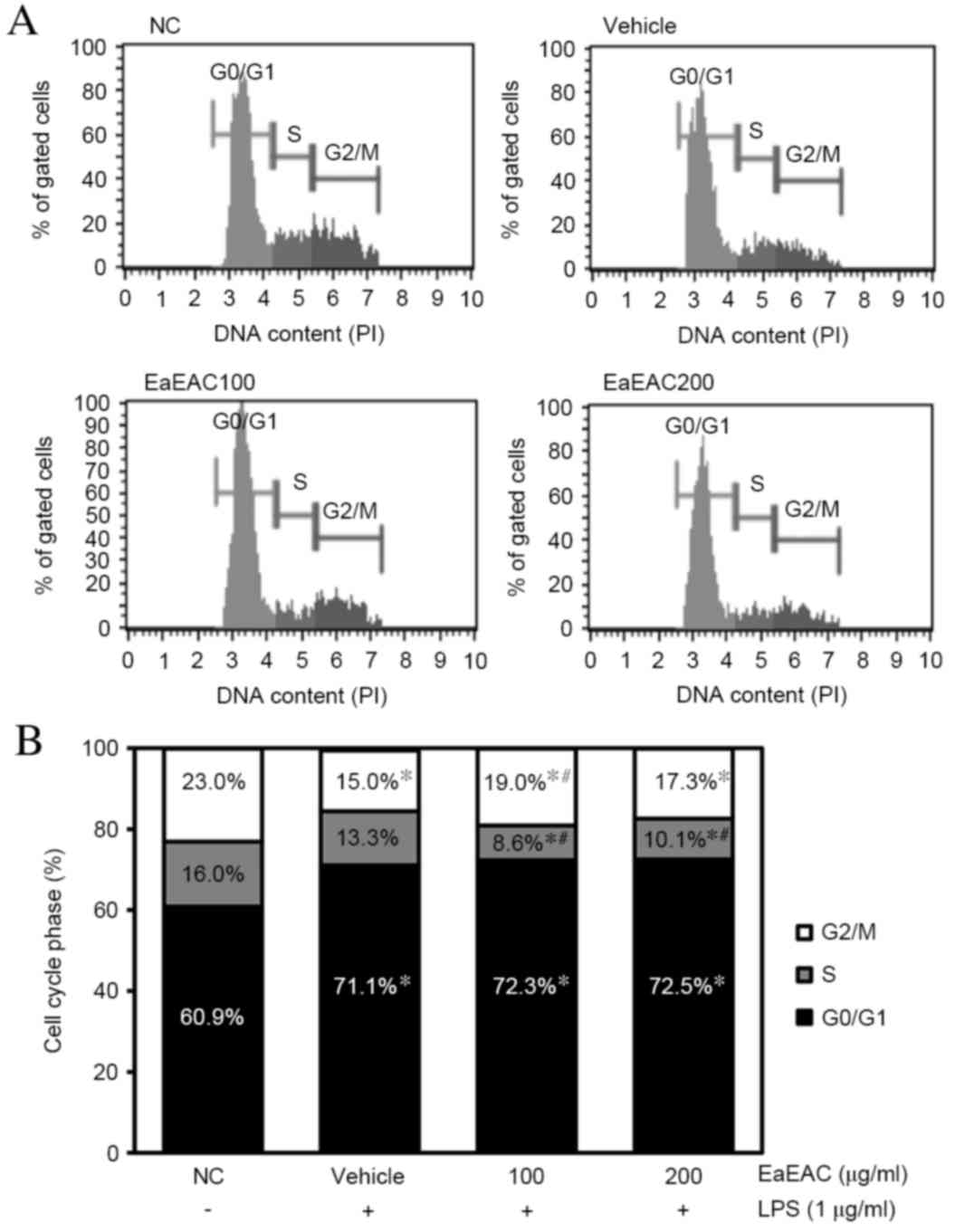
|
1
|
Xiong DS, Yu LX, Yan X, Guo C and Xiong Y:
Effects of root and stem extracts of Asparagus cochinchinensis on
biochemical indicators related to aging in the brain and liver of
mice. Am J Chinese Med. 39:719–726. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Xiao PG: Modern Chinese material medica.
Chemical Industry Press; Beijing: pp. 1502002
|
|
3
|
Liu YZ, Qu FY and Zhang PX: Effect of
chloroform extract of Tiandong on the brain antioxidation of
D-galatose-induced senile mice. Heilongjiang Med Pharm. 24:7–8.
2001.
|
|
4
|
Ni JM, Zhao R and Wang R: Comparison on
amino acid content in prepared and unprepared Asparagus
cochinchinensis. Chin Tradit Herb Drugs. 23:182–183. 1992.
|
|
5
|
Tenji K and Junzo S: Studies on the
constituents of Asparagi Radix. I. On the structures of furostanol
oligosides of Asparagus cochinchinensis (LOUREIO) MERRILL. Chem
Pharm Bull. 27:3086–3094. 1979. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Liang ZZ, Aquino R, De Simone F, Dini A,
Schettino O and Pizza C: Oligofurostanosides from Asparagus
cochinchinensis. Planta Med. 54:344–346. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yang YC, Huang SY and Shi JG: Two new
furostanol glycosides from Asparagus cochinchinensis. Chin Chem
Lett. 13:1185–1188. 2002.
|
|
8
|
Cong PZ and Keman S: Handbook of
analytical chemistry-mass volume. Chemical Industry Publishing
House; 2. Beijing: pp. 296–298. 2000
|
|
9
|
Gong YH: 13C NMR chemical shifts of
natural organic compounds. Yunnan Science and Technology Publishing
House Kunming. 2:2521986.
|
|
10
|
Yang MH: Steroidal sapogenins of
dioscorea. Chin Tradit Herb Drugs. 12:43–44. 1981.
|
|
11
|
Xu CL, Chen HS and Tan XQ: Studies on the
active constituents of Asparagi Radix. Nat Prod Res Dev.
17:128–130. 2005.
|
|
12
|
Shen Y, Chen HS and Wang Q: Studies on
chemical constituents of Asparagus cochinchinensis (II). J Second
Med Univ. 28:1241–1244. 2007.
|
|
13
|
Shen Y, Xu Cl, Xuan WD, Li HL, Liu RH, Xu
XK and Chen HS: A new furostanol saponin from Asparagus
cochinchinensis. Arch Pharm Res. 34:1587–1591. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li XN, Chu C, Cheng DP, Tong SQ and Yan
JZ: Norlignans from Asparagus Cochinchinensis. Nat Prod Commun.
7:1357–1358. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhu GL, Hao Q, Li RT and Li HZ: Steroidal
saponins from the roots of Asparagus cochinchinensis. Chin J Nat
Med. 12:213–217. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li M, Fei Y and Wang JK: Studies on
pharmacologic effects of Radix Asparagi. LiShiZhen Med Mater Med
Res. 16:580–582. 2005.
|
|
17
|
Qu FY, Wei XD, Li SL, Wang YM and Bai SG:
Experimental study of Asparagus cochinchinensis delay aging. Acta
Chin Med Pharm. 2:68–70. 1999.
|
|
18
|
Zhao YJ, Meng XL, Li XL and Qu FY:
Influence of Radix Asparagi nano-pharmaceutics on NOS NO, LPF of
aging mice. Chin Wild Plant Resour. 24:49–51. 2005.
|
|
19
|
Wen JY, Li Y, Ding SS and Li QH: Nine
Pharmacological screening of medicinal plants of China Liliaceae
Asparagus. J Acta Acad Med Shanghai. 20:107–111. 1993.
|
|
20
|
Luo J, Long Q, Li C, Li L and Huang N:
Inhibitory effects of ALWB and ACM on mice bearing tumor. J GuiYang
Med Coll. 25:15–16. 2000.
|
|
21
|
Koo HN, Jeong HJ, Choi JY, Choi SD, Choi
TJ, Cheon YS, Kim KS, Kang BK, Park ST, Chang CH, et al: Inhibition
of tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced apoptosis by Asparagus
cochlnchinensis in Hep G2 cells. J Ethnopharmacol. 73:137–143.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yu FR, Lian XZ and Guo HY: Effect of lucid
asparagus extract on the regulation of blood sugar. Chin J Clin
Rehabil. 10:57–59. 2006.
|
|
23
|
Jun L, Qingde L, Chengxiu L, Ling L,
Nenghui H, Min N and Peixian T: Comparison of antitussive,
expectorant and anti-asthmatic effect between ALWB and ACM. J
GuiYang Med Coll. 23:132–134. 1998.
|
|
24
|
Lv B and Liu WZ: Aspartate treatment of
hemodialysis patients with hypertension in 22 cases. J Tradit Chin
Med. 19:43–44. 2004.
|
|
25
|
Kim HM, Lee E, Lim T, Jung J and Lyu Y:
Inhibitory effect of Asparagus cochinchinensis on tumor necrosis
factor-alpha secretion from astrocytes. Int J Immunopharmacol.
20:153–162. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jian R, Zeng KW, Li J, Li N, Jiang Y and
Tu P: Anti-neuroinflammatory constituents from Asparagus
cochinchinensis. Fitoterapia. 84:80–84. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lee DY, Choo BK, Yoon T, Cheon MS, Lee HW,
Lee YA and Kim HK: Anti-inflammatory effects of Asparagus
cochinchinensis extract in acute and chronic cutaneous
inflammation. J Ethnopharmacol. 121:28–34. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jung KH, Choi HL, Park SJ, Lee GH, Kim MR,
Min JK, Min BI and Bae H: The effects of the standardized herbal
formula PM014 on pulmonary inflammation and airway responsiveness
in a murine model of cockroach allergen-induced asthma. J
Ethnopharmacol. 155:113–122. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chi H, Barry SP, Roth RJ, Wu JJ, Jones EA,
Bennett AM and Flavell RA: Dynamic regulation of pro- and
anti-inflammatory cytokines by MAPK phosphatase 1 (MKP-1) in innate
immune responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:2274–2279. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Oh H, Ko EK, Kim DH, Jang KK, Park SE, Lee
HS and Kim YC: Secoiridoid glucosides with free radical scavenging
activity from the leaves of Syringa dilatata. Phytother Res.
17:417–419. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Jie S, Xueji Z, Mark B and Harry F:
Measurement of nitric oxide production in biological systems by
using griess reaction assay. Sensors. 3:276–284. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Kim JE, Park SH, Kwak MH, Go J, Koh EK,
Song SH, Sung JE, Lee HS, Hong JT and Hwang DY: Characterization of
changes in global genes expression in the distal colon of
loperamide-induced constipation SD rats in response to the laxative
effects of Liriope platyphylla. PLoS One. 10:e01296642015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hou YC, Janczuk A and Wang PG: Current
trends in the development of nitric oxide donors. Curr Pharm Des.
5:417–441. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lee JH, Lim HJ, Lee CW, Son KH, Son JK,
Lee SK and Kim HP: Methyl protodioscin from the roots of Asparagus
cochinchinensis attenuates airway inflammation by inhibiting
cytokine production. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2015:6408462015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Rietschel ET, Kirikae T, Schade FU, Mamat
U, Schmidt G, Loppnow H, Ulmer AJ, Zähringer U, Seydel U and Di
Padova F: Bacterial endotoxin: Molecular relationships of structure
to activity and function. FASEB J. 8:217–25. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Stewart I, Schluter PJ and Shaw GR:
Cyanobacterial lipopolysaccharides and human health-a review.
Environ Health. 5:72006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Fujiwara N and Kobayashi K: Macrophages in
inflammation. Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy. 4:281–286. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Dalmas E, Tordjman J, Guerre-Millo M and
Clément K: Macrophages and inflammationAdipose Tissue Biology.
Symonds ME: Springer; New York, NY: pp. 167–193. 2012, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Jou IM, Lin CF, Tsai KJ and Wei SJ:
Macrophage-mediated inflammatory disorders. Mediators Inflamm.
2013:3164822013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yang GY, Liao J, Li C, Chung J, Yurkow EJ,
Ho CT and Yang CS: Effect of black and green tea polyphenols on
c-jun phosphorylation and H(2)O(2) production in transformed and
non-transformed human bronchial cell lines: Possible mechanisms of
cell growth inhibition and apoptosis induction. Carcinogenesis.
21:2035–2039. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lee SJ, Kang HY, Lee SY and Hur SJ: Green
tea polyphenol Epigallocatechin-3-O-Gallate attenuates
lipopolysaccharide-induced nitric oxide production in RAW264.7
cells. J Food Nutr Res. 2:425–428. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Hashimoto K and Sakagami H: Induction of
apoptosis by Epigallocatechin gallate and autophagy inhibitors in a
mouse macrophage-like cell line. Anticancer Res. 28:1713–1718.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kamijo R, Gerecitano J, Shapiro D, Green
SJ, Aguet M, Le J and Vilcek J: Generation of nitric oxide and
clearance of interferon-gamma after BCG infection are impaired in
mice that lack the interferon-gamma receptor. J Inflamm. 46:23–31.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Jian R, Zeng KW, Li J, Li N, Jiang Y and
Tu P: Anti-neuroinflammatory constituents from Asparagus
cochinchinensis. Fitoterapia. 84:80–84. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Scheller J, Chalaris A, Schmidt-Arras D
and Rose-John S: The pro- and anti-inflammatory properties of the
cytokine interleukin-6. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1813:878–888. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Szabó C: Role of nitric oxide in endotoxic
shock. An overview of recent advances. Ann N Y Acad Sci.
851:422–425. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Martel-Pelletier J, Pelletier JP and Fahmi
H: Cyclooxygenase-2 and prostaglandins in articular tissues. Semin
Arthritis Rheum. 33:155–167. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Berghe W Vanden, Plaisance S, Boone E, De
bosscher K, Schmitz ML, Fiers W and Haegeman G: p38 and
extracellular signal-regulated kinase mitogen-activated protein
kinase pathways are required for nuclear factor-kappaB p65
transactivation mediated by tumor necrosis factor. J Biol Chem.
273:3285–3290. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Weinstein SL, Sanghera JS, Lemke K,
DeFranco AL and Pelech SL: Bacterial lipopolysaccharide induces
tyrosine phosphorylation and activation of mitogen-activated
protein kinases in macrophages. J Biol Chem. 267:14955–14962.
1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Comalada M, Xaus J, Valledor AF,
López-López C, Pennington DJ and Celada A: PKC epsilon is involved
in JNK activation that mediates LPS-induced TNF-alpha, which
induces apoptosis in macrophages. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
285:C1235–C1245. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Ulevitch RJ and Tobias PS:
Receptor-dependent mechanisms of cell stimulation by bacterial
endotoxin. Annu Rev Immunol. 13:437–457. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Weinstein SL, Sanghera JS, Lemke K,
DeFranco AL and Pelech SL: Bacterial lipopolysaccharide induces
tyrosine phosphorylation and activation of mitogen-activated
protein kinases in macrophages. J Biol Chem. 267:14955–14962.
1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Kirouac L, Mathew M and Padmanabhan J:
Interplay between inflammation and cell cycle deregulation in
Alzheimer's disease. JSM Alzheimer's Dis and Related Dementia.
2:10182015.
|
|
54
|
Stockley JA, Walton GM, Lord JM and Sapey
E: Aberrant neutrophil functions in stable chronic obstructive
pulmonary disease: The neutrophil as an immunotherapeutic target.
Int Immunopharmacol. 17:1211–1217. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Dudhgaonkar S, Thyagarajan A and Sliva D:
Suppression of the inflammatory response by triterpenes isolated
from the mushromm Ganoderma lucidum. Int Immunopharmacol.
9:1272–1280. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Bak MJ, Truong VL, Kang HS, Jun MR and
Jeong WS: Anti-inflammatory effect of procyanidins from wild grape
(Vitis amurensis) seeds in LPS-induced RAW 264.7 cells. Oxid Med
Cell Longev. 2013:4093212013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Choi HS, Seo HS, Kim SR, Choi YK, Shin YC
and Ko SG: Anti-inflammatory and anti-proliferative effect of
herbal medicines (APR) in RAW264.7 cells. Mol Med Rep. 9:1569–1574.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Halliwell B: Reactive oxygen species and
the central nervous system. J Neurochem. 59:1609–1623. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Xiong D, Yu LX, Yan X, Guo C and Xiong Y:
Effects of root and stem extracts of Asparagus cochinchinensis on
biochemical indicators related to aging in the brain and liver of
mice. Am J Chin Med. 39:719–726. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|