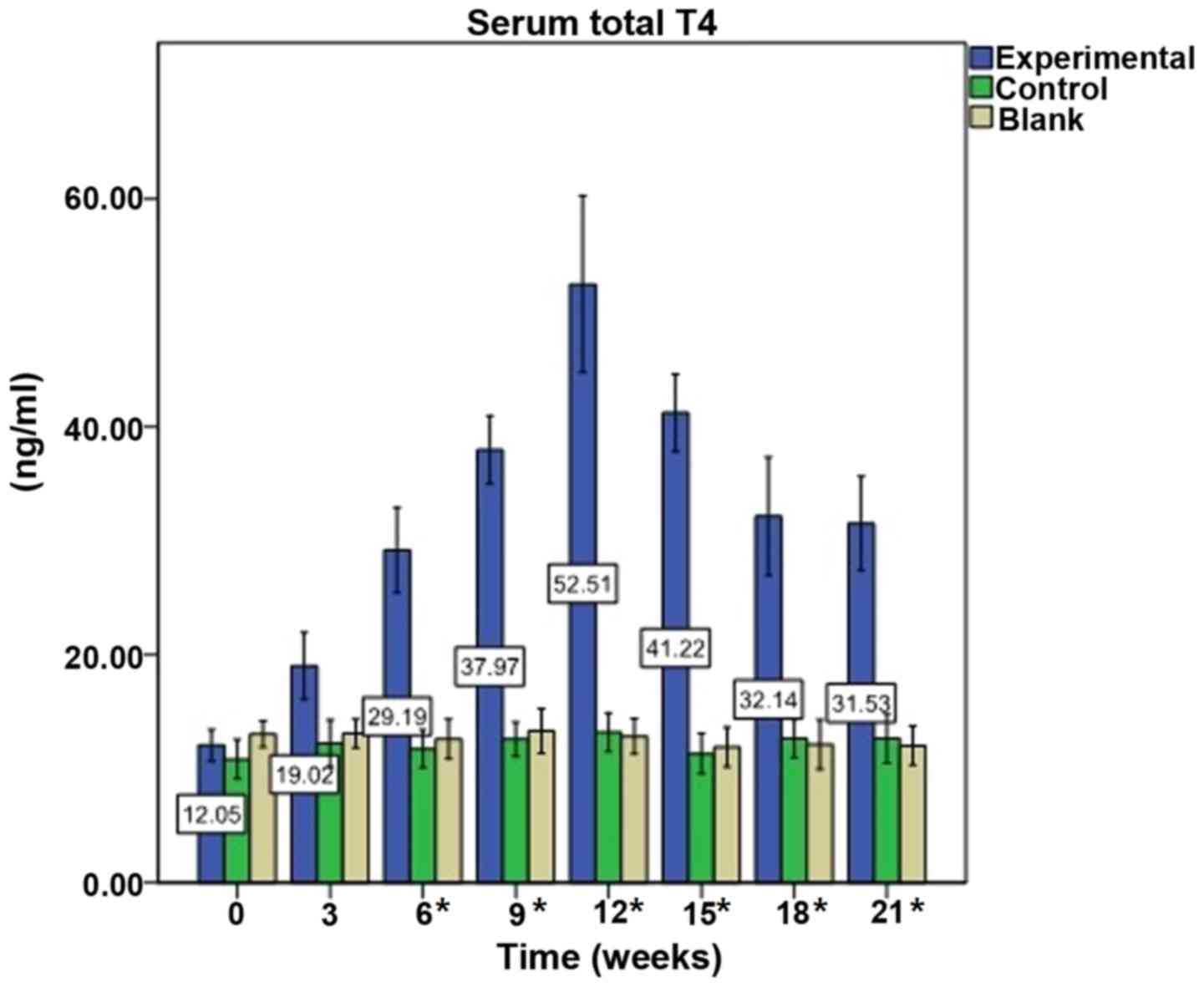
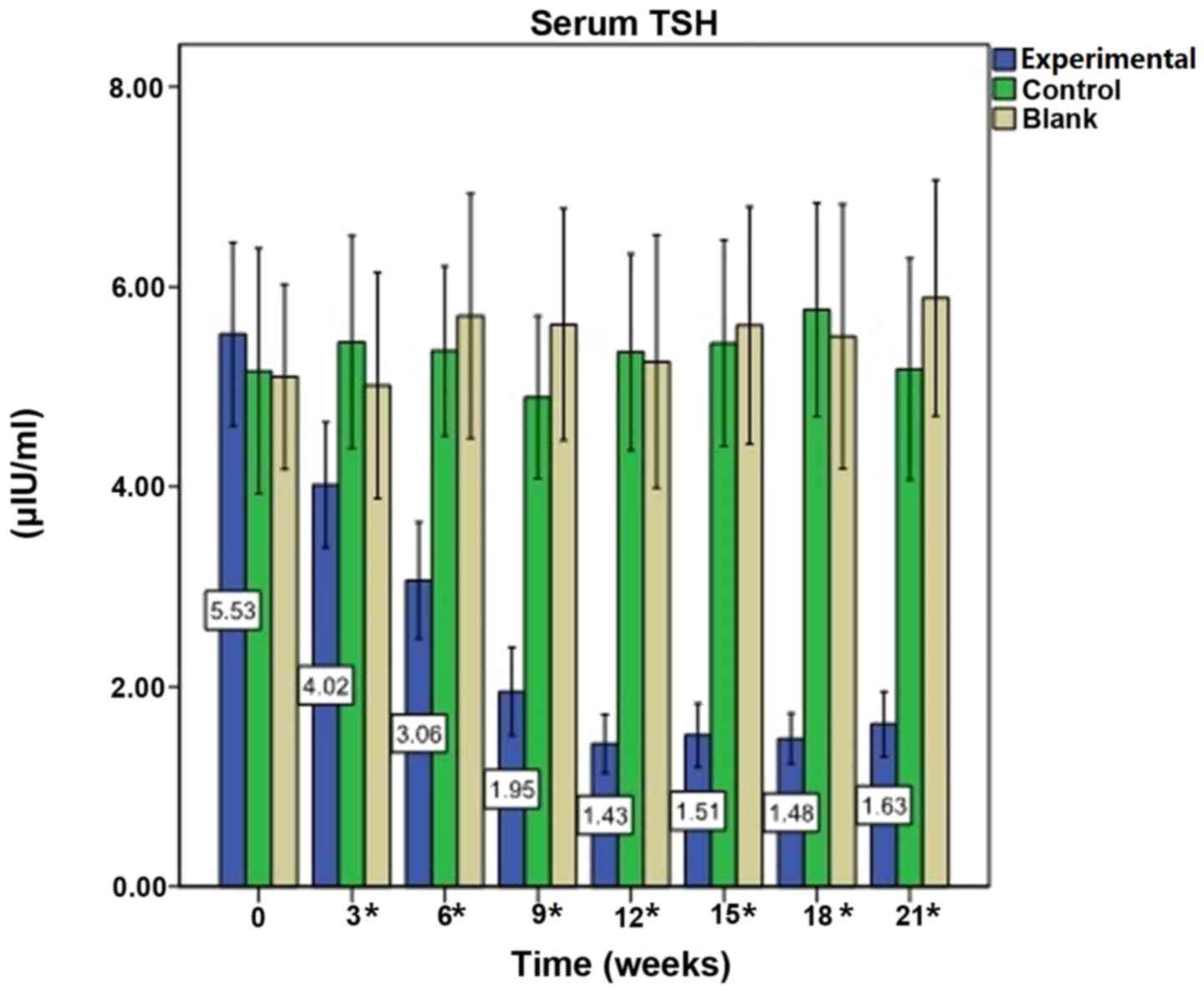
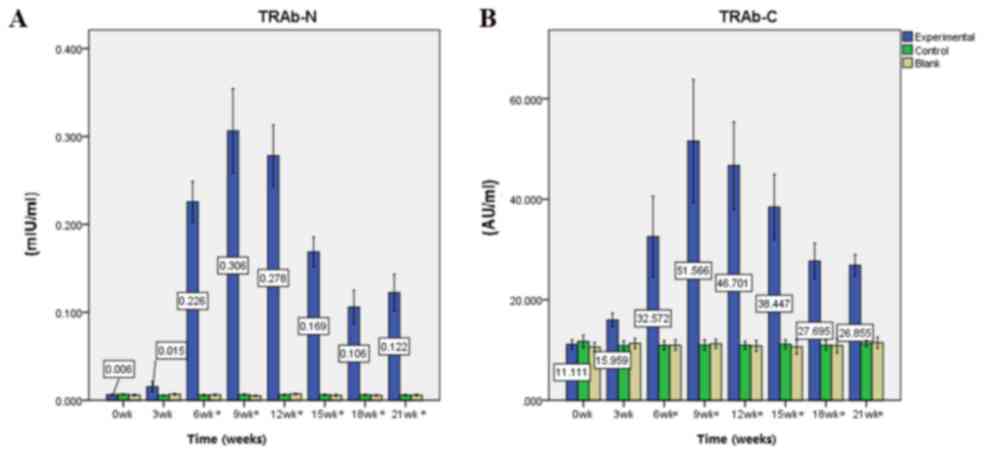
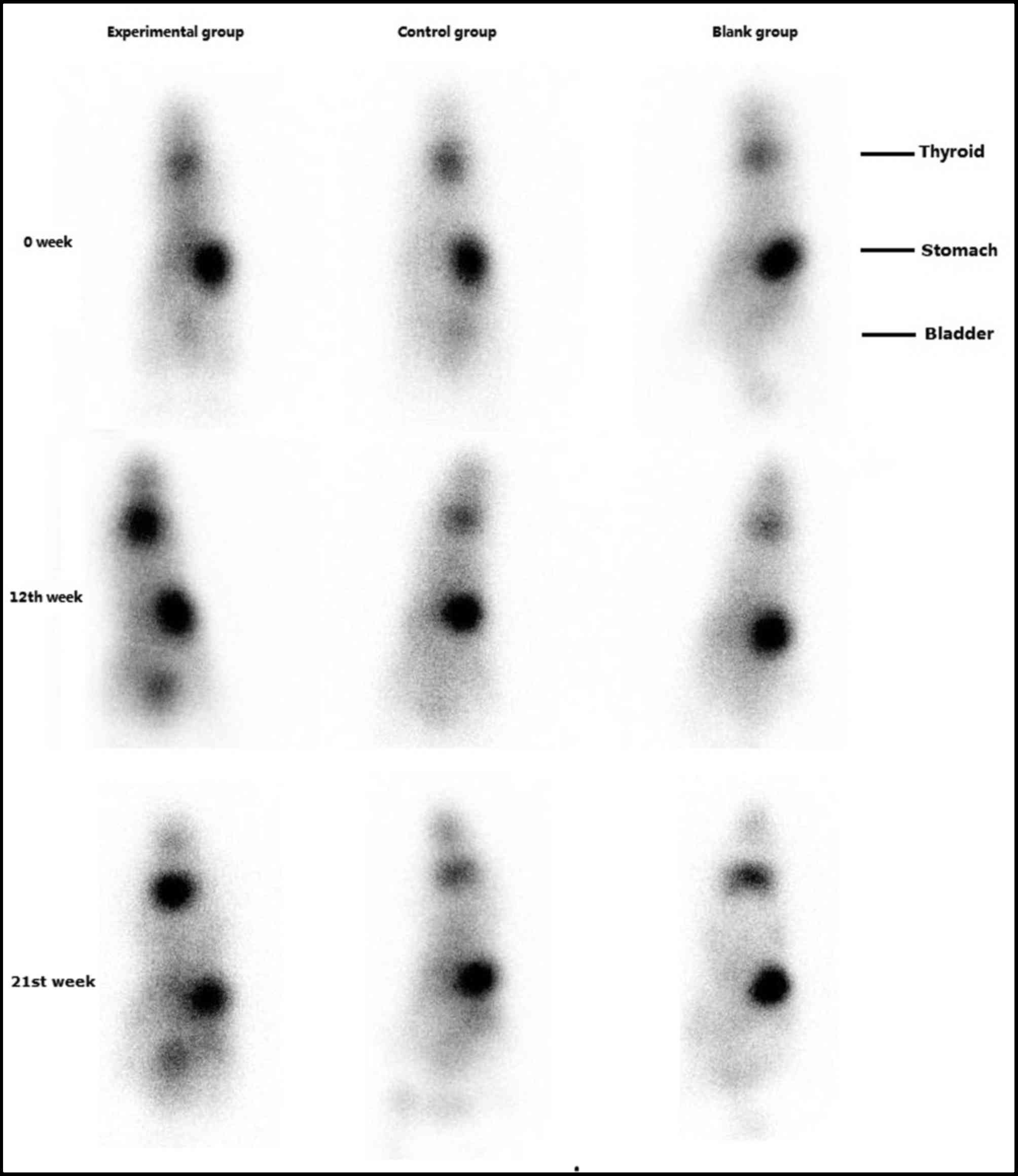
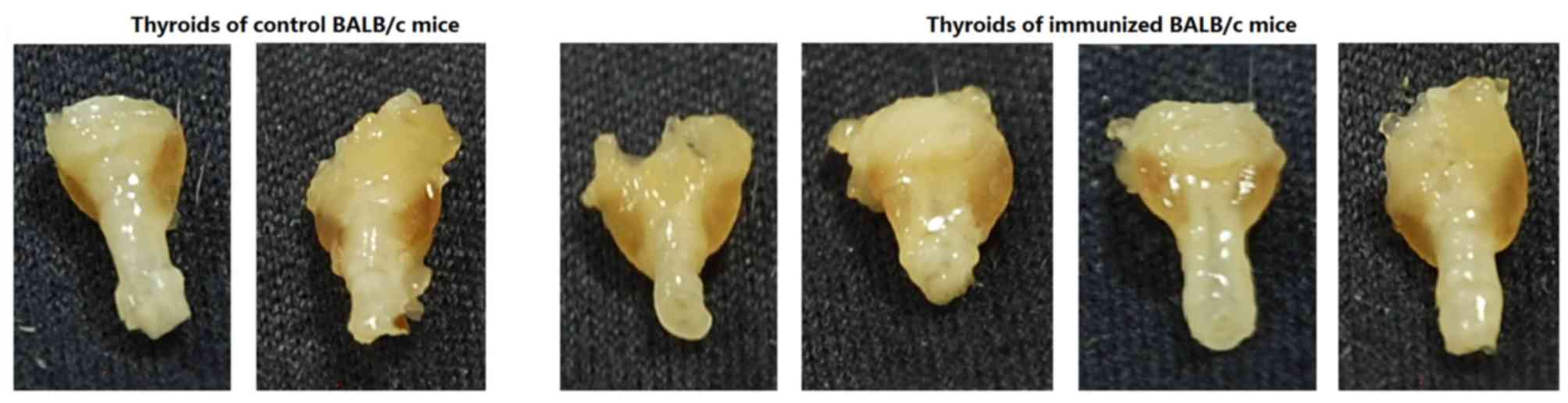
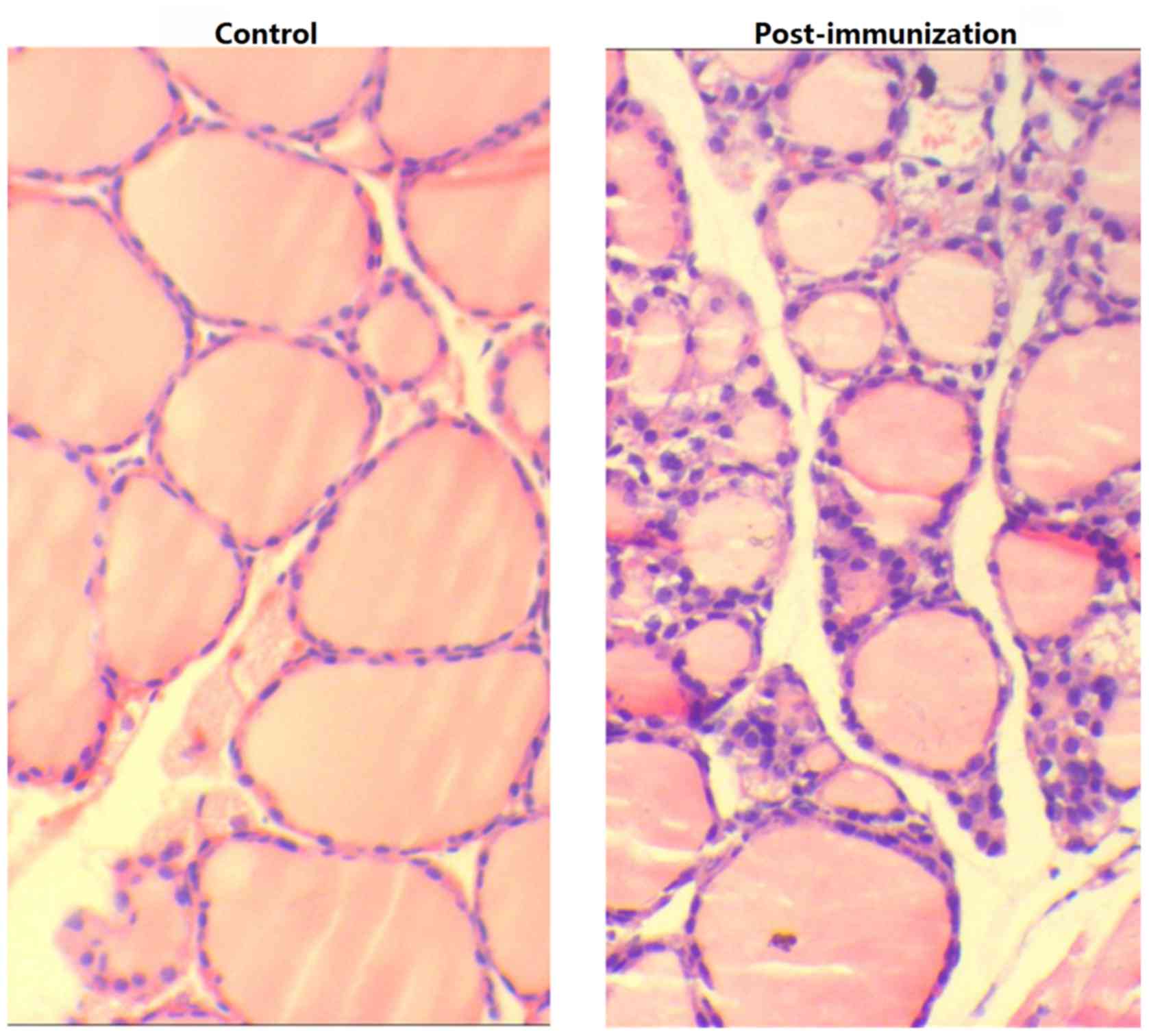
|
1
|
Teng W, Shan Z, Teng X, Guan H, Li Y, Teng
D, Jin Y, Yu X, Fan C, Chong W, et al: Effect of iodine intake on
thyroid diseases in China. N Engl J Med. 354:2783–2793. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Smith B Rees, McLachlan SM and Furmaniak
J: Autoantibodies to the thyrotropin receptor. Endocr Rev.
9:106–121. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rapoport B, Chazenbalk GD, Jaume JC and
McLachlan SM: The thyrotropin (TSH) receptor: Interaction with TSH
and autoantibodies. Endocr Rev. 19:673–716. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Andrade VA, Gross JL and Maia AL: Serum
thyrotropin-receptor autoantibodies levels after I therapy in
Graves' patients: Effect of pretreatment with methimazole evaluated
by a prospective, randomized study. Eur J Endocrinol. 151:467–474.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Takasu N, Kamijo K, Sato Y, Yoshimura H,
Nagata A and Ochi Y: Sensitive thyroid-stimulating antibody assay
with high concentrations of polyethylene glycol for the diagnosis
of Graves' disease. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 31:314–319. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
McKenna TJ: Graves' disease. Lancet.
357:1793–1796. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ross DS, Burch HB, Cooper DS, Greenlee MC,
Laurberg P, Maia AL, Rivkees SA, Samuels M, Sosa JA, Stan MN and
Walter MA: 2016 American thyroid association guidelines for
diagnosis and management of hyperthyroidism and other causes of
thyrotoxicosis. Thyroid. 26:1343–1421. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Shimojo N, Kohno Y, Yamaguchi K, Kikuoka
S, Hoshioka A, Niimi H, Hirai A, Tamura Y, Saito Y, Kohn LD and
Tahara K: Induction of Graves-like disease in mice by immunization
with fibroblasts transfected with the thyrotropin receptor and a
class II molecule. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 93:11074–11079. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Costagliola S, Many MC, Denef JF, Pohlenz
J, Refetoff S and Vassart G: Genetic immunization of outbred mice
with thyrotropin receptor cDNA provides a model of Graves' disease.
J Clin Invest. 105:803–811. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Vicat JM, Boisseau S, Jourdes P, Lainé M,
Wion D, Bouali-Benazzouz R, Benabid AL and Berger F: Muscle
transfection by electroporation with high-voltage and short-pulse
currents provides high-level and long-lasting gene expression. Hum
Gene Ther. 11:909–916. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li N, Fang P, Zhang Y and Li S: A novel
human TSHR antibody ELISA using recombinant extracellular domain
fragments of human TSH receptor as antigen and initial clinical
evaluation. Chin J Nucl Med. 29:348–351. 2009.
|
|
12
|
Olesen H: Properties and units in the
clinical laboratory sciences. I. Syntax and semantic rules
(recommendation 1995). International union of pure and applied
chemistry (IUPAC) and international federation of clinical
chemistry (IFCC). Eur J Clin Chem Clin Biochem. 33:627–636.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hine IF: Block staining of mammalian
tissues with hematoxylin and eosin. Stain Technol. 56:119–123.
1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Morshed SA, Latif R and Davies TF:
Delineating the autoimmune mechanisms in Graves' disease. Immunol
Res. 54:191–203. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Marino M, Chiovato L and Pinchera A:
Graves' diseaseDe Groot LJ and Jameson JL: Endocrinology eds. 5th
edition. Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders. 1979–1994. 2006,
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Zheng W, Tan J, Zhang G, Meng Z and Wang
R: Analysis of 131I therapy and correlation factors of Graves'
disease patients: A 4-year retrospective study. Nucl Med Commun.
33:97–101. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Morshed SA, Latif R and Davies TF:
Characterization of thyrotropin receptor antibody-induced signaling
cascades. Endocrinology. 150:519–529. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ochi Y, Kajita Y, Hachiya T and Hamaoki M:
A novel hypothesis for the etiology of Graves' disease: TSAb may be
thyroid stimulating animal IgG-like hormone and TBAb may be the
precursor of TSAb. Med Hypotheses. 78:781–786. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nagayama Y: Animal models of Graves'
hyperthyroidism. Endocr J. 52:385–394. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ye F, Shi B, Wu X, Hou P, Gao L, Ma X, Xu
L and Wu L: Experience with lentivirus-mediated CD40 gene silencing
in a mouse model of Graves' disease. J Endocrinol. 208:285–291.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kaneda T, Honda A, Hakozaki A, Fuse T,
Muto A and Yoshida T: An improved Graves' disease model established
by using in vivo electroporation exhibited long-term immunity to
hyperthyroidism in BALB/c mice. Endocrinology. 148:2335–2344. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Nagayama Y, Kita-Furuyama M, Ando T, Nakao
K, Mizuguchi H, Hayakawa T, Eguchi K and Niwa M: A novel murine
model of Graves' hyperthyroidism with intramuscular injection of
adenovirus expressing the thyrotropin receptor. J Immunol.
168:2789–2794. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wu LP, Shi BY, Xun LR, Guo LY, Yang J and
Xu L: An exploration of induction methodology and experimental
duration of Graves disease animal model. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi.
51:793–797. 2012.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ludgate M: Animal models of Graves'
disease. Eur J Endocrinol. 142:1–8. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|