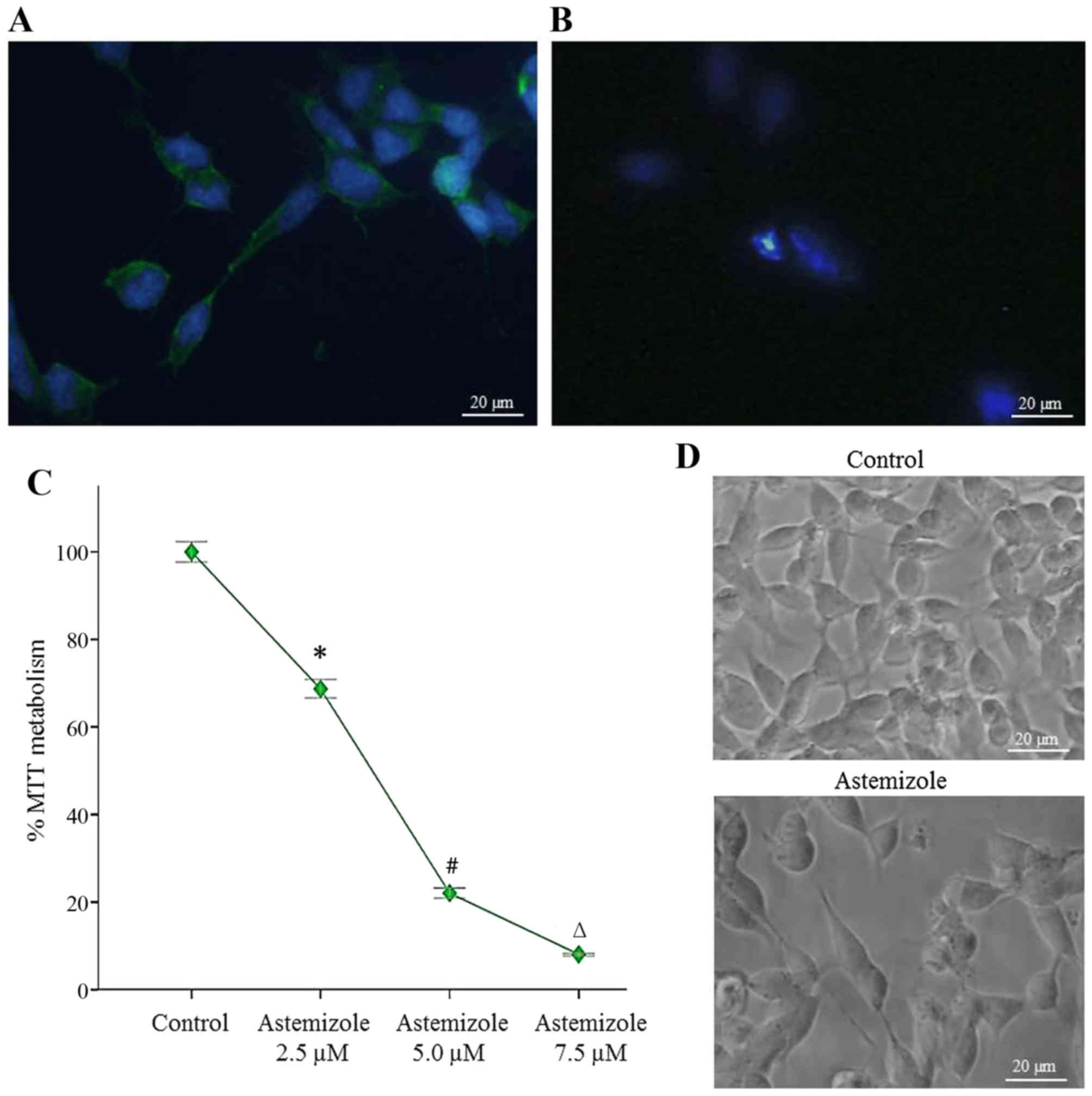
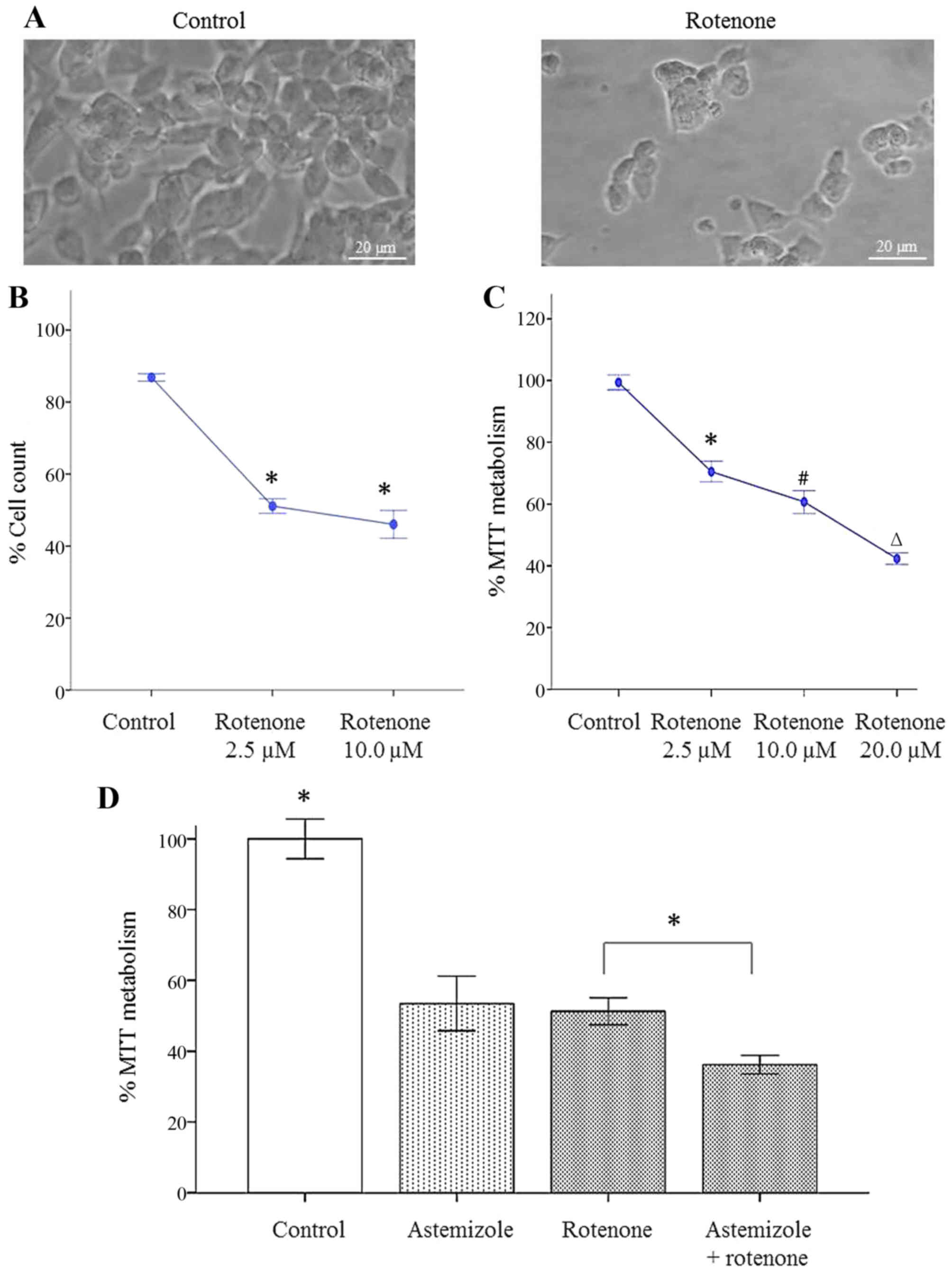
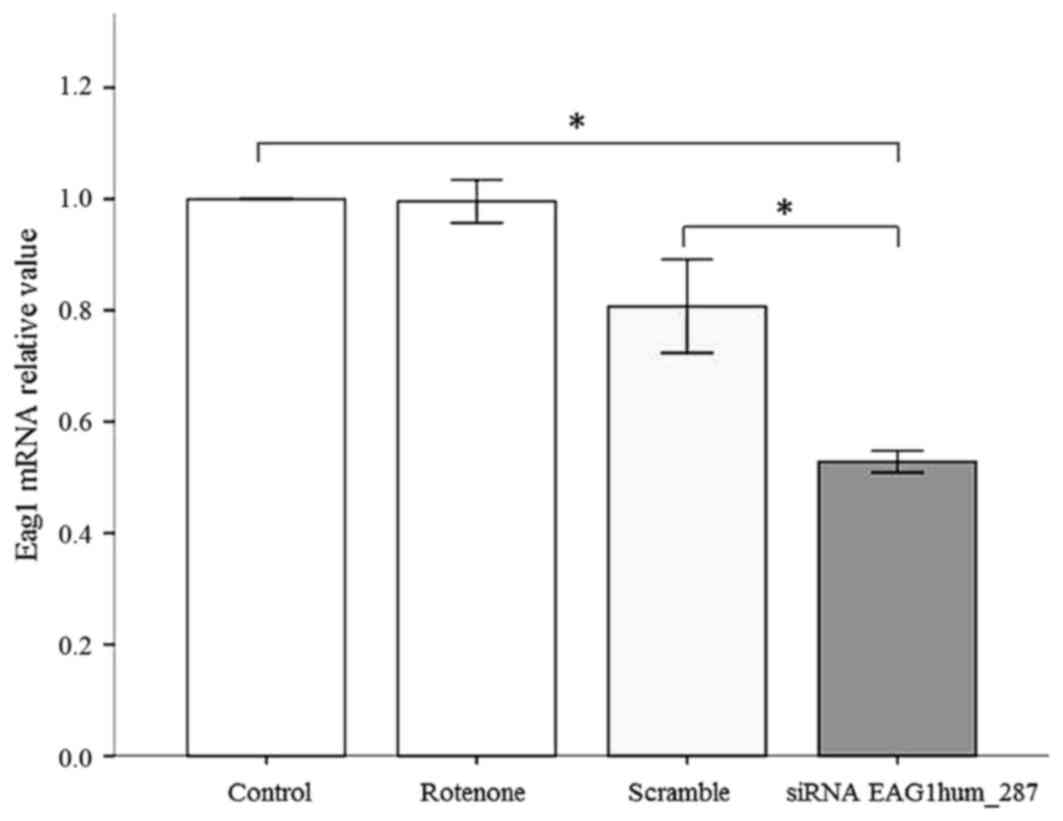
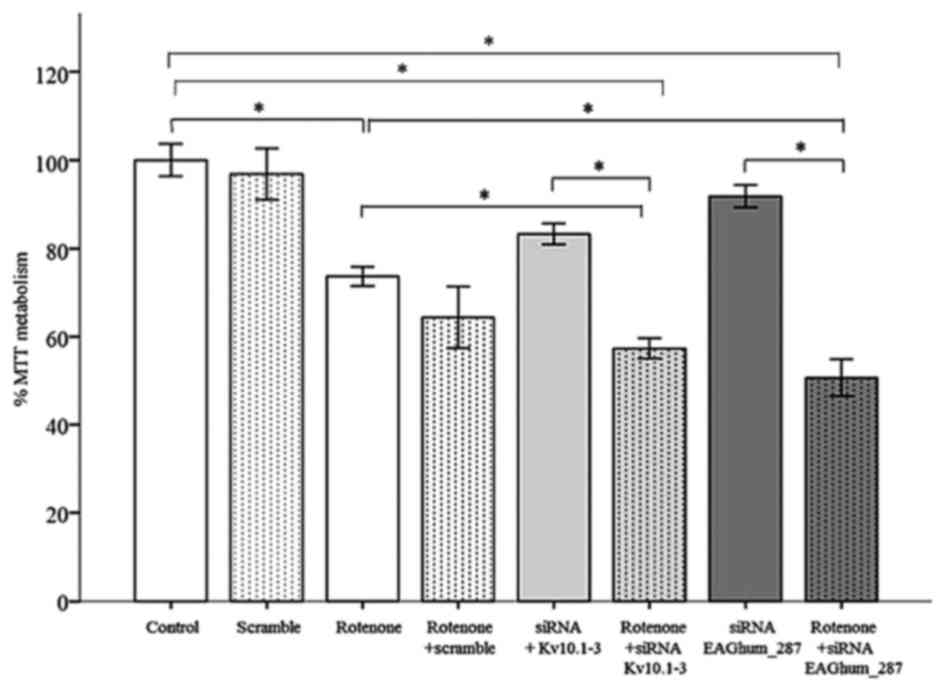
|
1
|
Shulman JM, De Jager PL and Feany MB:
Parkinson's disease: Genetics and pathogenesis. Annu Rev Pathol.
6:193–222. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tanner CM, Kamel F, Ross GW, Hoppin JA,
Goldman SM, Korell M, Marras C, Bhudhikanok GS, Kasten M, Chade AR,
et al: Rotenone, paraquat, and Parkinson's disease. Environ Health
Perspect. 119:866–872. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bové J, Prou D, Perier C and Przedborski
S: Toxin-induced models of Parkinson's disease. NeuroRx. 2:484–494.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Betarbet R, Sherer TB, MacKenzie G,
Garcia-Osuna M, Panov AV and Greenamyre JT: Chronic systemic
pesticide exposure reproduces features of Parkinson's disease. Nat
Neurosci. 3:1301–1306. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Dauer W and Przedborski S: Parkinson's
disease: Review. mechanisms and models. Neuron. 39:889–909. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Uversky VN: Neurotoxicant-induced animal
models of Parkinson's disease: Understanding the role of rotenone,
maneb and paraquat in neurodegeneration. Cell Tissue Res.
318:225–241. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Przedborski S: Pathogenesis of nigral cell
death in Parkinson's disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 11 Suppl
1:S3–S7. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xie HR, Hu LS and Li GY: SH-SY5Y human
neuroblastoma cell line: In vitro cell model of dopaminergic
neurons in Parkinson's desease. Chin Med J (Engl). 123:1086–1092.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lin H, Li Z, Chen C, Luo X, Xiao J, Dong
D, Lu Y, Yang B and Wang Z: Transcriptional and
post-transcriptional mechanisms for oncogenic overexpression of
ether à go-go K+ channel. PLoS One. 6:e203622011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bernstein AI, Garrison SP, Zambetti GP and
O'Malley KL: 6-OHDA generated ROS induces DNA damage and p53- and
PUMA-dependent cell death. Mol Neurodegener. 6:22011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ferreira NR, Mitkovski M, Stühmer W, Pardo
LA and Del Bel EA: Ether-à-go-go 1 (Eag1) potassium channel
expression in dopaminergic neurons of the basal ganglia is
modulated by 6-hydroxydopamine lesion. Neurotox Res. 21:317–333.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Brüggemann A, Pardo LA, Stühmer W and
Pongs O: Ether-a-go-go encodes a voltage-gated channel permeable to
K+ and Ca2+ and modulated by cAMP. Nature. 365:445–448. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kondratskyi A, Kondratska K, Skryma R and
Prevarskaya N: Ion channels in the regulation of apoptosis. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1848:2532–2546. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Urrego D, Tomczak AP, Zahed F, Stühmer W
and Pardo LA: Potassium channels in cell cycle and cell
proliferation. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci.
369:201300942014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Manfredsson FP, Lewin AS and Mandel RJ:
RNA knockdown as a potential therapeutic strategy in Parkinson's
disease. Gene Ther. 13:517–24. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Weber C, De Queiroz F Mello, Downie BR,
Suckow A, Stühmer W and Pardo LA: Silencing the activity and
proliferative properties of the human Eag1 potassium channel by RNA
interference. J Biol Chem. 281:13030–13037. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cunha LC, Del Bel E, Pardo L, Stühmer W
and Titze-de-Almeida R: RNA interference with EAG1 enhances
interferon gamma injury to glioma cells in vitro. Anticancer Res.
33:865–870. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Junn E and Mouradian MM: MicroRNAs in
neurodegenerative diseases and their therapeutic potential.
Pharmacol Ther. 133:142–50. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Heman-Ackah SM, Hallegger M, Rao MS and
Wood MJ: RISC in PD: The impact of microRNAs in Parkinson's disease
cellular and molecular pathogenesis. Front Mol Neurosci.
20:402013.
|
|
20
|
Hu K, Xie YY, Zhang C, Ouyang DS, Long HY,
Sun DN, Long LL, Feng L, Li Y and Xiao B: MicroRNA expression
profile of the hippocampus in a rat model of temporal lobe epilepsy
and miR-34a-targeted neuroprotection against hippocampal neurone
cell apoptosis post-status epilepticus. BMC Neurosci. 13:1152012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sano T, Reynolds JP, Jimenez-Mateos EM,
Matsushima S, Taki W and Henshall DC: MicroRNA-34a upregulation
during seizure-induced neuronal death. Cell Death Dis. 3:e2872012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kwon MJ, Oh E, Lee S, Roh MR, Kim SE, Lee
Y, Choi YL, In YH, Park T, Koh SS and Shin YK: Identification of
novel reference genes using multiplatform expression data and their
validation for quantitative gene expression analysis. PLoS One.
4:e61622009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ririe KM, Rasmussen RP and Wittwer CT:
Product differentiation by analysis of DNA melting curves during
the polymerase chain reaction. Anal Biochem. 245:154–460. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Agid Y: Parkinson's disease:
Pathophysiology. Lancet. 337:1321–1324. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Alberio T, Lopiano L and Fasano M:
Cellular models to investigate biochemical pathways in Parkinson's
disease. FEBS J. 297:1146–1155. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Meyer R and Heinemann SH: Characterization
of an eag-like potassium channel in human neuroblastoma cells. J
Physiol. 508:49–56. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kazmierczak M, Zhang X, Chen B, Mulkey DK,
Shi Y, Wagner PG, Pivaroff-Ward K, Sassic JK, Bayliss DA and Jegla
T: External pH modulates EAG superfamily K+ channels through
EAG-specific acidic residues in the voltage sensor. J Gen Physiol.
141:721–735. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang Y, Yang PL, Tang JF, Lin JF, Cai XH,
Wang XT and Zheng GQ: Potassium channels: Possible new therapeutic
targets in Parkinson's disease. Med Hypotheses. 71:546–550. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sanguinetti MC and Spector PS: Potassium
channelopathies. Neuropharmacology. 36:755–762. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shieh CC, Coghlan M, Sullivan JP and
Gopalakrishnan M: Potassium channels: Molecular defects, diseases,
and therapeutic opportunities. Pharmacol Rev. 52:557–594.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Berridge MV, Tan AS, McCoy KD and Wang R:
The biochemical and cellular basis of cell proliferation assays
that use tetrazolium salts. Biochemica. 4:14–19. 1996.
|
|
33
|
Kosik KS: The neuronal microRNA system.
Nat Rev Neurosci. 7:911–920. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hébert SS and De Strooper B: Alterations
of the microRNA network cause neurodegenerative disease. Trends
Neurosci. 32:199–206. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Weinberg MS and Wood MJ: Short non-coding
RNA biology and neurodegenerative disorders: Novel disease targets
and therapeutics. Hum Mol Genet. 18:R27–R39. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Baek D, Villén J, Shin C, Camargo FD, Gygi
SP and Bartel DP: The impact of microRNAs on protein output.
Nature. 455:64–71. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Selbach M, Schwanhäusser B, Thierfelder N,
Fang Z, Khanin R and Rajewsky N: Widespread changes in protein
synthesis induced by microRNAs. Nature. 455:58–63. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Seeliger MA and Moll UM:
p73-constitutively open for business. Cell Death Differ.
20:972–973. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Olsen L, Klausen M, Helboe L, Nielsen FC
and Werge T: MicroRNAs show mutually exclusive expression patterns
in the brain of adult male rats. PLoS One. 4:e72252009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Sales TT, Resende FF, Chaves NL,
Titze-de-Almeida SS, Báo SN, Brettas ML and Titze-de-almeida R:
Suppression of the Eag1 potassium channel sensitizes glioblastoma
cells to injury caused by temozolomide. Oncol Lett. 12:2581–2589.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Alural B, Ozerdem A, Allmer J, Genc K and
Genc S: Lithium protects against paraquat neurotoxicity by NRF2
activation and miR-34a inhibition in SH-SY5Y cells. Front Cell
Neurosci. 9:2092015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Jimenez-Mateos EM, Engel T, Merino-Serrais
P, McKiernan RC, Tanaka K, Mouri G, Sano T, O'Tuathaigh C,
Waddington JL, Prenter S, et al: Silencing microRNA-134 produces
neuroprotective and prolonged seizure-suppressive effects. Nat Med.
18:1087–1094. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Jimenez-Mateos EM, Engel T, Merino-Serrais
P, Fernaud-Espinosa I, Rodriguez-Alvarez N, Reynolds J, Reschke CR,
Conroy RM, McKiernan RC, deFelipe J and Henshall DC: Antagomirs
targeting microRNA-134 increase hippocampal pyramidal neuron spine
volume in vivo and protect against pilocarpine-induced status
epilepticus. Brain Struct Funct. 220:2387–2399. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|