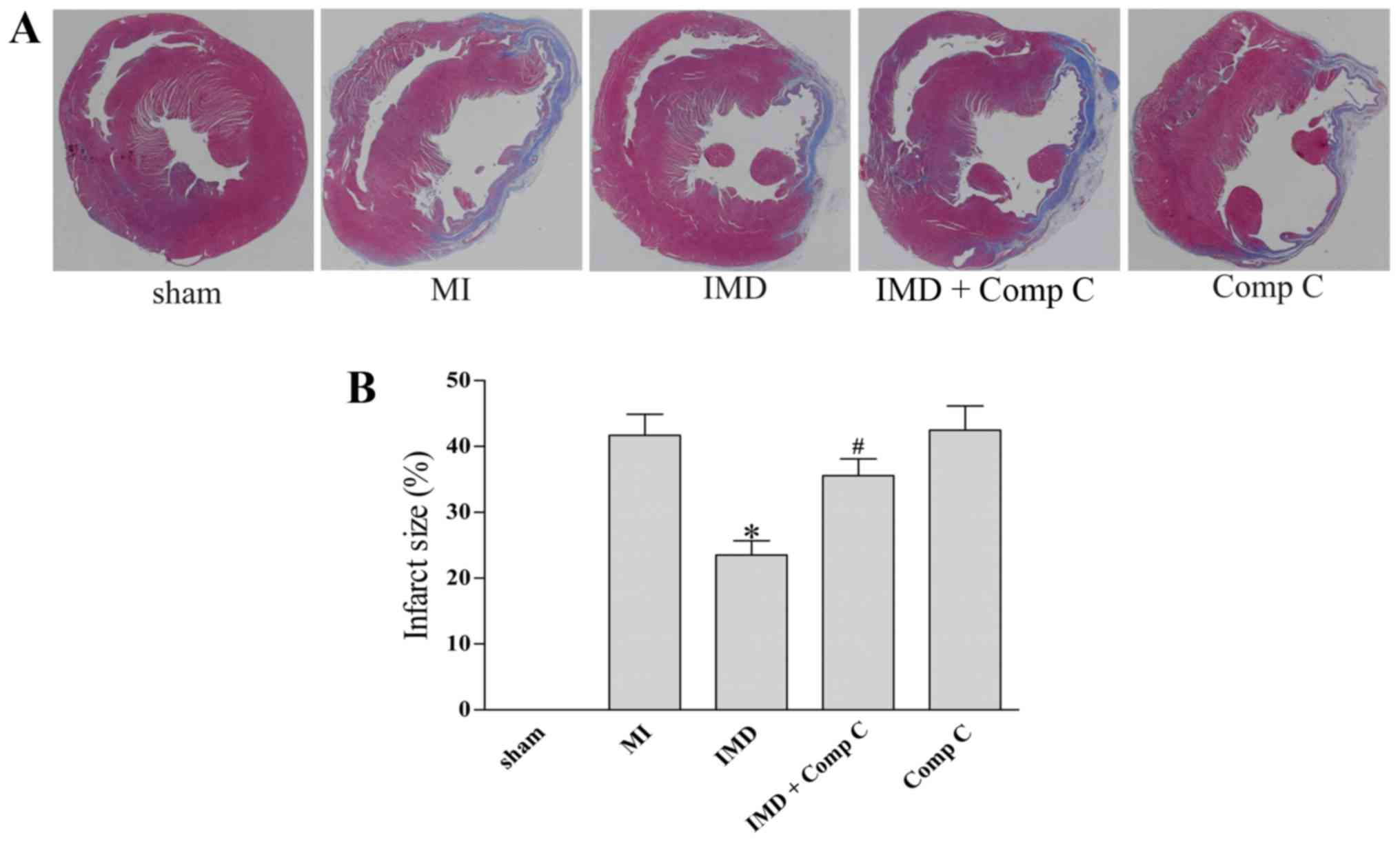
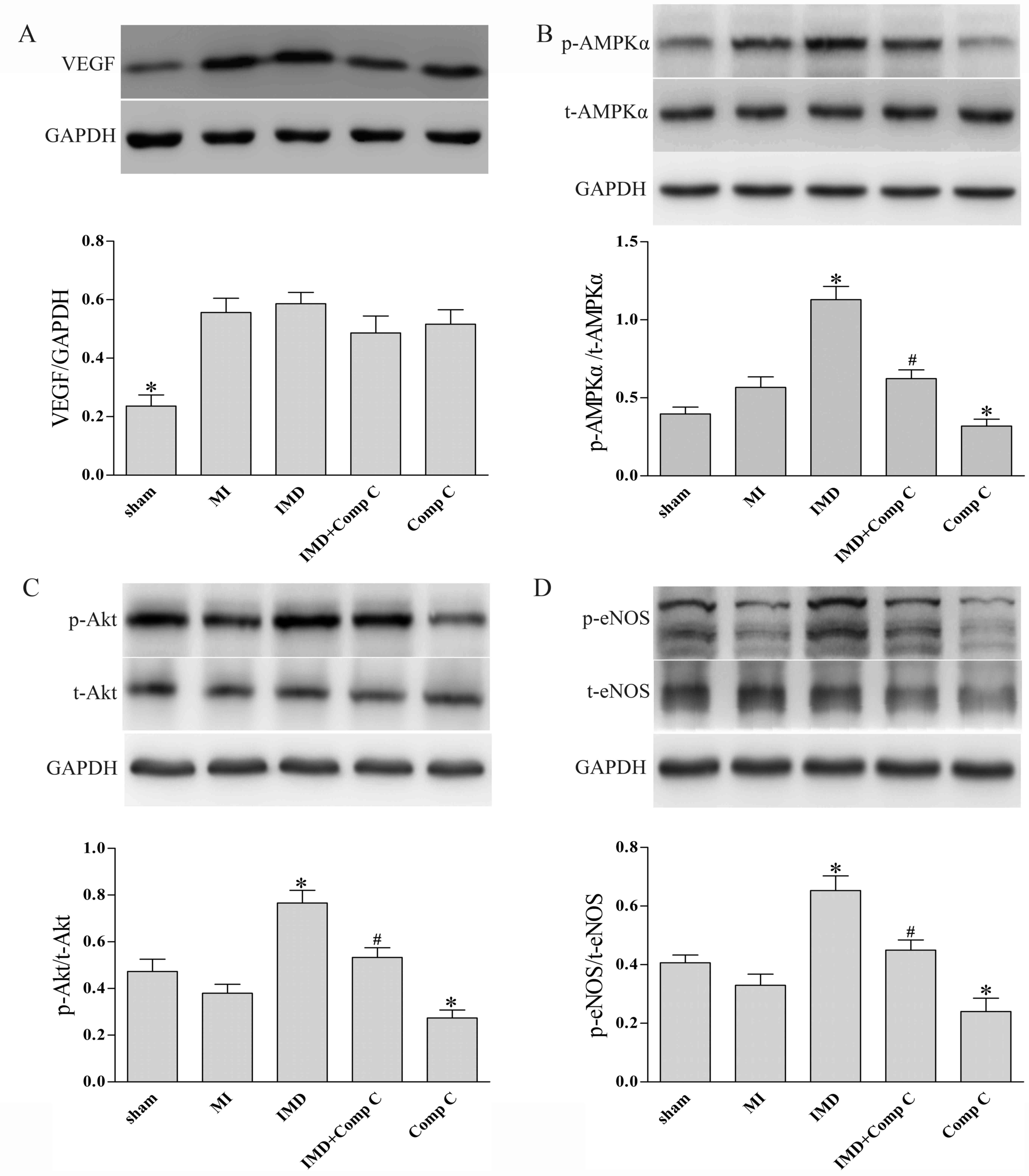
|
1
|
Pfeffer MA and Braunwald E: Ventricular
remodeling after myocardial infarction. Experimental observations
and clinical implications. Circulation. 81:1161–1172. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jessup M and Brozena S: Heart failure. N
Engl J Med. 348:2007–2018. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mozaffarian D, Benjamin EJ, Go AS, Arnett
DK, Blaha MJ, Cushman M, De Ferranti S, Després JP, Fullerton HJ,
Howard VJ, et al: Heart disease and stroke statistics-2015 update:
A report from the American Heart Association. Circulation.
131:e29–e322. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Oka T, Akazawa H, Naito AT and Komuro I:
Angiogenesis and cardiac hypertrophy: Maintenance of cardiac
function and causative roles in heart failure. Circ Res.
114:565–571. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yang JH, Jia YX, Pan CS, Zhao J, Ouyang M,
Yang J, Chang JK, Tang CS and Qi YF: Effects of intermedin(1–53) on
cardiac function and ischemia/reperfusion injury in isolated rat
hearts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 327:713–719. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhao L, Peng DQ, Zhang J, Song JQ, Teng X,
Yu YR, Tang CS and Qi YF: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2
activation is involved in intermedin1-53 attenuating myocardial
oxidative stress injury induced by ischemia/reperfusion. Peptides.
33:329–335. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yang X, Zhang H, Jia Y, Ni L, Li G, Xue L
and Jiang Y: Effects of intermedin1-53 on myocardial fibrosis. Acta
Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 45:141–148. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chen H, Wang X, Tong M, Wu D, Wu S, Chen
J, Wang X, Wang X, Kang Y, Tang H, et al: Intermedin suppresses
pressure overload cardiac hypertrophy through activation of
autophagy. PLoS One. 8:e647572013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lu WW, Zhao L, Zhang JS, Hou YL, Yu YR,
Jia MZ, Tang CS and Qi YF: Intermedin1-53 protects against cardiac
hypertrophy by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress via
activating AMP-activated protein kinase. J Hypertens. 33:1676–1687.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Smith RS Jr, Gao L, Bledsoe G, Chao L and
Chao J: Intermedin is a new angiogenic growth factor. Am J Physiol
Heart Circ Physiol. 297:H1040–H1047. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang W, Wang LJ, Xiao F, Wei Y, Ke W and
Xin HB: Intermedin: A novel regulator for vascular remodeling and
tumor vessel normalization by regulating vascular
endothelial-cadherin and extracellular signal-regulated kinase.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 32:2721–2732. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Derumeaux G, Mulder P, Richard V,
Chagraoui A, Nafeh C, Bauer F, Henry JP and Thuillez C: Tissue
Doppler imaging differentiates physiological from pathological
pressure-overload left ventricular hypertrophy in rats.
Circulation. 105:1602–1608. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang F, Huang D, Zhu W, Li S, Yan M, Wei M
and Li J: Selective inhibition of PKCβ2 preserves cardiac function
after myocardial infarction and is associated with improved
angiogenesis of ischemic myocardium in diabetic rats. Int J Mol
Med. 32:1037–1046. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Nagata D, Mogi M and Walsh K:
AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) signaling in endothelial cells
is essential for angiogenesis in response to hypoxic stress. J Biol
Chem. 278:31000–31006. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yang JH, Pan CS, Jia YX, Zhang J, Zhao J,
Pang YZ, Yang J, Tang CS and Qi YF: Intermedin1-53 activates
L-arginine/nitric oxide synthase/nitric oxide pathway in rat
aortas. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 341:567–572. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Roh J, Chang CL, Bhalla A, Klein C and Hsu
SY: Intermedin is a calcitonin/calcitonin gene-related peptide
family peptide acting through the calcitonin receptor-like
receptor/receptor activity-modifying protein receptor complexes. J
Biol Chem. 279:7264–7274. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sutton MG and Sharpe N: Left ventricular
remodeling after myocardial infarction: Pathophysiology and
therapy. Circulation. 101:2981–2988. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kocher AA, Schuster MD, Szabolcs MJ,
Takuma S, Burkhoff D, Wang J, Homma S, Edwards NM and Itescu S:
Neovascularization of ischemic myocardium by human
bone-marrow-derived angioblasts prevents cardiomyocyte apoptosis,
reduces remodeling and improves cardiac function. Nat Med.
7:430–436. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li J, Zhang Y, Li C, Xie J, Liu Y, Zhu W,
Zhang X, Jiang S, Liu L and Ding Z: HSPA12B attenuates cardiac
dysfunction and remodelling after myocardial infarction through an
eNOS-dependent mechanism. Cardiovasc Res. 99:674–684. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Vandoorne K, Vandsburger MH, Raz T, Shalev
M, Weisinger K, Biton I, Brumfeld V, Raanan C, Nevo N, Eilam R, et
al: Chronic Akt1 deficiency attenuates adverse remodeling and
enhances angiogenesis after myocardial infarction. Circ Cardiovasc
Imaging. 6:992–1000. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhao X, Balaji P, Pachon R, Beniamen DM,
Vatner DE, Graham RM and Vatner SF: Overexpression of cardiomyocyte
α1A-Adrenergic receptors attenuates postinfarct remodeling by
inducing angiogenesis through heterocellular signaling.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 35:2451–2459. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Grahame Hardie D: AMP-activated protein
kinase: A key regulator of energy balance with many roles in human
disease. J Intern Med. 276:543–559. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ahluwalia A and Tarnawski AS: Activation
of the metabolic sensor-AMP activated protein kinase reverses
impairment of angiogenesis in aging myocardial microvascular
endothelial cells. Implications for the aging heart. J Physiol
Pharmacol. 62:583–587. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Izumi Y, Shiota M, Kusakabe H, Hikita Y,
Nakao T, Nakamura Y, Muro T, Miura K, Yoshiyama M and Iwao H:
Pravastatin accelerates ischemia-induced angiogenesis through
AMP-activated protein kinase. Hypertens Res. 32:675–679. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shimano M, Ouchi N, Shibata R, Ohashi K,
Pimentel DR, Murohara T and Walsh K: Adiponectin deficiency
exacerbates cardiac dysfunction following pressure overload through
disruption of an AMPK-dependent angiogenic response. J Mol Cell
Cardiol. 49:210–220. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Su KH, Yu YB, Hou HH, Zhao JF, Kou YR,
Cheng LC, Shyue SK and Lee TS: AMP-activated protein kinase
mediates erythropoietin-induced activation of endothelial nitric
oxide synthase. J Cell Physiol. 227:3053–3062. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zheng S, Li W, Xu M, Bai X, Zhou Z, Han J,
Shyy JY and Wang X: Calcitonin gene-related peptide promotes
angiogenesis via AMP-activated protein kinase. Am J Physiol Cell
Physiol. 299:C1485–C1492. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|