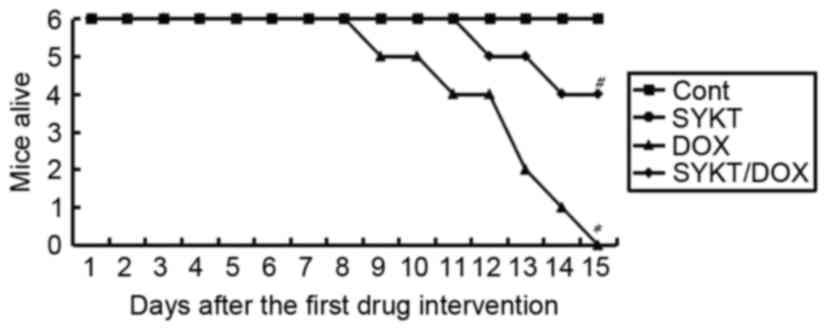
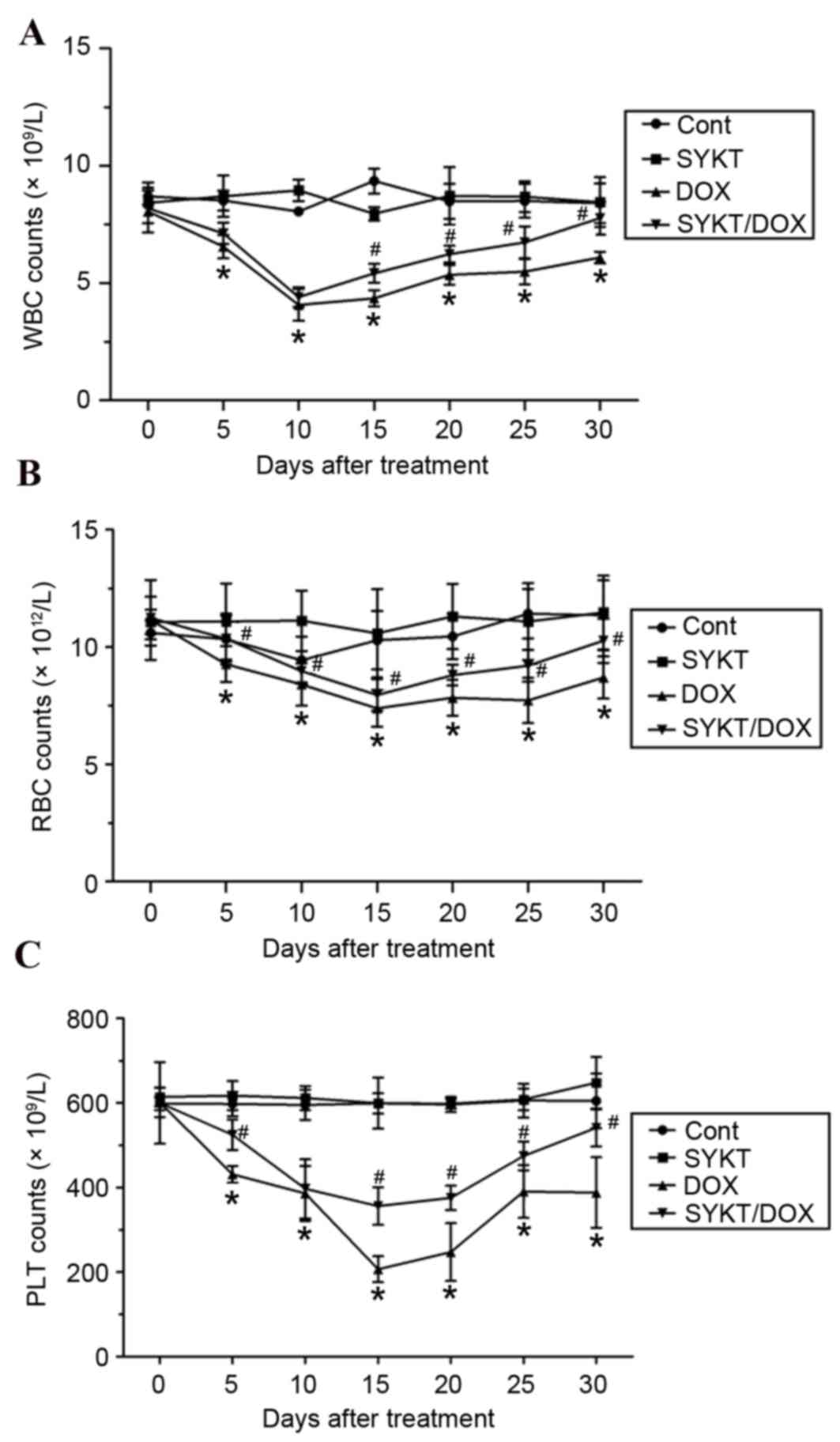
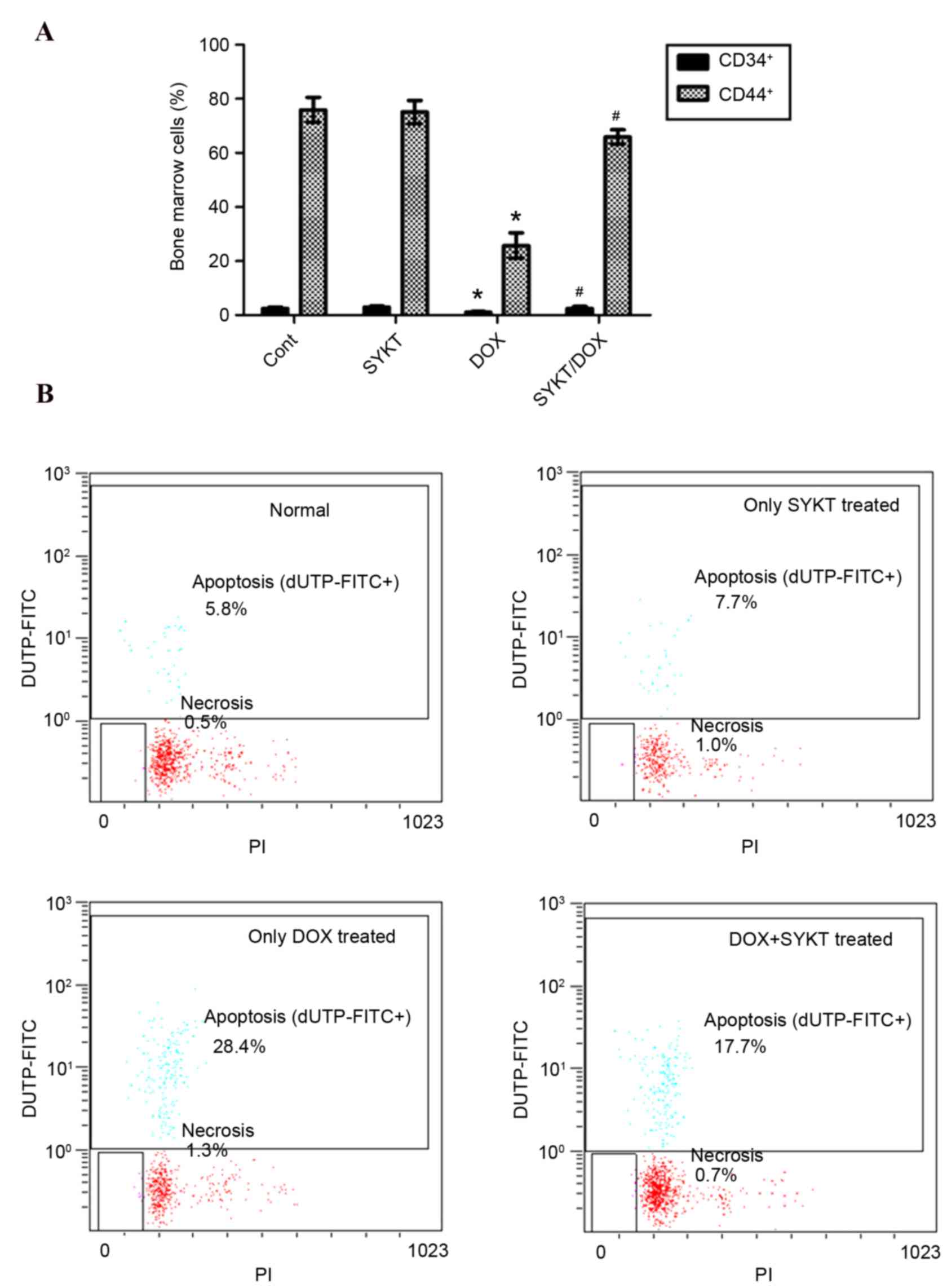
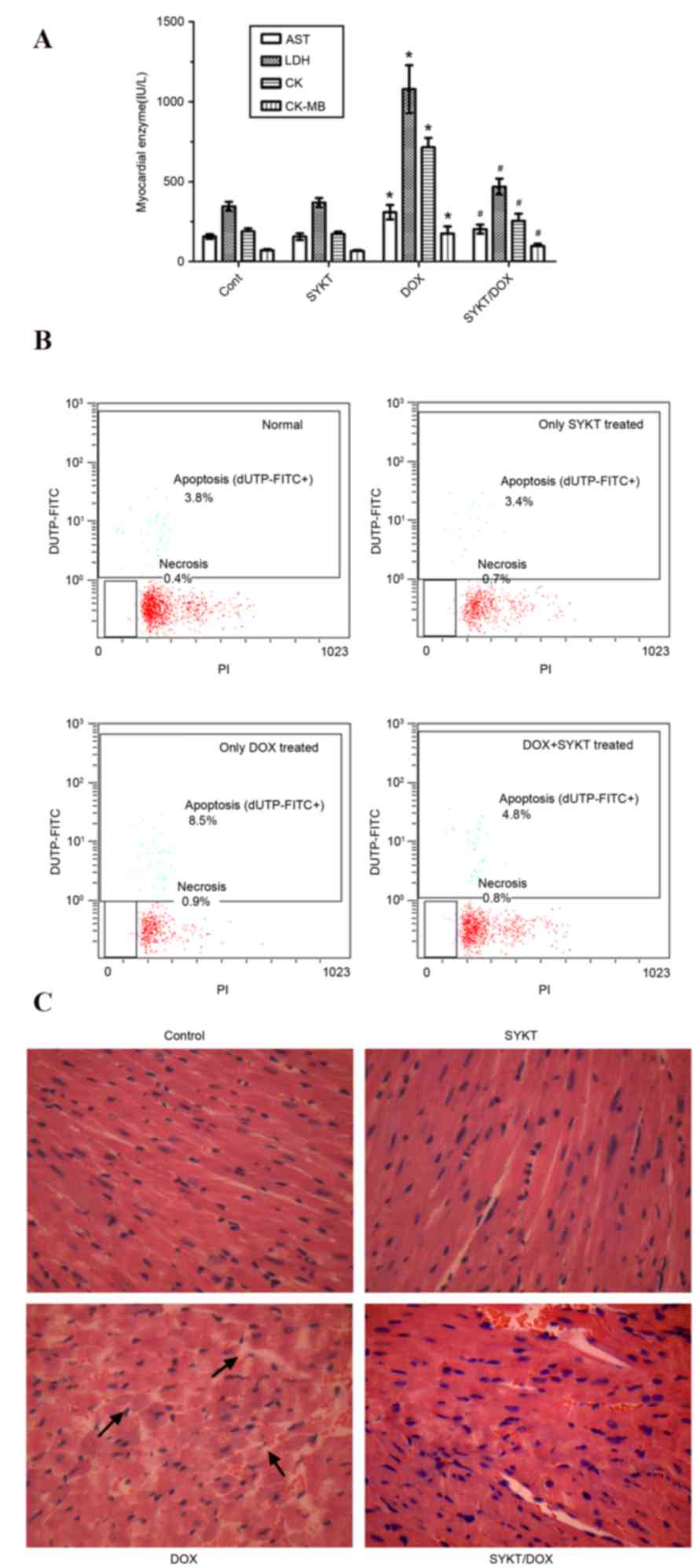
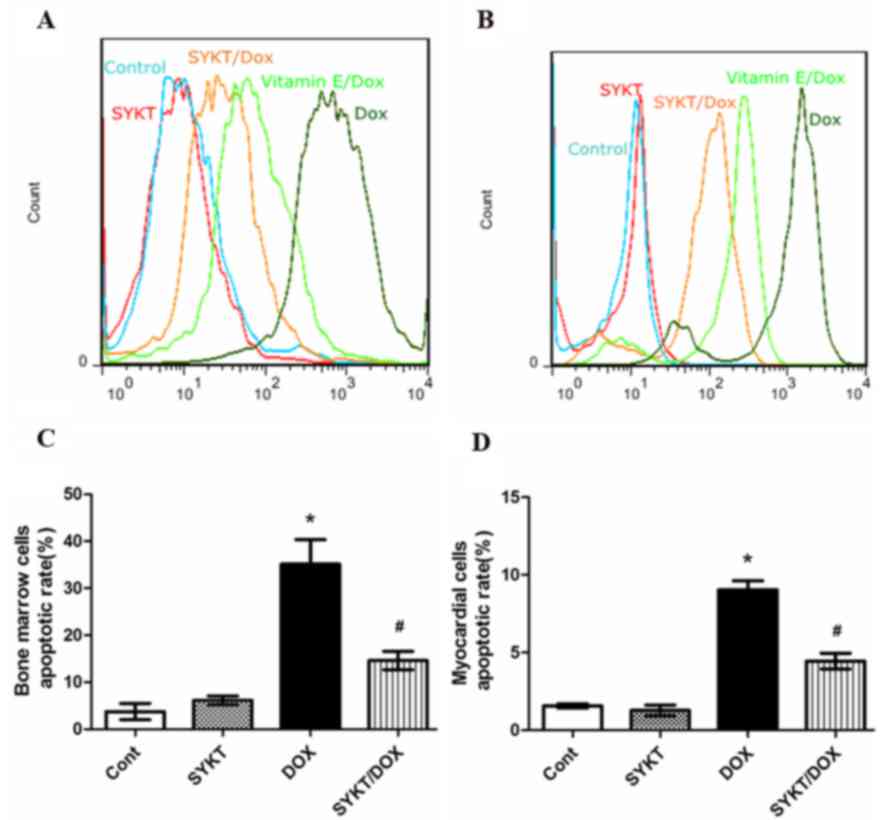
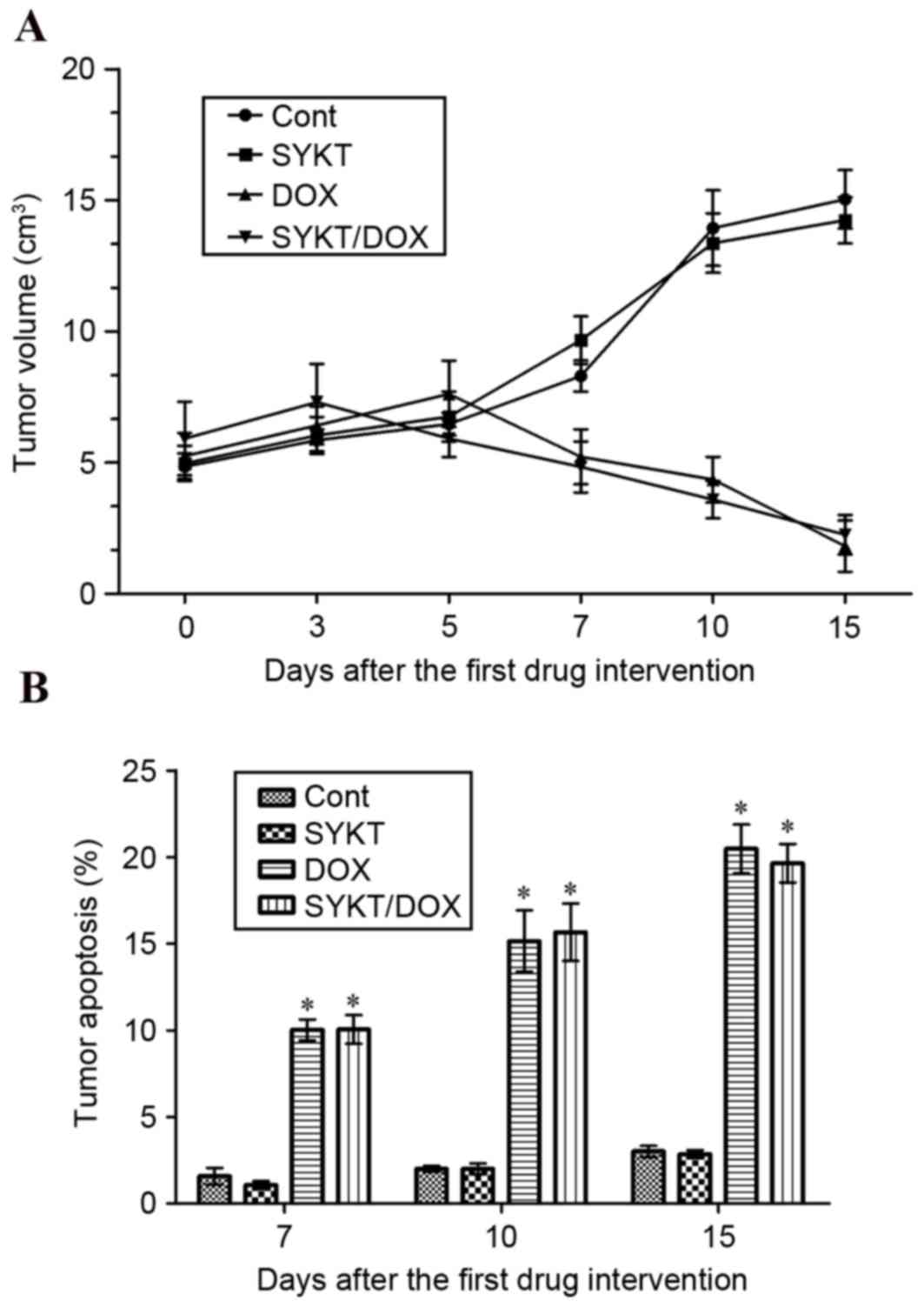
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. Cancer J Clin. 61:69–90.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Emadi A, Jones RJ and Brodsky RA:
Cyclophosphamide and cancer: Golden anniversary. Nat Rev Clin
Oncol. 6:638–647. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Swain SM: Doxorubicin-induced
cardiomyopathy. N Engl J Med. 340:6541999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Vadhan-Raj S, Patel S, Bueso-Ramos C,
Folloder J, Papadopolous N, Burgess A, Broemeling LD, Broxmeyer HE
and Benjamin RS: Importance of predosing of recombinant human
thrombopoietin to reduce chemotherapy-induced early
thrombocytopenia. J Clin Oncol. 21:3158–3167. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chen Y, Jungsuwadee P, Vore M, Butterfield
DA and St Clair DK: Collateral damage in cancer chemotherapy:
Oxidative stress in nontargeted tissues. Mol Interv. 7:147–156.
2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kim EJ, Lim KM, Kim KY, Bae ON, Noh JY,
Chung SM, Shin S, Yun YP and Chung JH: Doxorubicin-induced platelet
cytotoxicity: A new contributory factor for doxorubicin-mediated
thrombocytopenia. J Thromb Haemost. 7:1172–1183. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kluza J, Marchetti P, Gallego MA, Lancel
S, Fournier C, Loyens A, Beauvillain JC and Bailly C: Mitochondrial
proliferation during apoptosis induced by anticancer agents:
Effects of doxorubicin and mitoxantrone on cancer and cardiac
cells. Oncogene. 23:7018–7030. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Afanasev I: Detection of superoxide in
cells, tissues and whole organisms. Front Biosci (Elite Ed).
1:153–160. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ingold KU and Pratt DA: Advances in
radical-trapping antioxidant chemistry in the 21st century: A
kinetics and mechanisms perspective. Chem Rev. 114:9022–9046. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Guimarães R, Barreira JC, Barros L,
Carvalho AM and Ferreira IC: Effects of oral dosage form and
storage period on the antioxidant properties of four species used
in traditional herbal medicine. Phytother Res. 25:484–492. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ohnishi S and Takeda H: Herbal medicines
for the treatment of cancer chemotherapy-induced side effects.
Front Pharmacol. 6:142015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hua Hou, Hong-Wen Sun, Pei-Zhu Zhao, et
al: Effect of Neoadjuvant radio-chemotherapy of sanyang xuedai
mixture on Myelosuppression in patients with squamous carcinoma.
Chinese J Experimental Traditional Med Formulae. 21:173–176.
2015.
|
|
13
|
Ji-Ma Lv, Lu-Hua Wang, Li-Jun LI, et al:
Concurrent radiotherapy and SYKT for local advanced non-small cell
lung cancer. China Cancer. 13:743–746. 2004.
|
|
14
|
Jahnukainen K, Jahnukainen T, Salmi TT,
Svechnikov K, Eksborg S and Söder O: Amifostine protects against
early but not late toxic effects of doxorubicin in infant rats.
Cancer Res. 61:6423–6427. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu TJ, Yeh YC, Ting CT, Lee WL, Wang LC,
Lee HW, Wang KY and Lai HC and Lai HC: Ginkgo biloba extract 761
reduces doxorubicin-induced apoptotic damage in rat hearts and
neonatal cardiomyocytes. Cardiovasc Res. 80:227–235. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Huffmyer J and Raphael J: Physiology and
pharmacology of myocardial preconditioning and postconditioning.
Semin Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 13:5–18. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Angermann CE and Ertl G: Natriuretic
peptides-new diagnostic markers in heart disease. Herz. 29:609–617.
2004.(In German). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Billingham ME, Mason JW, Bristow MR and
Daniels JR: Anthracycline cardiomyopathy monitored by morphologic
changes. Cancer Treat Rep. 62:865–872. 1978.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bjelogrlic SK, Radic J, Jovic V and
Radulovic S: Activity of d,l-alpha-tocopherol (vitamin E) against
cardiotoxicity induced by doxorubicin and doxorubicin with
cyclophosphamide in mice. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 97:311–319.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kitsis RN and Jialal I: Limiting
myocardial damage during acute myocardial infarction by inhibiting
C-reactive protein. N Engl J Med. 355:513–515. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ferrans V, Sanchez J and Herman E: The
role of myocardial biopsy in the diagnosis of anthracycline
cardiotoxicityCancer treatment and the heart. Muggia F..Green
M..Speyer J: John Hopkins University; Baltimore, MD: pp. 198–216.
1992
|
|
22
|
Keizer HG, Pinedo HM, Schuurhuis GJ and
Joenje H: Doxorubicin (adriamycin): A critical review of free
radical-dependent mechanisms of cytotoxicity. Pharmacol Ther.
47:219–231. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Olson RD and Mushlin PS: Doxorubicin
cardiotoxicity: Analysis of prevailing hypotheses. FASEB J.
4:3076–3086. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
van Acker FA, Boven E, Kramer K, Haenen
GR, Bast A and van der Vijgh WJ: Frederine, a new and promising
protector against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Clin Cancer
Res. 7:1378–1384. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Keefe DL: Anthracycline-induced
cardiomyopathy. Semin Oncol. 28(4 Suppl 12): S2–S7. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Bally MB, Nayar R, Masin D, Cullis PR and
Mayer LD: Studies on the myelosuppressive activity of doxorubicin
entrapped in liposomes. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 27:13–19. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang S, Liu X, Bawa-Khalfe T, Lu LS, Lyu
YL, Liu LF and Yeh ET: Identification of the molecular basis of
doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Nat Med. 18:1639–1642. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Guo KJ, Xu SF, Yin P, Wang W, Song XZ, Liu
FH, Xu JQ and Zoccarato I: Active components of common traditional
Chinese medicine decoctions have antioxidantfunctions. J Anim Sci.
89:3107–3115. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhao J, Zhang L, Li J, Wu T, Wang M, Xu G,
Zhang F, Liu L, Yang J and Sun S: A novel pyrazolone-based
derivative induces apoptosis in human esophageal cells via reactive
oxygen species (ROS) generation and caspase-dependent
mitochondria-mediated pathway. Chem Biol Interact. 231:1–9. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Circu ML and Aw TY: Reactive oxygen
species, cellular redox systems, and apoptosis. Free Radic Biol
Med. 48:749–762. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ryter SW, Kim HP, Hoetzel A, Park JW,
Nakahira K, Wang X and Choi AM: Mechanisms of cell death in
oxidative stress. Antioxid Redox Signal. 9:49–89. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Turrens JF: Mitochondrial formation of
reactive oxygen species. J Physiol. 552:335–344. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Venkatesan B, Prabhu SD, Venkatachalam K,
Mummidi S, Valente AJ, Clark RA, Delafontaine P and Chandrasekar B:
WNT1-inducible signaling pathway protein-1 activates diverse cell
survival pathways and blocks doxorubicin-induced cardiomyocyte
death. Cell Signal. 22:809–820. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lou H, Danelisen I and Singal PK:
Involvement of mitogen-activated protein kinases in
adriamycin-induced cardiomyopathy. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
288:H1925–H1930. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kim BJ, Ryu SW and Song BJ: JNK- and p38
kinase-mediated phosphorylation of Bax leads to its activation and
mitochondrial translocation and to apoptosis of human hepatoma
HepG2 cells. J Biol Chem. 281:21256–21265. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang GW, Klein JB and Kang YJ:
Metallothionein inhibits doxorubicin-induced mitochondrial
cytochrome c release and caspase-3 activation in cardiomyocytes. J
Pharmacol Exp Ther. 298:461–468. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li P, Nijhawan D, Budihardjo I,
Srinivasula SM, Ahmad M, Alnemri ES and Wang X: Cytochrome c and
dATP-dependent formation of Apaf-1/caspase-9 complex initiates an
apoptotic protease cascade. Cell. 91:479–489. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wang S, Konorev EA, Kotamraju S, Joseph J,
Kalivendi S and Kalyanaraman B: Doxorubicin induces apoptosis in
normal and tumor cells via distinctly different mechanisms.
Intermediacy of H(2)O(2)- and p53-dependent pathways. J Biol Chem.
279:25535–25543. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|