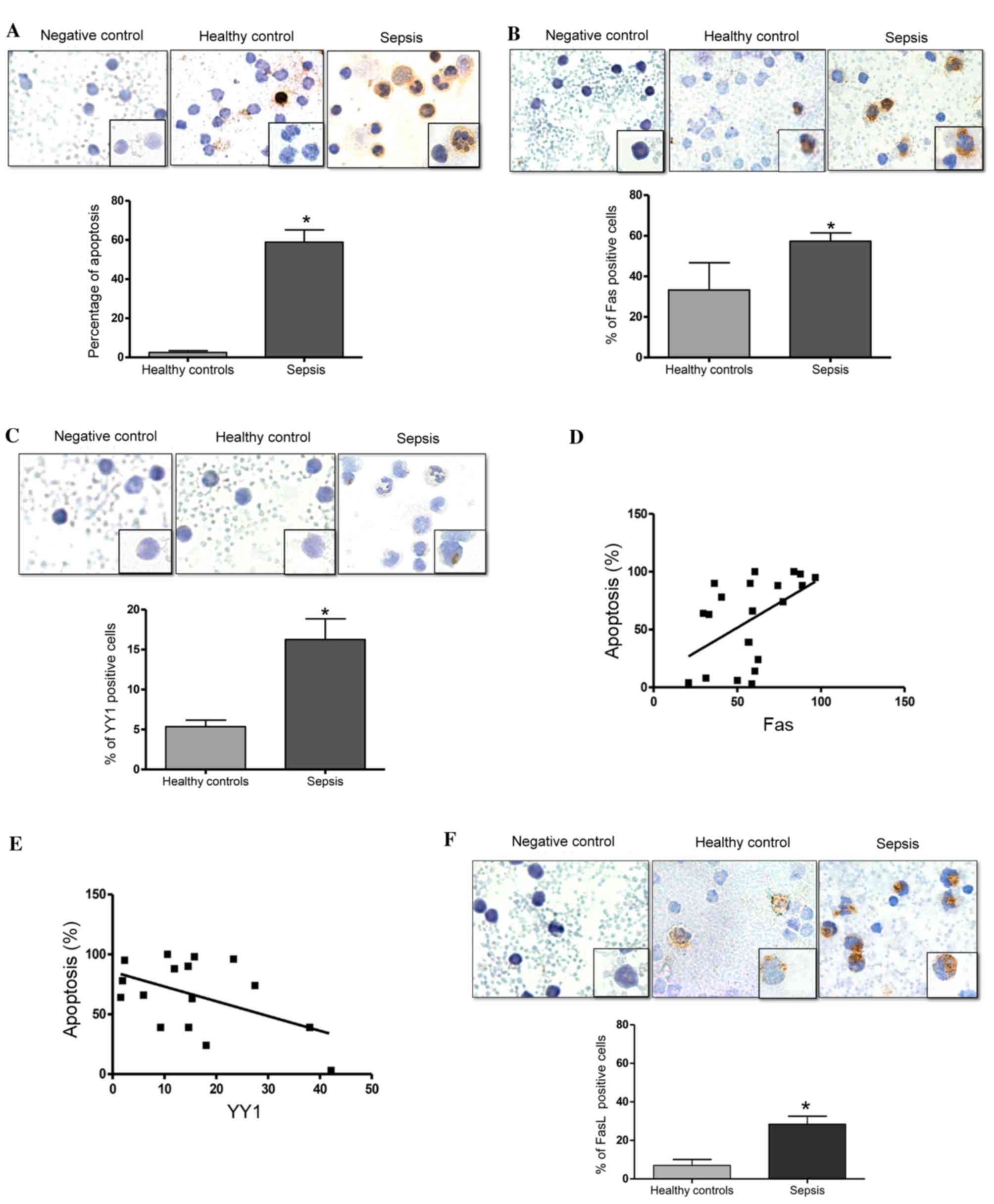
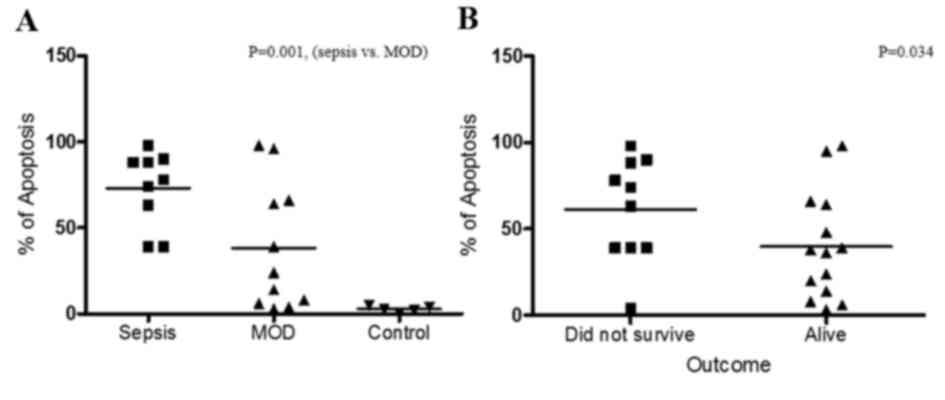
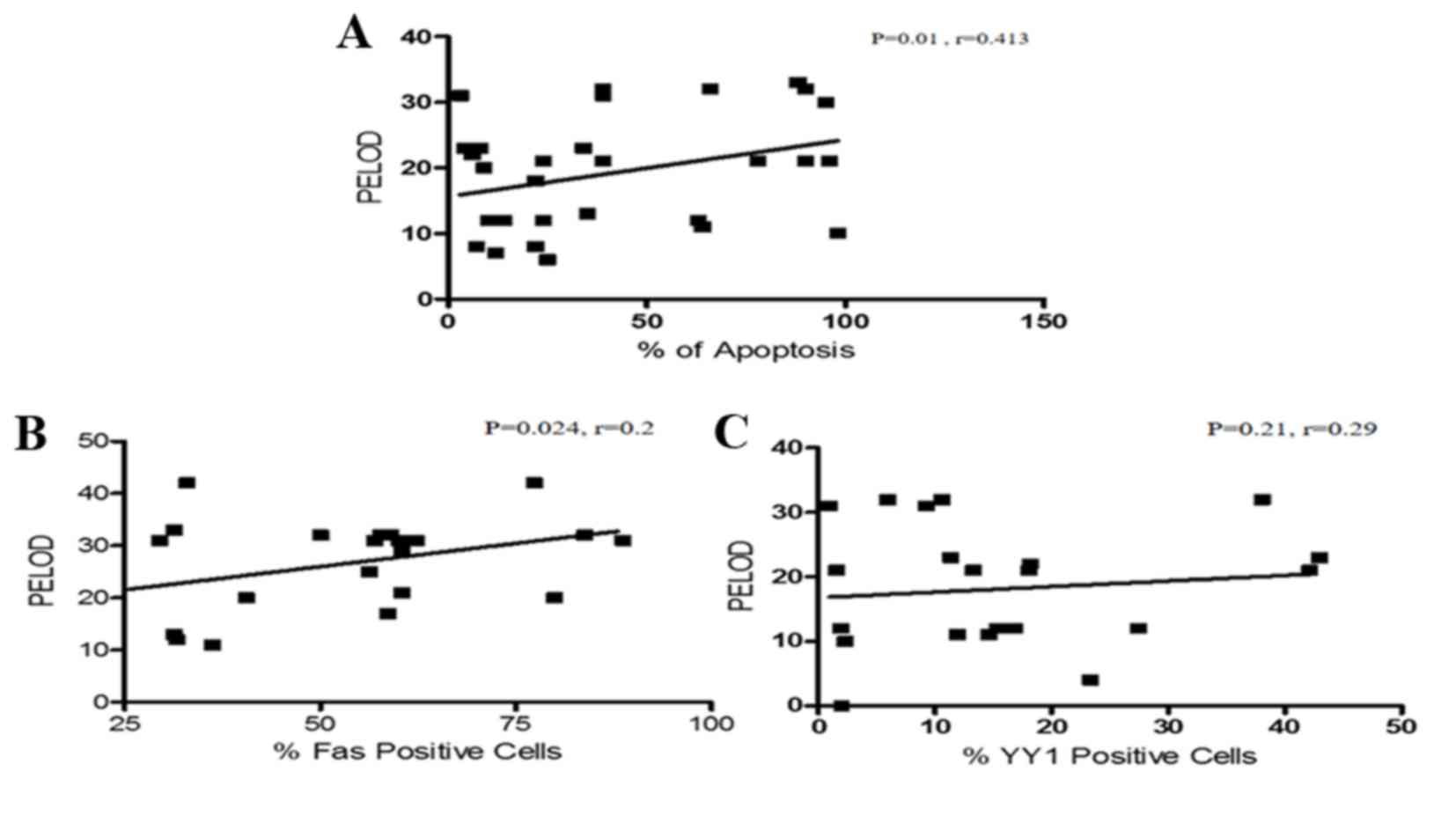
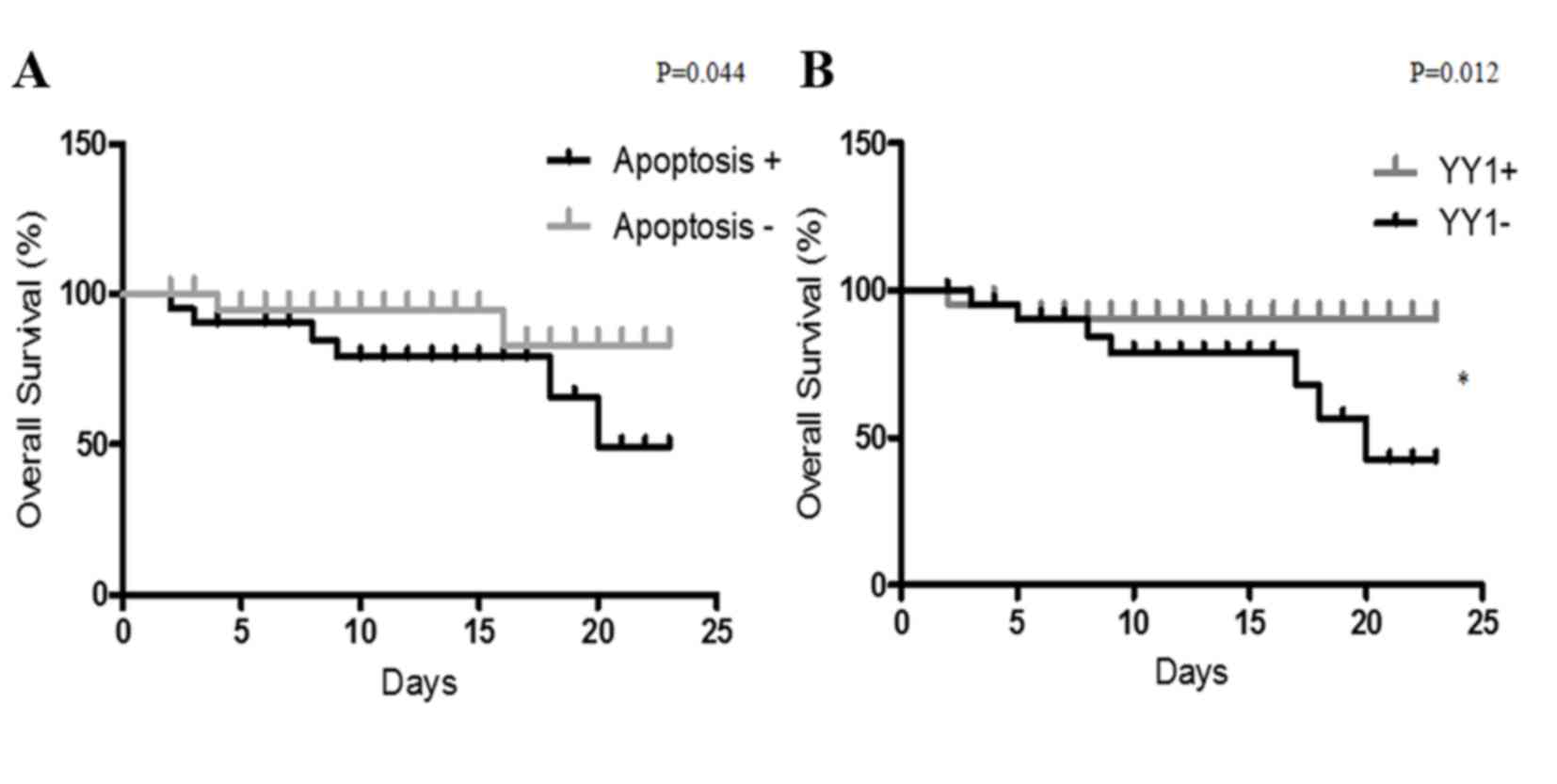
|
1
|
Hotchkiss RS and Nicholson DW: Apoptosis
and caspases regulate death and inflammation in sepsis. Nat Rev
Immunol. 6:813–822. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rayo AC, Hernández GL, Huerta GL, Ortiz
AV, Reyes RM and Gómez RG: Mecanismos patogénicos en sepsis y
choque séptico. Med Interna Mex. 24:38–42. 2008.
|
|
3
|
Carrillo-Esper R, Carrillo-Cordova JR and
Carrillo-Cordova LD: Epidemiological study of sepsis in Mexican
intensive care units. Cir Cir. 77:279–385. 2009.(In Spanish).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hotchkiss RS, Swanson PE, Freeman BD,
Tinsley KW, Cobb JP, Matuschak GM, Buchman TG and Karl IE:
Apoptotic cell death in patients with sepsis, shock, and multiple
organ dysfunction. Crit Care Med. 27:1230–1251. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hotchkiss RS, Swanson PE, Cobb JP,
Jacobson A, Buchman TG and Karl IE: Apoptosis in lymphoid and
parenchymal cells during sepsis: Findings in normal and T- and
B-cell-deficient mice. Crit Care Med. 25:1298–1307. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hotchkiss RS, Swanson PE, Knudson CM,
Chang KC, Cobb JP, Osborne DF, Zollner KM, Buchman TG, Korsmeyer SJ
and Karl IE: Overexpression of Bcl-2 in transgenic mice decreases
apoptosis and improves survival in sepsis. J Immunol.
162:4148–4156. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chung CS, Song GY, Moldawer LL, Chaudry IH
and Ayala A: Neither fas ligand nor endotoxin is responsible for
inducible peritoneal phagocyte apoptosis during sepsis/peritonitis.
J Surg Res. 91:147–153. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hotchkiss RS, Osmon SB, Chang KC, Wagner
TH, Coopersmith CM and Karl IE: Accelerated lymphocyte death in
sepsis occurs by both the death receptor and mitochondrial
pathways. J Immunol. 174:5110–5118. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Niu J, Azfer A and Kolattukudy PE:
Protection against lipopolysaccharide-induced myocardial
dysfunction in mice by cardiac-specific expression of soluble Fas.
J Mol Cell Cardiol. 44:160–169. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ren Y, Xie Y, Jiang G, Fan J, Yeung J, Li
W, Tam PK and Savill J: Apoptotic cells protect mice against
lipopolysaccharide-induced shock. J Immunol. 180:4978–4985. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gautier EL, Huby T, Saint-Charles F,
Ouzilleau B, Chapman MJ and Lesnik P: Enhanced dendritic cell
survival attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced immunosuppression
and increases resistance to lethal endotoxic shock. J Immunol.
180:6941–6946. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Unsinger J, Herndon JM, Davis CG, Muenzer
JT, Hotchkiss RS and Ferguson TA: The role of TCR engagement and
activation-induced cell death in sepsis-induced T cell apoptosis. J
Immunol. 177:7968–7973. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ayala A, Urbanich MA, Herdon CD and
Chaudry IH: Is sepsis-induced apoptosis associated with macrophage
dysfunction? J Trauma. 40:568–574. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sharshar T, Gray F, Poron F, Raphael JC,
Gajdos P and Annane D: Multifocal necrotizing leukoencephalopathy
in septic shock. Crit Care Med. 30:2371–2375. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gordon S, Akopyan G, Garban H and Bonavida
B: Transcription factor YY1: Structure, function, and therapeutic
implications in cancer biology. Oncogene. 25:1125–1142. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Huerta-Yepez S, Vega M, Garban H and
Bonavida B: Involvement of the TNF-alpha autocrine-paracrine loop,
via NF-kappaB and YY1, in the regulation of tumor cell resistance
to Fas-induced apoptosis. Clin Immunol. 120:297–309. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Garbán HJ and Bonavida B: Nitric oxide
inhibits the transcription repressor Yin-Yang 1 binding activity at
the silencer region of the Fas promoter: A pivotal role for nitric
oxide in the up-regulation of Fas gene expression in human tumor
cells. J Immunol. 167:75–81. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
De Freitas I, Fernández-Somoza M,
Essenfeld-Sekler E and Cardier JE: Serum levels of the
apoptosis-associated molecules, tumor necrosis factor-alpha/tumor
necrosis factor type-I receptor and Fas/FasL, in sepsis. Chest.
125:2238–2246. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hotchkiss RS, Tinsley KW and Karl IE: Role
of apoptotic cell death in sepsis. Scand J Infect Dis. 35:585–592.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Adrie C, Bachelet M, Vayssier-Taussat M,
Russo-Marie F, Bouchaert I, Adib-Conquy M, Cavaillon JM, Pinsky MR,
Dhainaut JF and Polla BS: Mitochondrial membrane potential and
apoptosis peripheral blood monocytes in severe human sepsis. Am J
Respir Crit Care Med. 164:389–395. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
World Medical Association: World Medical
Association Declaration of Helsinki: Ethical principles for medical
research involving human subjects. JAMA. 310:2191–2194. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Holmström TH and Eriksson JE:
Phosphorylation-based signaling in Fas receptor-mediated apoptosis.
Crit Rev Immunol. 20:121–152. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Rathmell JC and Thompson CB: Pathways of
apoptosis in lymphocyte development, homeostasis, and disease.
Cell. 109:(Suppl). S97–S107. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Fadeel B and Orrenius S: Apoptosis: A
basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging implications in human
disease. J Intern Med. 258:479–517. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wyllie AH, Morris RG, Smith AL and Dunlop
D: Chromatin cleavage in apoptosis: Association with condensed
chromatin morphology and dependence on macromolecular synthesis. J
Pathol. 142:67–77. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Porter BO and Malek TR: Prostaglandin E2
inhibits T cell activation-induced apoptosis and Fas-mediated
cellular cytotoxicity by blockade of Fas-ligand induction. Eur J
Immunol. 29:2360–2365. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
McCarthy NJ, Smith CA and Williams GT:
Apoptosis in the development of the immune system: Growth factors,
clonal selection and bcl-2. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 11:157–178.
1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Newton K and Strasser A: Cell death
control in lymphocytes. Adv Immunol. 76:179–226. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Toledano BJ, Bastien Y, Noya F and Mazer
B: Characterization of B lymphocytes rescued from apoptosis by
platelet-activating factor. Cell Immunol. 191:60–68. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ashare A, Monick MM, Powers LS, Yarovinsky
T and Hunninghake GW: Severe bacteremia results in a loss of
hepatic bacterial clearance. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
173:644–652. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Stearns-Kurosawa DJ, Osuchowski MF,
Valentine C, Kurosawa S and Remick DG: The pathogenesis of sepsis.
Annu Rev Pathol. 6:19–48. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hotchkiss RS, Tinsley KW, Swanson PE,
Schmieg RE Jr, Hui JJ, Chang KC, Osborne DF, Freeman BD, Cobb JP,
Buchman TG and Karl IE: Sepsis-induced apoptosis causes progressive
profound depletion of B and CD4+ T lymphocytes in humans. J
Immunol. 166:6952–6963. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hotchkiss RS, Chang KC, Swanson PE,
Tinsley KW, Hui JJ, Klender P, Xanthoudakis S, Roy S, Black C,
Grimm E, et al: Caspase inhibitors improve survival in sepsis: A
critical role of the lymphocyte. Nat Immunol. 1:496–501. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Roth E and Pircher H: IFN-gamma promotes
Fas ligand- and perforin-mediated liver cell destruction by
cytotoxic CD8 T cells. J Immunol. 172:1588–1594. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Doughty L, Clark RS, Kaplan SS, Sasser H
and Carcillo J: sFas and sFas ligand and pediatric sepsis-induced
multiple organ failure syndrome. Pediatr Res. 52:922–927. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Vega MI, Jazirehi AR, Huerta-Yepez S and
Bonavida B: Rituximab-induced inhibition of YY1 and Bcl-xL
expression in Ramos non-Hodgkin's lymphoma cell line via inhibition
of NF-kappa B activity: Role of YY1 and Bcl-xL in Fas resistance
and chemoresistance, respectively. J Immunol. 175:2174–2183. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Krippner-Heidenreich A, Walsemann G,
Beyrouthy MJ, Speckgens S, Kraft R, Thole H, Talanian RV, Hurt MM
and Lüscher B: Caspase-dependent regulation and subcellular
redistribution of the transcriptional modulator YY1 during
apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol. 25:3704–3714. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Guo J, Casolaro V, Seto E, Yang WM, Chang
C, Seminario MC, Keen J and Georas SN: Yin-Yang 1 Activates
Interleukin-4 Gene Expression in T Cells. J Biol Chem.
276:48871–48878. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Denlinger LC and Proctor RA: Potential
risk factors for developing apoptosis during septic shock. Crit
Care Med. 28:2133–2134. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Sakhinia E, Glennie C, Hoyland JA, Menasce
LP, Brady G, Miller C, Radford JA and Byers RJ: Clinical
quantitation of diagnostic and predictive gene expression levels in
follicular and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by RT-PCR gene
expression profiling. Blood. 109:3922–3928. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Krammer PH: CD95(APO-1/Fas)-mediated
apoptosis: Live and let die. Adv Immunol. 71:163–210. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hofer S, Brenner T, Bopp C, Steppan J,
Lichtenstern C, Weitz J, Bruckner T, Martin E, Hoffmann U and
Weigand MA: Cell death serum biomarkers are early predictors for
survival in severe septic patients with hepatic dysfunction. Crit
Care. 13:R932009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Leteurtre S, Martinot A, Duhamel A, Proulx
F, Grandbastien B, Cotting J, Gottesman R, Joffe A, Pfenninger J,
Hubert P, et al: Validation of the paediatric logistic organ
dysfunction (PELOD) score: Prospective, observational, multicentre
study. Lancet. 362:192–197. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Proulx F, Gauthier M, Nadeau D, Lacroix J
and Farrell CA: Timing and predictors of death in pediatric
patients with multiple organ system failure. Crit Care Med.
22:1025–1031. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|