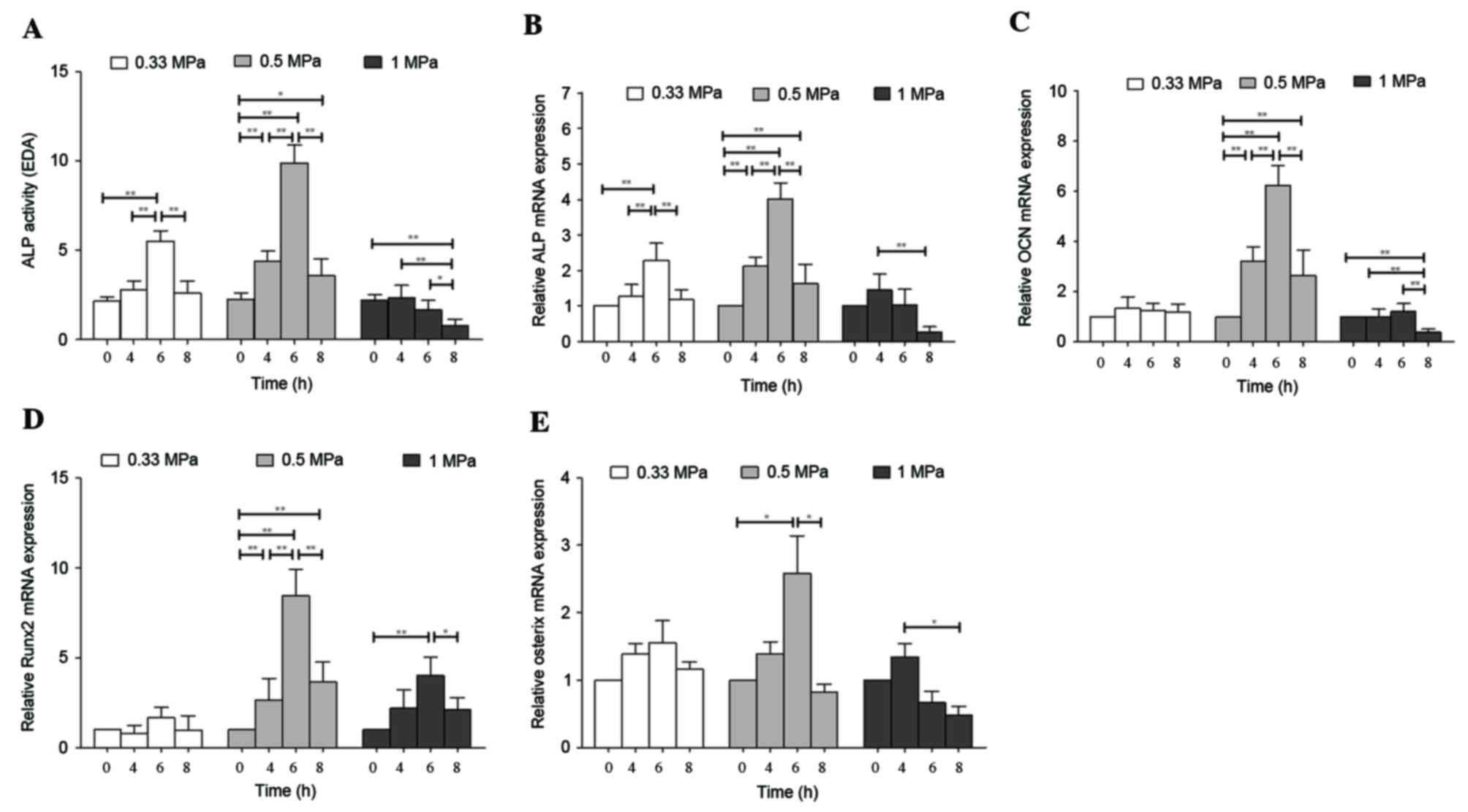
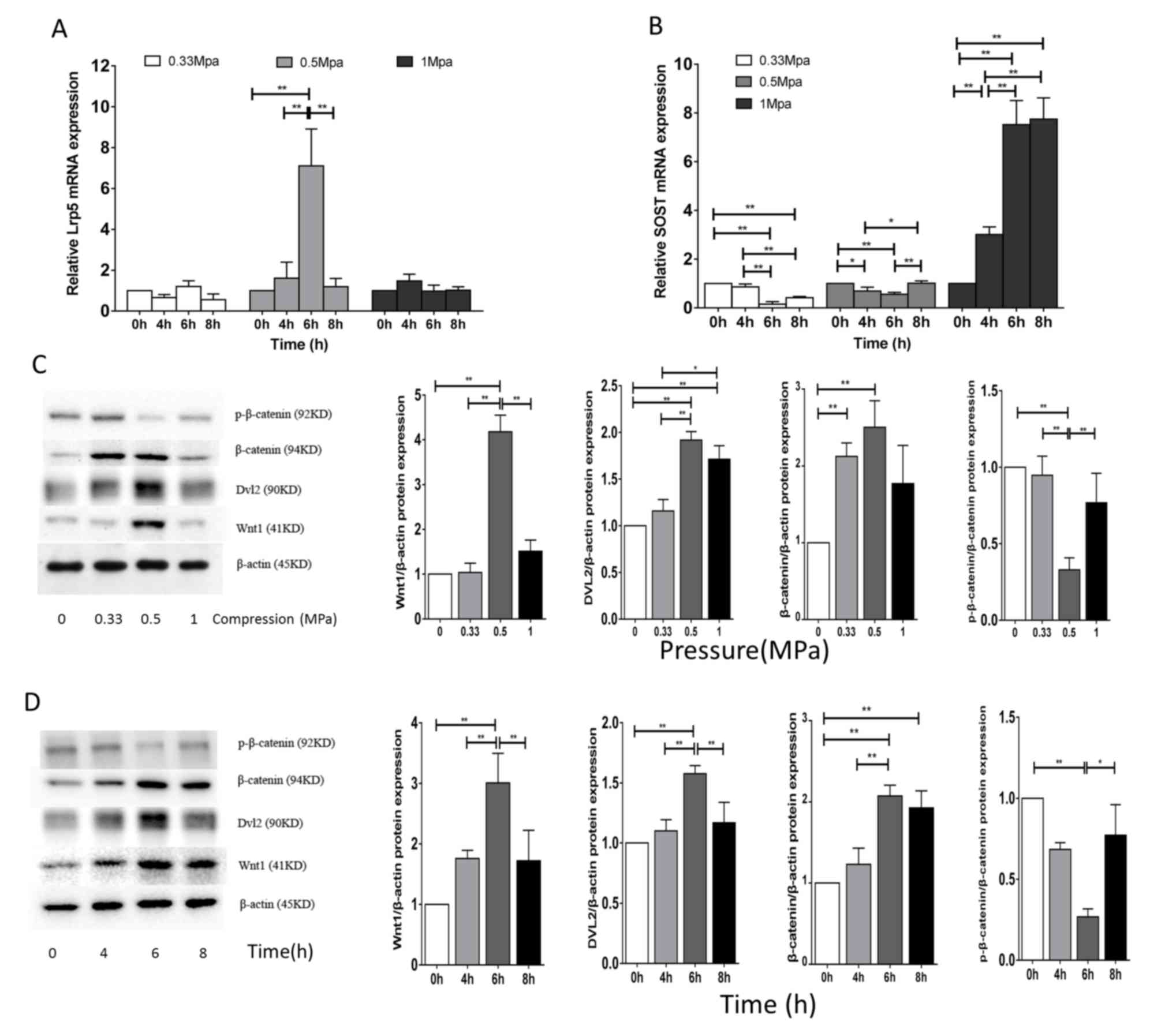
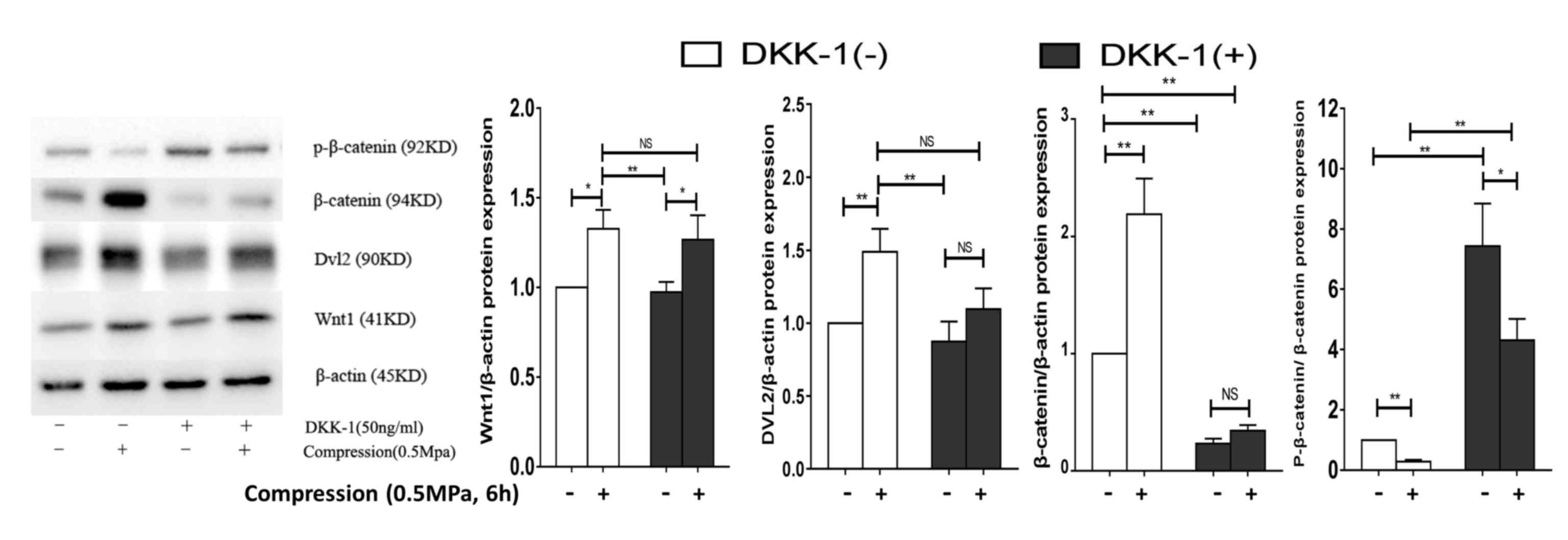
|
1
|
NIH Consensus Development Panel on
Osteoporosis Prevention, Diagnosis, and Therapy: Osteoporosis
prevention, diagnosis, and therapy. JAMA. 285:785–795. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bliuc D, Alarkawi D, Nguyen TV, Eisman JA
and Center JR: Risk of subsequent fractures and mortality in
elderly women and men with fragility fractures with and without
osteoporotic bone density: The dubbo osteoporosis epidemiology
study. J Bone Miner Res. 30:637–646. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zaidi M: Skeletal remodeling in health and
disease. Nature Med. 13:791–801. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lang T, LeBlanc A, Evans H, Lu Y, Genant H
and Yu A: Cortical and trabecular bone mineral loss from the spine
and hip in long-duration spaceflight. J Bone Miner Res.
19:1006–1012. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kim CH, Kim KH and Jacobs CR: Effects of
high frequency loading on RANKL and OPG mRNA expression in ST-2
murine stromal cells. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 10:1092009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ponik SM, Triplett JW and Pavalko FM:
Osteoblasts and osteocytes respond differently to oscillatory and
unidirectional fluid flow profiles. J Cell Biochem. 100:794–807.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Carinci F, Pezzetti F, Spina AM, Palmieri
A, Carls F, Laino G, De Rosa A, Farina E, Illiano F, Stabellini G,
et al: An in vitro model for dissecting distraction osteogenesis. J
Craniofac Surg. 16:71–79. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sittichockechaiwut A, Scutt AM, Ryan AJ,
Bonewald LF and Reilly GC: Use of rapidly mineralising osteoblasts
and short periods of mechanical loading to accelerate matrix
maturation in 3D scaffolds. Bone. 44:822–829. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhong Z, Zeng XL, Ni JH and Huang XF:
Comparison of the biological response of osteoblasts after tension
and compression. Eur J Orthod. 35:59–65. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Thompson WR, Rubin CT and Rubin J:
Mechanical regulation of signaling pathways in bone. Gene.
503:179–193. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Robling AG, Niziolek PJ, Baldridge LA,
Condon KW, Allen MR, Alam I, Mantila SM, Gluhak-Heinrich J, Bellido
TM, Harris SE and Turner CH: Mechanical stimulation of bone in vivo
reduces osteocyte expression of Sost/sclerostin. J Biol Chem.
283:5866–5875. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wozniak M, Fausto A, Carron CP, Meyer DM
and Hruska KA: Mechanically strained cells of the osteoblast
lineage organize their extracellular matrix through unique sites of
alphavbeta3-integrin expression. J Bone Miner Res. 15:1731–1745.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Day TF, Guo X, Garrett-Beal L and Yang Y:
Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in mesenchymal progenitors controls
osteoblast and chondrocyte differentiation during vertebrate
skeletogenesis. Dev Cell. 8:739–750. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bennett CN, Longo KA, Wright WS, Suva LJ,
Lane TF, Hankenson KD and MacDougald OA: Regulation of
osteoblastogenesis and bone mass by Wnt10b. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
102:3324–3329. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Canalis E: Wnt signalling in osteoporosis:
Mechanisms and novel therapeutic approaches. Nat Rev Endocrinol.
9:575–583. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kato M, Patel MS, Levasseur R, Lobov I,
Chang BH, Glass DA II, Hartmann C, Li L, Hwang TH, Brayton CF, et
al: Cbfa1-independent decrease in osteoblast proliferation,
osteopenia and persistent embryonic eye vascularization in mice
deficient in Lrp5, a Wnt coreceptor. J Cell Biol. 157:303–314.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Krishnan V, Bryant HU and Macdougald OA:
Regulation of bone mass by Wnt signaling. J Clin Invest.
116:1202–1209. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gong Y, Slee RB, Fukai N, Rawadi G,
Roman-Roman S, Reginato AM, Wang H, Cundy T, Glorieux FH, Lev D, et
al: LDL receptor-related protein 5 (LRP5) affects bone accrual and
eye development. Cell. 107:513–523. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cui Y, Niziolek PJ, MacDonald BT, Zylstra
CR, Alenina N, Robinson DR, Zhong Z, Matthes S, Jacobsen CM, Conlon
RA, et al: Lrp5 functions in bone to regulate bone mass. Nat Med.
17:684–691. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lian JB, Stein GS, Javed A, van Wijnen AJ,
Stein JL, Montecino M, Hassan MQ, Gaur T, Lengner CJ and Young DW:
Networks and hubs for the transcriptional control of
osteoblastogenesis. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 7:1–16. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Javed A, Bae JS, Afzal F, Gutierrez S,
Pratap J, Zaidi SK, Lou Y, van Wijnen AJ, Stein JL, Stein GS and
Lian JB: Structural coupling of Smad and Runx2 for execution of the
BMP2 osteogenic signal. J Biol Chem. 283:8412–8422. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sawakami K, Robling AG, Ai M, Pitner ND,
Liu D, Warden SJ, Li J, Maye P, Rowe DW, Duncan RL, et al: The Wnt
co-receptor LRP5 is essential for skeletal mechanotransduction but
not for the anabolic bone response to parathyroid hormone
treatment. J Biol Chem. 281:23698–23711. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sen B, Guilluy C, Xie Z, Case N, Styner M,
Thomas J, Oguz I, Rubin C, Burridge K and Rubin J: Mechanically
induced focal adhesion assembly amplifies anti-adipogenic pathways
in mesenchymal stem cells. Stem cells. 29:1829–1836. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tu X, Rhee Y, Condon KW, Bivi N, Allen MR,
Dwyer D, Stolina M, Turner CH, Robling AG, Plotkin LI and Bellido
T: Sost downregulation and local Wnt signaling are required for the
osteogenic response to mechanical loading. Bone. 50:209–217. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sanchez C, Pesesse L, Gabay O, Delcour JP,
Msika P, Baudouin C and Henrotin YE: Regulation of subchondral bone
osteoblast metabolism by cyclic compression. Arthritis Rheum.
64:1193–1203. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Koike M, Shimokawa H, Kanno Z, Ohya K and
Soma K: Effects of mechanical strain on proliferation and
differentiation of bone marrow stromal cell line ST2. J Bone Miner
Metab. 23:219–225. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jacobs C, Grimm S, Ziebart T, Walter C and
Wehrbein H: Osteogenic differentiation of periodontal fibroblasts
is dependent on the strength of mechanical strain. Arch Oral Biol.
58:896–904. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sanchez C, Gabay O, Salvat C, Henrotin YE
and Berenbaum F: Mechanical loading highly increases IL-6
production and decreases OPG expression by osteoblasts.
Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 17:473–481. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Fermor B, Weinberg JB, Pisetsky DS,
Misukonis MA, Banes AJ and Guilak F: The effects of static and
intermittent compression on nitric oxide production in articular
cartilage explants. J Orthop Res. 19:729–737. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Xue Y, Yan Y, Gong H, Fang B, Zhou Y, Ding
Z, Yin P, Zhang G, Ye Y, Yang C, et al: Insulin-like growth factor
binding protein 4 enhances cardiomyocytes induction in
murine-induced pluripotent stem cells. J Cell Biochem.
115:1495–1504. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lviak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Dumas V, Perrier A, Malaval L, Laroche N,
Guignandon A, Vico L and Rattner A: The effect of dual frequency
cyclic compression on matrix deposition by osteoblast-like cells
grown in 3D scaffolds and on modulation of VEGF variant expression.
Biomaterials. 30:3279–3288. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
David V, Guignandon A, Martin A, Malaval
L, Lafage-Proust MH, Rattner A, Mann V, Noble B, Jones DB and Vico
L: Ex Vivo bone formation in bovine trabecular bone cultured in a
dynamic 3D bioreactor is enhanced by compressive mechanical strain.
Tissue Eng Part A. 14:117–126. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Peptan AI, Lopez A, Kopher RA and Mao JJ:
Responses of intramembranous bone and sutures upon in vivo cyclic
tensile and compressive loading. Bone. 42:432–438. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Goel S, Chin EN, Fakhraldeen SA, Berry SM,
Beebe DJ and Alexander CM: Both LRP5 and LRP6 receptors are
required to respond to physiological Wnt ligands in mammary
epithelial cells and fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 287:16454–16466.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Colaianni G, Cuscito C, Mongelli T,
Pignataro P, Tamma R, Oranger A, Colucci S and Grano M: Cellular
Mechanisms of Bone Regeneration: Role of Wnt-1 in Bone-Muscle
Interaction during Physical Activity39. J Biol Regul Homeost
Agents. 29:(4 Suppl). S39–S45. 2015.
|
|
37
|
MacDonald BT, Tamai K and He X:
Wnt/beta-catenin signaling: Components, mechanisms, and diseases.
Dev Cell. 17:9–26. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Baron R and Kneissel M: WNT signaling in
bone homeostasis and disease: From human mutations to treatments.
Nat Med. 19:179–192. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Robinson JA, Chatterjee-Kishore M,
Yaworsky PJ, Cullen DM, Zhao W, Li C, Kharode Y, Sauter L, Babij P,
Brown EL, et al: Wnt/beta-catenin signaling is a normal
physiological response to mechanical loading in bone. J Biol Chem.
281:31720–31728. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
He XC, Zhang J, Tong WG, Tawfik O, Ross J,
Scoville DH, Tian Q, Zeng X, He X, Wiedemann LM, et al: BMP
signaling inhibits intestinal stem cell self-renewal through
suppression of Wnt-beta-catenin signaling. Nat Genet. 36:1117–1121.
2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Case N, Ma M, Sen B, Xie Z, Gross TS and
Rubin J: Beta-catenin levels influence rapid mechanical responses
in osteoblasts. J Biol Chem. 283:29196–29205. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|