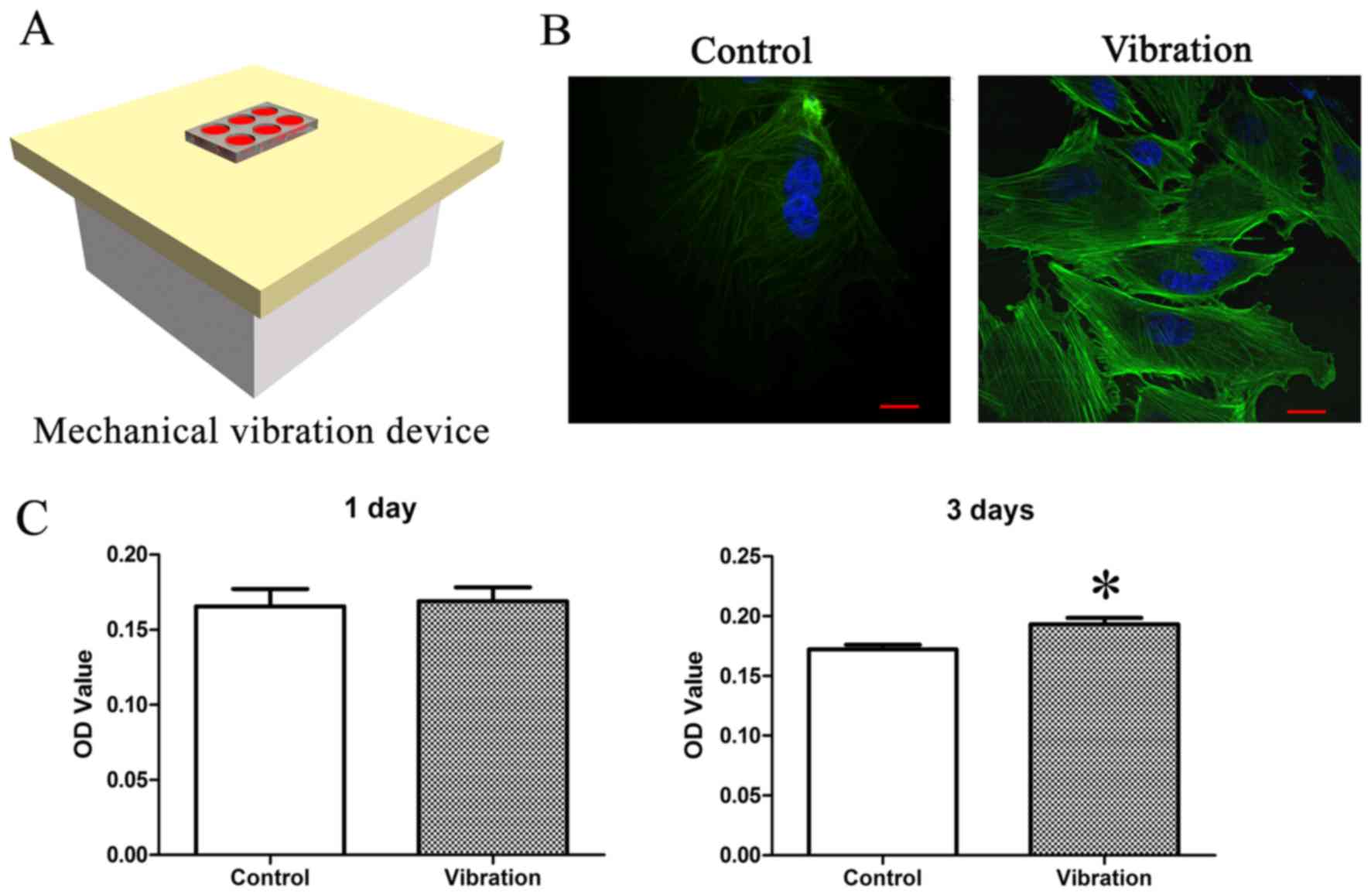
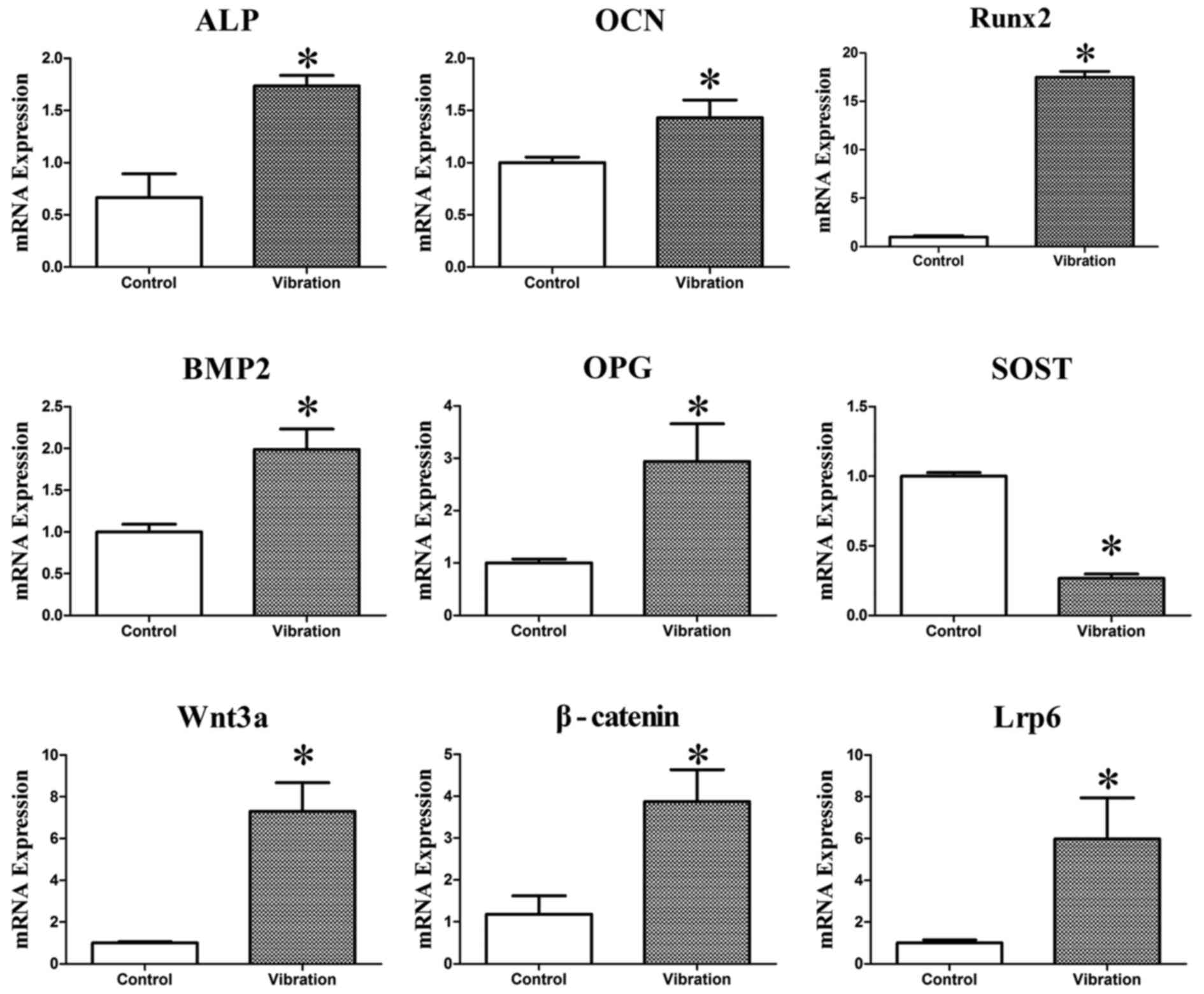
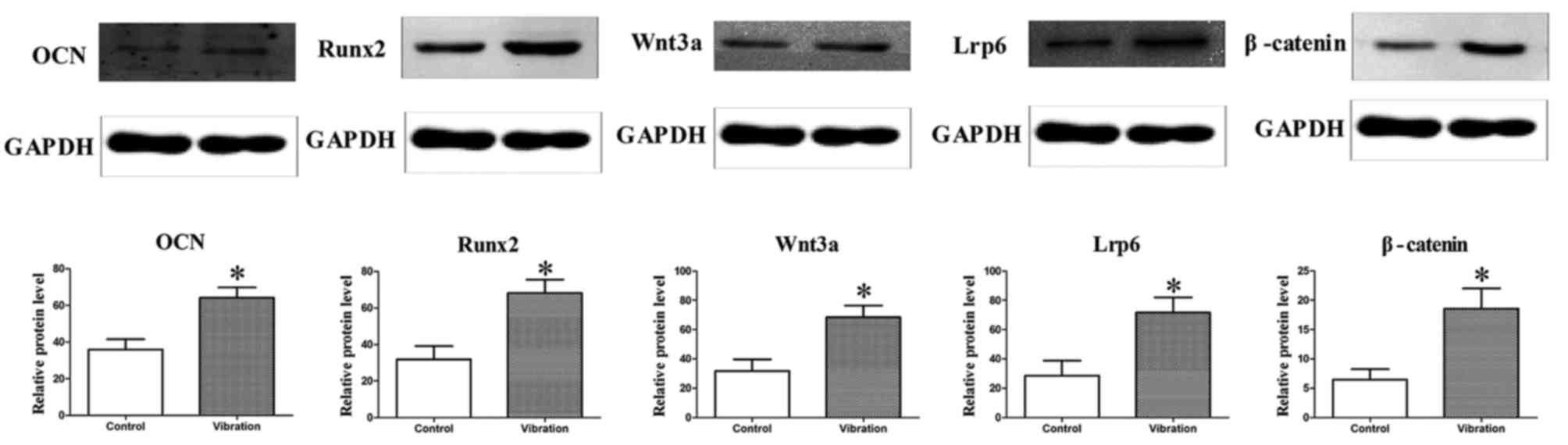
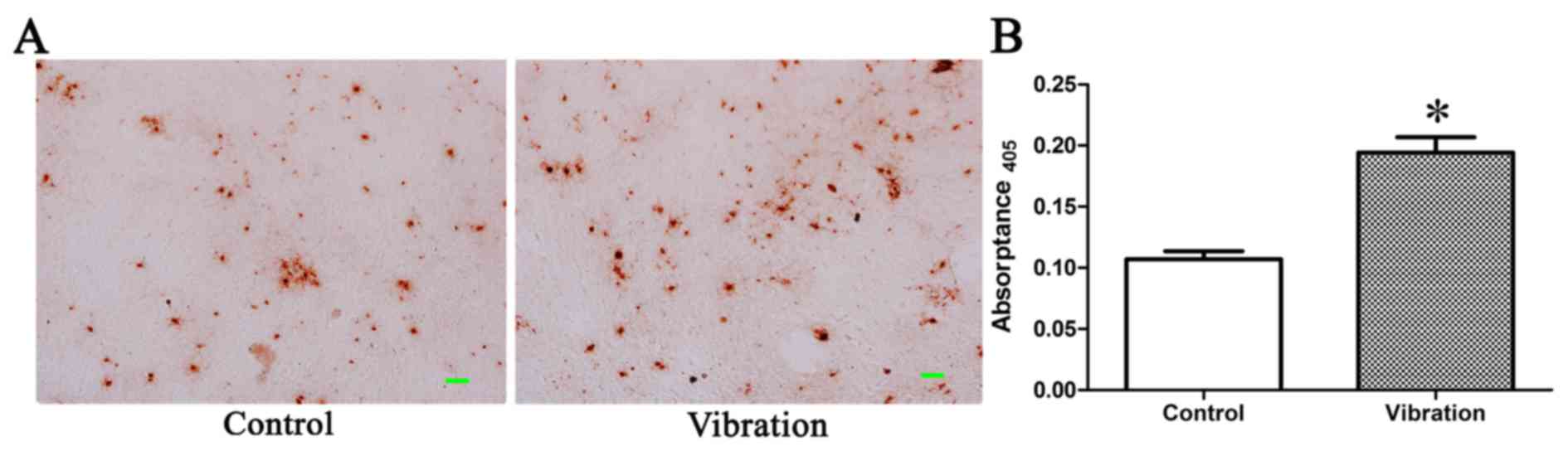
|
1
|
Xie L, Jacobson JM, Choi ES, Busa B,
Donahue LR, Miller LM, Rubin CT and Judex S: Low-level mechanical
vibrations can influence bone resorption and bone formation in the
growing skeleton. Bone. 39:1059–1066. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Xie P, Tang Z, Qing F, Chen X, Zhu X, Fan
Y, Yang X and Zhang X: Bone mineral density, microarchitectural and
mechanical alterations of osteoporotic rat bone under long-term
whole-body vibration therapy. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater.
53:341–349. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Judex S, Lei X, Han D and Rubin C:
Low-magnitude mechanical signals that stimulate bone formation in
the ovariectomized rat are dependent on the applied frequency but
not on the strain magnitude. J Biomech. 40:1333–1339. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jing D, Cai J, Wu Y, Shen G, Li F, Xu Q,
Xie K, Tang C, Liu J, Guo W, et al: Pulsed electromagnetic fields
partially preserve bone mass, microarchitecture, and strength by
promoting bone formation in hindlimb-suspended rats. J Bone Miner
Res. 29:2250–2261. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Garnero P: New developments in biological
markers of bone metabolism in osteoporosis. Bone. 66:46–55. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rubin C, Turner AS, Bain S, Mallinckrodt C
and McLeod K: Anabolism. Low mechanical signals strengthen long
bones. Nature. 412:603–604. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Rubin C, Xu G and Judex S: The anabolic
activity of bone tissue, suppressed by disuse, is normalized by
brief exposure to extremely low-magnitude mechanical stimuli. FASEB
J. 15:2225–2229. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Judex S, Donahue LR and Rubin C: Genetic
predisposition to low bone mass is paralleled by an enhanced
sensitivity to signals anabolic to the skeleton. FASEB J.
16:1280–1282. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chan ME, Adler BJ, Green DE and Rubin CT:
Bone structure and B-cell populations, crippled by obesity, are
partially rescued by brief daily exposure to low-magnitude
mechanical signals. FASEB J. 26:4855–4863. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sehmisch S, Galal R, Kolios L, Tezval M,
Dullin C, Zimmer S, Stuermer KM and Stuermer EK: Effects of
low-magnitude, high-frequency mechanical stimulation in the rat
osteopenia model. Osteoporos Int. 20:1999–2008. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gilsanz V, Wren TA, Sanchez M, Dorey F,
Judex S and Rubin C: Low-level, high-frequency mechanical signals
enhance musculoskeletal development of young women with low BMD. J
Bone Miner Res. 21:1464–1474. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shi HF, Cheung WH, Qin L, Leung AH and
Leung KS: Low-magnitude high-frequency vibration treatment augments
fracture healing in ovariectomy-induced osteoporotic bone. Bone.
46:1299–1305. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Christiansen BA and Silva MJ: The effect
of varying magnitudes of whole-body vibration on several skeletal
sites in mice. Ann Biomed Eng. 34:1149–1156. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rubin C, Recker R, Cullen D, Ryaby J,
McCabe J and McLeod K: Prevention of postmenopausal bone loss by a
low-magnitude, high-frequency mechanical stimuli: A clinical trial
assessing compliance, efficacy, and safety. J Bone Miner Res.
19:343–351. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Fritton SP, McLeod KJ and Rubin CT:
Quantifying the strain history of bone: Spatial uniformity and
self-similarity of low-magnitude strains. J Biomech. 33:317–325.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Coughlin TR and Niebur GL: Fluid shear
stress in trabecular bone marrow due to low-magnitude
high-frequency vibration. J Biomech. 45:2222–2229. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Caetano-Lopes J, Canhão H and Fonseca JE:
Osteoblasts and bone formation. Acta Reumatol Port. 32:103–110.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jiang T, Zhou B, Huang L, Wu H, Huang J,
Liang T, Liu H, Zheng L and Zhao J: Andrographolide exerts
pro-osteogenic effect by activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling
pathway in vitro. Cell Physiol Biochem. 36:2327–2339. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gaur T, Lengner CJ, Hovhannisyan H, Bhat
RA, Bodine PV, Komm BS, Javed A, van Wijnen AJ, Stein JL, Stein GS
and Lian JB: Canonical WNT signaling promotes osteogenesis by
directly stimulating Runx2 gene expression. J Biol Chem.
280:33132–33140. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang R, Oyajobi BO, Harris SE, Chen D,
Tsao C, Deng HW and Zhao M: Wnt/β-catenin signaling activates bone
morphogenetic protein 2 expression in osteoblasts. Bone.
52:145–156. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bennett CN, Longo KA, Wright WS, Suva LJ,
Lane TF, Hankenson KD and MacDougald OA: Regulation of
osteoblastogenesis and bone mass by Wnt10b. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
102:3324–3339. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang B, Jin H, Zhu M, Li J, Zhao L, Zhang
Y, Tang D, Xiao G, Xing L, Boyce BF and Chen D: Chondrocyte
beta-catenin signaling regulates postnatal bone remodeling through
modulation of osteoclast formation in a murine model. Arthritis
Rheumatol. 66:107–120. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li C, Wang W, Xie L, Luo X, Cao X and Wan
M: Lipoprotein receptor-related protein 6 is required for
parathyroid hormone-induced Sost suppression. Ann NYAcad Sci.
1364:62–73. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Wang Y, Li YP, Paulson C, Shao JZ, Zhang
X, Wu M and Chen W: Wnt and the Wnt signaling pathway in bone
development and disease. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 19:379–407.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xu C, Wang J, Zhu T, Shen Y, Tang X, Fang
L and Xu Y: Cross-talking between PPAR and WNT signaling and its
regulation in mesenchymal stem cell differentiation. Curr Stem Cell
Res Ther. 11:247–254. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Weivoda MM, Ruan M, Hachfeld CM, Pederson
L, Howe A, Davey RA, Zajac JD, Kobayashi Y, Williams BO, Westendorf
JJ, et al: Wnt signaling inhibits osteoclast differentiation by
activating canonical and noncanonical cAMP/PKA pathways. J Bone
Miner Res. 31:65–75. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wong GL and Cohn DV: Target cells in bone
for parathormone and calcitonin are different: Enrichment for each
cell type by sequential digestion of mouse calvaria and selective
adhesion to polymeric surfaces. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
72:3167–3171. 1975. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Williams DC, Boder GB, Toomey RE, Paul DC,
Hillman CC Jr, King KL, Van Frank RM and Johnston CC Jr:
Mineralization and metabolic response in serially passaged adult
rat bone cells. Calcif Tissue Int. 30:233–246. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shui C and Scutt A: Mild heat shock
induces proliferation, alkaline phosphatase activity, and
mineralization in human bone marrow stromal cells and Mg-63 cells
in vitro. J Bone Miner Res. 16:731–741. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ciapetti G, Ambrosio L, Savarino L,
Granchi D, Cenni E, Baldini N, Pagani S, Guizzardi S, Causa F and
Giunti A: Osteoblast growth and function in porous poly
epsilon-caprolactone matrices for bone repair: A preliminary study.
Biomaterials. 24:3815–3824. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Gori F, Hofbauer LC, Dunstan CR, Spelsberg
TC, Khosla S and Riggs BL: The expression of osteoprotegerin and
RANK ligand and the support of osteoclast formation by
stromal-osteoblast lineage cells is developmentally regulated.
Endocrinology. 141:4768–4776. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chow SK, Leung KS, Qin J, Guo A, Sun M,
Qin L and Cheung WH: Mechanical stimulation enhanced estrogen
receptor expression and callus formation in diaphyseal long bone
fracture healing in ovariectomy-induced osteoporotic rats.
Osteoporos Int. 27:2989–3000. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhang C, Lu Y, Zhang L, Liu Y, Zhou Y,
Chen Y and Yu H: Influence of different intensities of vibration on
proliferation and differentiation of human periodontal ligament
stem cells. Arch Med Sci. 11:638–646. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Uzer G, Pongkitwitoon S, Ete Chan M and
Judex S: Vibration induced osteogenic commitment of mesenchymal
stem cells is enhanced by cytoskeletal remodeling but not fluid
shear. J Biomech. 46:2296–2302. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Sato N, Kubo K, Yamada M, Hori N, Suzuki
T, Maeda H and Ogawa T: Osteoblast mechanoresponses on Ti with
different surface topographies. J Dent Res. 88:812–816. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Thompson WR, Rubin CT and Rubin J:
Mechanical regulation of signaling pathways in bone. Gene.
503:179–193. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Huang H, Kamm RD and Lee RT: Cell
mechanics and mechanotransduction: Pathways, probes, and
physiology. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 287:C1–C11. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Klein-Nulend J, Bacabac RG and Bakker AD:
Mechanical loading and how it affects bone cells: The role of the
osteocyte cytoskeleton in maintaining our skeleton. Eur Cell Mater.
24:278–291. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Tanaka SM, Li J, Duncan RL, Yokota H, Burr
DB and Turner CH: Effects of broad frequency vibration on cultured
osteoblasts. J Biomech. 36:73–80. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Otto F, Thornell AP, Crompton T, Denzel A,
Gilmour KC, Rosewell IR, Stamp GW, Beddington RS, Mundlos S, Olsen
BR, et al: Cbfa1, a candidate gene for cleidocranial dysplasia
syndrome, is essential for osteoblast differentiation and bone
development. Cell. 89:765–771. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wozney JM, Rosen V, Celeste AJ, Mitsock
LM, Whitters MJ, Kriz RW, Hewick RM and Wang EA: Novel regulators
of bone formation: Molecular clones and activities. Science.
242:1528–1534. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hofbauer LC and Schoppet M: Clinical
implications of the osteoprotegerin/RANKL/RANK system for bone and
vascular diseases. JAMA. 292:490–495. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Bonewald LF: The amazing osteocyte. J Bone
Miner Res. 26:229–238. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Burgers TA and Williams BO: Regulation of
Wnt/β-catenin signaling within and from osteocytes. Bone.
54:244–249. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Bellido T, Saini V and Pajevic PD: Effects
of PTH on osteocyte function. Bone. 54:250–257. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ellies DL, Viviano B, McCarthy J, Rey JP,
Itasaki N, Saunders S and Krumlauf R: Bone density ligand,
Sclerostin, directly interacts with LRP5 but not LRP5G171V to
modulate Wnt activity. J Bone Miner Res. 21:1738–1749. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Santos A, Bakker AD, Zandieh-Doulabi B,
Semeins CM and Klein-Nulend J: Pulsating fluid flow modulates gene
expression of proteins involved in Wnt signaling pathways in
osteocytes. J Orthop Res. 27:1280–1287. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Macsai CE, Foster BK and Xian CJ: Roles of
Wnt signalling in bone growth, remodelling, skeletal disorders and
fracture repair. J Cell Physiol. 215:578–587. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zhang R, Oyajobi BO, Harris SE, Chen D,
Tsao C, Deng HW and Zhao M: Wnt/β-catenin signaling activates bone
morphogenetic protein 2 expression in osteoblasts. Bone.
52:145–156. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Gaur T, Lengner CJ, Hovhannisyan H, Bhat
RA, Bodine PV, Komm BS, Javed A, van Wijnen AJ, Stein JL, Stein GS
and Lian JB: Canonical WNT signaling promotes osteogenesis by
directly stimulating Runx2 gene expression. J Biol Chem.
280:33132–3340. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Bennett CN, Longo KA, Wright WS, Suva LJ,
Lane TF, Hankenson KD and MacDougald OA: Regulation of
osteoblastogenesis and bone mass by Wnt10b. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
102:3324–3329. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Wang B, Jin H, Zhu M, Li J, Zhao L, Zhang
Y, Tang D, Xiao G, Xing L, Boyce BF and Chen D: Chondrocyte
β-catenin signaling regulates postnatal bone remodeling through
modulation of osteoclast formation in a murine model. Arthritis
Rheumatol. 66:107–120. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Rawadi G, Vayssière B, Dunn F, Baron R and
Roman-Roman S: BMP-2 controls alkaline phosphatase expression and
osteoblast mineralization by a Wnt autocrine loop. J Bone Miner
Res. 18:1842–1853. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|