|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Dutton SJ, Ferry DR, Blazeby JM, Abbas H,
Dahle-Smith A, Mansoor W, Thompson J, Harrison M, Chatterjee A,
Falk S, et al: Gefitinib for oesophageal cancer progressing after
chemotherapy (COG): A phase 3, multicentre, double-blind,
placebo-controlled randomised trial. Lancet Oncol. 15:894–904.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Conroy T, Galais MP, Raoul JL, Bouché O,
Gourgou-Bourgade S, Douillard JY, Etienne PL, Boige V, Martel-Lafay
I, Michel P, et al: Definitive chemoradiotherapy with FOLFOX versus
fluorouracil and cisplatin in patients with oesophageal cancer
(PRODIGE5/ACCORD17): Final results of a randomised, phase 2/3
trial. Lancet Oncol. 15:305–314. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhu HD, Guo JH, Mao AW, Lv WF, Ji JS, Wang
WH, Lv B, Yang RM, Wu W, Ni CF, et al: Conventional stents versus
stents loaded with (125)iodine seeds for the treatment of
unresectable oesophageal cancer: A multicentre, randomised phase 3
trial. Lancet Oncol. 15:612–619. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
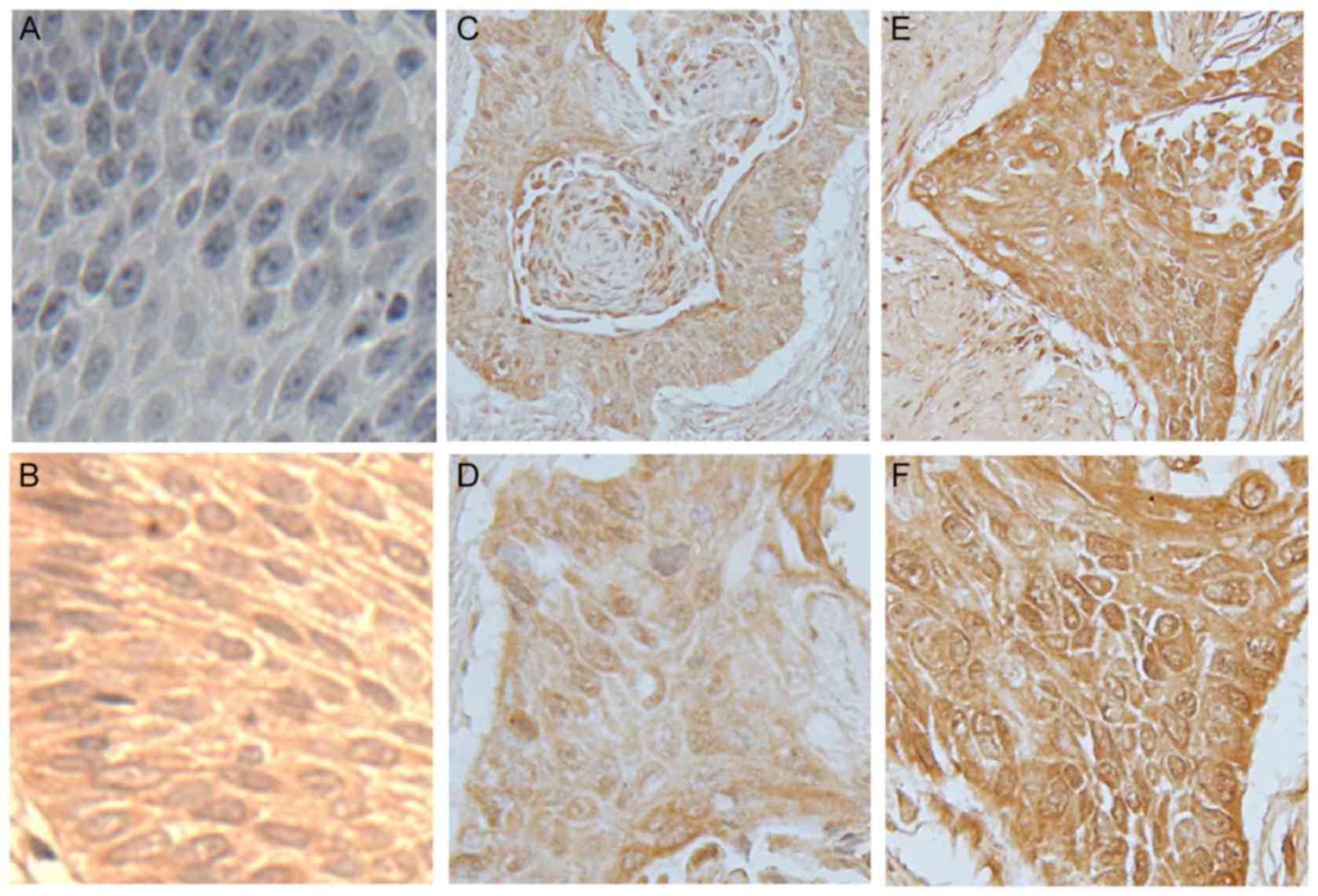
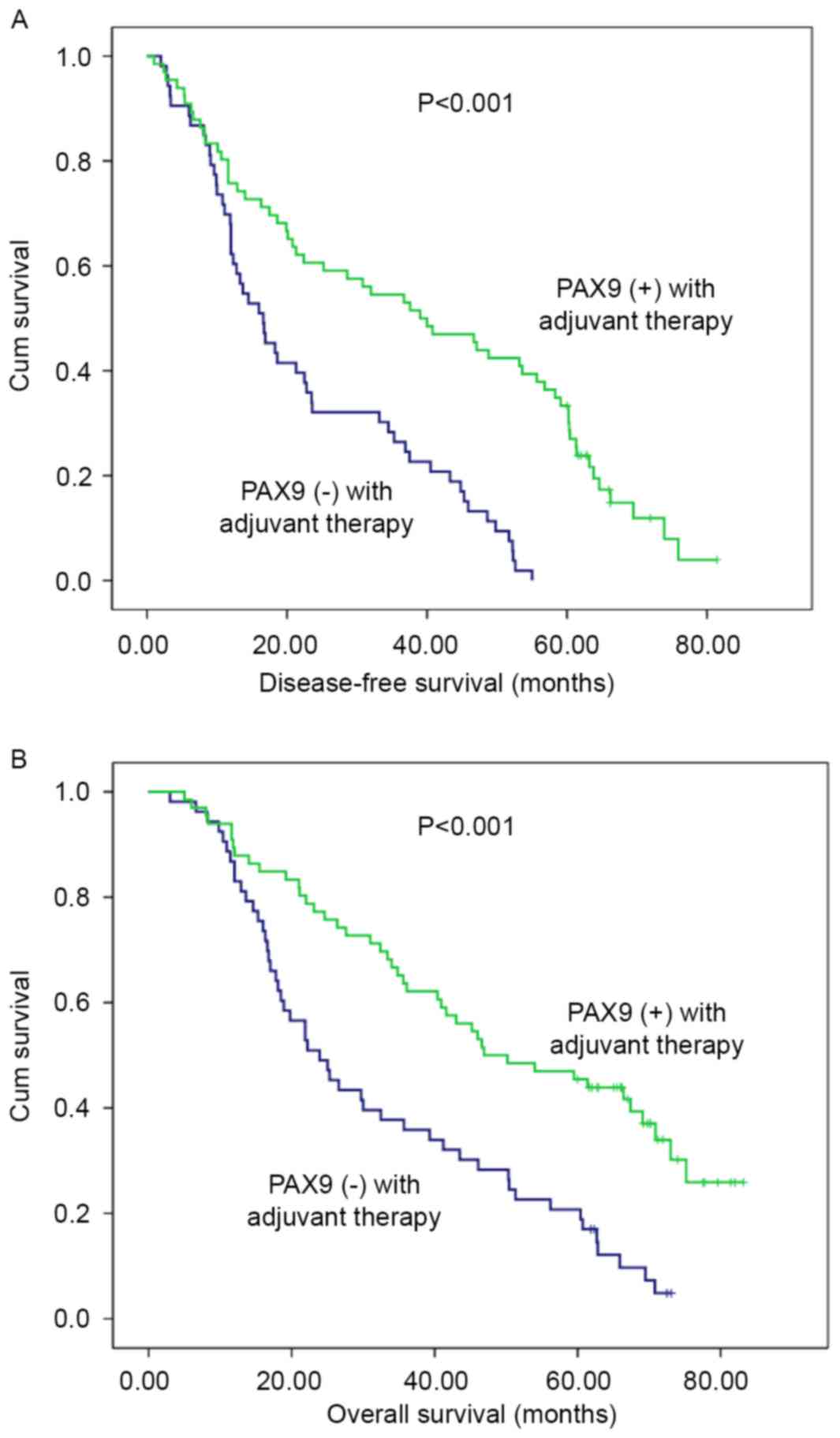
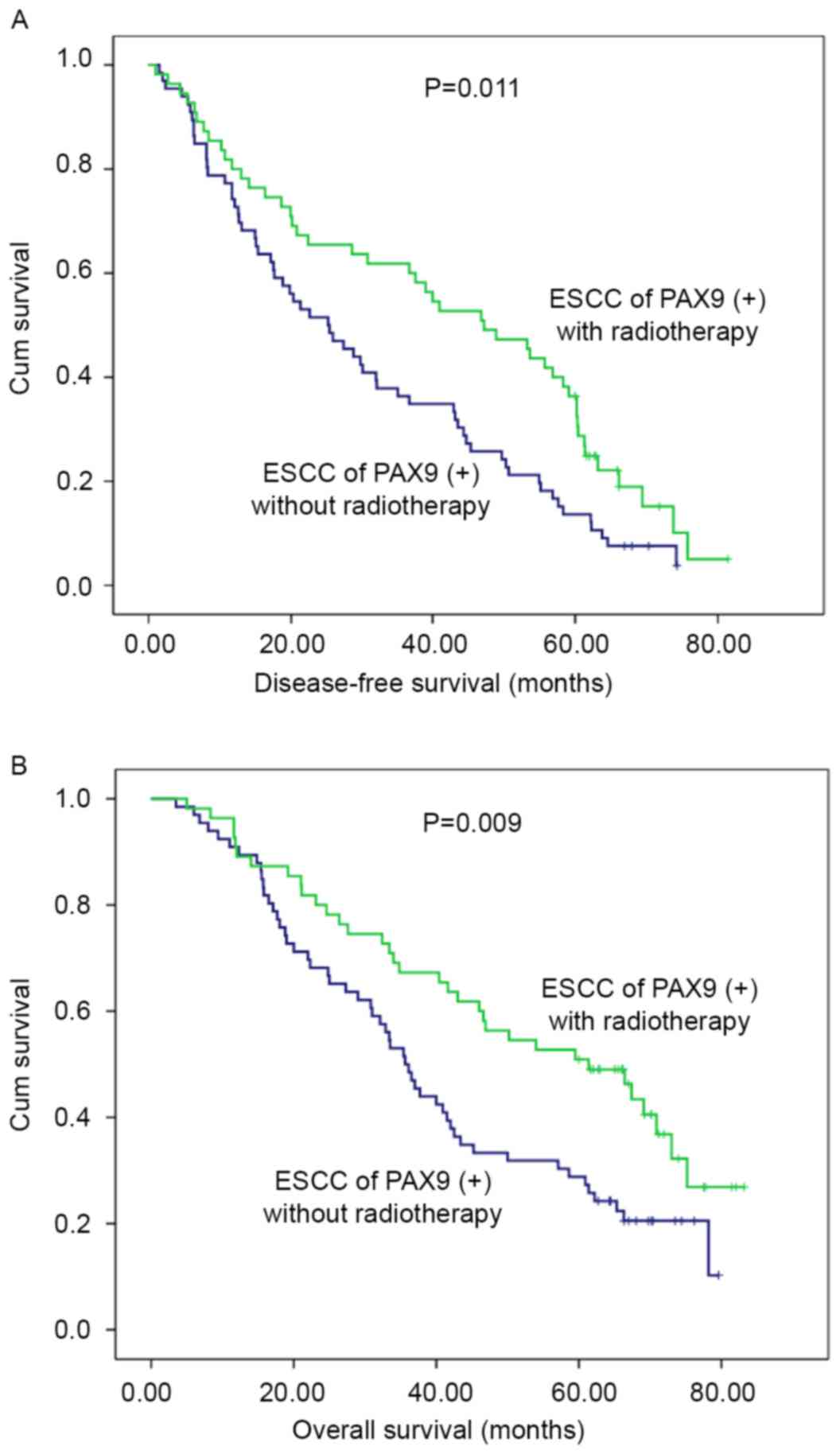
Graf D, Vallböhmer D, Knoefel WT, Budach W
and Häussinger D: Multimodal treatment of esophageal carcinoma.
Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 139:2141–2147. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Paul S and Altorki N: Outcomes in the
management of esophageal cancer. J Surg Oncol. 110:599–610. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang N, Liu F, Cao F, Jia Y, Wang J, Ma W,
Tan B, Wang K, Song Q and Cheng Y: RACK1 predicts poor prognosis
and regulates progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
through its epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Biol Ther.
16:528–540. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Urakawa N, Utsunomiya S, Nishio M,
Shigeoka M, Takase N, Arai N, Kakeji Y, Koma Y and Yokozaki H:
GDF15 derived from both tumor-associated macrophages and esophageal
squamous cell carcinomas contributes to tumor progression via Akt
and Erk pathways. Lab Inves. 95:491–503. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Nishi T, Takeuchi H, Matsuda S, Ogura M,
Kawakubo H, Fukuda K, Nakamura R, Takahashi T, Wada N, Saikawa Y,
et al: CXCR2 expression and postoperative complications affect
long-term survival in patients with esophageal cancer. World J Surg
Oncol. 13:2322015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Usui A, Hoshino I, Akutsu Y, Sakata H,
Nishimori T, Murakami K, Kano M, Shuto K and Matsubara H: The
molecular role of Fra-1 and its prognostic significance in human
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer. 118:3387–3396. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Forghanifard MM, Khales Ardalan S,
Javdani-Mallak A, Rad A, Farshchian M and Abbaszadegan MR: Stemness
state regulators SALL4 and SOX2 are involved in progression and
invasiveness of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Med Oncol.
31:9222014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Paixão-Côrtes VR, Salzano FM and Bortolini
MC: Evolutionary history of chordate PAX genes: Dynamics of change
in a complex gene family. PLoS One. 8:e735602013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dressler GR: Patterning and early cell
lineage decisions in the developing kidney: The role of Pax genes.
Pediatr Nephrol. 26:1387–1394. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li CG and Eccles MR: PAX Genes in Cancer;
Friends or Foes? Front Genet. 3:62012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Robson EJ, He SJ and Eccles MR: A PANorama
of PAX genes in cancer and development. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:52–62.
2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang Q, Fang WH, Krupinski J, Kumar S,
Slevin M and Kumar P: Pax genes in embryogenesis and oncogenesis. J
Cell Mol Med. 12:2281–2294. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lang D, Powell SK, Plummer RS, Young KP
and Ruggeri BA: PAX genes: Roles in development, pathophysiology,
and cancer. Biochem Pharmacol. 73:1–14. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Muratovska A, Zhou C, He S, Goodyer P and
Eccles MR: Paired-Box genes are frequently expressed in cancer and
often required for cancer cell survival. Oncogene. 22:7989–7997.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kubic JD, Little EC, Lui JW, Iizuka T and
Lang D: PAX3 and ETS1 synergistically activate MET expression in
melanoma cells. Oncogene. 34:4964–4974. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Curto GG, Gard C and Ribes V: Structures
and properties of PAX linked regulatory networks architecting and
pacing the emergence of neuronal diversity. Semin cell Dev Biol.
44:75–86. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mentrikoski MJ, Wendroth SM and Wick MR:
Immunohistochemical distinction of renal cell carcinoma from other
carcinomas with clear-cell histomorphology: Utility of CD10 and
CA-125 in addition to PAX-2, PAX-8, RCCma, and adipophilin. Appl
Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 22:635–641. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu W, Li X, Chu ES, Go MY, Xu L, Zhao G,
Li L, Dai N, Si J, Tao Q, et al: Paired box gene 5 is a novel tumor
suppressor in hepatocellular carcinoma through interaction with p53
signaling pathway. Hepatology. 53:843–853. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ribeiro MM, Teixeira GS, Martins L,
Marques MR, de Souza AP and Line SR: G-quadruplex formation
enhances splicing efficiency of PAX9 intron 1. Hum Genet.
134:37–44. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Narasimhan K, Hilbig A, Udayasuryan B,
Jayabal S, Kolatkar PR and Jauch R: Crystallization and preliminary
X-ray diffraction analysis of the Pax9 paired domain bound to a DC5
enhancer DNA element. Acta crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun.
70:1357–1361. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mitsui SN, Yasue A, Masuda K, Watanabe K,
Horiuchi S, Imoto I and Tanaka E: Novel PAX9 mutations cause
non-syndromic tooth agenesis. J Dent Res. 93:245–249. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Boeira BR Jr and Echeverrigaray S: Novel
missense mutation in PAX9 gene associated with familial tooth
agenesis. J Oral Pathol Med. 42:99–105. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhu J, Yang X, Zhang C, Ge L and Zheng S:
A novel nonsense mutation in PAX9 is associated with sporadic
hypodontia. Mutagenesis. 27:313–317. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liang J, Song G, Li Q and Bian Z: Novel
missense mutations in PAX9 causing oligodontia. Arch Oral Biol.
57:784–789. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kendall J, Liu Q, Bakleh A, Krasnitz A,
Nguyen KC, Lakshmi B, Gerald WL, Powers S and Mu D: Oncogenic
cooperation and coamplification of developmental transcription
factor genes in lung cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
104:16663–16668. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lee JC, Sharma M, Lee YH, Lee NH, Kim SY,
Yun JS, Nam SY, Hwang PH, Jhee EC and Yi HK: Pax9 mediated cell
survival in oral squamous carcinoma cell enhanced by c-myb. Cell
Biochem Funct. 26:892–899. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bandla S, Pennathur A, Luketich JD, Beer
DG, Lin L, Bass AJ, Godfrey TE and Litle VR: Comparative genomics
of esophageal adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. Ann
Thorac Surg. 93:1101–1106. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Edge SB and Compton CC: The American joint
committee on cancer: The 7th edition of the AJCC cancer staging
manualand the future of TNM. Ann Surg Oncol. 17:1471–1474. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zeidan AM, Salem MR, Mazoit JX, Abdullah
MA, Ghattas T and Crystal GJ: The effectiveness of cricoid pressure
for occluding the esophageal entrance in anesthetized and paralyzed
patients: An experimental and observational glidescope study.
Anesth Analq. 118:580–586. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Prasad B, Kashyap B, Babu GS, Kumar GR and
Manyam R: Expression of podoplanin in different grades of oral
squamous cell carcinoma. Ann Med Health Sci Res. 5:299–304. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Bonds J, Pollan-White S, Xiang L, Mues G
and D'Souza R: Is there a link between ovarian cancer and tooth
agenesis? Eur J Med Genet. 57:235–239. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Sun MM, Li JF, Guo LL, Xiao HT, Dong L,
Wang F, Huang FB, Cao D, Qin T, Yin XH, et al: TGF-beta1
suppression of microRNA-450b-5p expression: A novel mechanism for
blocking myogenic differentiation of rhabdomyosarcoma. Oncogene.
33:2075–2086. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Harris T, Pan Q, Sironi J, Lutz D, Tian J,
Sapkar J, Perez-Soler R, Keller S and Locker J: Both gene
amplification and allelic loss occur at 14q13.3 in lung cancer.
Clin Cancer Res. 17:690–699. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Jiang WP, Wang Z and Jia Y: CEP55
overexpression predicts poor prognosis in patients with locally
advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Lett.
13:236–242. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Gerber JK, Richter T, Kremmer E, Adamski
J, Höfler H, Balling R and Peters H: Progressive loss of PAX9
expression correlates with increasing malignancy of dysplastic and
cancerous epithelium of the human oesophagus. J Pathol.
197:293–297. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Chen H, Beasley A, Hu Y and Chen X: A
Zebrafish model for studies on esophageal epithelial biology. PLoS
One. 10:e01438782015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Roesch A, Mueller AM, Stempfl T, Moehle C,
Landthaler M and Vogt T: RBP2-H1/JARID1B is a transcriptional
regulator with a tumor suppressive potential in melanoma cells. Int
J Cancer. 122:1047–1057. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Cooper JS, Guo MD, Herskovic A, Macdonald
JS, Martenson JA Jr, Al-Sarraf M, Byhardt R, Russell AH, Beitler
JJ, Spencer S, et al: Chemoradiotherapy of locally advanced
esophageal cancer: Long-term follow-up of a prospective randomized
trial (RTOG 85–01). Radiation therapy oncology group. JAMA.
281:1623–1627. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Minsky BD, Pajak TF, Ginsberg RJ, Pisansky
TM, Martenson J, Komaki R, Okawara G, Rosenthal SA and Kelsen DP:
INT 0123 (Radiation Therapy Oncology Group 94–05) phase III trial
of combined-modality therapy for esophageal cancer: High-dose
versus standard-dose radiation therapy. J Clin Oncol. 20:1167–1174.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Liu R, Gu J, Jiang P, Zheng Y, Liu X,
Jiang X, Huang E, Xiong S, Xu F, Liu G, et al: DNMT1-microRNA126
epigenetic circuit contributes to esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma growth via ADAM9-EGFR-AKT signaling. Clin Cancer Res.
21:854–863. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Lee KW, Sung CO, Kim JH, Kang M, Yoo HY,
Kim HH, Um SH and Kim SH: CD10 expression is enhanced by Twist1 and
associated with poor prognosis in esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma with facilitating tumorigenicity in vitro and in vivo.
Int J Cancer. 136:310–321. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Hein AL, Ouellette MM and Yan Y:
Radiation-induced signaling pathways that promote cancer cell
survival (review). Int J Oncol. 45:1813–1819. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Hsu DS, Acharya CR, Balakumaran BS, Riedel
RF, Kim MK, Stevenson M, Tuchman S, Mukherjee S, Barry W, Dressman
HK, et al: Characterizing the developmental pathways TTF-1, NKX2-8,
and PAX9 in lung cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:5312–5317.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Chen J, Kwong DL, Cao T, Hu Q, Zhang L,
Ming X, Chen J, Fu L and Guan X: Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
(ESCC): Advance in genomics and molecular genetics. Dis Esophagus.
28:84–89. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Bu F, Liu X, Li J, Chen S, Tong X, Ma C,
Mao H, Pan F, Li X, Chen B, et al: TGF-β1 induces epigenetic
silence of TIP30 to promote tumor metastasis in esophageal
carcinoma. Oncotarget. 6:2120–2133. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Mishra A and Verma M: Cancer biomarkers:
Are we ready for the prime time? Cancers (Basel). 2:190–208. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|