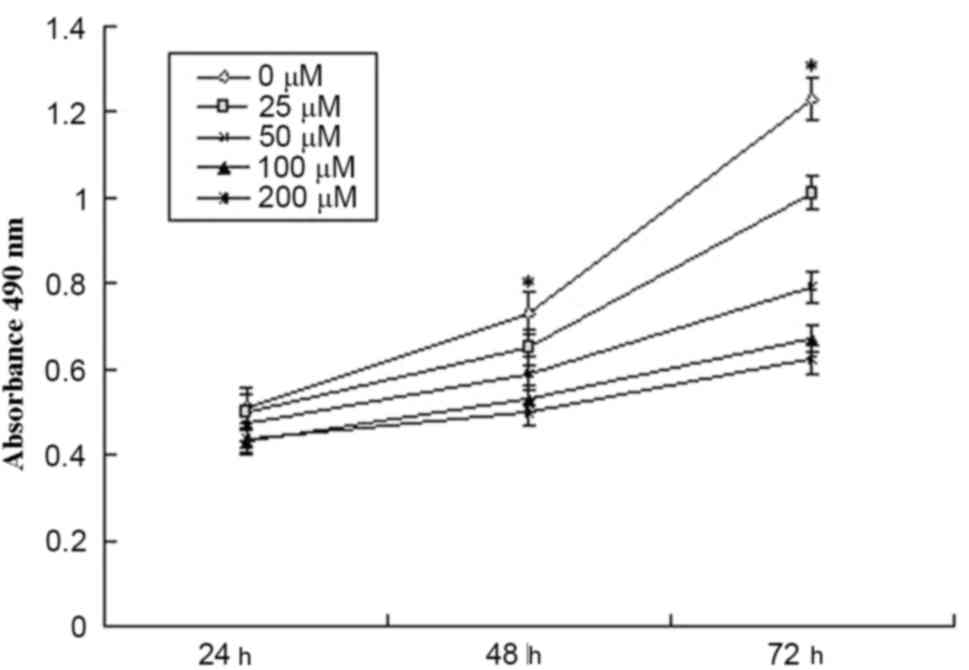
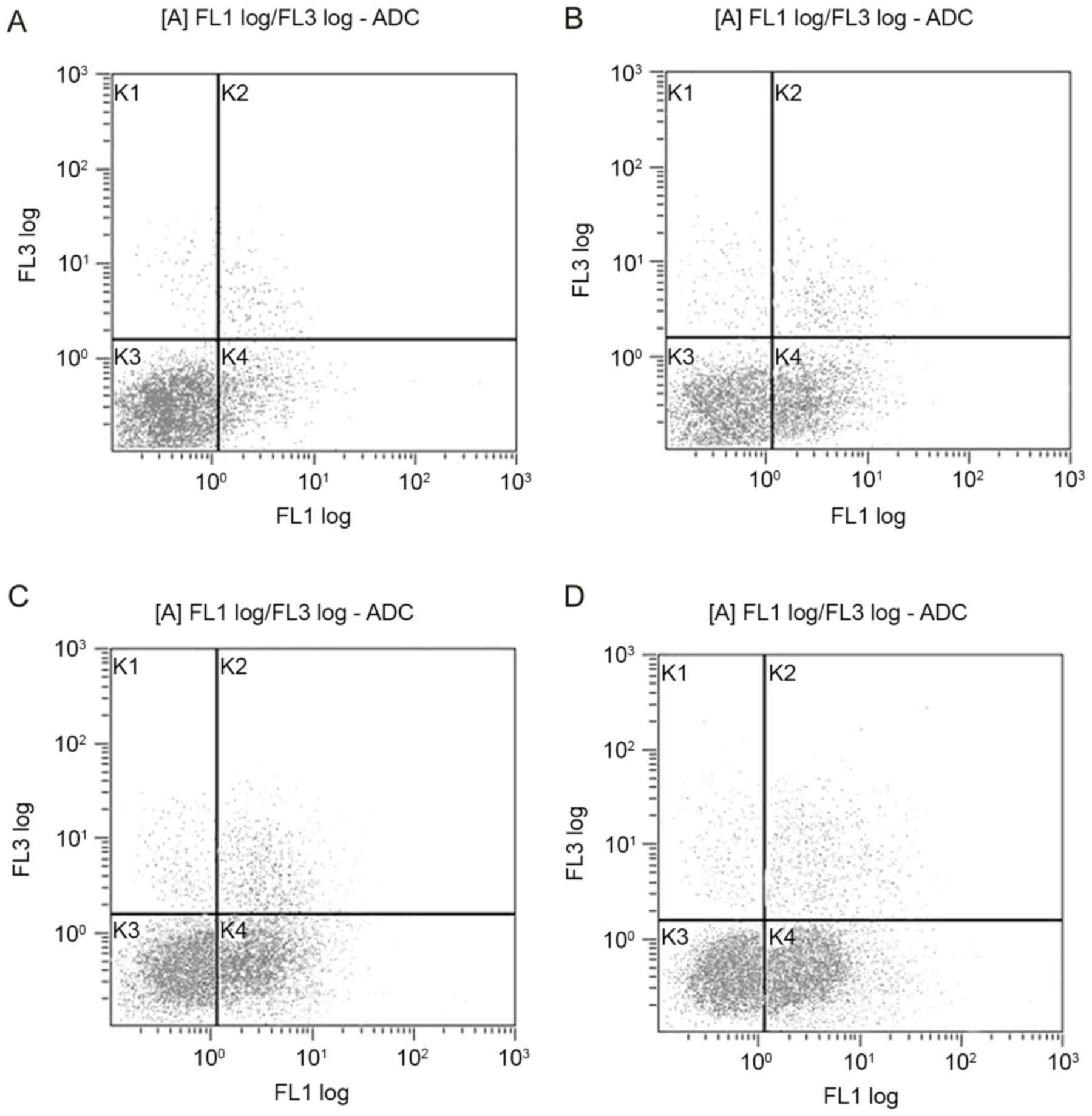
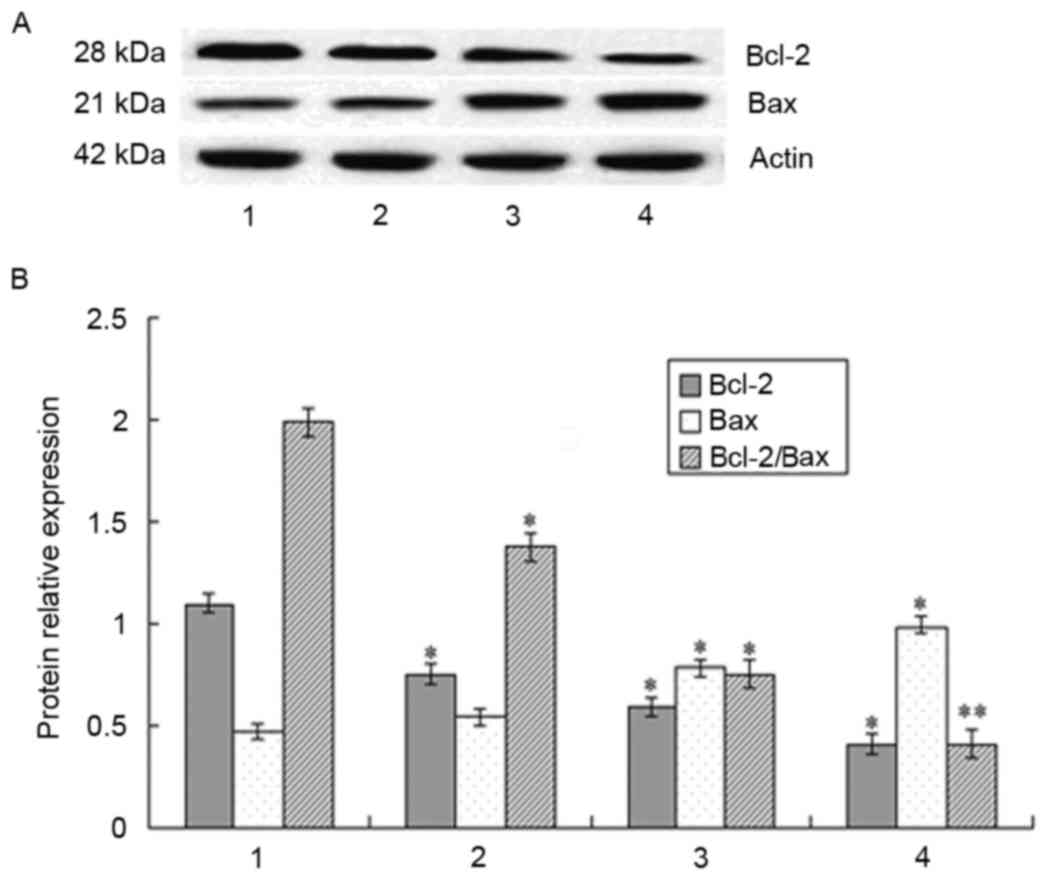
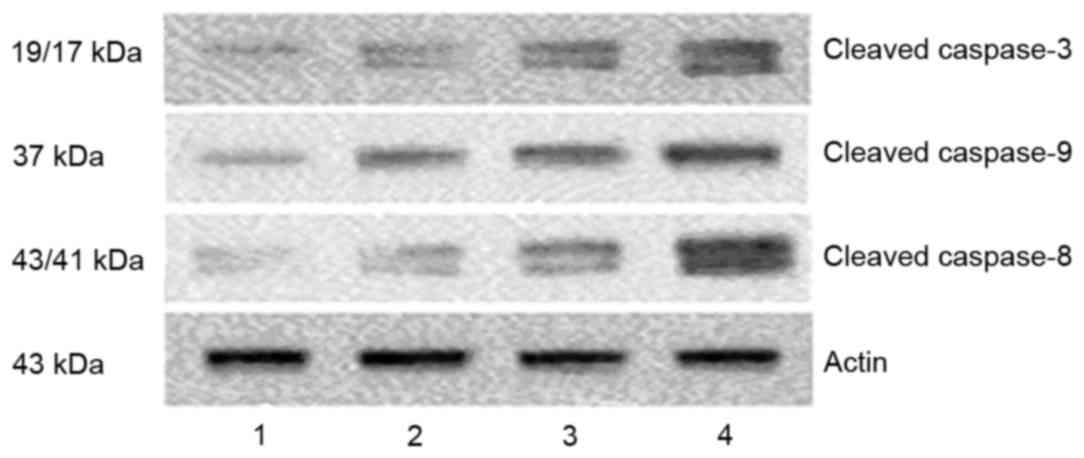
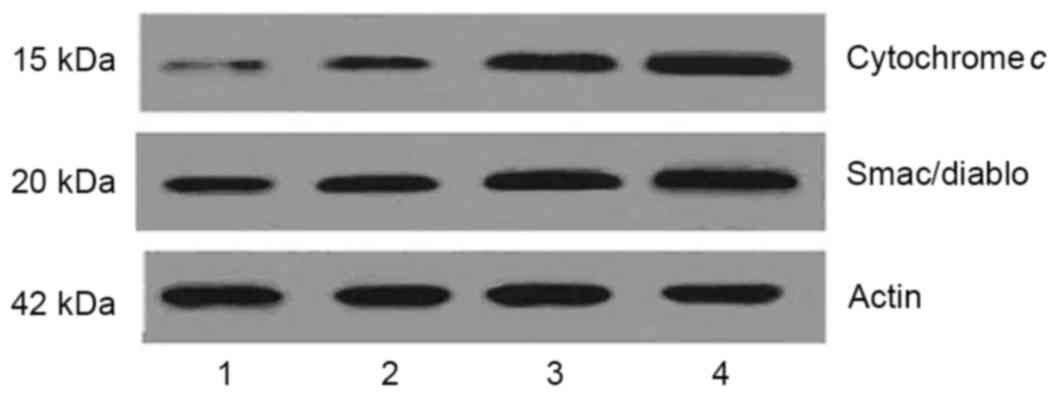
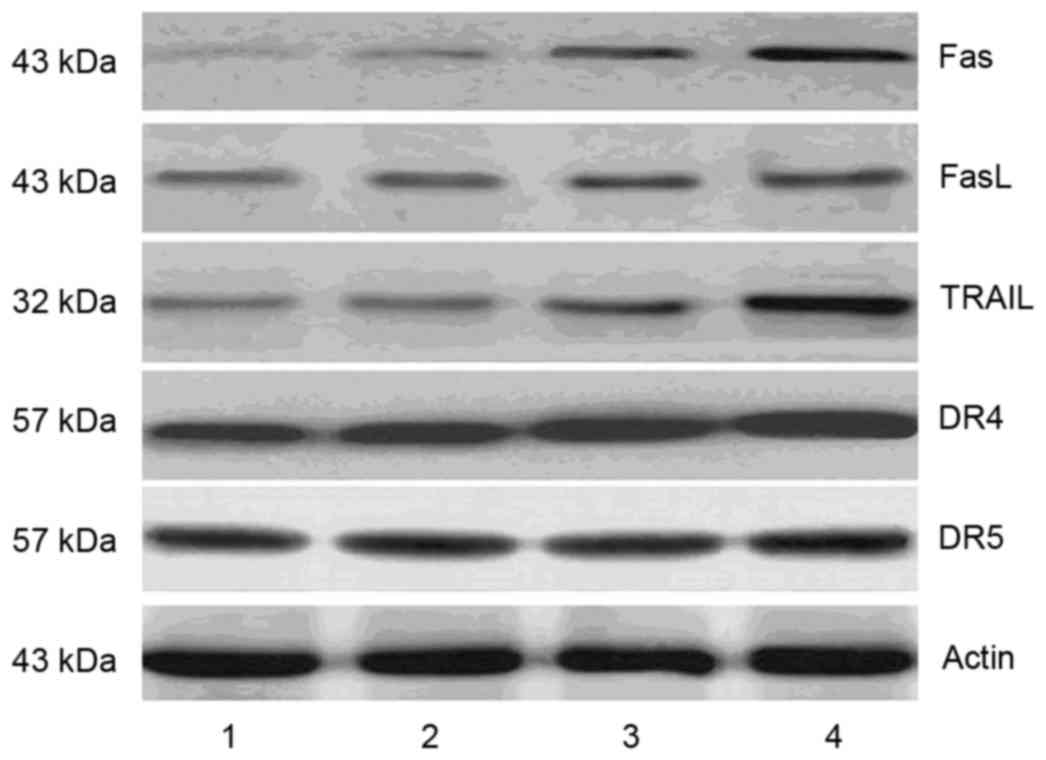
|
1
|
Umemoto N, Ishii H, Kamoi D, Aoyama T,
Sakakibara T, Takahashi H, Tanaka A, Yasuda Y, Suzuki S, Matsubara
T and Murohara T: Reverse association of omega-3/omega-6
polyunsaturated fatty acids ratios with carotid atherosclerosis in
patients on hemodialysis. Atherosclerosis. 249:65–69. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Molfino A, Gioia G, Fanelli Rossi F and
Muscaritoli M: The role for dietary omega-3 fatty acids
supplementation in older adults. Nutrients. 6:4058–4073. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gomez-Candela C, Puchalt Roldan MC, Palma
Milla S, Lopez Plaza B and Bermejo L: The role of omega-3 fatty
acids in diets. J Am Coll Nutr. 34:(Suppl 1). S42–S47. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Bartram HP, Gostner A, Scheppach W, Reddy
BS, Rao CV, Dusel G, Richter F, Richter A and Kasper H: Effects of
fish oil on rectal cell proliferation, mucosal fatty acids, and
prostaglandin E2 release in healthy subjects. Gastroenterology.
105:1317–1322. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liu J and Ma DW: The role of n-3
polyunsaturated fatty acids in the prevention and treatment of
breast cancer. Nutrients. 6:5184–5223. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Laviano A, Rianda S, Molfino A and Fanelli
FR: Omega-3 fatty acids in cancer. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care.
16:156–161. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang F and Chen Y, Long J, Dong L, Wang Y
and Chen Y: Effect of n-3 and n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids on
lipid metabolic genes and estrogen receptor expression in MCF-7
breast cancer cells. Clin Lab. 61:397–403. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xue M, Wang Q, Zhao J, Dong L, Ge Y, Hou
L, Liu Y and Zheng Z: Docosahexaenoic acid inhibited the
Wnt/β-catenin pathway and suppressed breast cancer cells in vitro
and in vivo. J Nutr Biochem. 25:104–110. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Larsson SC, Kumlin M, Ingelman-Sundberg M
and Wolk A: Dietary long-chain n-3 fatty acids for the prevention
of cancer: A review of potential mechanisms. Am J Clin Nutr.
79:935–945. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chapkin RS, McMurray DN and Lupton JR:
Colon cancer, fatty acids and anti-inflammatory compounds. Curr
Opin Gastroenterol. 23:48–54. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
McCarty MF: Fish oil may impede tumour
angiogenesis and invasiveness by down-regulating protein kinase C
and modulating eicosanoid production. Med Hypotheses. 46:107–115.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Collett ED, Davidson LA, Fan YY, Lupton JR
and Chapkin RS: N-6 and n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids
differentially modulate oncogenic Ras activation in colonocytes. Am
J Physiol Cell Physiol. 280:C1066–C1075. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sauer LA, Blask DE and Dauchy RT: Dietary
factors and growth and metabolism in experimental tumors. J Nutr
Biochem. 18:637–649. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cavazos DA, Price RS, Apte SS and
deGraffenried LA: Docosahexaenoic acid selectively induces human
prostate cancer cell sensitivity to oxidative stress through
modulation of NF-κB. Prostate. 71:1420–1428. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Carmichael J, DeGraff WG, Gazdar AF, Minna
JD and Mitchell JB: Evaluation of a tetrazolium-based semiautomated
colorimetric assay: Assessment of radiosensitivity. Cancer Res.
47:943–946. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cho HJ, Kim WK, Kim EJ, Jung KC, Park S,
Lee HS, Tyner AL and Park JH: Conjugated linoleic acid inhibits
cell proliferation and ErbB3 signaling in HT-29 human colon cell
line. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 284:G996–G1005.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Choudhuri T, Pal S, Agwarwal ML, Das T and
Sa G: Curcumin induces apoptosis in human breast cancer cells
through p53-dependent Bax induction. FEBS Lett. 512:334–340. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bruey JM, Bruey-Sedano N, Luciano F, Zhai
D, Balpai R, Xu C, Kress CL, Bailly-Maitre B, Li X, Osterman A, et
al: Bcl-2 and Bcl-XL regulate proinflammatory caspase-1 activation
by interaction with NALP1. Cell. 129:45–56. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cho MY, Park SY, Park S, Lee YR, Han GD
and Kim JA: Geranyl derivative of phloroacetophenone induces cancer
cell-specific apoptosis through Bax-mediated mitochondrial pathway
in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Biol Pharm Bull. 35:98–104.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li P, Nijhawan D, Budihardjo I,
Srinivasula SM, Ahmad M, Alnemri ES and Wang X: Cytochrome c
and dATP-dependent formation of Apaf-1/caspase-9 complex initiates
an apoptotic protease cascade. Cell. 91:479–489. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sun H, Berquin IM, Owens RT, O'Flaherty JT
and Edwards IJ: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor
gamma-mediated up-regulation of syndecan-1 by n-3 fatty acids
promotes apoptosis of human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res.
68:2912–2919. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sauer LA, Dauchy RT, Blask DE, Krause JA,
Davidson LK and Dauchy EM: Eicosapentaenoic acid suppresses cell
proliferation in MCF-7 human breast cancer xenografts in nude rats
via a pertussis toxin-sensitive signal transduction pathway. J
Nutr. 135:2124–2129. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Siddiqui RA, Jenski LJ, Neff K, Harvey K,
Kovacs RJ and Stillwell W: Docosahexanoic acid induces apoptosis in
Jurkat cells by a protein phosphatase-mediated process. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1499:265–275. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Arita K, Yamamoto Y, Takehara Y, Utsumi T,
Kanno T, Miyaguchi C, Akiyama J, Yoshioka T and Utsumi K:
Mechanisms of enhanced apoptosis in HL-60 cells by UV-irradiated
n-3 and n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids. Free Radic Biol Med.
35:189–199. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Reese AC, Fradet V and Witte JS: Omega-3
fatty acids, genetic variants in COX-2 and prostate cancer. J
Nutrigenet Nutrigenomics. 2:149–158. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kang KS, Wang P, Yamabe N, Fukui M, Jay T
and Zhu BT: Docosahexaenoic acid induces apoptosis in MCF-7 cells
in vitro and in vivo via reactive oxygen species formation and
caspase 8 activation. PLoS One. 5:e102962010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bougnoux P, Hajjaji N, Ferrasson MN,
Giraudeau B, Couet C and Le Floch O: Improving outcome of
chemotherapy of metastatic breast cancer by docosahexaenoic acid: A
phase II trial. Br J Cancer. 101:1978–1985. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Dimri M, Bommi PV, Sahasrabuddhe AA,
Khandekar JD and Dimri GP: Dietary omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty
acids suppress expression of EZH2 in breast cancer cells.
Carcinogenesis. 31:489–495. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Rose DP and Connolly JM: Regulation of
tumor angiogenesis by dietary fatty acids and eicosanoids. Nutr
Cancer. 37:119–127. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Altenburg JD and Siddiqui RA: Omega-3
polyunsaturated fatty acids down-modulate CXCR4 expression and
function in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer Res.
7:1013–1020. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|