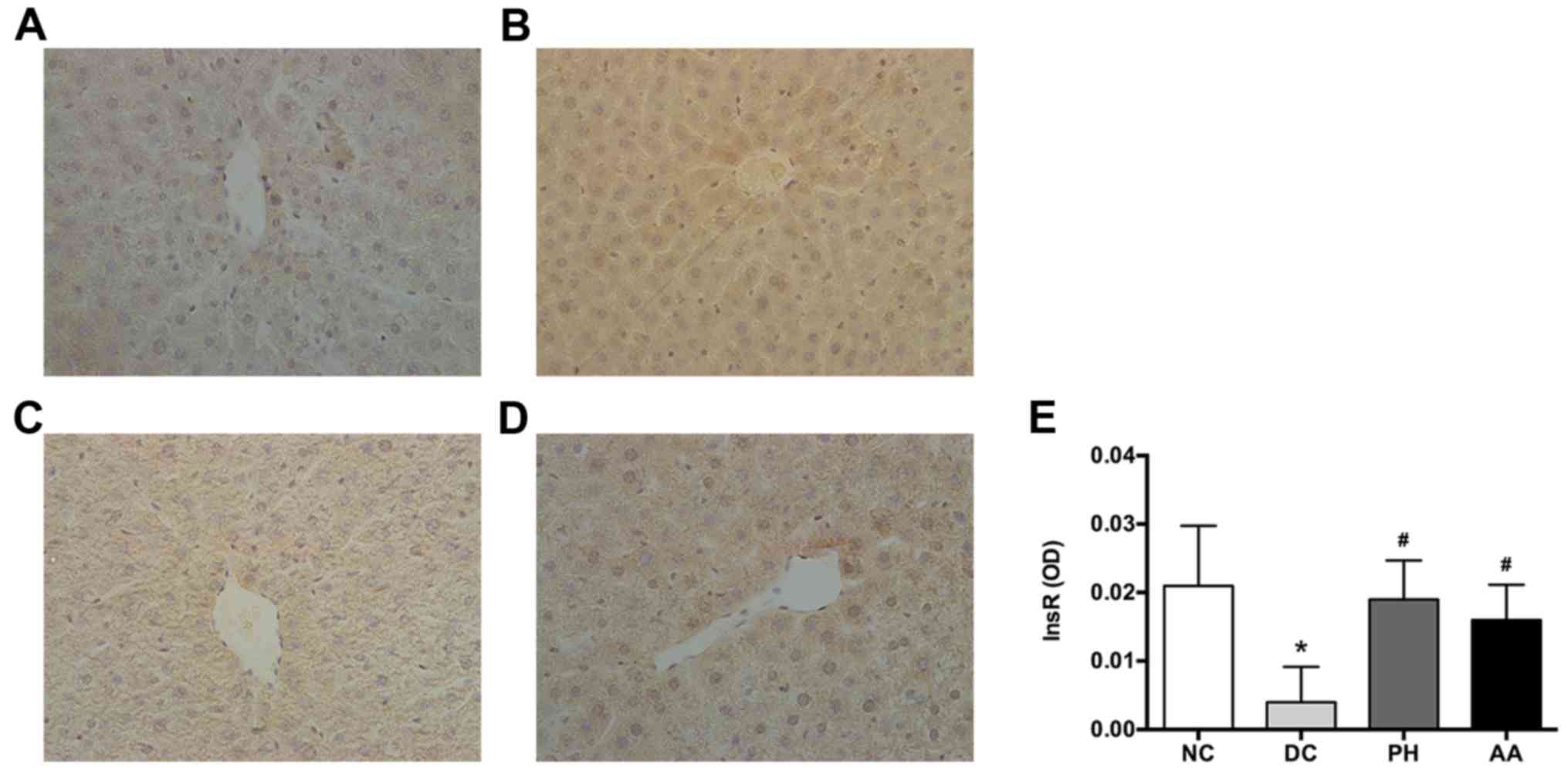
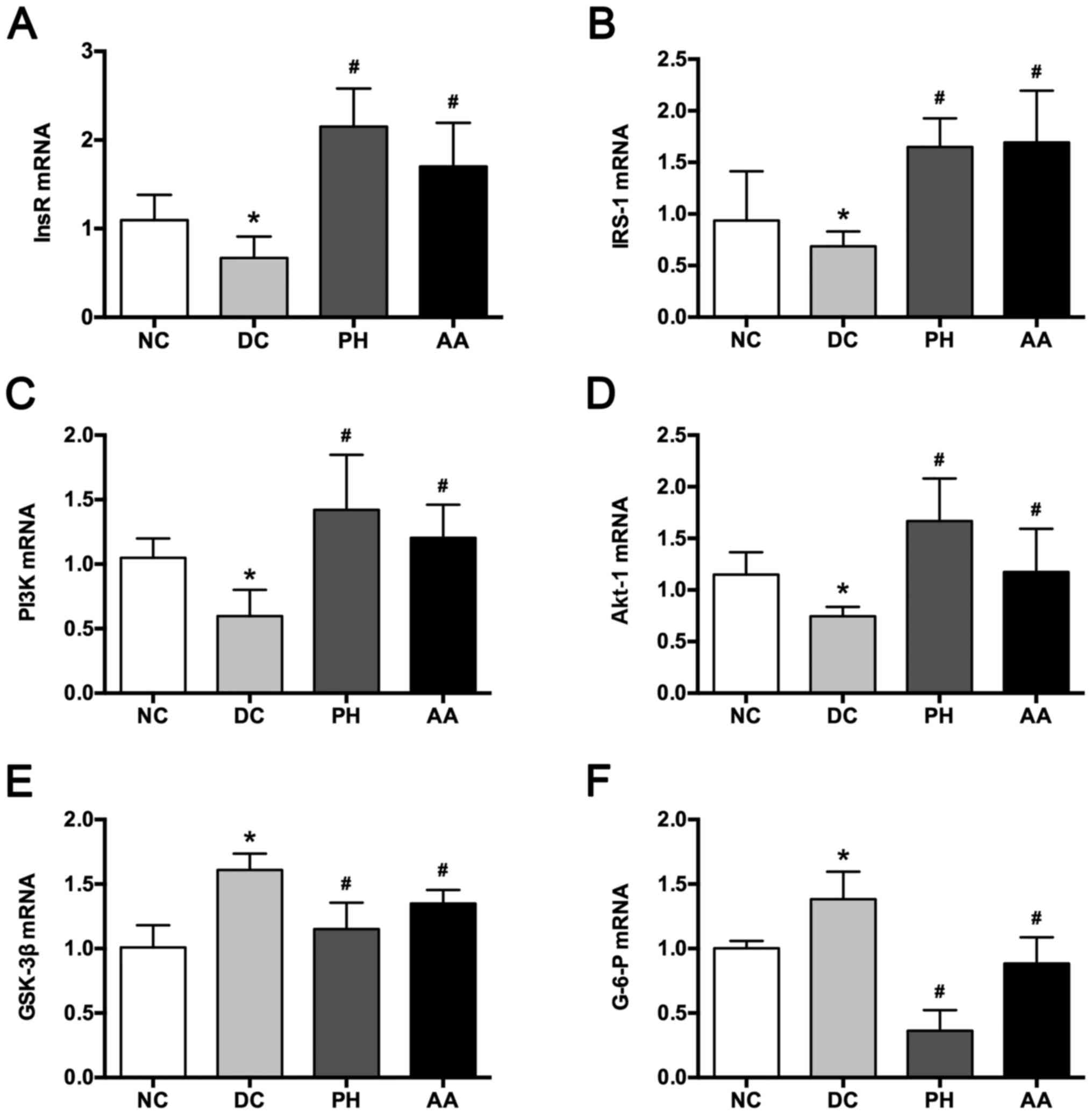
|
1
|
Anna V, van der Ploeg HP, Cheung NW,
Huxley RR and Bauman AE: Sociodemographic correlates of the
increasing trend in prevalence of gestational diabetes mellitus in
a large population of women between 1995 and 2005. Diabetes Care.
31:2288–2293. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kaul K, Apostolopoulou M and Roden M:
Insulin resistance in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Metabolism.
64:1629–1639. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Srinivasan K, Viswanad B, Asrat L, Kaul CL
and Ramarao P: Combination of high-fat diet-fed and low-dose
streptozotocin-treated rat: A model for type 2 diabetes and
pharmacological screening. Pharmacol Res. 52:313–320. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
von W, ilamowitz-Moellendorff A, Hunter
RW, García-Rocha M, Kang L, López-Soldado I, Lantier L, Patel K,
Peggie MW, Martinez-Pons C, Voss M, et al:
Glucose-6-phosphate-mediated activation of liver glycogen synthase
plays a key role in hepatic glycogen synthesis. Diabetes.
62:4070–4082. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
MacAulay K and Woodgett JR: Targeting
glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) in the treatment of Type 2
diabetes. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 12:1265–1274. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ciaraldi TP, Carter L, Mudaliar S and
Henry RR: GSK-3beta and control of glucose metabolism and insulin
action in human skeletal muscle. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 315:153–158.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Patel S, Doble BW, MacAulay K, Sinclair
EM, Drucker DJ and Woodgett JR: Tissue-specific role of glycogen
synthase kinase 3beta in glucose homeostasis and insulin action.
Mol Cell Biol. 28:6314–6328. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Park KS: The search for genetic risk
factors of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab J. 35:12–22.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Inzucchi SE, Bergenstal RM, Buse JB,
Diamant M, Ferrannini E, Nauck M, Peters AL, Tsapas A, Wender R and
Matthews DR: Management of hyperglycaemia in type 2 diabetes: A
patient-centered approach. Position statement of the American
Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the
Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetologia. 55:1577–1596. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yang LX, Liu TH, Huang ZT, Li JE and Wu
LL: Research progress on the mechanism of single-Chinese medicinal
herbs in treating diabetes mellitus. Chin J Integr Med. 17:235–240.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Prabhakar PK and Doble M: Mechanism of
action of natural products used in the treatment of diabetes
mellitus. Chin J Integr Med. 17:563–574. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Orhan IE: Centella asiatica (L.) Urban:
From traditional medicine to modern medicine with neuroprotective
potential. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012:9462592012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Pakdeechote P, Bunbupha S, Kukongviriyapan
U, Prachaney P, Khrisanapant W and Kukongviriyapan V: Asiatic acid
alleviates hemodynamic and metabolic alterations via restoring
eNOS/iNOS expression, oxidative stress, and inflammation in
diet-induced metabolic syndrome rats. Nutrients. 6:355–370. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li Y, Yang F, Yuan M, Jiang L, Yuan L,
Zhang X, Li Y, Dong L, Bao X and Yin S: Synthesis and evaluation of
asiatic acid derivatives as anti-fibrotic agents:
Structure/activity studies. Steroids. 96:44–49. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ramachandran V, Saravanan R and
Senthilraja P: Antidiabetic and antihyperlipidemic activity of
asiatic acid in diabetic rats, role of HMG CoA: In vivo and in
silico approaches. Phytomedicine. 21:225–232. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang J, Ai L, Lv T, Jiang X and Liu F:
Asiatic acid, a triterpene, inhibits cell proliferation through
regulating the expression of focal adhesion kinase in multiple
myeloma cells. Oncol Lett. 6:1762–1766. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang X, Lu Q, Yu DS, Chen YP, Shang J,
Zhang LY, Sun HB and Liu J: Asiatic acid mitigates hyperglycemia
and reduces islet fibrosis in Goto-Kakizaki rat, a spontaneous type
2 diabetic animal model. Chin J Nat Med. 13:529–534.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ramachandran V and Saravanan R: Efficacy
of asiatic acid, a pentacyclic triterpene on attenuating the key
enzymes activities of carbohydrate metabolism in
streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Phytomedicine. 20:230–236.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ramachandran V and Saravanan R: Glucose
uptake through translocation and activation of GLUT4 in PI3K/Akt
signaling pathway by asiatic acid in diabetic rats. Hum Exp
Toxicol. 34:884–893. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
McKeown NM, Meigs JB, Liu S, Saltzman E,
Wilson PW and Jacques PF: Carbohydrate nutrition, insulin
resistance, and the prevalence of the metabolic syndrome in the
Framingham Offspring Cohort. Diabetes Care. 27:538–546. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
King AJ: The use of animal models in
diabetes research. Br J Pharmacol. 166:877–894. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang YW, Sun GD, Sun J, Liu SJ, Wang J, Xu
XH and Miao LN: Spontaneous type 2 diabetic rodent models. J
Diabetes Res. 2013:4017232013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu J, He T, Lu Q, Shang J, Sun H and
Zhang L: Asiatic acid preserves beta cell mass and mitigates
hyperglycemia in streptozocin-induced diabetic rats. Diabetes Metab
Res Rev. 26:448–454. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ramachandran V and Saravanan R: Asiatic
acid prevents lipid peroxidation and improves antioxidant status in
rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes. J Funct Foods.
5:1077–1087. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Guilherme A, Virbasius JV, Puri V and
Czech MP: Adipocyte dysfunctions linking obesity to insulin
resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 9:367–377.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Guo S: Insulin signaling, resistance, and
the metabolic syndrome: Insights from mouse models into disease
mechanisms. J Endocrinol. 220:T1–T23. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Fornoni A, Pileggi A, Molano RD, Sanabria
NY, Tejada T, Gonzalez-Quintana J, Ichii H, Inverardi L, Ricordi C
and Pastori RL: Inhibition of c-jun N terminal kinase (JNK)
improves functional beta cell mass in human islets and leads to AKT
and glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) phosphorylation.
Diabetologia. 51:298–308. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bertsch S, Lang CH and Vary TC: Inhibition
of glycogen synthase kinase 3[beta] activity with lithium in vitro
attenuates sepsis-induced changes in muscle protein turnover.
Shock. 35:266–274. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Nikoulina SE, Ciaraldi TP, Mudaliar S,
Mohideen P, Carter L and Henry RR: Potential role of glycogen
synthase kinase-3 in skeletal muscle insulin resistance of type 2
diabetes. Diabetes. 49:263–271. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jiang SJ, Dong H, Li JB, Xu LJ, Zou X,
Wang KF, Lu FE and Yi P: Berberine inhibits hepatic gluconeogenesis
via the LKB1-AMPK-TORC2 signaling pathway in streptozotocin-induced
diabetic rats. World J Gastroenterol. 21:7777–7785. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang L, Chen J, Gong Y, Liu J, Zhang L,
Hua W and Sun H: Synthesis and biological evaluation of asiatic
acid derivatives as inhibitors of glycogen phosphorylases. Chem
Biodivers. 6:864–874. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|