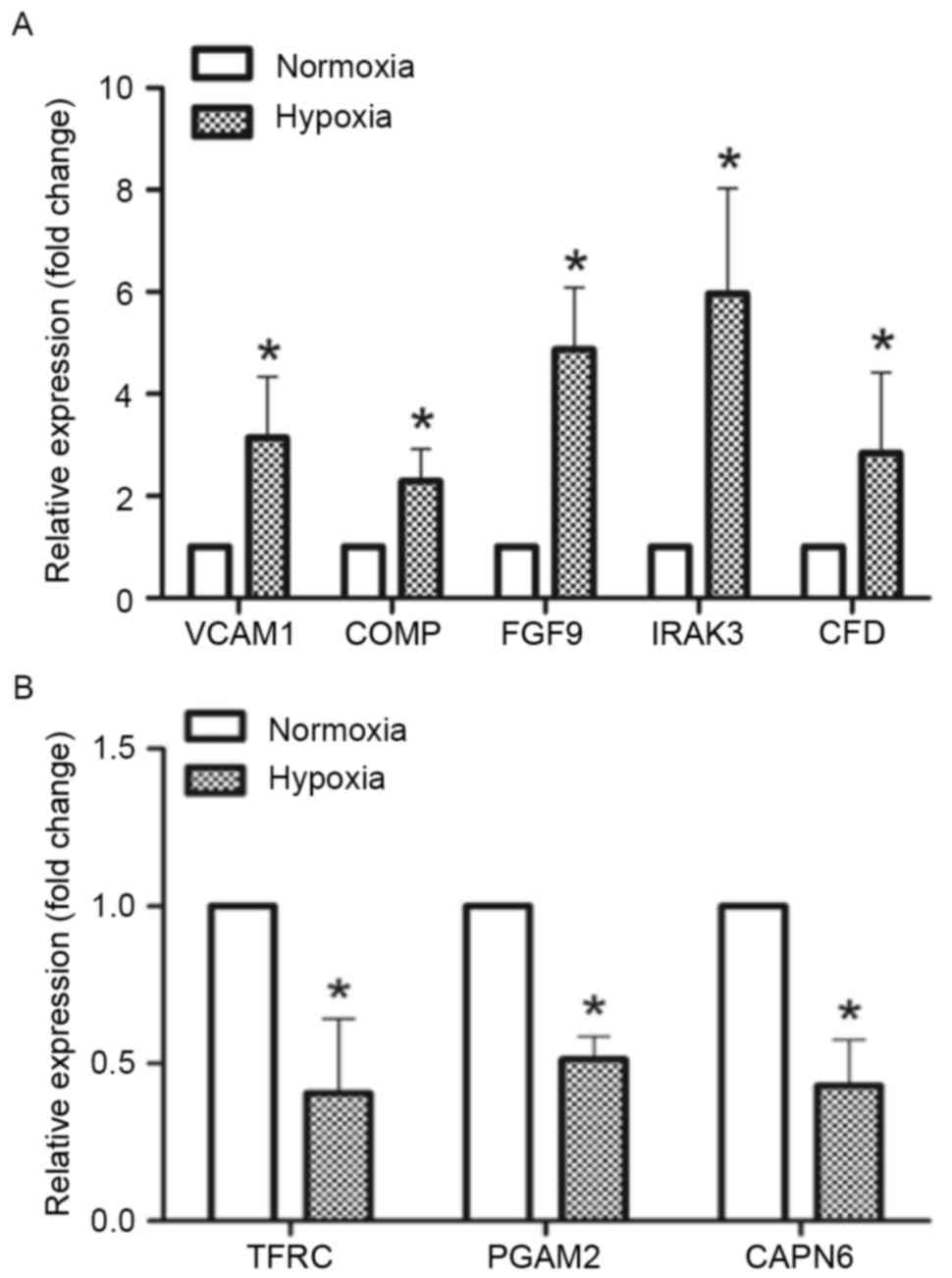
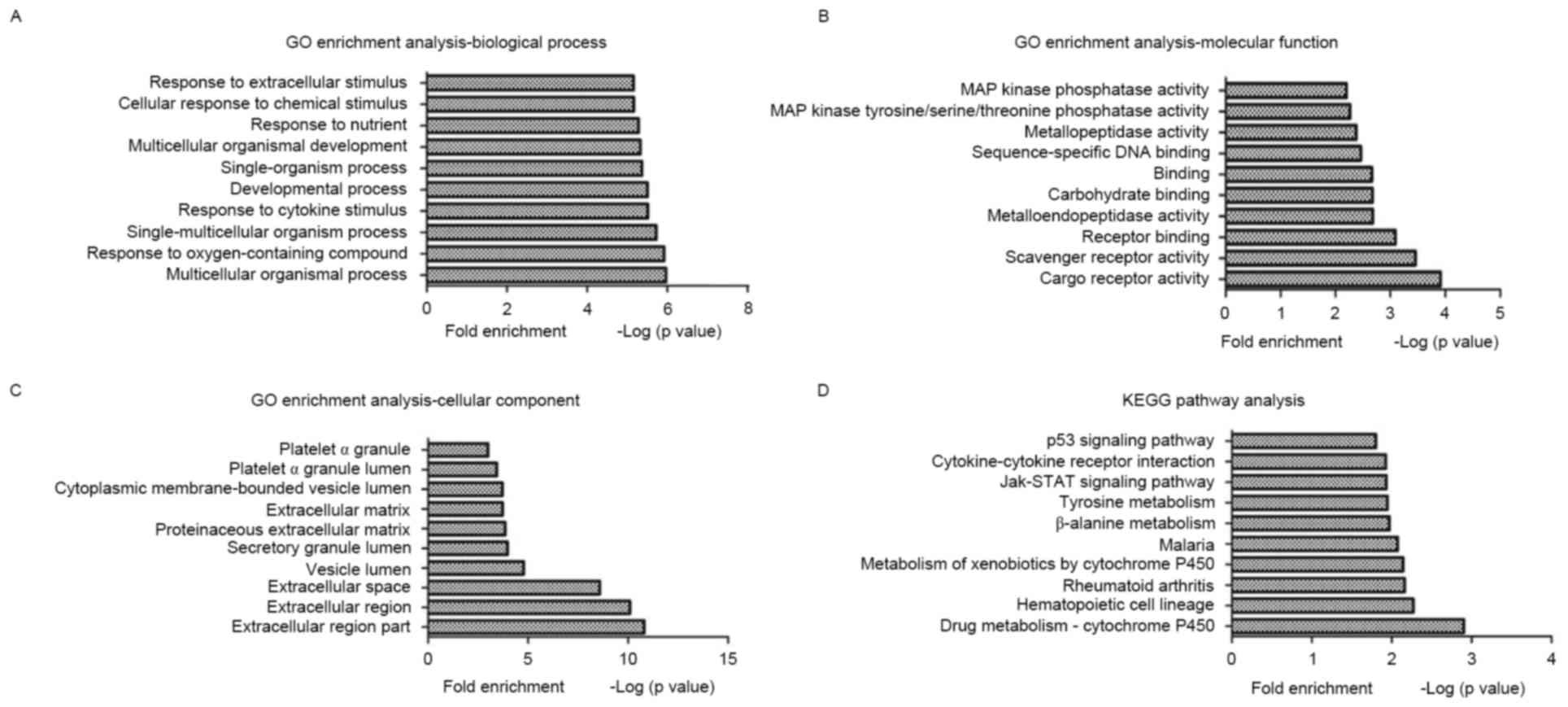
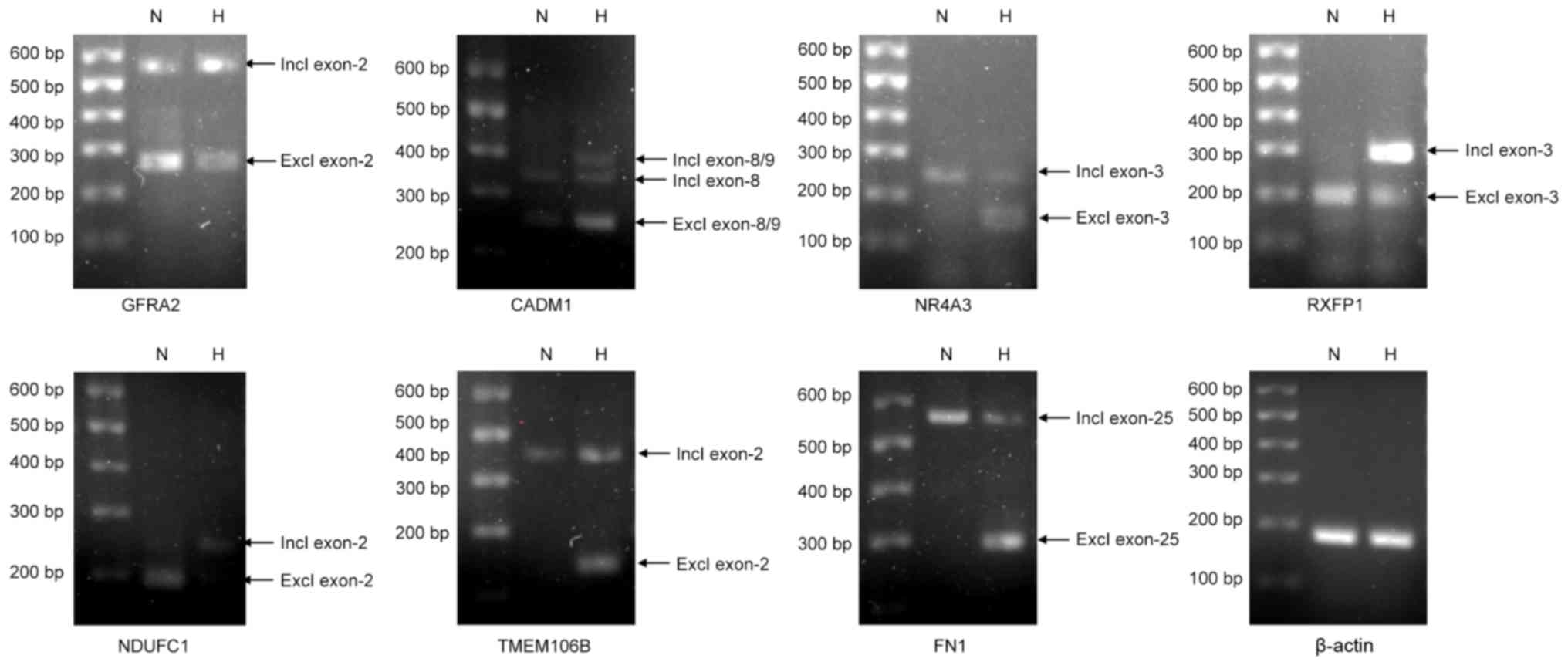
|
1
|
Andersson GB: Epidemiological features of
chronic low-back pain. Lancet. 354:581–585. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Le Maitre CL, Freemont AJ and Hoyland JA:
Accelerated cellular senescence in degenerate intervertebral discs:
A possible role in the pathogenesis of intervertebral disc
degeneration. Arthritis Res Ther. 9:R452007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Peng B, Hao J, Hou S, Wu W, Jiang D, Fu X
and Yang Y: Possible pathogenesis of painful intervertebral disc
degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 31:560–566. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang AM, Cao P, Yee A, Chan D and Wu EX:
Detection of extracellular matrix degradation in intervertebral
disc degeneration by diffusion magnetic resonance spectroscopy.
Magn Reson Med. 73:1703–1712. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Buckwalter JA: Aging and degeneration of
the human intervertebral disc. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 20:1307–1314.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Holm S, Maroudas A, Urban JP, Selstam G
and Nachemson A: Nutrition of the intervertebral disc: Solute
transport and metabolism. Connect Tissue Res. 8:101–119. 1981.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Raj PP: Intervertebral disc:
Anatomy-physiology-pathophysiology-treatment. Pain Pract. 8:18–44.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li FC, Zhang N, Chen WS and Chen QX:
Endplate degeneration may be the origination of the vacuum
phenomenon in intervertebral discs. Med Hypotheses. 75:169–171.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu LT, Huang B, Li CQ, Zhuang Y, Wang J
and Zhou Y: Characteristics of stem cells derived from the
degenerated human intervertebral disc cartilage endplate. PLoS One.
6:e262852011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Boskey AL: Signaling in response to
hypoxia and normoxia in the intervertebral disc. Arthritis Rheum.
58:3637–3639. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Carmeliet P, Dor Y, Herbert JM, Fukumura
D, Brusselmans K, Dewerchin M, Neeman M, Bono F, Abramovitch R,
Maxwell P, et al: Role of HIF-1alpha in hypoxia-mediated apoptosis,
cell proliferation and tumour angiogenesis. Nature. 394:485–490.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Merceron C, Vinatier C, Portron S, Masson
M, Amiaud J, Guigand L, Chérel Y, Weiss P and Guicheux J:
Differential effects of hypoxia on osteochondrogenic potential of
human adipose-derived stem cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
298:C355–C364. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Makino Y, Kanopka A, Wilson WJ, Tanaka H
and Poellinger L: Inhibitory PAS domain protein (IPAS) is a
hypoxia-inducible splicing variant of the hypoxia-inducible
factor-3alpha locus. J Biol Chem. 277:32405–32408. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tacconelli A, Farina AR, Cappabianca L,
Desantis G, Tessitore A, Vetuschi A, Sferra R, Rucci N, Argenti B,
Screpanti I, et al: TrkA alternative splicing: A regulated
tumor-promoting switch in human neuroblastoma. Cancer Cell.
6:347–360. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kazantseva J, Kivil A, Tints K, Kazantseva
A, Neuman T and Palm K: Alternative splicing targeting the
hTAF4-TAFH domain of TAF4 represses proliferation and accelerates
chondrogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. PLoS
One. 8:e747992013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gabut M, Samavarchi-Tehrani P, Wang X,
Slobodeniuc V, O'Hanlon D, Sung HK, Alvarez M, Talukder S, Pan Q,
Mazzoni EO, et al: An alternative splicing switch regulates
embryonic stem cell pluripotency and reprogramming. Cell.
147:132–146. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hang X, Li P, Li Z, Qu W, Yu Y, Li H, Shen
Z, Zheng H, Gao Y, Wu Y, et al: Transcription and splicing
regulation in human umbilical vein endothelial cells under hypoxic
stress conditions by exon array. BMC Genomics. 10:1262009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Moller-Levet CS, Betts GN, Harris AL,
Homer JJ, West CM and Miller CJ: Exon array analysis of head and
neck cancers identifies a hypoxia related splice variant of LAMA3
associated with a poor prognosis. PLoS Comput Biol. 5:e10005712009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shang J, Fan X, Shangguan L, Liu H and
Zhou Y: Global Gene expression profiling and alternative splicing
events during the chondrogenic differentiation of human cartilage
endplate-derived stem cells. Biomed Res Int. 2015:6049722015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yao Y, Shang J, Song W, Deng Q, Liu H and
Zhou Y: Global profiling of the gene expression and alternative
splicing events during hypoxia-regulated chondrogenic
differentiation in human cartilage endplate-derived stem cells.
Genomics. 107:170–177. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lee DC, Adams CS, Albert TJ, Shapiro IM,
Evans SM and Koch CJ: In situ oxygen utilization in the rat
intervertebral disc. J Anat. 210:294–303. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Nerlich AG, Schaaf R, Wälchli B and Boos
N: Temporo-spatial distribution of blood vessels in human lumbar
intervertebral discs. Eur Spine J. 16:547–555. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Freemont AJ, Watkins A, Le Maitre C, Baird
P, Jeziorska M, Knight MT, Ross ER, O'Brien JP and Hoyland JA:
Nerve growth factor expression and innervation of the painful
intervertebral disc. J Pathol. 197:286–292. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Walsh DA, McWilliams DF, Turley MJ, Dixon
MR, Fransès RE, Mapp PI and Wilson D: Angiogenesis and nerve growth
factor at the osteochondral junction in rheumatoid arthritis and
osteoarthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 49:1852–1861. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Amorin B, Alegretti AP, Valim VS, Silva
AM, Silva MA, Sehn F and Silla L: Characteristics of mesenchymal
stem cells under hypoxia. Cell Bio. 2:11–19. 2013.
|
|
27
|
Schiller ZA, Schiele NR, Sims JK, Lee K
and Kuo CK: Adipogenesis of adipose-derived stem cells may be
regulated via the cytoskeleton at physiological oxygen levels in
vitro. Stem Cell Res Ther. 4:792013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Redshaw Z and Loughna PT: Oxygen
concentration modulates the differentiation of muscle stem cells
toward myogenic and adipogenic fates. Differentiation. 84:193–202.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
D'Ippolito G, Diabira S, Howard GA, Roos
BA and Schiller PC: Low oxygen tension inhibits osteogenic
differentiation and enhances stemness of human MIAMI cells. Bone.
39:513–522. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Dos Santos F, Andrade PZ, Boura JS,
Abecasis MM, da Silva CL and Cabral JM: Ex vivo expansion of human
mesenchymal stem cells: A more effective cell proliferation
kinetics and metabolism under hypoxia. J Cell Physiol. 223:27–35.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Potier E, Ferreira E, Meunier A, Sedel L,
Logeart-Avramoglou D and Petite H: Prolonged hypoxia concomitant
with serum deprivation induces massive human mesenchymal stem cell
death. Tissue Eng. 13:1325–1331. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kobayashi K, Hernandez LD, Galán JE,
Janeway CA Jr, Medzhitov R and Flavell RA: IRAK-M is a negative
regulator of Toll-like receptor signaling. Cell. 110:191–202. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Fernandes-Alnemri T, Kang S, Anderson C,
Sagara J, Fitzgerald KA and Alnemri ES: Cutting edge: TLR signaling
licenses IRAK1 for rapid activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome. J
Immunol. 191:3995–3999. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cohen P: The TLR and IL-1 signalling
network at a glance. J Cell Sci. 127:2383–2390. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sprong T, Roos D, Weemaes C, Neeleman C,
Geesing CL, Mollnes TE and van Deuren M: Deficient alternative
complement pathway activation due to factor D deficiency by 2 novel
mutations in the complement factor D gene in a family with
meningococcal infections. Blood. 107:4865–4870. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Rohrer B, Guo Y, Kunchithapautham K and
Gilkeson GS: Eliminating complement factor D reduces photoreceptor
susceptibility to light-induced damage. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
48:5282–5289. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Anderson DH, Radeke MJ, Gallo NB, Chapin
EA, Johnson PT, Curletti CR, Hancox LS, Hu J, Ebright JN, Malek G,
et al: The pivotal role of the complement system in aging and
age-related macular degeneration: Hypothesis re-visited. Prog Retin
Eye Res. 29:95–112. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zeng J, Chen Y, Tong Z, Zhou X, Zhao C,
Wang K, Hughes G, Kasuga D, Bedell M, Lee C, et al: Lack of
association of CFD polymorphisms with advanced age-related macular
degeneration. Mol Vis. 16:2273–2278. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Schraufstatter IU, Khaldoyanidi SK and
DiScipio RG: Complement activation in the context of stem cells and
tissue repair. World J Stem Cells. 7:1090–1108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Lee DS, Yi TG, Lee HJ, Kim SN, Park S,
Jeon MS and Song SU: Mesenchymal stem cells infected with
Mycoplasma arginini secrete complement C3 to regulate
immunoglobulin production in B lymphocytes. Cell Death Dis.
5:e11922014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Soland MA, Bego M, Colletti E, Zanjani ED,
St Jeor S, Porada CD and Almeida-Porada G: Mesenchymal stem cells
engineered to inhibit complement-mediated damage. PLoS One.
8:e604612013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Collard CD, Väkevä A, Morrissey MA, Agah
A, Rollins SA, Reenstra WR, Buras JA, Meri S and Stahl GL:
Complement activation after oxidative stress: Role of the lectin
complement pathway. Am J Pathol. 156:1549–1556. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Cowell RM, Plane JM and Silverstein FS:
Complement activation contributes to hypoxic-ischemic brain injury
in neonatal rats. J Neurosci. 23:9459–9468. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Olszowski T, Poziomkowska-Gęsicka I,
Jensenius JC and Adler G: Lectin pathway of complement activation
in a Polish woman with MASP-2 deficiency. Immunobiology.
219:261–262. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Almeida AR, Arroz-Madeira S,
Fonseca-Pereira D, Ribeiro H, Lasrado R, Pachnis V and
Veiga-Fernandes H: RET/GFRα signals are dispensable for thymic T
cell development in vivo. PloS One. 7:e529492012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Vargas-Leal V, Bruno R, Derfuss T,
Krumbholz M, Hohlfeld R and Meinl E: Expression and function of
glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor family ligands and
their receptors on human immune cells. J Immunol. 175:2301–2308.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Liu CF and Lefebvre V: The transcription
factors SOX9 and SOX5/SOX6 cooperate genome-wide through
super-enhancers to drive chondrogenesis. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:8183–8203. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Choung HW, Lee DS, Lee HK, Shon WJ and
Park JC: Preameloblast-derived factors mediate osteoblast
differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by
Runx2-Osterix-BSP signaling. Tissue Eng Part A. 22:93–102. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Haddad JJ: Endotoxin-mediated regulation
of nuclear factor-kappaB nuclear translocation and activation in
the hippocampus of the central nervous system: Modulation by
intracerebroventricular treatment with thymulin and the
immunomodulatory role of the IkappaB-alpha/pIkappaB-alpha pathway.
Neuroscience. 164:1509–1520. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Nguyen TL Xuan, Choi JW, Lee SB, Ye K, Woo
SD, Lee KH and Ahn JY: Akt phosphorylation is essential for nuclear
translocation and retention in NGF-stimulated PC12 cells. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 349:789–798. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Mathieu PS and Loboa EG: Cytoskeletal and
focal adhesion influences on mesenchymal stem cell shape,
mechanical properties and differentiation down osteogenic,
adipogenic and chondrogenic pathways. Tissue Eng Part B Rev.
18:436–444. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Lee HJ, Jang M, Kim H, Kwak W, Park W,
Hwang JY, Lee CK, Jang GW, Park MN, Kim HC, et al: Comparative
transcriptome analysis of adipose tissues reveals that ECM-Receptor
interaction is involved in the depot-specific adipogenesis in
cattle. PLoS One. 8:e662672013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|