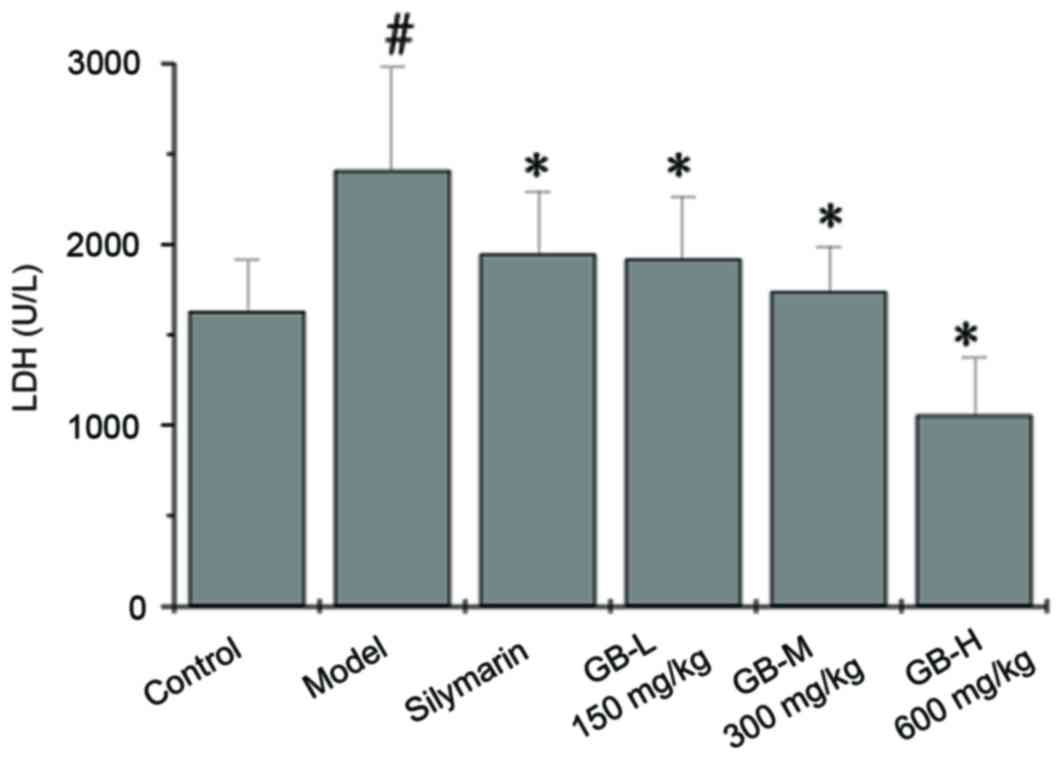
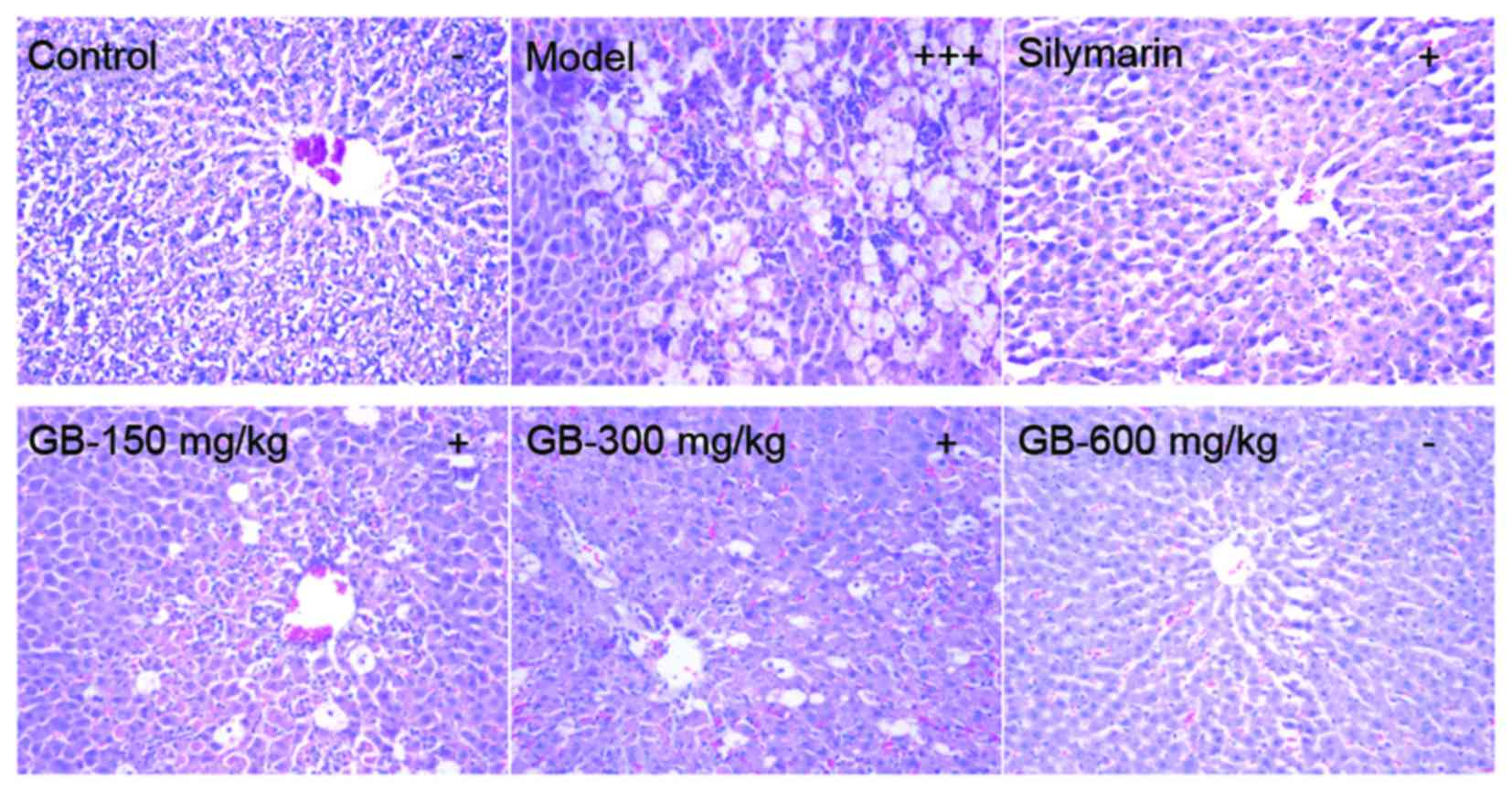
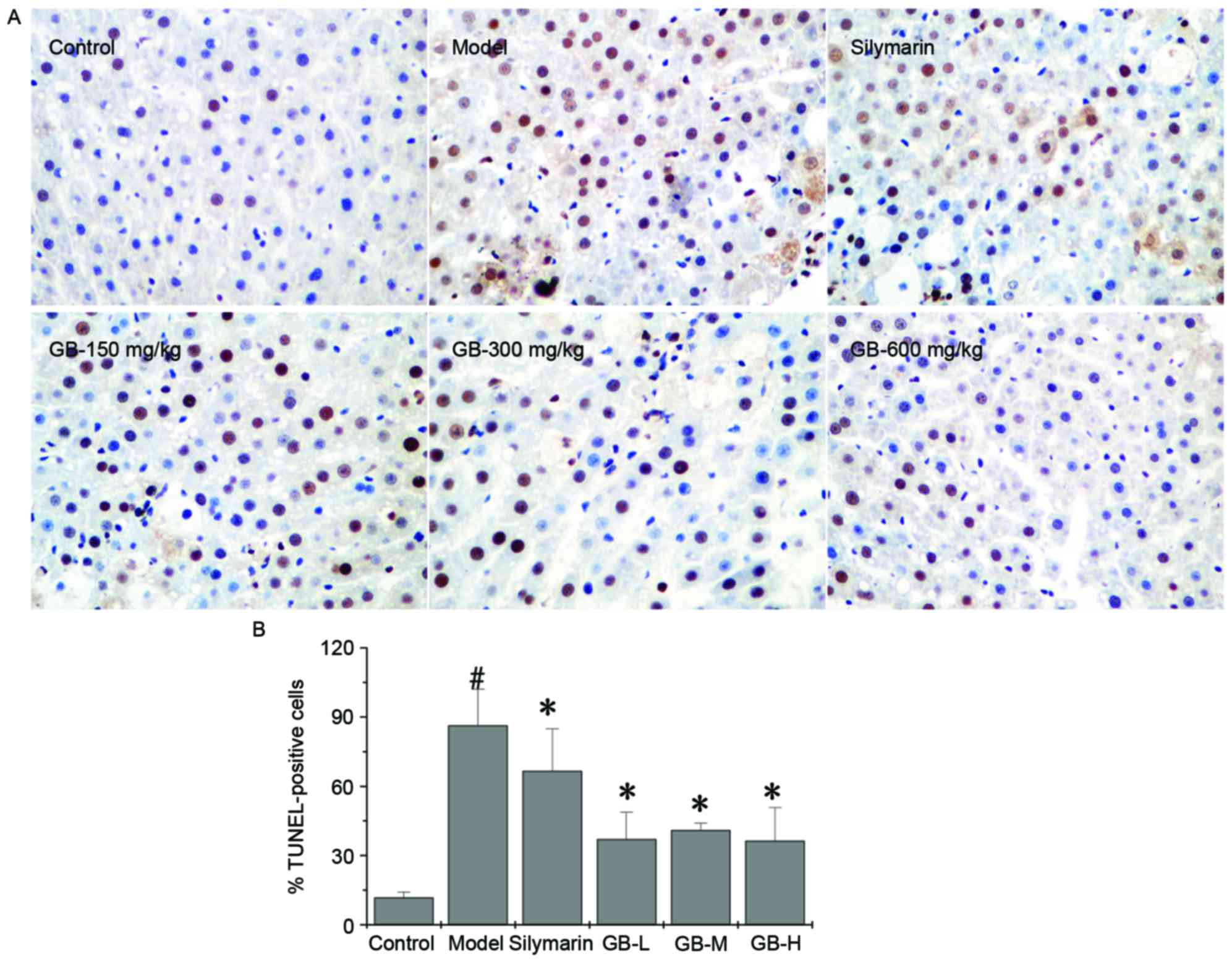
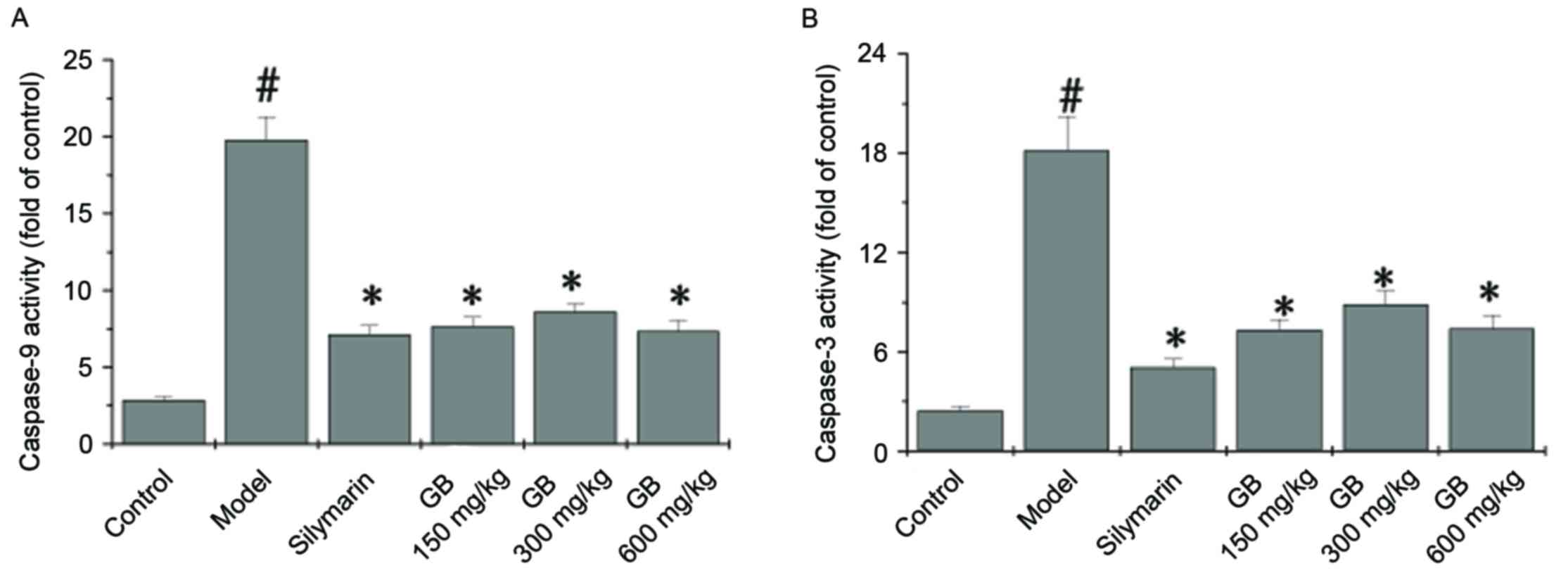
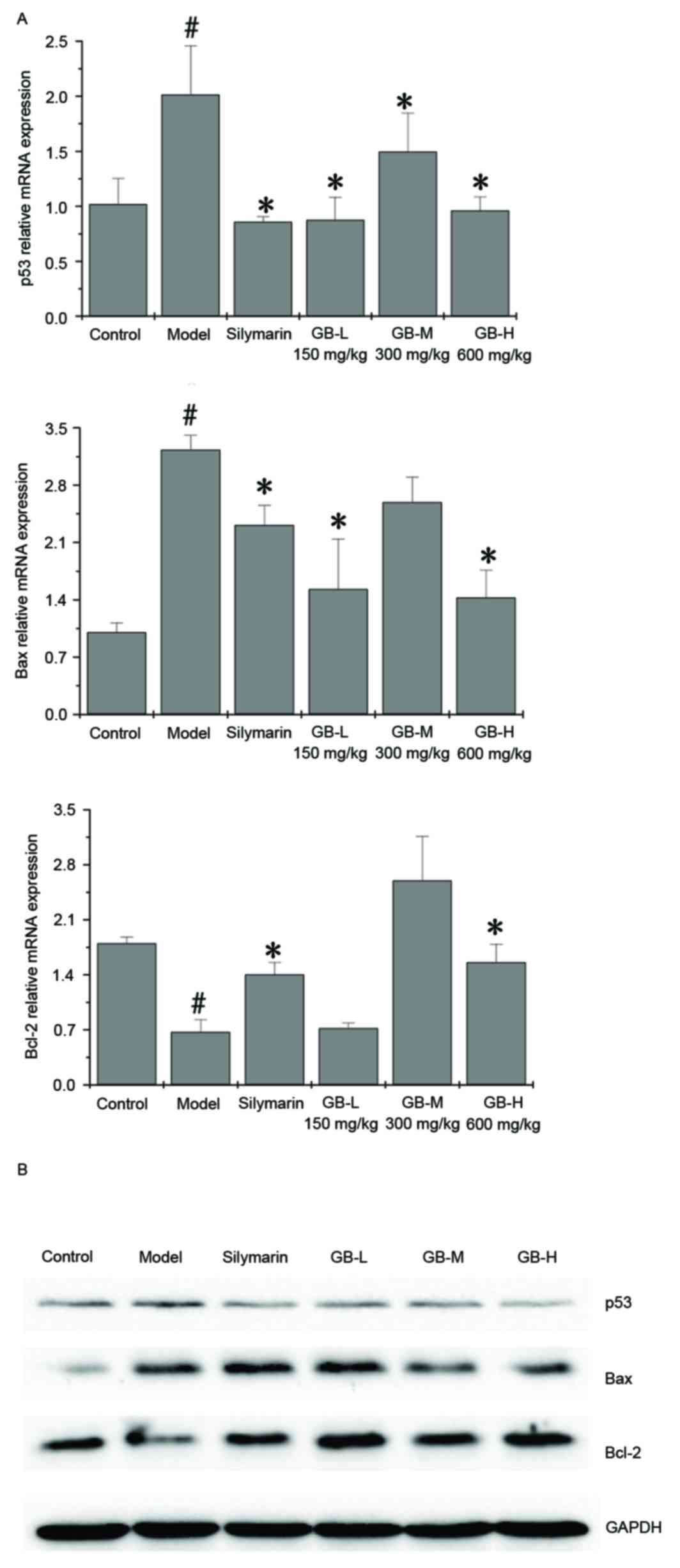
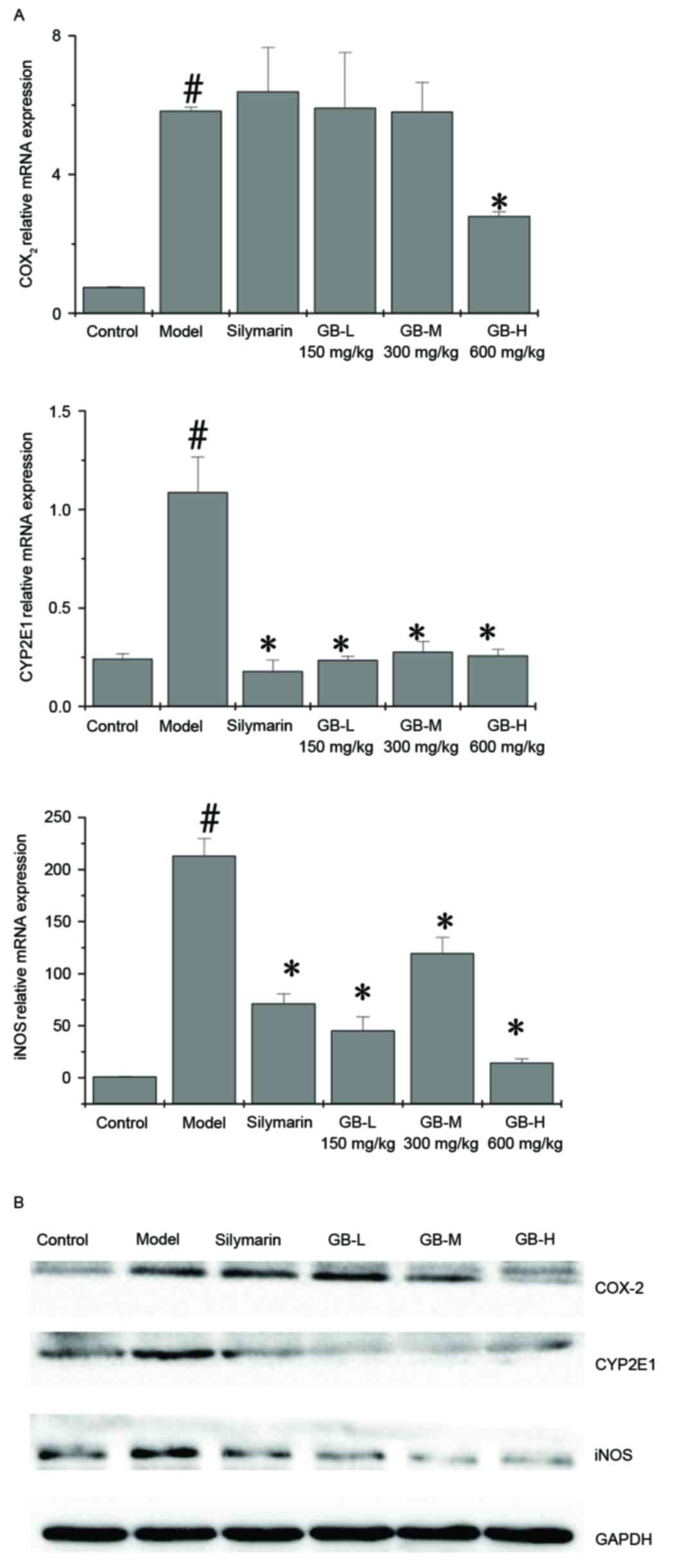
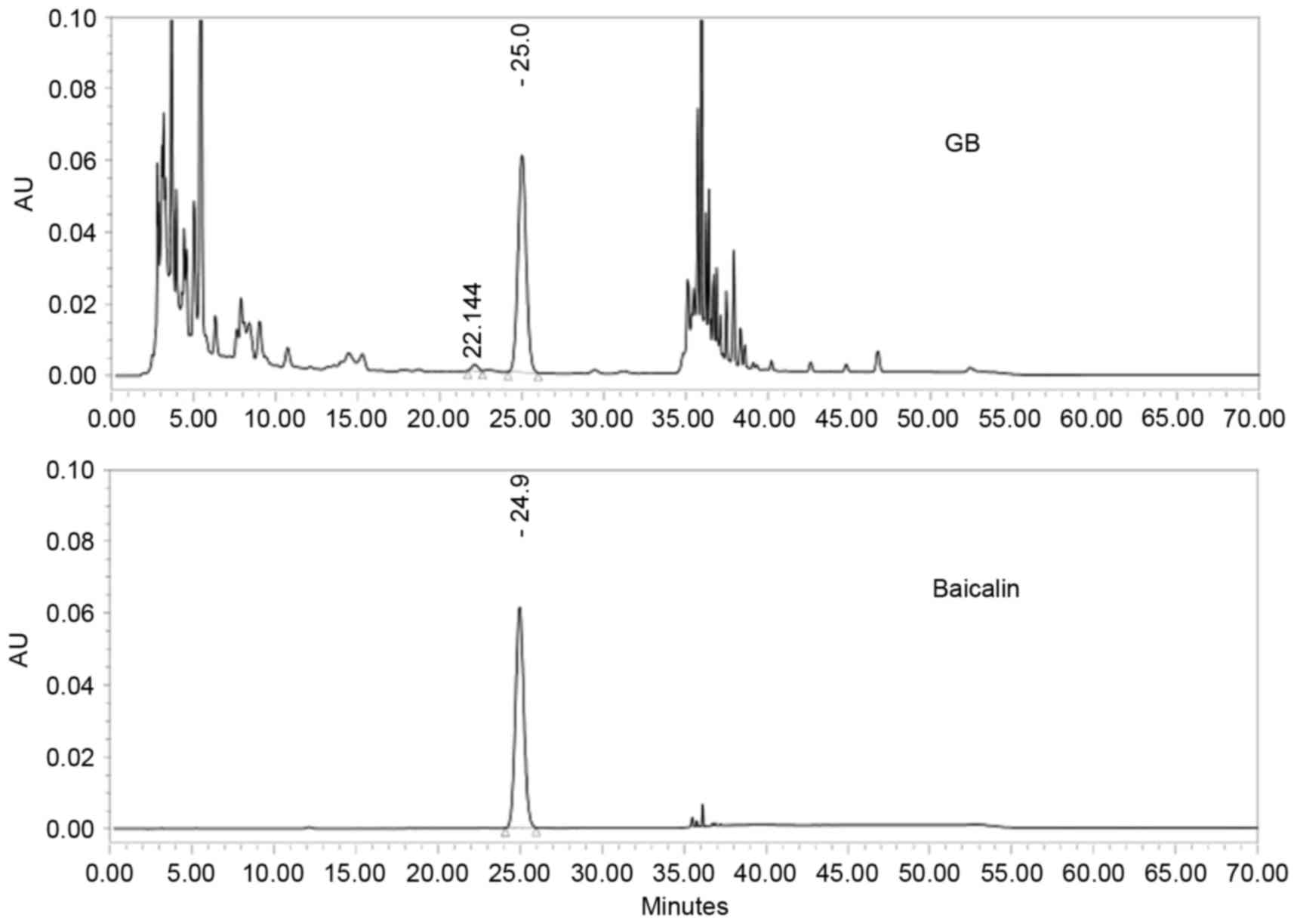
|
1
|
Kumar CH, Ramesh A, Kumar JN Suresh and
Ishaq BM: A review on hepatoprotective activity of medicinal
plants. Int J Pharmaceut Sci Res. 23:501–515. 2011.
|
|
2
|
Ahsan R, Islam KM, Bulbul IJ, Musaddik A
and Haque E: Hepatoprotective activity of methanol extract of some
medicinal plants against carbon tetrachloride-induced
hepatotoxicity in rats. Eur J Sci Res. 37:302–310. 2009.
|
|
3
|
Chattopadhyay RR: Possible mechanism of
hepatoprotective activity of Azadirachta indica leaf extract: part
II. J Ethnopharmacol. 89:217–219. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Recknagel RO, Glende EA Jr, Dolak JA and
Waller RL: Mechanisms of carbon tetrachloride toxicity. Pharmacol
Ther. 43:139–154. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Williams AT and Burk RF: Carbon
tetrachloride hepatotoxicity: An example of free radical-mediated
injury. Semin Liver Dis. 10:279–284. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Slater TF: Free radicals as reactive
intermediates in tissue injury. Adv Exp Med Biol. 136:575–589.
1981.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Brattin WJ, Glende EA Jr and Recknagel RO:
Pathological mechanisms in carbon tetrachloride hepatotoxicity. J
Free Radic Biol Med. 1:27–38. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cederbaum AI: Role of CYP2E1 in
ethanol-induced oxidant stress, fatty liver and hepatotoxicity. Dig
Dis. 28:802–811. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bartosz G: Reactive oxygen species:
Destroyers or messengers? Biochem Pharmacol. 77:1303–1315. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cadenas E and Davies KJ: Mitochondrial
free radical generation, oxidative stress, and aging. Free Radic
Biol Med. 29:222–230. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Circu ML and Aw TY: Reactive oxygen
species, cellular redox systems, and apoptosis. Free Radic Biol
Med. 48:749–762. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Shi J, Aisaki K, Ikawa Y and Wake K:
Evidence of hepatocyte apoptosis in rat liver after the
administration of carbon tetrachloride. Am J Pathol. 153:515–525.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hoek JB, Cahill A and Pastorino JG:
Alcohol and mitochondria: A dysfunctional relationship.
Gastroenterology. 122:2049–2063. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Volkmann N, Marassi FM, Newmeyer DD and
Hanein D: The rheostat in the membrane: BCL-2 family proteins and
apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 21:206–215. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Takebe H, Sato I, Tajima S, Ikeda Y, Ito K
and Nose T: Effects of cianidanol (KB-53) on liver cirrhosis
induced by CCl4 in rats: A pathological investigation.
Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 81:585–591. 1983.(In Japanese). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Merino N, González R, González A and
Remirez D: Histopathological evaluation on the effect of red
propolis on liver damage induced by CCl4 in rats. Arch
Med Res. 27:285–289. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yadav SS, Sindram D, Perry DK and Clavien
PA: Ischemic preconditioning protects the mouse liver by inhibition
of apoptosis through a caspase-dependent pathway. Hepatology.
30:1223–1231. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Perry DK, Smyth MJ, Stennicke HR, Salvesen
GS, Duriez P, Poirier GG and Hannun YA: Zinc is a potent inhibitor
of the apoptotic protease, caspase-3. A novel target for zinc in
the inhibition of apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 272:18530–18533. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yao Y, Huang C, Li ZF, Wang AY, Liu LY,
Zhao XG, Luo Y, Ni L, Zhang WG and Song TS: Exogenous
phosphatidylethanolamine induces apoptosis of human hepatoma HepG2
cells via the bcl-2/Bax pathway. World J Gastroenterol.
15:1751–1758. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jin S and Dai CL: Attenuation of
reperfusion-induced hepatocyte apoptosis is associated with
reversed bcl-2/bax ratio in hemi-hepatic artery-preserved portal
occlusion. J Surg Res. 174:298–304. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu B, Shi Y, Peng W, Zhang Q, Liu J, Chen
N and Zhu R: Diosmetin induces apoptosis by upregulating p53 via
the TGF-β signal pathway in HepG2 hepatoma cells. Mol Med Rep.
14:159–164. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ortega JF, de Conti A, Tryndyak V, Furtado
KS, Heidor R, Horst MA, Fernandes LH, Tavares PE, Pogribna M,
Shpyleva S, et al: Suppressing activity of tributyrin on
hepatocarcinogenesis is associated with inhibiting the p53-CRM1
interaction and changing the cellular compartmentalization of p53
protein. Oncotarget. 7:24339–24347. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Allam A, Gabr S, Ajarem J and
Abdel-Maksoud M: Bcl-2 and p53 expression in hepatic tissues of
Egyptian patients with Chronic Hepatitis C. J Pak Med Assoc.
65:1186–1192. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li X, Yu J, Brock MV, Tao Q, Herman JG,
Liang P and Guo M: Epigenetic silencing of BCL6B inactivates p53
signaling and causes human hepatocellular carcinoma cell resist to
5-FU. Oncotarget. 6:11547–11560. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Guo XL, Liang B, Wang XW, Fan FG, Jin J,
Lan R, Yang JH, Wang XC, Jin L and Cao Q: Glycyrrhizic acid
attenuates CCl4-induced hepatocyte apoptosis in rats via
a p53-mediated pathway. World J Gastroenterol. 19:3781–3791. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Rechnagel RO and Glende EA Jr: Carbon
tetrachloride hepatotoxicity: An example of lethal cleavage. CRC
Crit Rev Toxicol. 2:263–297. 1973. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Al-Shabanah OA, Alam K, Nagi MN, Al-Rikabi
AC and Al-Bekairi AM: Protective effect of aminoguanidine, a nitric
oxide synthase inhibitor, against carbon tetrachloride induced
hepatotoxicity in mice. Life Sci. 66:265–270. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Badger DA, Sauer JM, Hoglen NC, Jolley CS
and Sipes IG: The role of inflammatory cells and cytochrome P450 in
the potentiation of CCl4-induced liver injury by a
single dose of retinol. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 141:507–519. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lowenstein CJ and Snyder SH: Nitric oxide,
a novel biologic messenger. Cell. 70:705–707. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Inoue T, Kwon AH, Oda M, Kaibori M,
Kamiyama Y, Nishizawa M, Ito S and Okumura T: Hypoxia and heat
inhibit inducible nitric oxide synthase gene expression by
different mechanisms in rat hepatocytes. Hepatology. 32:1037–1044.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Nadler EP, Dickinson EC, Beer-Stolz D,
Alber SM, Watkins SC, Pratt DW and Ford HR: Scavenging nitric oxide
reduces hepatocellular injury after endotoxin challenge. Am J
Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 281:G173–G181. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chun KS and Surh YJ: Signal transduction
pathways regulating cyclooxygenase-2 expression: Potential
molecular targets for chemoprevention. Biochem Pharmacol.
68:1089–1100. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chang YC, Li PC, Chen BC, Chang MS, Wang
JL, Chiu WT and Lin CH: Lipoteichoic acid-induced nitric oxide
synthase expression in RAW 264.7 macrophages is mediated by
cyclooxygenase-2, prostaglandin E2, protein kinase A, p38 MAPK, and
nuclear factor-κB pathways. Cell Signal. 18:1235–1243. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|