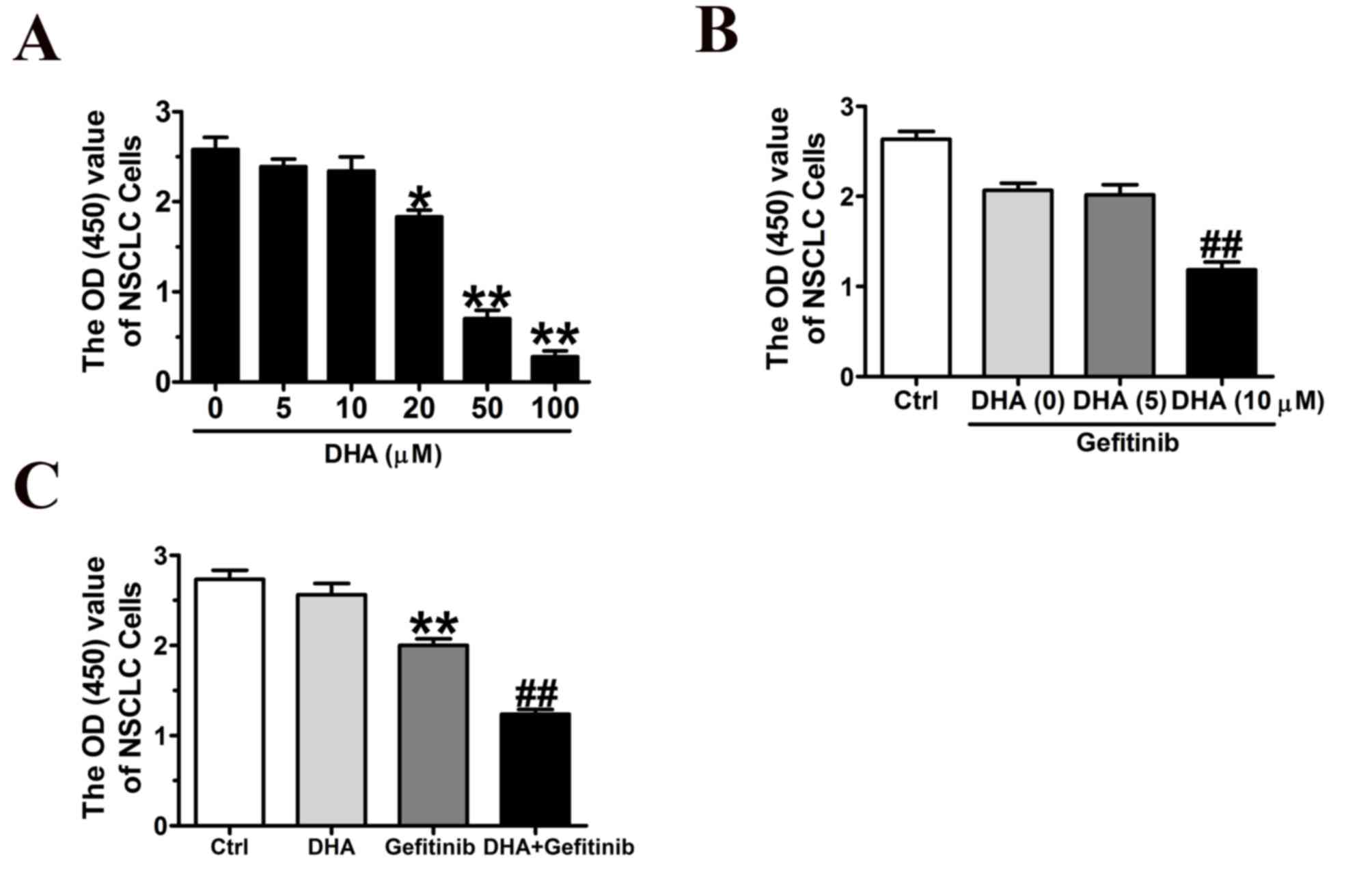
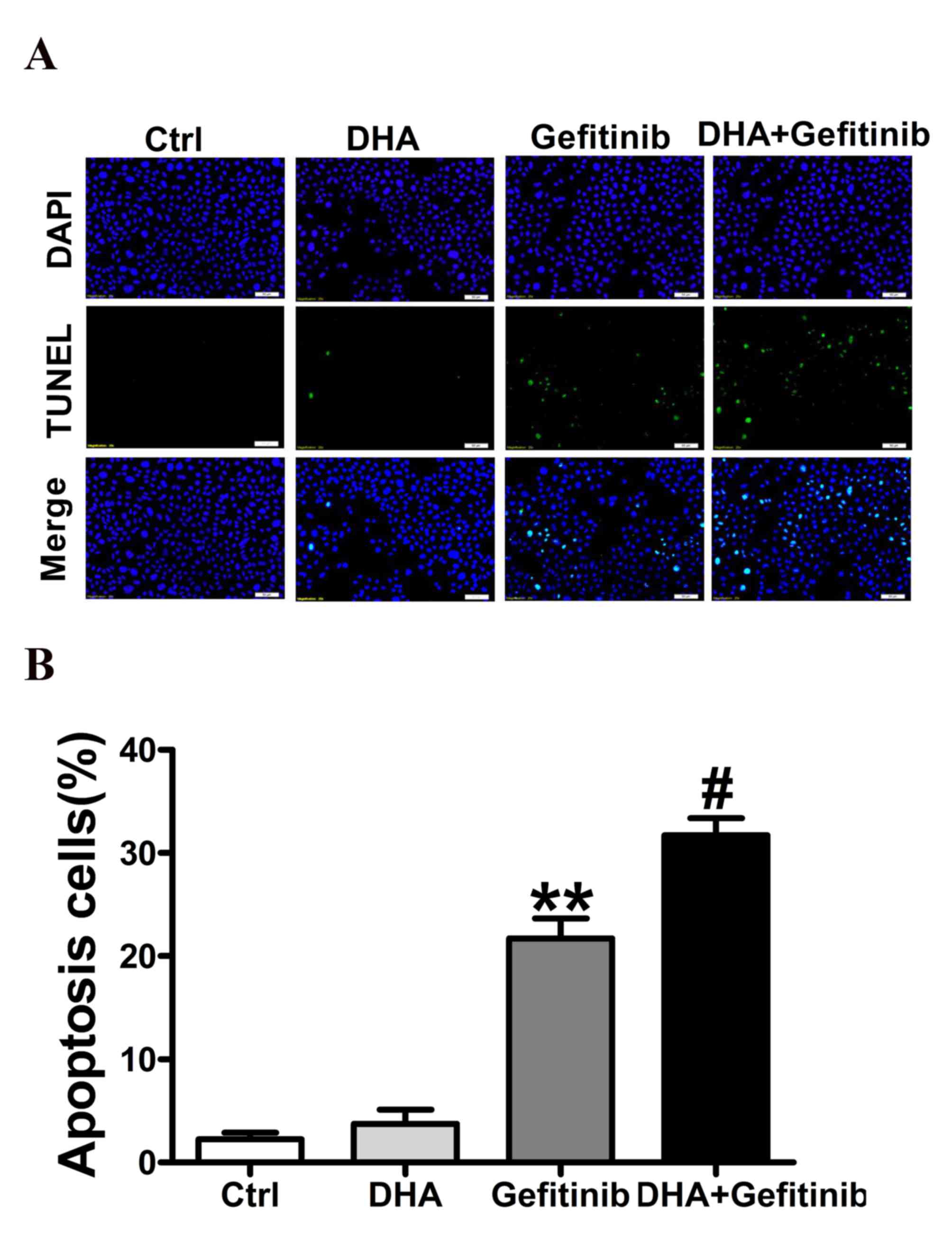
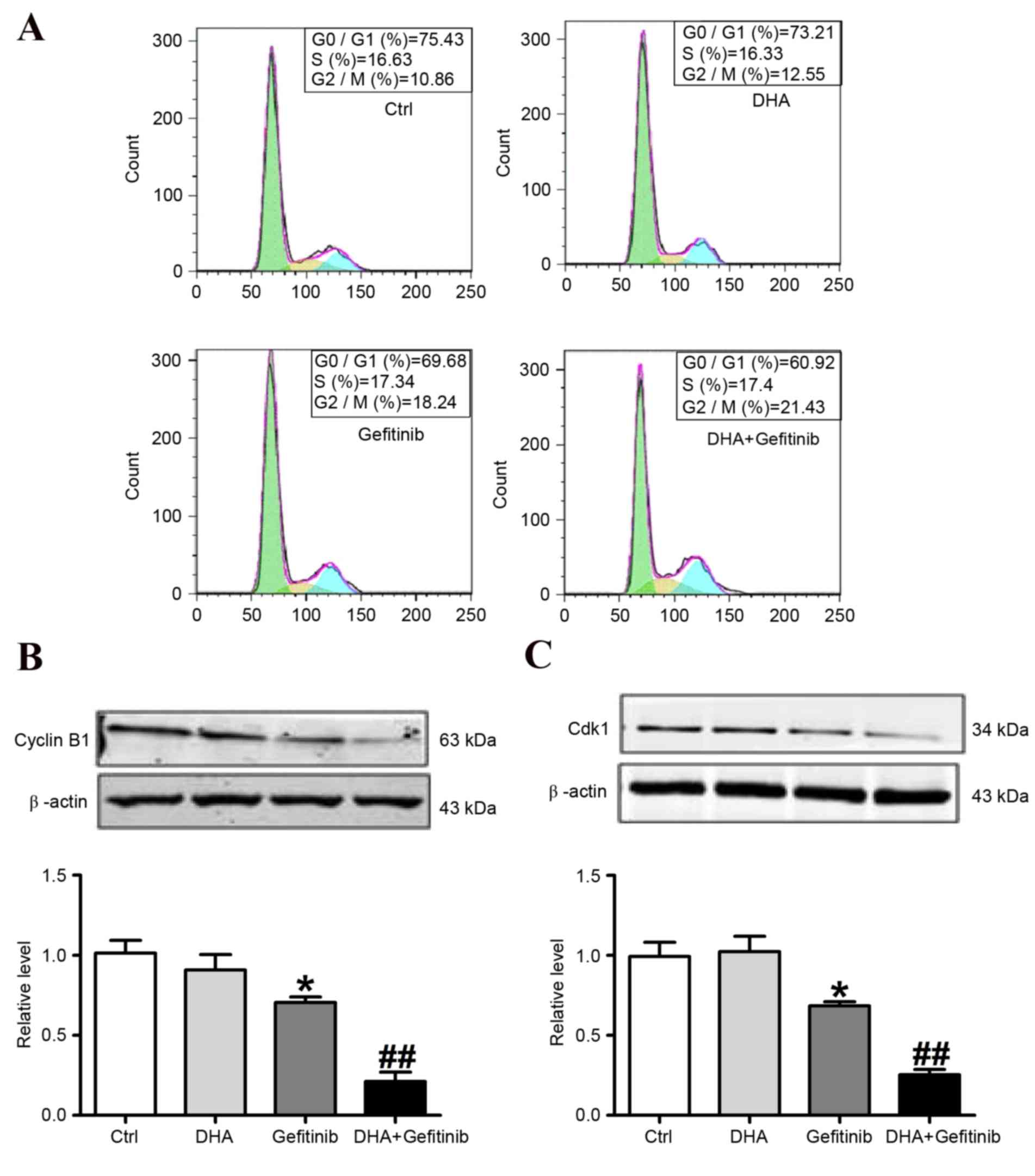
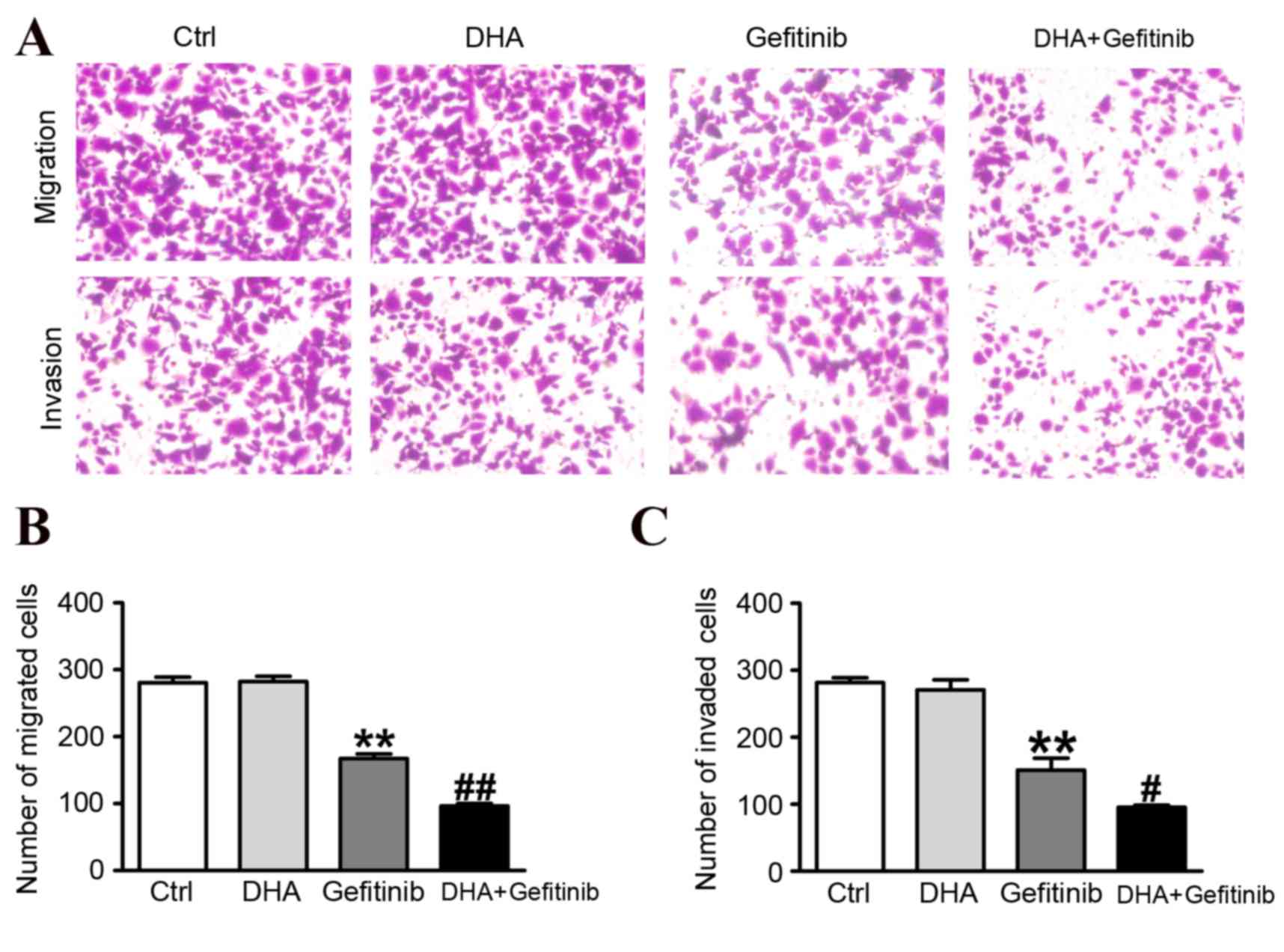
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Song L, Xiong H, Li J, Liao W, Wang L, Wu
J and Li M: Sphingosine kinase-1 enhances resistance to apoptosis
through activation of PI3K/Akt/NF-κB pathway in human non-small
cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 17:1839–1849. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chemotherapy in non-small cell lung
cancer: A meta-analysis using updated data on individual patients
from 52 randomised clinical trials. Non-small Cell Lung Cancer
Collaborative Group. BMJ. 311:899–909. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Iwamoto Y, Mitsudomi T, Sakai K, Yamanaka
T, Yoshioka H, Takahama M, Yoshimura M, Yoshino I, Takeda M,
Sugawara S, et al: Randomized phase II study of adjuvant
chemotherapy with long-term S-1 versus cisplatin+S-1 in completely
resected stage II–IIIA non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
21:5245–5252. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Scagliotti GV, Fossati R, Torri V, Crinò
L, Giaccone G, Silvano G, Martelli M, Clerici M, Cognetti F, Tonato
M, et al: Adjuvant Lung Project Italy/European Organisation for
Research Treatment of Cancer-Lung Cancer Cooperative Group
Investigators: Randomized study of adjuvant chemotherapy for
completely resected stage I, II, or IIIA non-small-cell lung
cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 95:1453–1461. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cohen MH, Williams GA, Sridhara R, Chen G,
McGuinn WD Jr, Morse D, Abraham S, Rahman A, Liang C, Lostritto R,
et al: United States food and drug administration drug approval
summary: Gefitinib (ZD1839; Iressa) tablets. Clin Cancer Res.
10:1212–1218. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R,
Gurubhagavatula S, Okimoto RA, Brannigan BW, Harris PL, Haserlat
SM, Supko JG, Haluska FG, et al: Activating mutations in the
epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of
non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med.
350:2129–2139. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hu CJ, Zhou L and Cai Y:
Dihydroartemisinin induces apoptosis of cervical cancer cells via
upregulation of RKIP and downregulation of bcl-2. Cancer Biol Ther.
15:279–288. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dong Q, Chen L, Lu Q, Sharma S, Li L,
Morimoto S and Wang G: Quercetin attenuates doxorubicin
cardiotoxicity by modulating Bmi-1 expression. Br J Pharmacol.
171:4440–4454. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang S, Ma Y, Jiang J, Dai Z, Gao X, Yin
X, Xi W1 and Min W: Inhibition of urokinase-type plasminogen
activator expression by dihydroartemisinin in breast cancer cells.
Oncol Lett. 7:1375–1380. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhou HJ, Zhang JL, Li A, Wang Z and Lou
XE: Dihydro-artemisinin improves the efficiency of
chemotherapeutics in lung carcinomas in vivo and inhibits murine
Lewis lung carcinoma cell line growth in vitro. Cancer Chemother
Pharmacol. 66:21–29. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mi YJ, Geng GJ, Zou ZZ, Gao J, Luo XY, Liu
Y2, Li N, Li CL, Chen YQ, Yu XY2 and Jiang J: Dihydroartemisinin
inhibits glucose uptake and cooperates with glycolysis inhibitor to
induce apoptosis in non-small cell lung carcinoma cells. PLoS One.
10:e01204262015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hermeking H: The miR-34 family in cancer
and apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 17:193–199. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang J, Wei H, Zhao B, Li M, Lv W, Lv L,
Song B and Lv S: The reverse effect of X-ray irradiation on
acquired gefitinib resistance in non-small cell lung cancer cell
line NCI-H1975 in vitro. J Mol Histol. 45:641–652. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Fan Y, Chen M, Meng J, Yu L, Tu Y, Wan L,
Fang K and Zhu W: Arsenic trioxide and resveratrol show synergistic
anti-leukemia activity and neutralized cardiotoxicity. PLoS One.
9:e1058902014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhao X, Zhong H, Wang R, Liu D, Waxman S,
Zhao L and Jing Y: Dihydroartemisinin and its derivative induce
apoptosis in acute myeloid leukemia through Noxa-mediated pathway
requiring iron and endoperoxide moiety. Oncotarget. 6:5582–5596.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhao C, Gao W and Chen T: Synergistic
induction of apoptosis in A549 cells by dihydroartemisinin and
gemcitabine. Apoptosis. 19:668–681. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Maemondo M, Inoue A, Kobayashi K, Sugawara
S, Oizumi S, Isobe H, Gemma A, Harada M, Yoshizawa H and Kinoshita
I: Gefitinib or chemotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer with
mutated EGFR. N Engl J Med. 362:2380–2388. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yusuf SW, Kim P and Durand JB: Erlotinib
or gefitinib for non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med.
364:2367–2368. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Matsui TA, Murata H, Sakabe T, Sowa Y,
Horie N, Nakanishi R, Sakai T and Kubo T: Sulforaphane induces cell
cycle arrest and apoptosis in murine osteosarcoma cells in vitro
and inhibits tumor growth in vivo. Oncol Rep. 18:1263–1268.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jakubikova J, Bao Y and Sedlak J:
Isothiocyanates induce cell cycle arrest, apoptosis and
mitochondrial potential depolarization in HL-60 and
multidrug-resistant cell lines. Anticancer Res. 25:3375–3386.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chang A: Chemotherapy, chemoresistance and
the changing treatment landscape for NSCLC. Lung Cancer. 71:3–10.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Simmons TL, Andrianasolo E, McPhail K,
Flatt P and Gerwick WH: Marine natural products as anticancer
drugs. Mol Cancer Ther. 4:333–342. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gordaliza M: Natural products as leads to
anticancer drugs. Clinical Translational Oncol. 9:767–776. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Altmann KH and Gertsch J: Anticancer drugs
from nature-natural products as a unique source of new
microtubule-stabilizing agents. Nat Prod Rep. 24:327–357. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Newman DJ and Cragg GM: Natural products
as sources of new drugs over the last 25 years. J Nat Prod.
70:461–477. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sun H, Meng X, Han J, Zhang Z, Wang B, Bai
X and Zhang X: Anti-cancer activity of DHA on gastric cancer-an in
vitro and in vivo study. Tumour Biol. 34:3791–3800. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Follo MY, Manzoli L, Poli A, McCubrey JA
and Cocco L: PLC and PI3K/Akt/mTOR signalling in disease and
cancer. Adv Biol Regul. 57:10–16. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Cornu M, Albert V and Hall MN: mTOR in
aging, metabolism, and cancer. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 23:53–62. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Faried LS, Faried A, Kanuma T, Nakazato T,
Tamura T, Kuwano H and Minegishi T: Inhibition of the mammalian
target of rapamycin (mTOR) by rapamycin increases chemosensitivity
of CaSki cells to paclitaxel. Eur J Cancer. 42:934–947. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li YC, He SM, He ZX, Li M, Yang Y, Pang
JX, Zhang X, Chow K, Zhou Q, Duan W, et al: Plumbagin induces
apoptotic and autophagic cell death through inhibition of the
PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in human non-small cell lung cancer cells.
Cancer Lett. 344:239–259. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Feng X, Li L, Jiang H, Jiang K, Jin Y and
Zheng J: Dihydro-artemisinin potentiates the anticancer effect of
cisplatin via mTOR inhibition in cisplatin-resistant ovarian cancer
cells: involvement of apoptosis and autophagy. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 444:376–381. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wu GS, Lu JJ, Guo JJ, Huang MQ, Gan L,
Chen XP and Wang YT: Synergistic anti-cancer activity of the
combination of dihydroartemisinin and doxorubicin in breast cancer
cells. Pharmacol Rep. 65:453–459. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Adams JM and Cory S: The Bcl-2 protein
family: Arbiters of cell survival. Science. 281:1322–1326. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sheng H, Shao J, Morrow JD, Beauchamp RD
and DuBois RN: Modulation of apoptosis and Bcl-2 expression by
prostaglandin E2 in human colon cancer cells. Cancer Res.
58:362–366. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
McDonnell TJ, Troncoso P, Brisbay SM,
Logothetis C, Chung LW, Hsieh JT, Tu SM and Campbell ML: Expression
of the protooncogene bcl-2 in the prostate and its association with
emergence of androgen-independent prostate cancer. Cancer Res.
52:6940–6944. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Katz HR: bcl-2 protein in non-small-cell
lung carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 330:2211994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Miyashita T, Krajewski S, Krajewska M,
Wang HG, Lin HK, Liebermann DA, Hoffman B and Reed JC: Tumor
suppressor p53 is a regulator of bcl-2 and bax gene expression in
vitro and in vivo. Oncogene. 9:1799–1805. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhang L, Yu J, Park BH, Kinzler KW and
Vogelstein B: Role of BAX in the apoptotic response to anticancer
agents. Science. 290:989–992. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Choudhuri T, Pal S, Agwarwal ML, Das T and
Sa G: Curcumin induces apoptosis in human breast cancer cells
through p53-dependent Bax induction. FEBS Lett. 512:334–340. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Brambilla E, Negoescu A, Gazzeri S,
Lantuejoul S, Moro D, Brambilla C and Coll JL: Apoptosis-related
factors p53, Bcl2, and Bax in neuroendocrine lung tumors. Am J
Pathol. 149:1941–1952. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Gupta S, Afaq F and Mukhtar H: Involvement
of nuclear factor-kappa B, Bax and Bcl-2 in induction of cell cycle
arrest and apoptosis by apigenin in human prostate carcinoma cells.
Oncogene. 21:3727–3738. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Sakamoto KM, Grant S, Saleiro D, Crispino
JD, Hijiya N, Giles F, Platanias L and Eklund EA: Targeting novel
signaling pathways for resistant acute myeloid leukemia. Mol Genet
Metab. 114:397–402. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
He SQ, Gao M, Fu YF and Zhang YN:
Glycyrrhizic acid inhibits leukemia cell growth and migration via
blocking AKT/mTOR/STAT3 signaling. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
8:5175–5181. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|