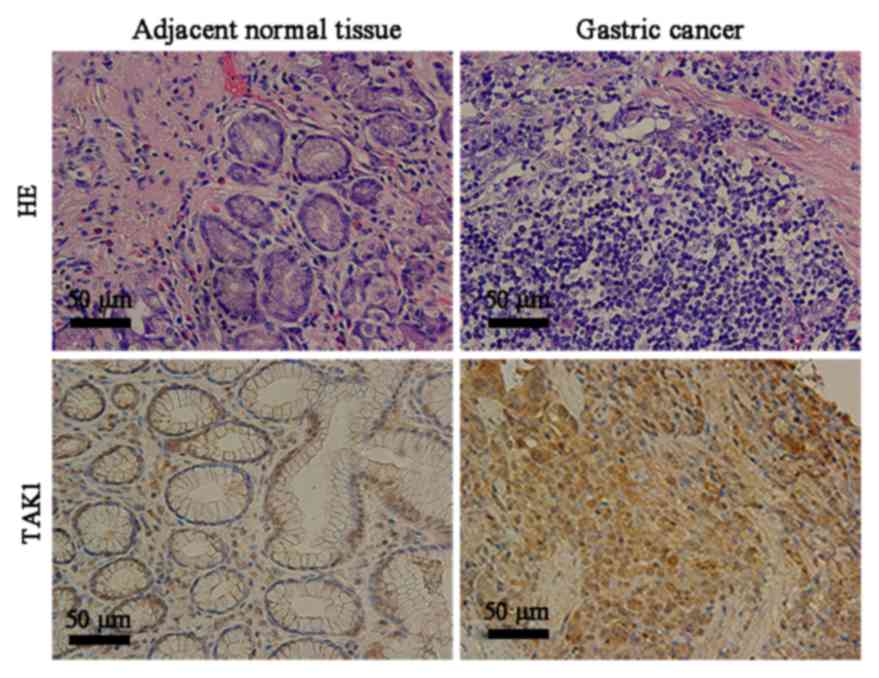
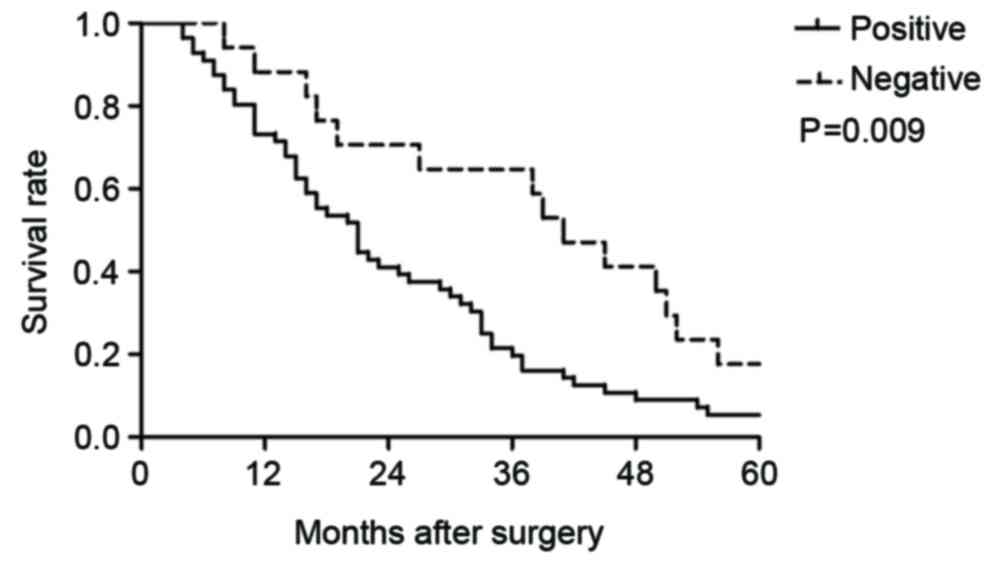
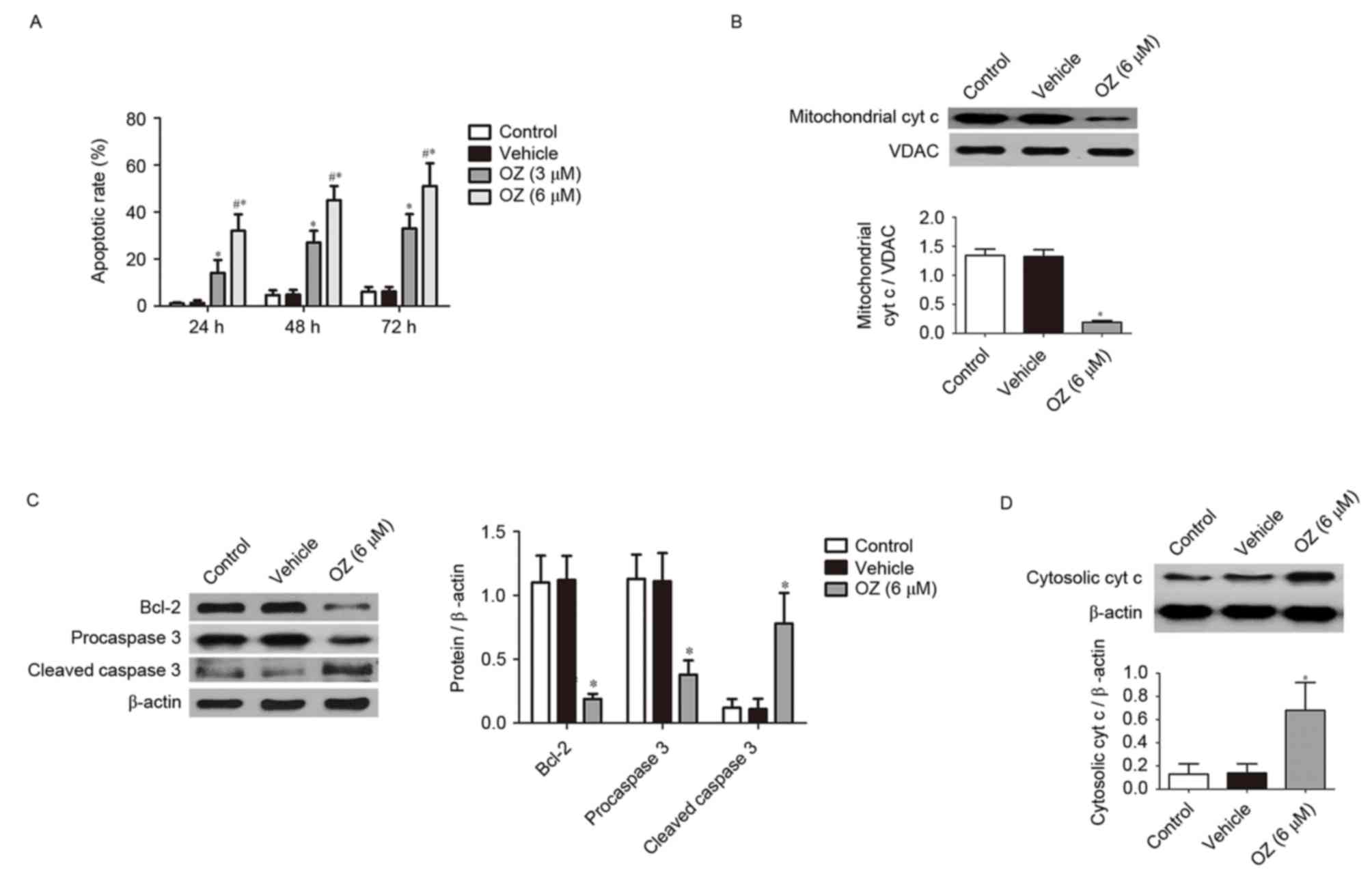
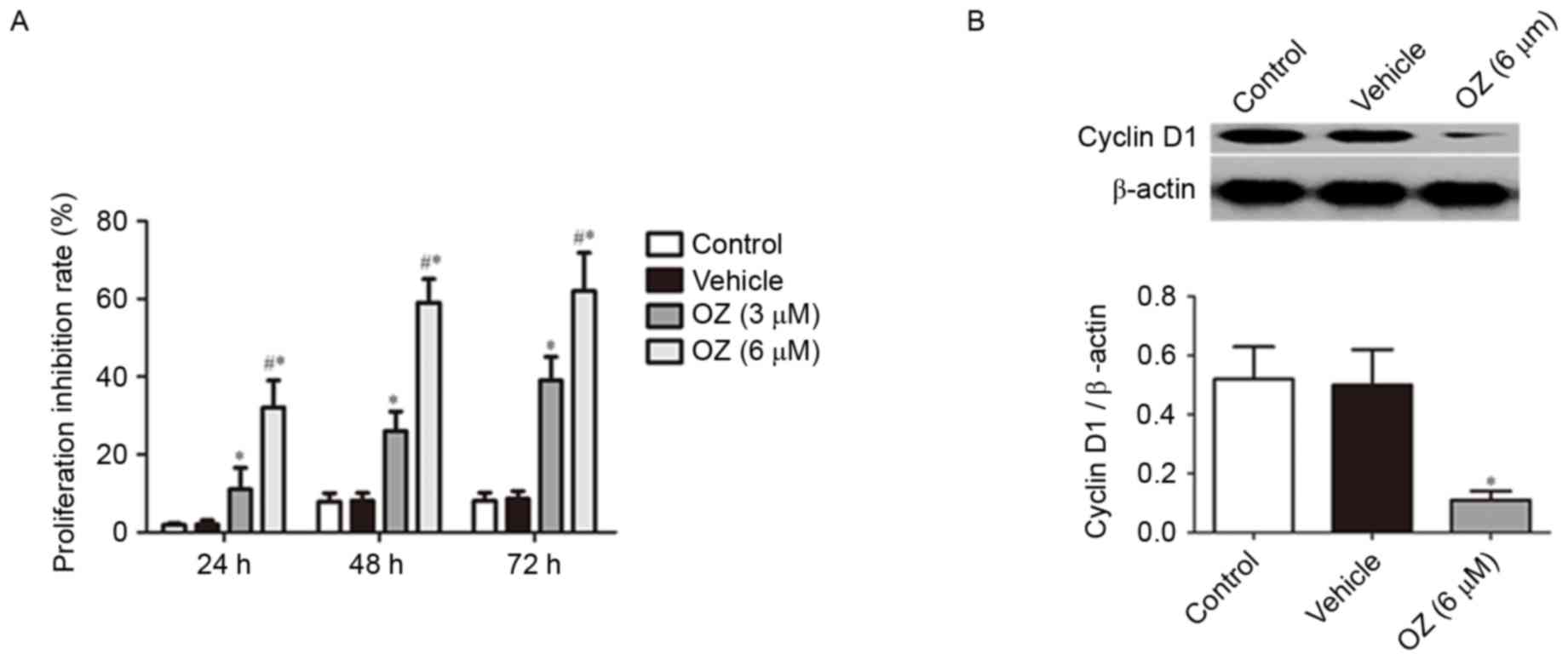
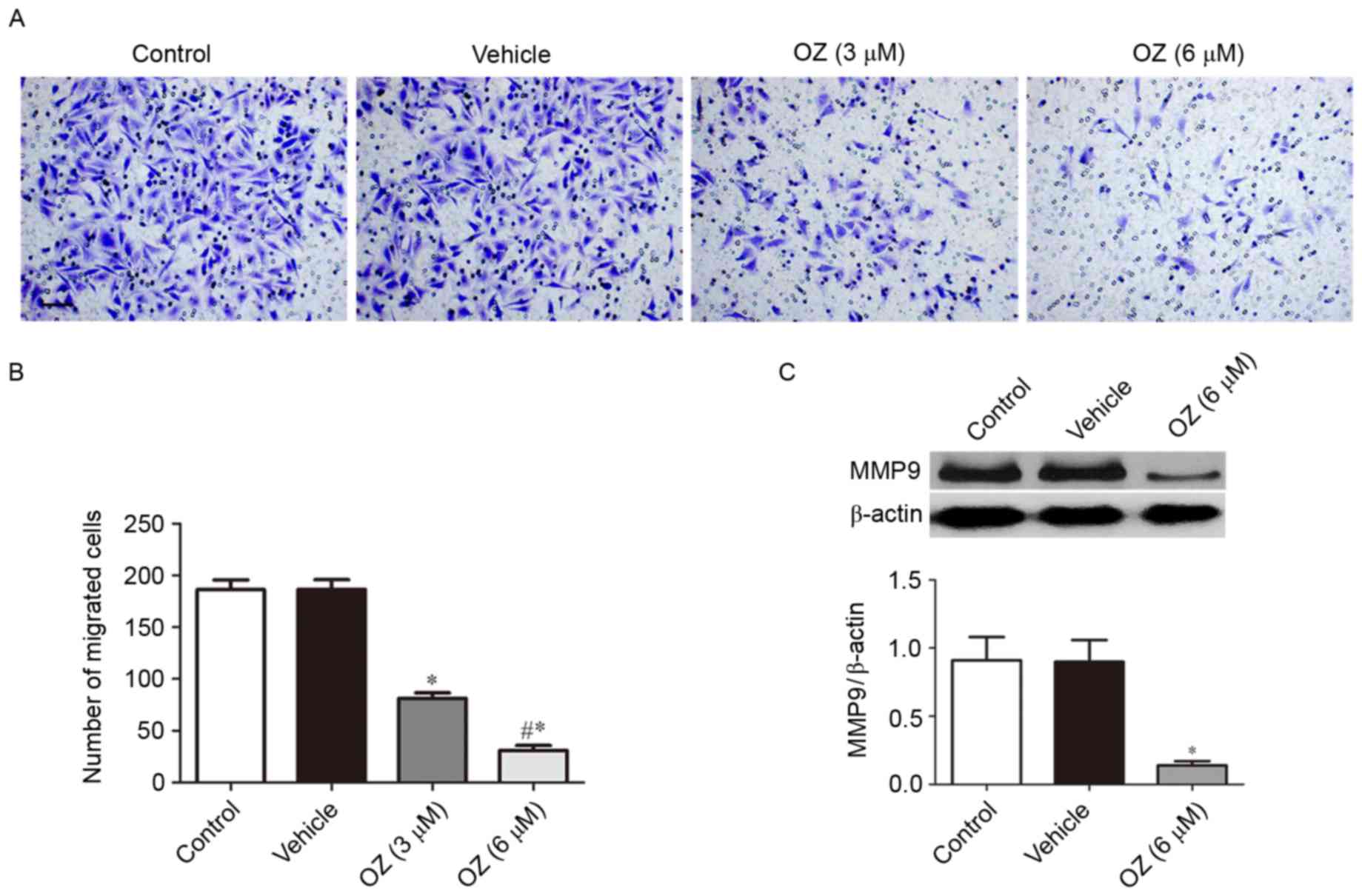
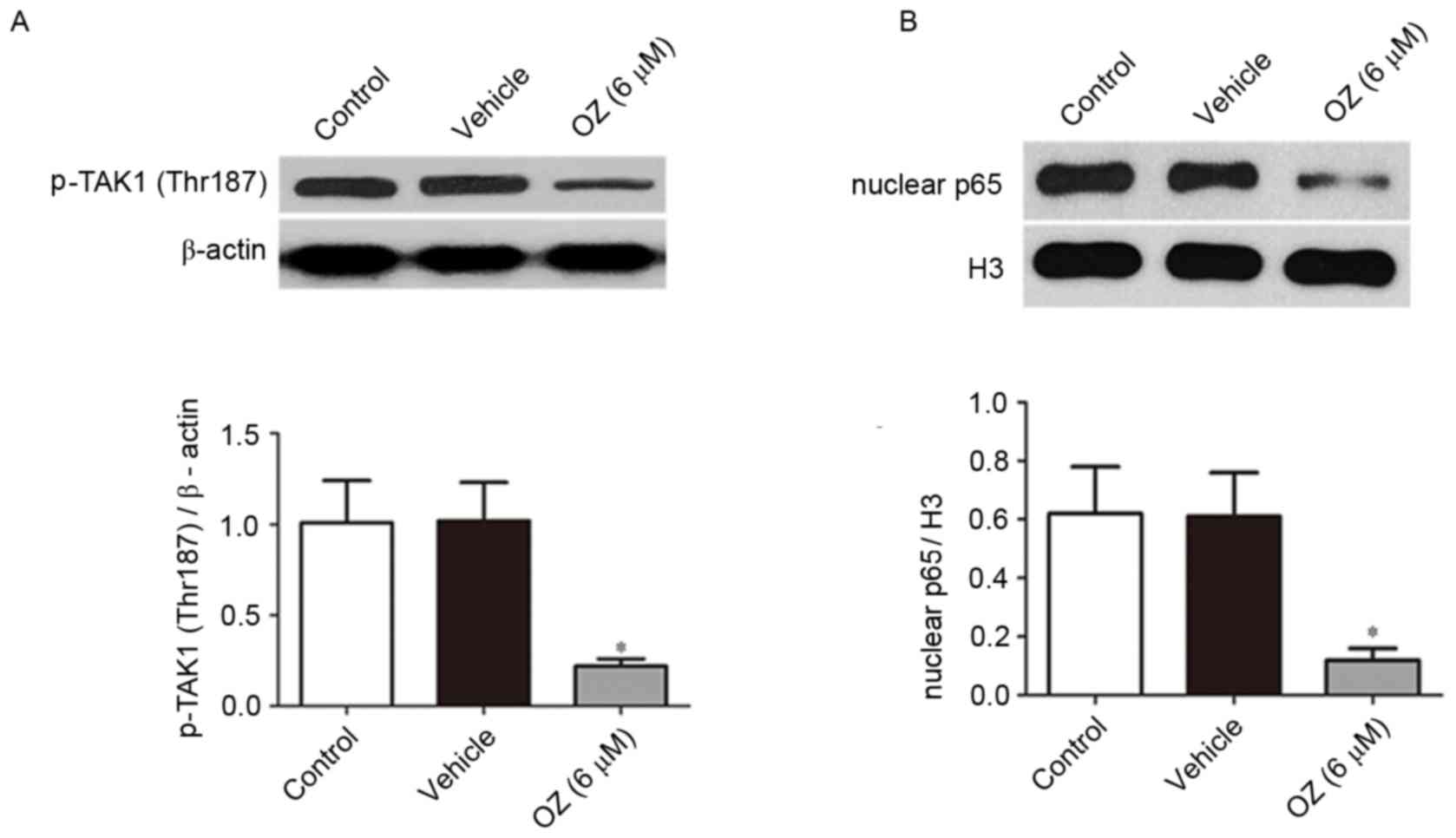
|
1
|
Digklia A and Wagner AD: Advanced gastric
cancer: Current treatment landscape and future perspectives. World
J Gastroenterol. 22:2403–2414. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lordick F and Janjigian YY: Clinical
impact of tumour biology in the management of gastroesophageal
cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 13:348–360. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tomasello G, Ghidini M, Liguigli W, Ratti
M, Toppo L and Passalacqua R: Targeted therapies in gastric cancer
treatment: Where we are and where we are going. Invest New Drugs.
34:378–393. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Karimi P, Islami F, Anandasabapathy S,
Freedman ND and Kamangar F: Gastric cancer: Descriptive
epidemiology, risk factors, screening and prevention. Cancer
Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 23:700–713. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liu X and Meltzer SJ: Gastric cancer in
the era of precision medicine. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol.
3:348–358. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lee SY and Oh SC: Changing strategies for
target therapy in gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol.
22:1179–1189. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sakurai H: Targeting of TAK1 in
inflammatory disorders and cancer. Trends Pharmacol Sci.
33:522–530. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Huang HL, Chiang CH, Hung WC and Hou MF:
Targeting of TGF-β-activated protein kinase 1 inhibits chemokine
(C-C motif) receptor 7 expression, tumor growth and metastasis in
breast cancer. Oncotarget. 6:995–1007. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lin P, Niu W, Peng C, Zhang Z and Niu J:
The role of TAK1 expression in thyroid cancer. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 8:14449–14456. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wu M, Shi L, Cimic A, Romero L, Sui G,
Lees CJ, Cline JM, Seals DF, Sirintrapun JS, McCoy TP, et al:
Suppression of Tak1 promotes prostate tumorigenesis. Cancer Res.
72:2833–2843. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bosman MC, Schepers H, Jaques J,
Brouwers-Vos AZ, Quax WJ, Schuringa JJ and Vellenga E: The
TAK1-NF-κB axis as therapeutic target for AML. Blood.
124:3130–3140. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kilty I and Jones LH: TAK1 selective
inhibition: State of the art and future opportunities. Future Med
Chem. 7:23–33. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wu J, Powell F, Larsen NA, Lai Z, Byth KF,
Read J, Gu RF, Roth M, Toader D, Saeh JC and Chen H: Mechanism and
in vitro pharmacology of TAK1 inhibition by (5Z)-7-Oxozeaenol. ACS
Chem Biol. 8:643–650. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fakhouri L, El-Elimat T, Hurst DP, Reggio
PH, Pearce CJ, Oberlies NH and Croatt MP: Isolation, semisynthesis,
covalent docking and transforming growth factor beta-activated
kinase 1 (TAK1)-inhibitory activities of (5Z)-7-oxozeaenol
analogues. Bioorg Med Chem. 23:6993–6999. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Arici DS, Tuncer E, Ozer H, Simek G and
Koyuncu A: Expression of retinoblastoma and cyclin D1 in gastric
carcinoma. Neoplasma. 56:63–67. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Seo JH, Jeong ES and Choi YK: Therapeutic
effects of lentivirus-mediated shRNA targeting of cyclin D1 in
human gastric cancer. BMC Cancer. 14:1752014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Akter H, Park M, Kwon OS, Song EJ, Park WS
and Kang MJ: Activation of matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) by
neurotensin promotes cell invasion and migration through ERK
pathway in gastric cancer. Tumour Biol. 36:6053–6062. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhu J, Li Q, He JT and Liu GY: Expression
of TAK1/TAB1 expression in non-small cell lung carcinoma and
adjacent normal tissues and their clinical significance. Int J Clin
Exp Pathol. 8:15801–15807. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yang M and Huang CZ: Mitogen-activated
protein kinase signaling pathway and invasion and metastasis of
gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 21:11673–11679. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li X, Tu J, Zhang D, Xu Z, Yang G, Gong L
and Yu M: The clinical significance of HER-2 and NF-KB expression
in gastric cancer. Hepatogastroenterology. 60:1519–1523.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li Q, Yu YY, Zhu ZG, Ji YB, Zhang Y, Liu
BY, Chen XH and Lin YZ: Effect of NF-kappaB constitutive activation
on proliferation and apoptosis of gastric cancer cell lines. Eur
Surg Res. 37:105–110. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Uetsuka H, Haisa M, Kimura M, Gunduz M,
Kaneda Y, Ohkawa T, Takaoka M, Murata T, Nobuhisa T, Yamatsuji T,
et al: Inhibition of inducible NF-kappaB activity reduces
chemoresistance to 5-fluorouracil in human stomach cancer cell
line. Exp Cell Res. 289:27–35. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Pak KH, Kim DH, Kim H, Lee DH and Cheong
JH: Differences in TGF-b1 signaling and clinicopathologic
characteristics of histologic subtypes of gastric cancer. BMC
Cancer. 16:602015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Zhang J, Li B, Wu H, Ou J, Wei R, Liu J,
Cai W, Liu X, Zhao S, Yang J, et al: Synergistic action of
5Z-7-oxozeaenol and bortezomib in inducing apoptosis of Burkitt
lymphoma cell line Daudi. Tumour Biol. 37:531–539. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hrabe JE, O'Leary BR, Fath MA, Rodman SN,
Button AM, Domann FE, Spitz DR and Mezhir JJ: Disruption of
thioredoxin metabolism enhances the toxicity of transforming growth
factor β-activated kinase 1 (TAK1) inhibition in KRAS-mutated colon
cancer cells. Redox Biol. 5:319–327. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Cai PC, Shi L, Liu VW, Tang HW, Liu IJ,
Leung TH, Chan KK, Yam JW, Yao KM, Ngan HY and Chan DW: Elevated
TAK1 augments tumor growth and metastatic capacities of ovarian
cancer cells through activation of NF-κB signaling. Oncotarget.
5:7549–7562. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Fan Y, Cheng J, Vasudevan SA, Patel RH,
Liang L, Xu X, Zhao Y, Jia W, Lu F, Zhang H, et al: TAK1 inhibitor
5Z-7-oxozeaenol sensitizes neuroblastoma to chemotherapy.
Apoptosis. 18:1224–1234. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Singhirunnusorn P, Suzuki S, Kawasaki N,
Saiki I and Sakurai H: Critical roles of threonine 187
phosphorylation in cellular stress-induced rapid and transient
activation of transforming growth factor-beta-activated kinase 1
(TAK1) in a signaling complex containing TAK1-binding protein TAB1
and TAB2. J Biol Chem. 280:7359–7368. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Choo MK, Kawasaki N, Singhirunnusorn P,
Koizumi K, Sato S, Akira S, Saiki I and Sakurai H: Blockade of
transforming growth factor-beta-activated kinase 1 activity
enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis through activation of a caspase
cascade. Mol Cancer Ther. 5:2970–2976. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cao H, Lu J, Du J, Xia F, Wei S, Liu X,
Liu T, Liu Y and Xiang M: TAK1 inhibition prevents the development
of autoimmune diabetes in NOD mice. Sci Rep. 5:145932015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Song Z, Zhu X, Jin R, Wang C, Yan J, Zheng
Q, Nanda A, Granger DN and Li G: Roles of the kinase TAK1 in
CD40-mediated effects on vascular oxidative stress and neointima
formation after vascular injury. PloS One. 9:e1016712014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Guo JQ, Li SJ and Guo GX: Long noncoding
RNA AFAP1-AS1 promotes cell proliferation and apoptosis of gastric
cancer cells via PTEN/p-AKT pathway. Dig Dis Sci. Apr 27–2017.(Epub
ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Tong K, Xin C and Chen W: Isoimperatorin
induces apoptosis of the SGC-7901 human gastric cancer cell line
via the mitochondria-mediated pathway. Oncol Lett. 13:518–524.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang D, Li Y, Cui P, Zhao Q, Tan BB, Zhang
ZD, Liu Y and Jia N: Zerumbone induces gastric cancer cells
apoptosis: Involving cyclophilin A. Biomed Pharmacother.
83:740–745. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Shen X, Si Y, Wang Z, Wang J, Guo Y and
Zhang X: Quercetin inhibits the growth of human gastric cancer stem
cells by inducing mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis through the
inhibition of PI3K/Akt signaling. Int J Mol Med. 38:619–626.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yang LQ, Fang DC, Wang RQ and Yang SM:
Effect of NF-kappaB, survivin, Bcl-2 and Caspase3 on apoptosis of
gastric cancer cells induced by tumor necrosis factor related
apoptosis inducing ligand. World J Gastroenterol. 10:22–25.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chang MS, Lee HS, Jung EJ, Kim CW, Lee BL
and Kim WH: Cell-cycle regulators, bcl-2 and NF-kappaB in
Epstein-Barr virus-positive gastric carcinomas. Int J Oncol.
27:1265–1272. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Dolcet X, Llobet D, Pallares J and
Matias-Guiu X: NF-kB in development and progression of human
cancer. Virchows Arch. 446:475–482. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Buglio D, Palakurthi S, Byth K, Vega F,
Toader D, Saeh J, Neelapu SS and Younes A: Essential role of TAK1
in regulating mantle cell lymphoma survival. Blood. 120:347–355.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Park BB, Yoon Js, Kim Es, Choi J, Won Yw,
Choi Jh and Lee YY: Inhibitory effects of eupatilin on tumor
invasion of human gastric cancer MKN-1 cells. Tumour Biol.
34:875–885. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhang QW, Liu L, Chen R, Wei YQ, Li P, Shi
HS and Zhao YW: Matrix metalloproteinase-9 as a prognostic factor
in gastric cancer: A meta-analysis. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
13:2903–2908. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hinz M, Krappmann D, Eichten A, Heder A,
Scheidereit C and Strauss M: NF-kappaB function in growth control:
Regulation of cyclin D1 expression and G0/G1-to-S-phase transition.
Mol Cell Biol. 19:2690–2698. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lam CR, Tan C, Teo Z, Tay CY, Phua T, Wu
YL, Cai PQ, Tan LP, Chen X, Zhu P and Tan NS: Loss of TAK1
increases cell traction force in a ROS-dependent manner to drive
epithelial-mesenchymal transition of cancer cells. Cell Death Dis.
4:e8482013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Omori E, Matsumoto K, Zhu S, Smart RC and
Ninomiya-Tsuji J: Ablation of TAK1 upregulates reactive oxygen
species and selectively kills tumor cells. Cancer Res.
70:8417–8425. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|