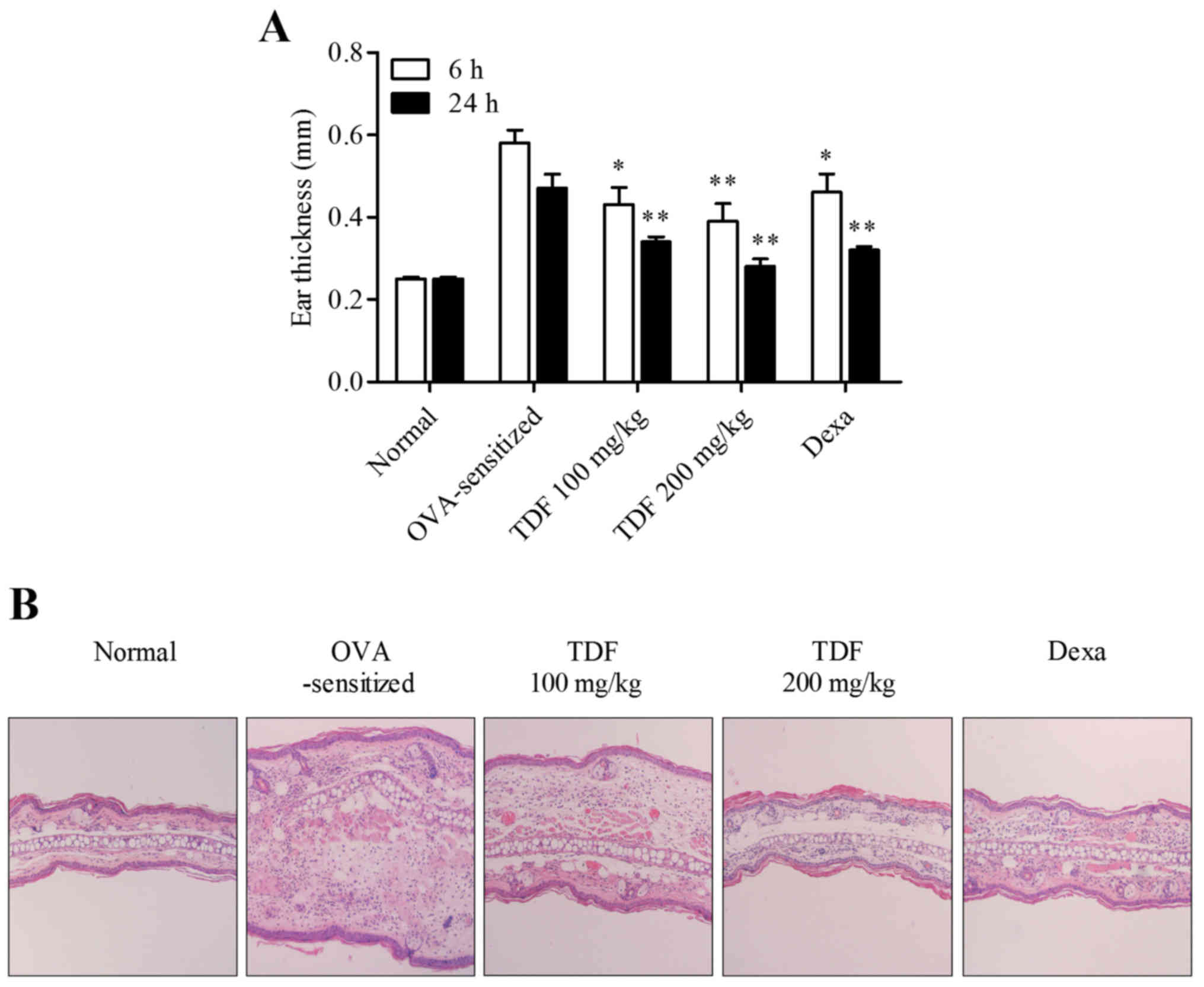
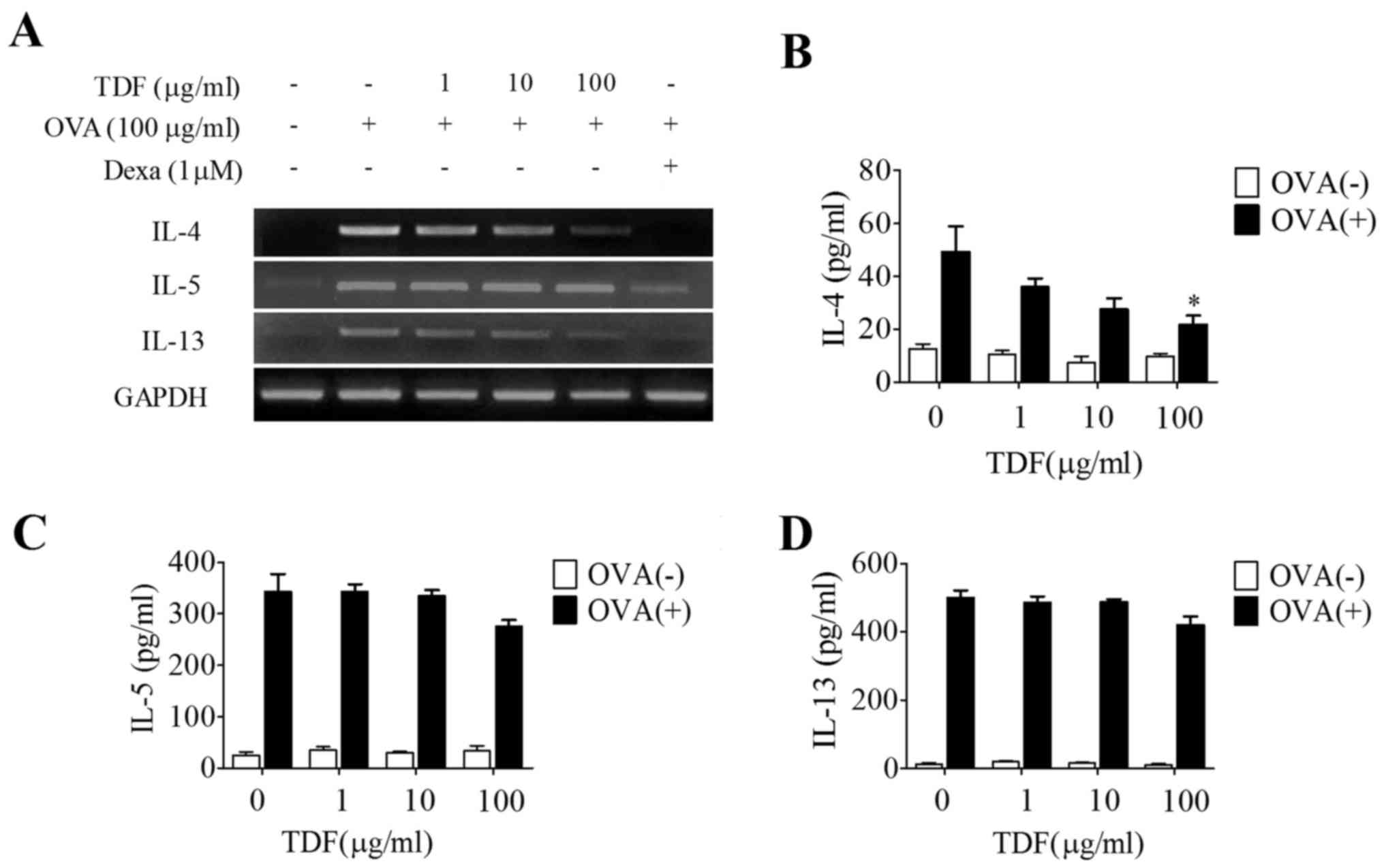
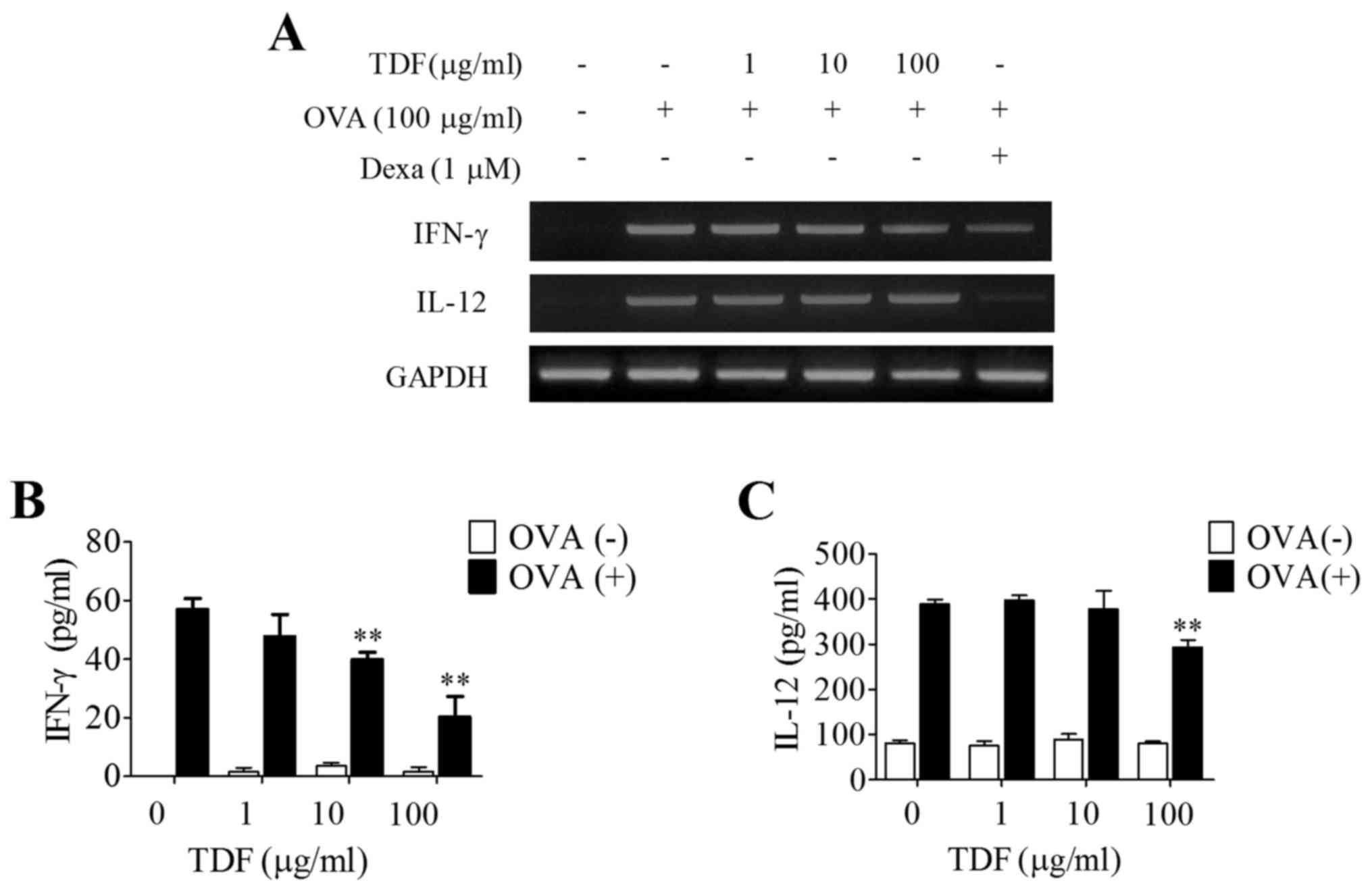
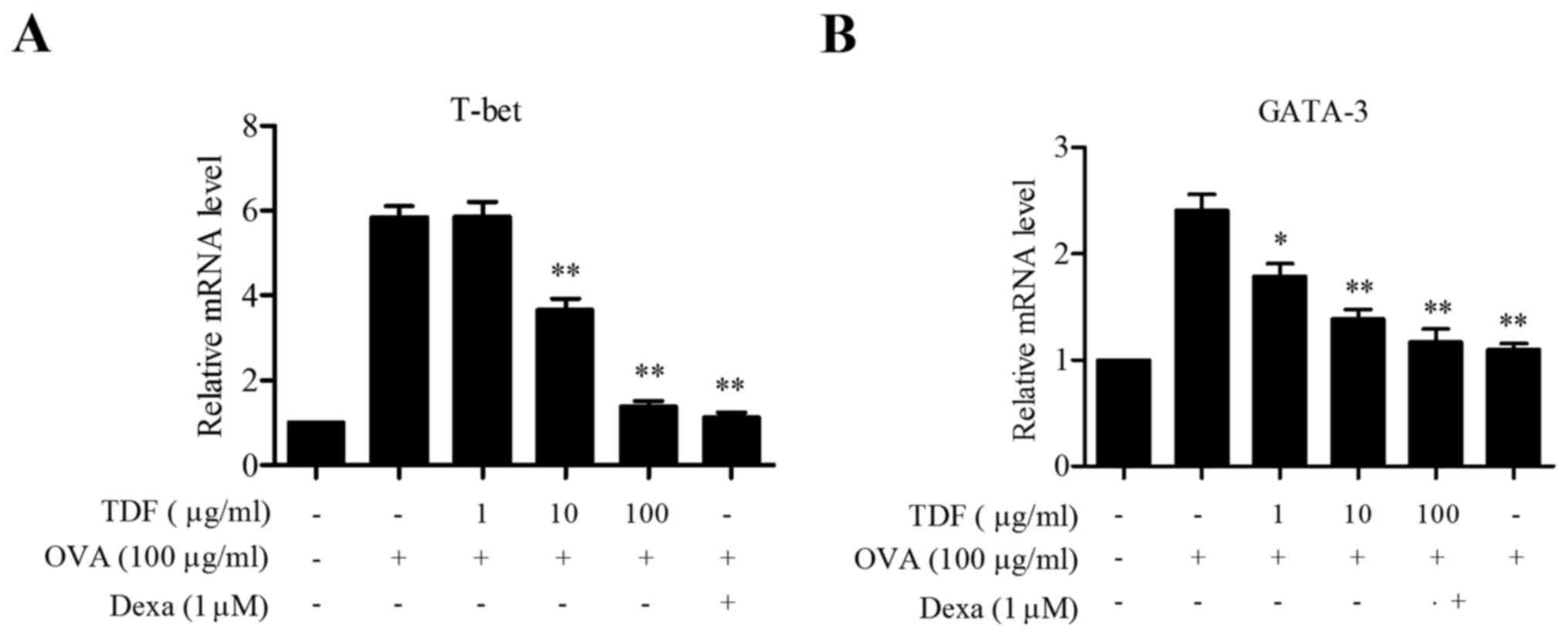
|
1
|
Amin K: The role of mast cells in allergic
inflammation. Respir Med. 106:9–14. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Larché M, Akdis CA and Valenta R:
Immunological mechanisms of allergen-specific immunotherapy. Nat
Rev immunol. 6:761–771. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bosnjak B, Stelzmueller B, Erb KJ and
Epstein MM: Treatment of allergic asthma: Modulation of Th2 cells
and their responses. Respir Res. 12:1142011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Romagnani S: The role of lymphocytes in
allergic disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 105:399–408. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Simons FE: Advances in H1-antihistamines.
N Engl J Med. 351:2203–2217. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Buchman AL: Side effects of corticosteroid
therapy. J Clin Gastroenterol. 33:289–294. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Warrington TP and Bostwick JM: Psychiatric
adverse effects of corticosteroids. Mayo Clin Proc. 81:1361–1367.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Petry JJ and Hadley SK: Medicinal herbs:
Answers and advice, part 1. Hosp Pract (1995). 36:57–60. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Balandrin MF, Klocke JA, Wurtele ES and
Bollinger WH: Natural plant chemicals: Sources of industrial and
medicinal materials. Science. 228:1154–1160. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mujoriya R and Bodla RB: A study on wheat
grass and its Nutritional value. Food Sci Qual Manag. 2:2224–6088.
2011.
|
|
11
|
Wardlaw AJ, Brightling C, Greesn R,
Woltmann G and Pavord I: Eosinophils in asthma and other allergic
diseases. Br Med Bull. 56:985–1003. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Till S, Dickason R, Huston D, Humbert M,
Robinson D, Larché M, Durham S, Kay AB and Corrigan C: IL-5
secretion by allergen-stimulated CD4+ T cells in primary
culture: Relationship to expression of allergic disease. J Allergy
Clin Immunol. 99:563–569. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Desai TR, Solanki JK, Buch Pankaj and
Goyal RK: Triticum aestivum (Wheatgrass): An alternate
treatment for the patients with Thalassemia. Orient Pharm Exp Med.
7:466–476. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Luyen BT, Thao NP, Tai BH, Lim JY, Ki HH,
Kim DK, Lee YM and Kim YH: Chemical constituents of Triticum
aestivum and their effects on adipogenic differentiation of
3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Arch Pharm Res. 38:1011–1018. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Han NR, Kim HM and Jeong HJ: The potential
anti-proliferative effect of β-sitosterol on human mast cell line-1
cells. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 93:979–983. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Mahajan SG and Mehta AA: Suppression of
ovalbumin-induced Th2-driven airway inflammation by β-sitosterol in
a guinea pig model of asthma. Eur J Pharmacol. 650:458–464. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Arm JP, Boyce JA, Wang L, Chhay H, Zahid
M, Patil V, Govindarajulu U, Ivester P, Weaver KL, Sergeant S, et
al: Impact of botanical oils on polyunsaturated fatty acid
metabolism and leukotriene generation in mild asthmatics. Lipids
Health Dis. 12:1412013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Barros R, Moreira A, Fonseca J, Delgado L,
Castel-Branco MG, Haahtela T, Lopes C and Moreira P: Dietary intake
of α-linolenic acid and low ratio of n-6:n-3 PUFA are associated
with decreased exhaled NO and improved asthma control. Br J Nutr.
106:441–450. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Park EJ, Kim B, Eo H, Park K, Kim Y, Lee
HJ, Son M, Chang YS, Cho SH, Kim S and Jin M: Control of IgE and
selective TH1 and TH2 cytokines by PG102 isolated from Actinidia
arguta. J Clin Immunol. 116:1151–1157. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Schouten B, van Esch BC, Hofman GA, van
den Elsen LW, Willemsen LE and Garssen J: Acute allergic skin
reactions and intestinal contractility changes in mice orally
sensitized against casein or whey. Int Arch Allergy Immunol.
147:125–134. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hogenkamp A, Thijssen S, van Vlies N and
Garssen J: Supplementing pregnant mice with a specific mixture of
nondigestible oligosaccharides reduces symptoms of allergic asthma
in male offspring. J Nutr. 145:640–646. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Poudel B, Yoon DS, Lee JH, Lee YM and Kim
DK: Collagen I enhances functional activities of human
monocyte-derived dendritic cells via discoidin domain receptor 2.
Cell Immunol. 278:95–102. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Poudel B, Nepali S, Xin M, Ki HH, Kim YH,
Kim DK and Lee YM: Flavonoids from Triticum aestivum inhibit
adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 cells by upregulating the insig pathway. Mol
Med Rep. 12:3139–3145. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Galli SJ, Tsai M and Piliponsky AM: The
development of allergic inflammation. Nature. 454:445–454. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Aversa G, Punnonen J, Cocks BG, de Waal
Malefyt R, Vega F Jr, Zurawski SM, Zurawski G and de Vries JE: An
interleukin 4 (IL-4) mutant protein inhibit both IL-4 or
IL-13-induced human immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4) and IgE synthesis and
B cell proliferation: Support for a common component shared by IL-4
and IL-13 receptors. J Exp Med. 178:2213–2218. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kidd P: Th1/Th2 balance: The hypothesis,
its limitations and implications for health and disease. Altern Med
Rev. 8:223–246. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Akdis CA: Allergy and hypersensitivity
Mechanisms of allergic disease. Curr Opin Immunol. 18:718–726.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yazdanbakhsh M, Kremsner PG and van Ree R:
Allergy, parasites, and the hygiene hypothesis. Science.
296:490–494. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Holgate ST and Polosa R: Treatment
strategies for allergy and asthma. Nat Rev Immunol. 8:218–230.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Nials AT and Uddin S: Mouse models of
allergic asthma: Acute and chronic allergen challenge. Dis Models
Mech. 1:213–220. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Jin H, He R, Oyoshi M and Geha RS: Animal
models of atopic dermatitis. J Invest Dermatol. 129:31–40. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zgraggen S, Ochsenbein AM and Detmar M: An
important role of blood and lymphatic vessels in inflammation and
allergy. J Allergy (Cairo). 2013:6723812013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Galli SJ and Tsai M: IgE and mast cells in
allergic disease. Nat Med. 18:693–704. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Heijink IH and Van Oosterhout AJ:
Strategies for targeting T-cells in allergic diseases and asthma.
Pharmacol Ther. 112:489–500. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chatila TA, Li N, Garcia-Lloret M, Kim HJ
and Nel AE: T-cell effector pathways in allergic diseases:
Aanscriptional mechanisms and therapeutic targets. J Allergy Clin
Immunol. 121:812–823. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Szabo SJ, Kim ST, Costa GL, Zhang X,
Fathman CG and Glimcher LH: A novel transcription factor, T-bet,
directs Th1 lineage commitment. Cell. 100:655–669. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lee SH, Xin M, Luyen BT, Cha JY, Im JY,
Kwon SU, Lim SW, Suh JW, Kim YH, Kim DK and Lee YM: Inhibitory
effect of Triticum aestivum ethanol extract on lipid
accumulation in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Yakhak Hoeji. 55:478–484.
2011.
|
|
38
|
Luyen BT, Tai BH, Thao NP, Cha JY, Lee YM
and Kim YH: A new phenolic component from Triticum aestivum
sprouts and its effects on LPS-stimulated production of nitric
oxide and TNF-α in RAW 264.7 cells. Phytother Res. 28:1064–1070.
2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kim DS, Son EJ, Kim M, Heo YM, Nam JB, Ro
JY and Woo SS: Antiallergic herbal composition from Scutellaria
baicalensis and Phyllostachys edulis. Planta Med.
76:678–682. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kritas SK, Saggini A, Varvara G, Murmura
G, Caraffa A, Antinolfi P, Toniato E, Pantalone A, Neri G, Frydas
S, et al: Luteolin inhibits mast cell-mediated allergic
inflammation. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 27:955–959.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lee JY, Kim JM and Kim CJ: Flavones
derived from nature attenuate the immediate and late-phase
asthmatic responses to aerosolized-ovalbumin exposure in conscious
guinea pigs. Inflamm Res. 63:53–60. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|