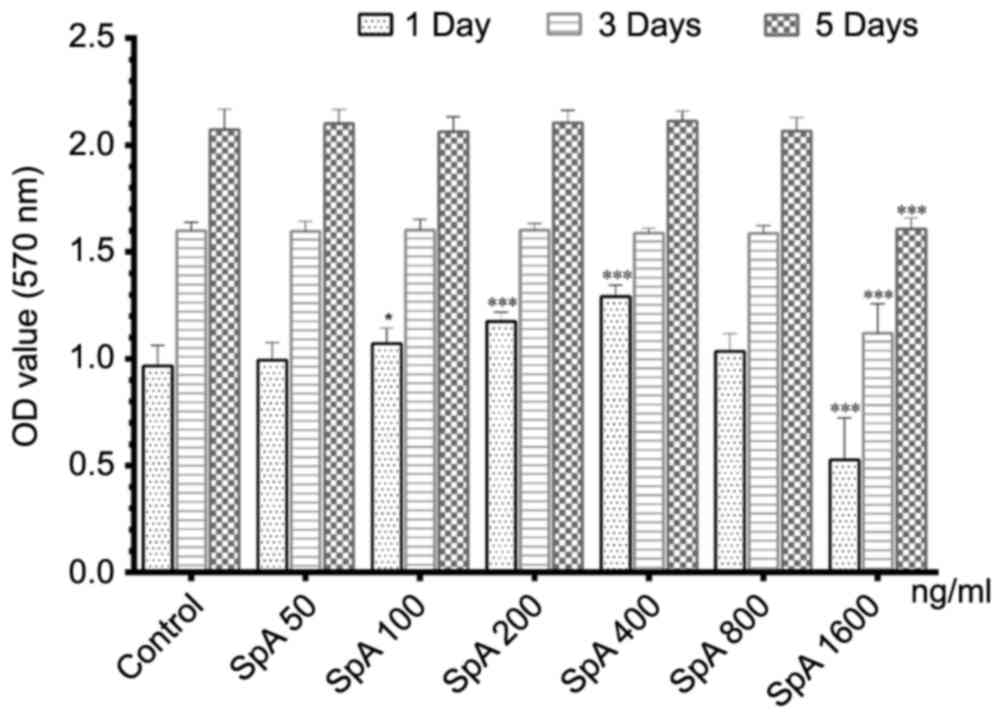
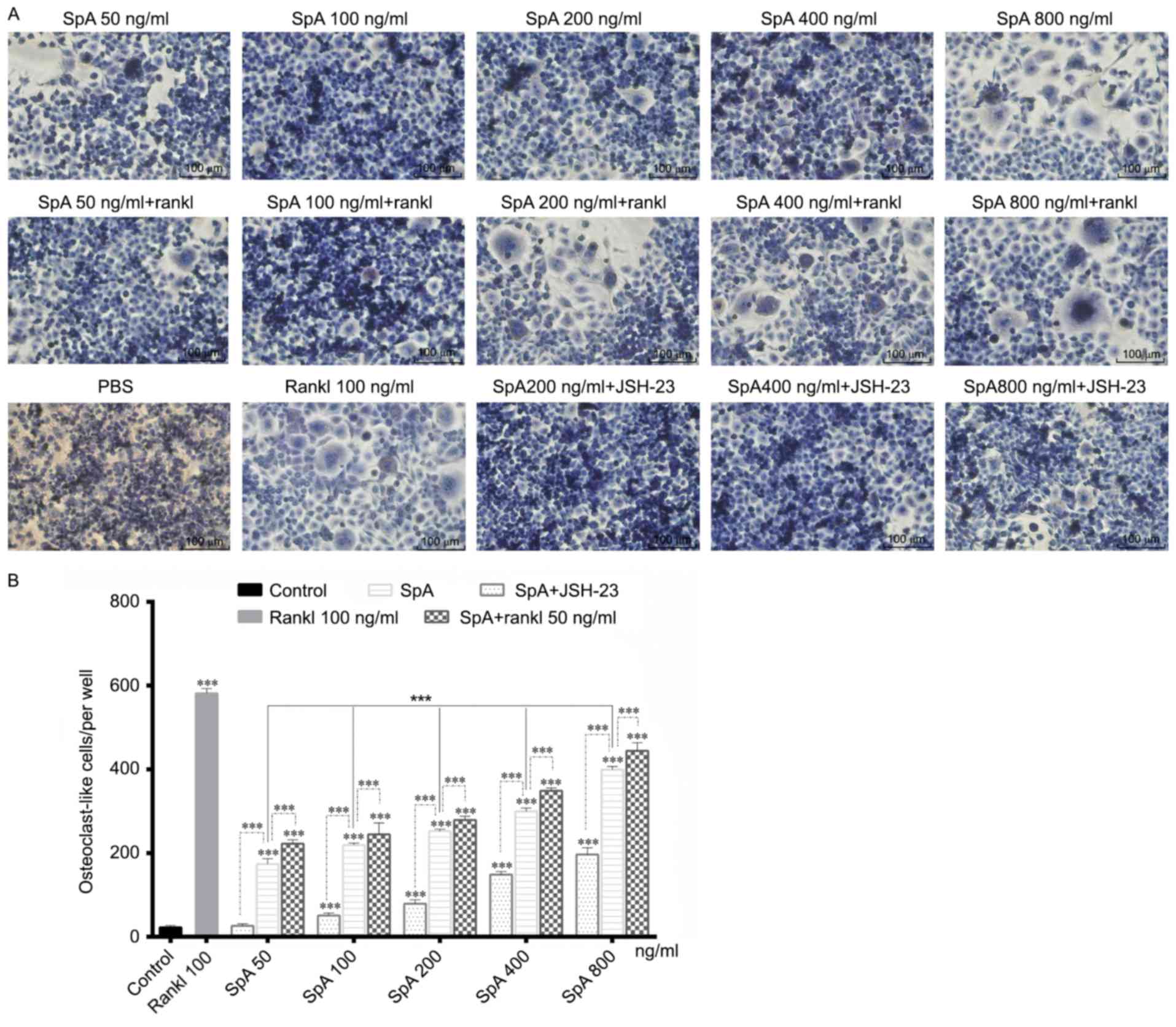
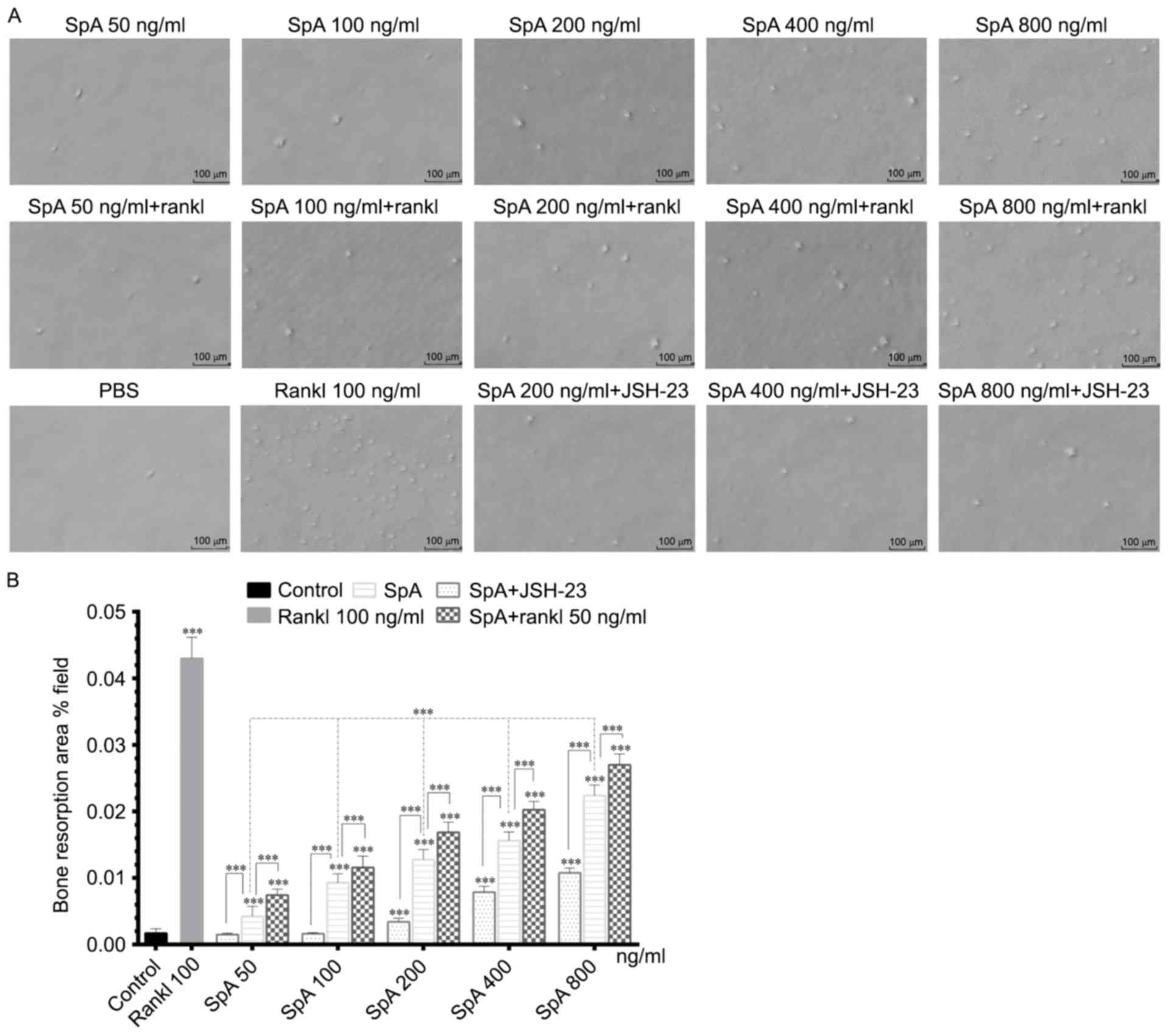
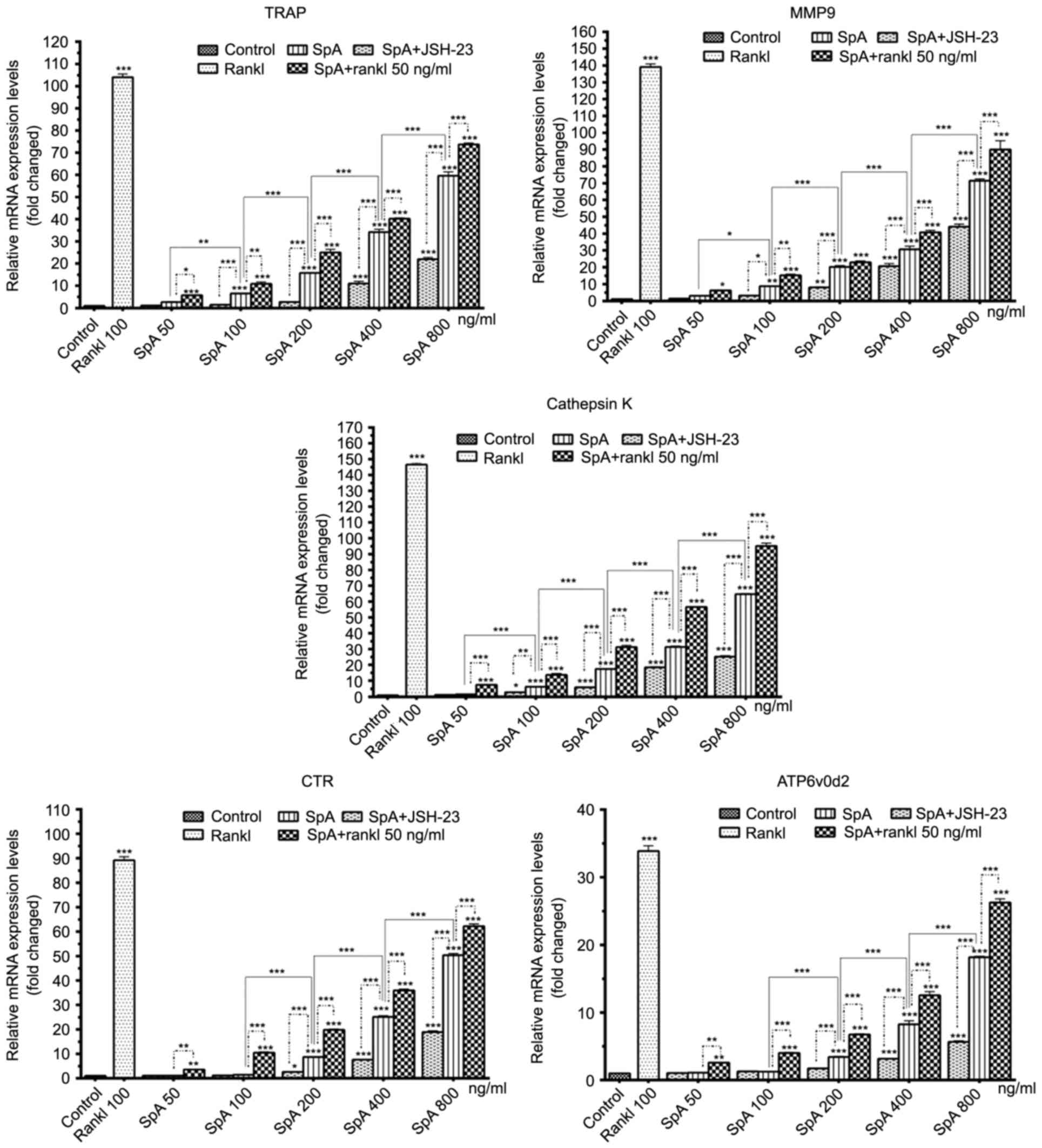
|
1
|
Jorge LS, Chueire AG and Rossit AR:
Osteomyelitis: A current challenge. Braz J Infect Dis. 14:310–315.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lew DP and Waldvogel FA: Osteomyelitis.
Lancet. 364:369–379. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Klosterhalfen B, Peters KM, Tons C,
Hauptmann S, Klein CL and Kirkpatrick CJ: Local and systemic
inflammatory mediator release in patients with acute and chronic
posttraumatic osteomyelitis. J Trauma. 40:372–378. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Parsons B and Strauss E: Surgical
management of chronic osteomyelitis. Am J Surg. 188 1A
Suppl:S57–S66. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Giannoudis PV and Atkins R: Management of
long-bone non-unions. Injury. 38 Suppl 2:S1–S2. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Feng X and McDonald JM: Disorders of bone
remodeling. Annu Rev Pathol. 6:121–145. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Taichman RS: Blood and bone: Two tissues
whose fates are intertwined to create the hematopoietic stem-cell
niche. Blood. 105:2631–2639. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Josse J, Velard F and Gangloff SC:
Staphylococcus aureus vs. Osteoblast: Relationship and consequences
in osteomyelitis. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 5:852015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fiedler T, Salamon A, Adam S, Herzmann N,
Taubenheim J and Peters K: Impact of bacteria and bacterial
components on osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of
adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Exp Cell Res.
319:2883–2892. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jin T, Zhu YL, Li J, Shi J, He XQ, Ding J
and Xu YQ: Staphylococcal protein A, Panton-Valentine leukocidin
and coagulase aggravate the bone loss and bone destruction in
osteomyelitis. Cell Physiol Biochem. 32:322–333. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ellington JK, Reilly SS, Ramp WK, Smeltzer
MS, Kellam JF and Hudson MC: Mechanisms of Staphylococcus aureus
invasion of cultured osteoblasts. Microb Pathog. 26:317–323. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hudson MC, Ramp WK, Nicholson NC, Williams
AS and Nousiainen MT: Internalization of Staphylococcus aureus by
cultured osteoblasts. Microb Pathog. 19:409–419. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rasigade JP, Trouillet-Assant S, Ferry T,
Diep BA, Sapin A, Lhoste Y, Ranfaing J, Badiou C, Benito Y, Bes M,
et al: PSMs of hypervirulent Staphylococcus aureus act as
intracellular toxins that kill infected osteoblasts. PLoS One.
8:e631762013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lau YS, Wang W, Sabokbar A, Simpson H,
Nair S, Henderson B, Berendt A and Athanasou NA: Staphylococcus
aureus capsular material promotes osteoclast formation. Injury. 37
Suppl 2:S41–S48. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Meghji S, Crean SJ, Hill PA, Sheikh M,
Nair SP, Heron K, Henderson B, Mawer EB and Harris M:
Surface-associated protein from staphylococcus aureus stimulates
osteoclastogenesis: Possible role in S. Aureus-induced bone
pathology. Br J Rheumatol. 37:1095–1101. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nair S, Song Y, Meghji S, Reddi K, Harris
M, Ross A, Poole S, Wilson M and Henderson B: Surface-associated
proteins from Staphylococcus aureus demonstrate potent bone
resorbing activity. J Bone Miner Res. 10:726–734. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Boyle WJ, Simonet WS and Lacey DL:
Osteoclast differentiation and activation. Nature. 423:337–342.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Woo KM, Kim HM and Ko JS: Macrophage
colony-stimulating factor promotes the survival of osteoclast
precursors by up-regulating Bcl-X(L). Exp Mol Med. 34:340–346.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fuller K, Owens JM, Jagger CJ, Wilson A,
Moss R and Chambers TJ: Macrophage colony-stimulating factor
stimulates survival and chemotactic behavior in isolated
osteoclasts. J Exp Med. 178:1733–1744. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Arai F, Miyamoto T, Ohneda O, Inada T,
Sudo T, Brasel K, Miyata T, Anderson DM and Suda T: Commitment and
differentiation of osteoclast precursor cells by the sequential
expression of c-Fms and receptor activator of nuclear factor kappaB
(RANK) receptors. J Exp Med. 190:1741–1754. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Soysa NS, Alles N, Aoki K and Ohya K:
Osteoclast formation and differentiation: An overview. J Med Dent
Sci. 59:65–74. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Nakashima T and Takayanagi H: New
regulation mechanisms of osteoclast differentiation. Ann N Y Acad
Sci. 1240:E13–E18. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shinohara M and Takayanagi H: Novel
osteoclast signaling mechanisms. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 5:67–72.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Peacock SJ, Moore CE, Justice A, Kantzanou
M, Story L, Mackie K, O'Neill G and Day NP: Virulent combinations
of adhesin and toxin genes in natural populations of Staphylococcus
aureus. Infect Immun. 70:4987–4996. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tuchscherr L, Heitmann V, Hussain M,
Viemann D, Roth J, von Eiff C, Peters G, Becker K and Löffler B:
Staphylococcus aureus small-colony variants are adapted phenotypes
for intracellular persistence. J Infect Dis. 202:1031–1040. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Claro T, Widaa A, McDonnell C, Foster TJ,
O'Brien FJ and Kerrigan SW: Staphylococcus aureus protein A binding
to osteoblast tumour necrosis factor receptor 1 results in
activation of nuclear factor kappa B and release of interleukin-6
in bone infection. Microbiology. 159:147–154. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Claro T, Widaa A, O'Seaghdha M, Miajlovic
H, Foster TJ, O'Brien FJ and Kerrigan SW: Staphylococcus aureus
protein A binds to osteoblasts and triggers signals that weaken
bone in osteomyelitis. PLoS One. 6:e187482011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hsu H, Lacey DL, Dunstan CR, Solovyev I,
Colombero A, Timms E, Tan HL, Elliott G, Kelley MJ, Sarosi I, et
al: Tumor necrosis factor receptor family member RANK mediates
osteoclast differentiation and activation induced by
osteoprotegerin ligand. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 96:3540–3545. 1999;
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yang J, Ryu YH, Yun CH and Han SH:
Impaired osteoclastogenesis by staphylococcal lipoteichoic acid
through Toll-like receptor 2 with partial involvement of MyD88. J
Leukoc Biol. 86:823–831. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chambers TJ, Revell PA, Fuller K and
Athanasou NA: Resorption of bone by isolated rabbit osteoclasts. J
Cell Sci. 66:383–399. 1984.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Suda T, Takahashi N, Udagawa N, Jimi E,
Gillespie MT and Martin TJ: Modulation of osteoclast
differentiation and function by the new members of the tumor
necrosis factor receptor and ligand families. Endocr Rev.
20:345–357. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Matsuzaki K, Udagawa N, Takahashi N,
Yamaguchi K, Yasuda H, Shima N, Morinaga T, Toyama Y, Yabe Y,
Higashio K and Suda T: Osteoclast differentiation factor (ODF)
induces osteoclast-like cell formation in human peripheral blood
mononuclear cell cultures. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 246:199–204.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Jimi E, Akiyama S, Tsurukai T, Okahashi N,
Kobayashi K, Udagawa N, Nishihara T, Takahashi N and Suda T:
Osteoclast differentiation factor acts as a multifunctional
regulator in murine osteoclast differentiation and function. J
Immunol. 163:434–442. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Moon JB, Kim JH, Kim K, Youn BU, Ko A, Lee
SY and Kim N: Akt induces osteoclast differentiation through
regulating the GSK3β/NFATc1 signaling cascade. J Immunol.
188:163–169. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
He Q, Zhang C, Wang L, Zhang P, Ma D, Lv J
and Liu F: Inflammatory signaling regulates hematopoietic stem and
progenitor cell emergence in vertebrates. Blood. 125:1098–1106.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
He L, Sun F, Wang Y, Zhu J, Fang J, Zhang
S, Yu Q, Gong Q, Ren B, Xiang X, et al: HMGB1 exacerbates
bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome via RAGE/NF-κB/HPSE signaling to
enhance latent TGF-β release from ECM. Am J Transl Res.
8:1971–1984. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Asagiri M, Sato K, Usami T, Ochi S,
Nishina H, Yoshida H, Morita I, Wagner EF, Mak TW, Serfling E and
Takayanagi H: Autoamplification of NFATc1 expression determines its
essential role in bone homeostasis. J Exp Med. 202:1261–1269. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Takayanagi H, Kim S, Koga T, Nishina H,
Isshiki M, Yoshida H, Saiura A, Isobe M, Yokochi T, Inoue J, et al:
Induction and activation of the transcription factor NFATc1 (NFAT2)
integrate RANKL signaling in terminal differentiation of
osteoclasts. Dev Cell. 3:889–901. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Collin-Osdoby P and Osdoby P:
RANKL-mediated osteoclast formation from murine RAW 264.7 cells.
Methods Mol Biol. 816:187–202. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Bertelli A Mendoza, Delpino MV, Lattar S,
Giai C, Llana MN, Sanjuan N, Cassat JE, Sordelli D and Gómez MI:
Staphylococcus aureus protein A enhances osteoclastogenesis via
TNFR1 and EGFR signaling. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1862:1975–1983.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ellingsen E, Morath S, Flo T, Schromm A,
Hartung T, Thiemermann C, Espevik T, Golenbock D, Foster D, Solberg
R, et al: Induction of cytokine production in human T cells and
monocytes by highly purified lipoteichoic acid: Involvement of
Toll-like receptors and CD14. Med Sci Monit. 8:BR149–BR156.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Takami M, Kim N, Rho J and Choi Y:
Stimulation by toll-like receptors inhibits osteoclast
differentiation. J Immunol. 169:1516–1523. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Gómez MI, O'Seaghdha M, Magargee M, Foster
TJ and Prince AS: Staphylococcus aureus protein A activates TNFR1
signaling through conserved IgG binding domains. J Biol Chem.
281:20190–20196. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Gómez MI, Seaghdha MO and Prince AS:
Staphylococcus aureus protein A activates TACE through
EGFR-dependent signaling. EMBO J. 26:701–709. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Cedergren L, Andersson R, Jansson B, Uhlén
M and Nilsson B: Mutational analysis of the interaction between
staphylococcal protein A and human IgG1. Protein Eng. 6:441–448.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Trouillet-Assant S, Gallet M, Nauroy P,
Rasigade JP, Flammier S, Parroche P, Marvel J, Ferry T, Vandenesch
F, Jurdic P and Laurent F: Dual impact of live Staphylococcus
aureus on the osteoclast lineage, leading to increased bone
resorption. J Infect Dis. 211:571–581. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zhao Q, Wang X, Liu Y, He A and Jia R:
NFATc1: Functions in osteoclasts. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
42:576–579. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Yi T, Lee HL, Cha JH, Ko SI, Kim HJ, Shin
HI, Woo KM, Ryoo HM, Kim GS and Baek JH: Epidermal growth factor
receptor regulates osteoclast differentiation and survival through
cross-talking with RANK signaling. J Cell Physiol. 217:409–422.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|