Introduction
Liver fibrosis is a frequent and chronic clinical
insult that induces wound-healing responses in the liver. It is
characterized by the excessive deposition of extracellular matrix
(ECM). Fibrosis is the predominant complication of chronic liver
diseases that are caused by viral infection, autoimmune hepatitis,
alcohol consumption, biliary obstruction and non-alcoholic fatty
liver disease (1,2). The fibrotic process is characterized
by the loss of parenchymal tissue and excessive accumulation of
ECM, followed by activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs)
(1,2).
The renin-angiotensin system (RAS) is a key mediator
of arterial blood pressure and body fluid homeostasis; it serves an
important role in the regulation of local hemodynamics in several
organs (3–6), and in the progression of chronic
liver diseases (3–6). In the RAS, angiotensin II (AT-II),
which is an octapeptide produced by the enzymatic cleavage of
angiotensin I by angiotensin I converting enzyme (ACE), serves a
central role in the activation and proliferation of HSCs into
activated HSCs (Ac-HSCs) (3).
Previous studies have demonstrated that pharmacological inhibition
of RAS effectively attenuates the development of liver fibrosis
(3–7). For instance, inhibitors of the
renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, including ACE inhibitors
(ACE-I), AT-II type I receptor blockers (ARBs), or selective
aldosterone blockers (SABs), which are commonly used as
antihypertensive agents, reportedly suppress the progression of
hepatic fibrosis (4).
A previous study demonstrated that AT-II induced the
expression of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 1 (TIMP-1),
which is a central molecule involved in fibrosis development
(7). TIMP-1 was induced in
Ac-HSCs, and this occurred via the AT-II type I receptor and
phosphokinase C. In addition, a number of previous studies have
indicated that the levels of periostin, a novel 90-kDa ECM protein,
were reported to increase in a rat model of cardiac fibrosis
development induced by continuous AT-II infusion, suggesting an
interaction between AT-II and periostin (8,9).
Periostin is secreted primarily from osteoblasts and fibroblasts
and is expressed under normal conditions in the bone and to a
lesser extent in the lungs, kidneys and heart valves of adult
mammals (10). The effect of AT-II
on periostin expression in hepatic fibrosis is currently unclear.
Therefore, the aim of the present study was to explore the role of
periostin in the development of liver fibrosis.
In the current study it was observed that periostin
expression, which was attenuated by ARB treatment, was
significantly and exclusively increased in Ac-HSCs in the
choline-deficient L-amino acid (CDAA)-defined diet-induced rat
model of liver fibrosis. The in vitro experiments indicated
that periostin augmented transforming growth factor (TGF) β1 and
collagen type 1 α1 (Col1a1) mRNA expression in human Ac-HSCs,
suggesting a potential role of an AT-II-periostin interaction in
liver fibrosis development.
Materials and methods
Animals and reagents
A total of 22 male Fischer 344 rats (age, 6 weeks;
weight, 100–120 g) were purchased from Japan SLC, Inc. (Hamamatsu,
Japan). Rats were individually housed under the following regulated
conditions: Controlled temperature (23.5±2°C) and relative humidity
(50±10%), with 10–15 air changes/h and 12-h light/dark cycles. The
losartan ARB was purchased from Merck Sharp and Dohme (Shanghai,
China). AT-II and conventional chemical agents were purchased from
Nacalai Tesque, Inc. (Kyoto, Japan). Human HSCs (LX2) were obtained
from the Japanese Collection of Research Bioresources Cell Bank
(JCRB, Osaka, Japan).
Animal treatment
The experimental period for all animal experiments
was 12 weeks. Rats were randomly divided into the following 3
groups: G1 (n=6), the negative control group where rats received a
choline-supplemented amino acid (CSAA) diet (Japan SLC, Inc.,
Shizuoka, Japan) and normal water; G2 (n=6), a liver fibrosis model
group where rats received a CDAA-defined diet (Japan SLC, Inc.) and
normal water; G3 (n=10), a liver fibrosis model group where rats
received a CDAA-defined diet and were administered with 30
mg/kg/day losartan in their drinking water. The animals were
allowed free access to food and water throughout the acclimation
and experimental periods. All rats were sacrificed at the end of
the experimental period, and blood was collected via cardiac
puncture. Serum markers, including albumin, bilirubin and alanine
aminotransferase (ALT) were measured by SRL, Inc. (Tokyo, Japan)
following sacrifice. Pieces of rat liver were cut from each of the
main 3 lobes and incubated in 10% formaldehyde for liver sectioning
as described below. The remainder of the liver was snap frozen in
liquid nitrogen and stored at −80°C for RNA and protein analysis.
All animal procedures were performed in accordance with the
recommendations for the proper care and use of laboratory animals
at Nara Medical University (Kashihara, Japan). The animal
experiments performed in the present study were approved by the
Animal Experimentation Committee of Nara Medical University.
Immunohistochemical staining and
semi-quantification
In all experimental groups, liver was fixed in 10%
formaldehyde for 24 h and embedded in paraffin. Liver sections were
cut at 5 µM thick from the liver block. The first liver section was
routinely stained with hematoxylin and eosin for histologic
examination and observed by light microscope (data not shown). A
separate tissue section was stained with Sirius red at Narabyouri
research Co. Ltd. (Nara, Japan) for the detection of liver
fibrosis. The remaining sections were used for immunohistochemical
staining with antibodies against α-smooth muscle actin (αSMA; Cat.
No. ab5694; Abcam, Tokyo, Japan) and periostin (Cat. No. ab14041;
Abcam). Antigen retrieval was performed with enzymatic antigen
retrieval solution (Cat. No. 415281; Nichirei Biosciences, Inc.,
Tokyo, Japan) for 15 min at 121°C. Endogenous peroxidase was
blocked using 0.3% H2O2 for 15 min at room
temperature, and then the sections were incubated overnight at 4°C
with each primary antibody or a rabbit IgG isotypic control (Cat.
No. ab27478; Abcam), diluted 1:100 in PBS + 4% goat serum (cat. No.
CL1200-100; Cosmo Bio Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan). The slides were
then incubated with MAX-PO Multi secondary antibody (cat. No.
424151; Nichirei Biosciences, Inc.) for 60 min at 37°C, and
subsequently stained with 3,3′-diaminobenzidine solution for 45 sec
at 37°C. Sections were then counterstained with hematoxylin
solution for 10 sec at room temperature. To quantify Sirius red,
periostin and αSMA positive areas, 10 independent fields
(magnification, ×100) were semi-quantified using ImageJ software
ver.1.45 (National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA) and the
mean ± standard deviation (SD) were calculated as described
previously (10).
Cell culture and WST-1 assay
Human LX2 HSCs (3×103 cells/200 µl) were
seeded into a 96-well plate and cultured in Dulbecco's Modified
Eagle's Medium (Nacalai Tesque, Inc.) supplemented with 10% fetal
bovine serum (Cat. No. FB-1365/500; Biosera, Kansas, USA) and 0.01%
penicillin-streptomycin-L-glutamine solution in a 5% CO2
humidified atmosphere at 37°C. The growth medium was refreshed
every other day. Cell viability was investigated using a WST-1
assay (cat. No. MK400; Premix WST-1 Cell Proliferation Assay
System; Takara Bio, Inc., Otsu, Japan) in the presence of periostin
and/or losartan, according to the manufacturer's protocol. Briefly,
cells were incubated for 24 h before the addition of media
containing periostin (0.1 or 1.0 µg/ml; Cat. No. C-60045; PromoCell
GmbH, Heidelberg, Germany) or Losartan (10 µM; Cat. No. 12353-04;
Nacalai Tesque, Inc.). Cells were incubated for a further 48 h and
then analyzed using a WST-1 assay. WST positivity was assessed
using a plate reader at 450 nm.
Reverse transcription quantitative
polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR)
Total RNA was extracted from liver tissue samples
and LX2 cells using an RNeasy RNA extraction kit (Qiagen GmbH,
Hilden, Germany). Total RNA (1 µg) was reverse transcribed to cDNA
using a High Capacity RNA-to-cDNA kit (Cat. No. 4387406; Applied
Biosystems; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc., Waltham, MA, USA)
according to the manufacturer's protocol. The mRNA levels of
TGF-β1, Col1a1 and periostin in the liver and HSC-LX2 cells were
measured by qPCR using a StepOnePlus™ Real-Time PCR system (Applied
Biosystems; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) as described previously
(11). The primer sequences were
as follows: GAPDH, forward, 5′-CGACCACTTTGTCAAGCTCA-3′, and
reverse, 5′-AGGGGAGATTCAGTGTGGTG-3′; TGF-β1, forward,
5′-CGGCAGCTGTACATTGACTT-3′, and reverse,
5′-AGCGCACGATCATGTTGGAC-3′; Col1a1, forward,
5′-AGCTCCTGGGCCTATCTGATGA-3′, and reverse,
5′-AATGGTGCTCTGAAACCCTGATG-3′; periostin, forward,
5′-GCCCAATTAGGCTTGGCATC-3′, and reverse,
5′-GTTTCCAGTATTTGCCCGTTGTA-3′. The thermal cycling conditions
employed were as described previously (11). Semi-quantification of the mRNA
expression level was performed according to the 2−ΔΔCq
method as described previously (12).
Expression of periostin in the
liver
The periostin protein levels in the liver tissues
from rats in each experimental group were measured using an
enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kit (Cat. No. SEH339Ra;
Cloud-Clone Corp., Katy, TX, USA) according to the manufacturer's
protocol. Protein was extracted from frozen liver using T-PER
Tissue Protein Extraction Regent with HALT™ protease inhibitor
cocktail (both from Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.). The protein
concentration in each sample were measured at 280 nm using a
NanoDrop™ Lite (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) and 100 µg protein
was used for the assessment of periostin protein levels.
Statistical analysis
Results were presented as the mean ± SD. To assess
the statistical significance of inter-group differences, one-way
analysis of variance was performed followed by Bonferroni's
multiple comparison tests using software EZR version 3.1.2
(13). Bartlett's test was
subsequently performed to determine the homology of variance.
P<0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically significant
difference.
Results
Clinical parameters
Information regarding the number of rats in each
group, their final body weights and relative liver weights in all
experimental groups is provided in Table I. CDAA-fed rats in groups G2 and G3
exhibited significantly higher serum ALT levels, lower body weights
and higher liver/body weight rates when compared with rats in the
G1 group. This is consistent with the results described previously
(11). Losartan-treated G3 rats
did not exhibit significantly different clinical parameters from
the rats in the G2 group (Table
I).
 | Table I.Physical and serum parameters of rats
in the three experimental groups. |
Table I.
Physical and serum parameters of rats
in the three experimental groups.
| Parameter | G1 | G2 | G3 |
|---|
| Number of rats | 6 | 6 | 10 |
| Body weight (g) |
325.1±8.5 |
239±10.5b |
244±16.4b |
| Liver/body weight
(%) |
9.9±0.05 |
11±0.09a |
11.1±0.05a |
| Alb (g/dl) |
4.4±0.1c |
4.1±0.1 |
4.3±0.1c |
| Total bilirubin
(mg/dl) |
0.06±0.006 |
0.13±0.01b |
0.12±0.03b |
| ALT (IU/l) |
57±10 |
245±50b |
300±31b |
Losartan reduces liver fibrosis
development
The effects of clinically comparable doses of
losartan on the development of liver fibrosis were investigated
(3). The CDAA diet induced
extensive fibrosis and severe steatohepatitis (Fig. 1). Treatment of rats in the G3 group
with losartan resulted in significant attenuation of liver fibrosis
when compared with the losartan-untreated G2 group (P<0.01);
however the level of steatosis was unaffected (Fig. 1). No liver fibrosis development was
observed in the CSAA diet-fed control rats in the G1 group
(Fig. 1). Immunohistochemical
analysis of αSMA was performed to confirm the inhibitory effect of
losartan on HSC activation during the development of liver
fibrosis. The number of Ac-HSCs, which express αSMA (1,2),
were significantly reduced in the livers of the losartan-treated
rats in the G3 group when compared with untreated rats in the G2
group (P<0.01; Fig. 2).
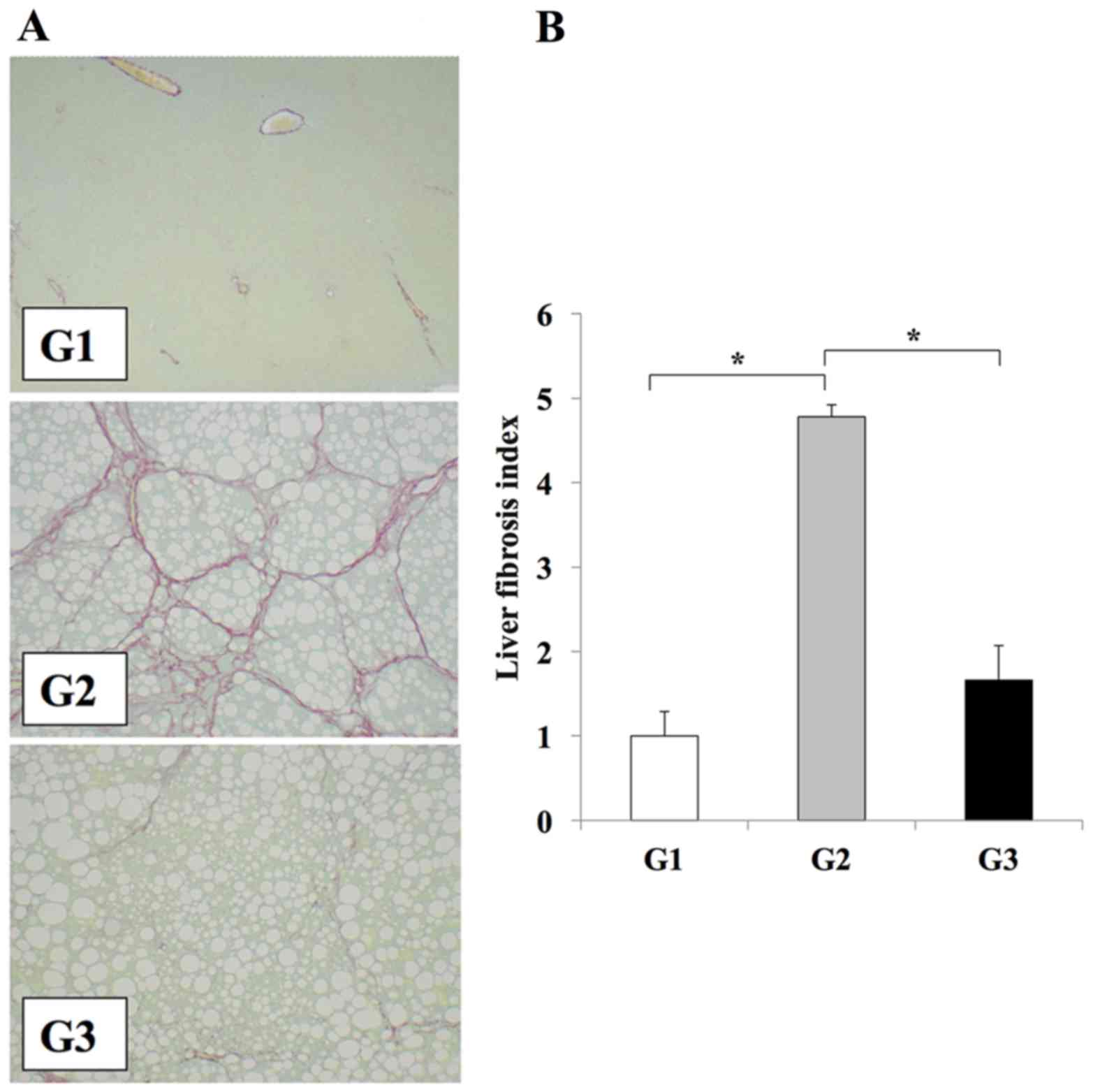 | Figure 1.Losartan reduces liver fibrosis in
rats. (A) Representative photomicrographs of fibrosis in liver
sections from rats in the G1, G2 and G3 experimental groups, as
determined by Sirius red staining (magnification, ×100). Fibrosis
is not observed liver tissues from rats in the G1 group; however,
extensive fibrosis accompanied by severe steatosis is evidence in
rats from the G2 group. A reduction in liver fibrosis is observed
in rats from the G3 group when compared with the G2 group. (B)
Semi-quantitative analysis of the area of liver fibrosis among the
different experimental groups. The results are presented as the
mean ± standard deviation (G1 and G2, n=6; G3, n=10). *P<0.01,
as indicated. G1, choline-supplemented amino acid diet-fed control
rats; G2, CDAA diet-fed rats; G3, losartan-treated CDAA diet-fed
rats; CDAA, choline-deficient L-amino acid. |
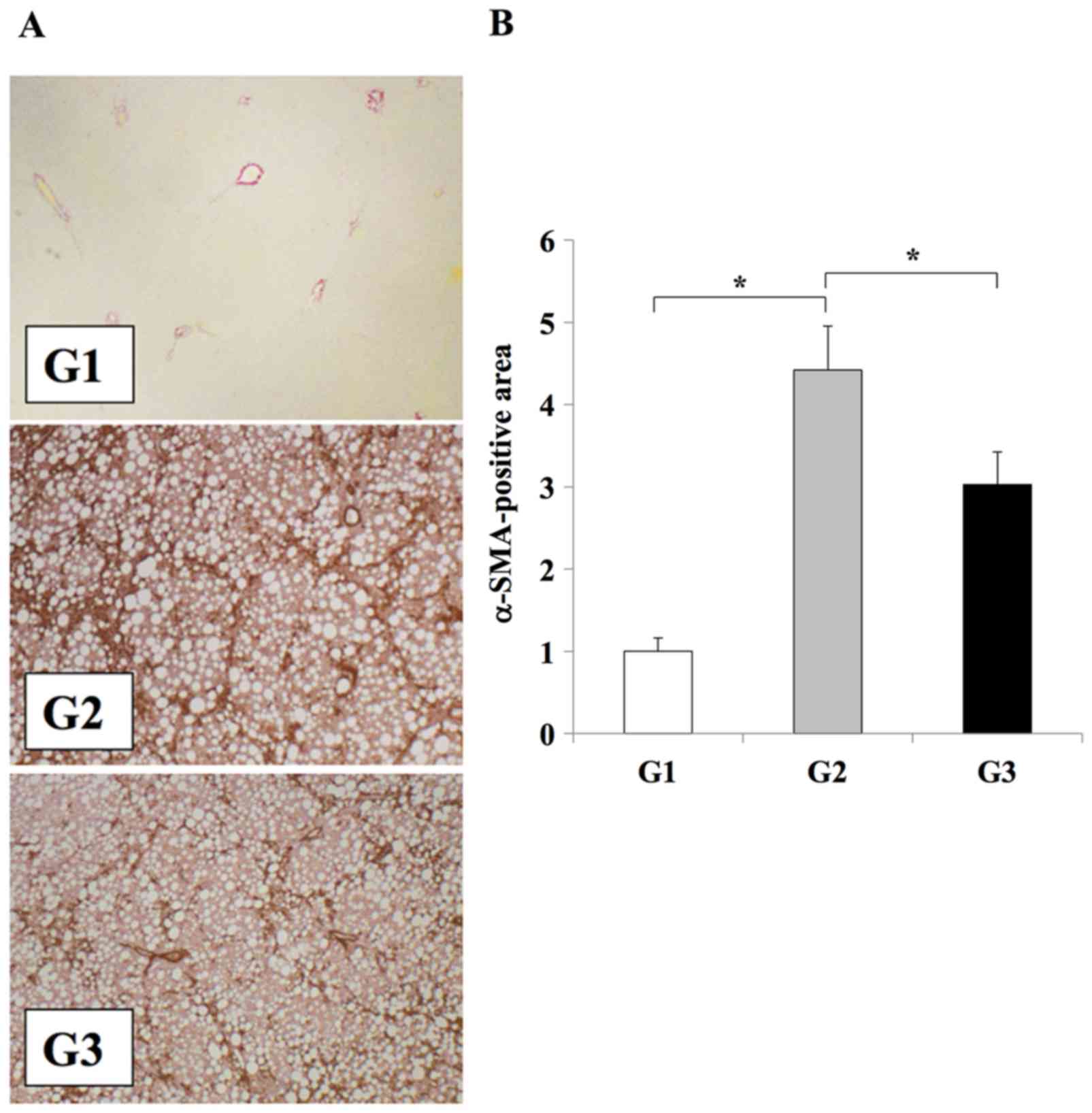 | Figure 2.Effect of losartan on Ac-HSC expansion
during liver fibrosis development. (A) Immunohistochemical analysis
αSMA expression in the liver tissues of rats from the G1, G2 or G3
experimental groups (magnification, ×100). (B) Semi-quantification
of αSMA expression in the liver. The results are presented as the
mean ± standard deviation (G1 and G2, n=6; G3, n=10). *P<0.01,
as indicated. Ac-HSC, activated hepatic stellate cells; αSMA, α
smooth muscle actin; G1, choline-supplemented amino acid diet-fed
control rats; G2, CDAA diet-fed rats; G3, losartan-treated CDAA
diet-fed rats; CDAA, choline-deficient L-amino acid. |
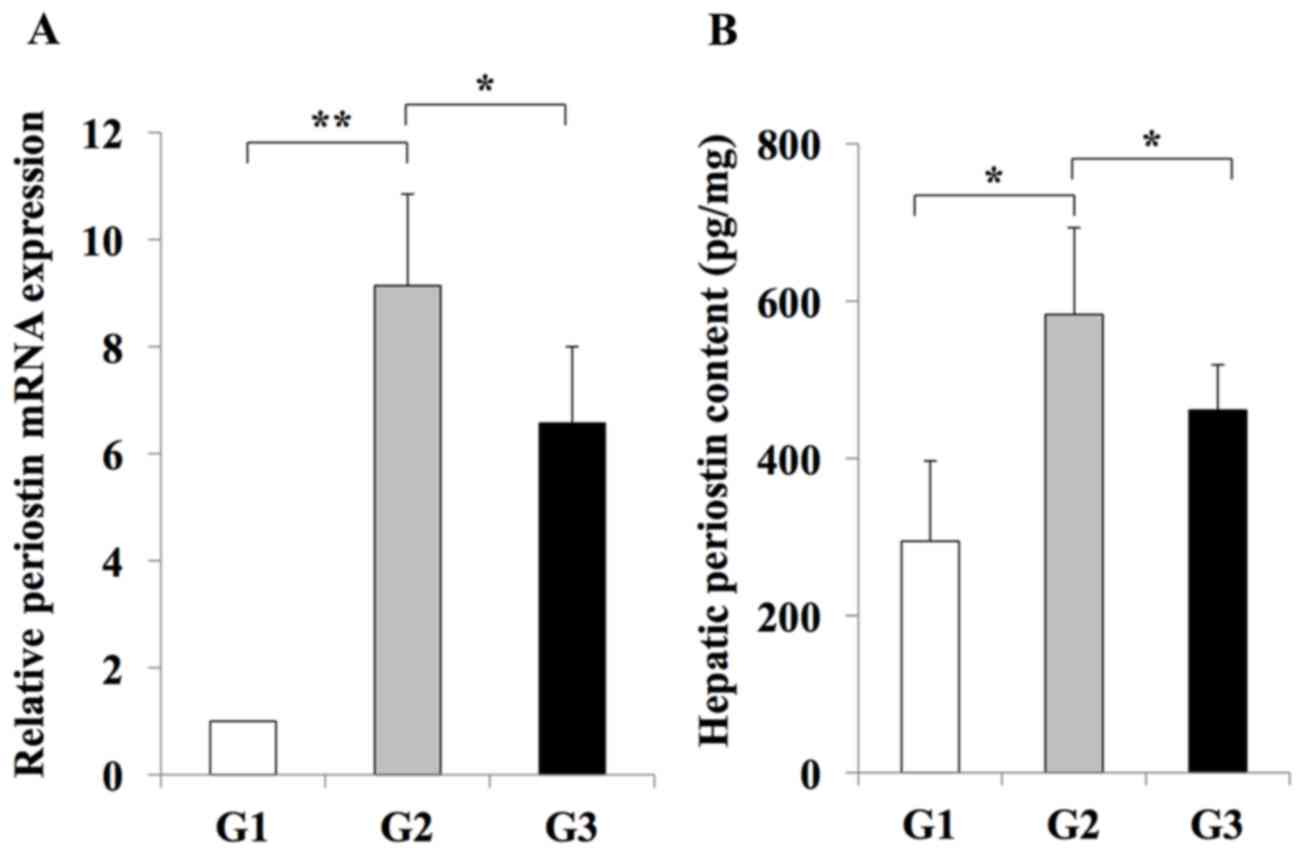
Immunohistochemistry was used to examine the levels
of periostin in the experimental models, in order to investigate
the association between liver fibrosis development and periostin.
The CDAA diet significantly induced periostin expression along the
fibrotic septa when compared with the CSAA diet (Fig. 3). Compared with rats in the G2
group, those in the G3 group exhibited a significant reduction in
periostin expression in the regions of fibrosis (P<0.05;
Fig. 3). No periostin expression
was observed in rats from the G1 group.
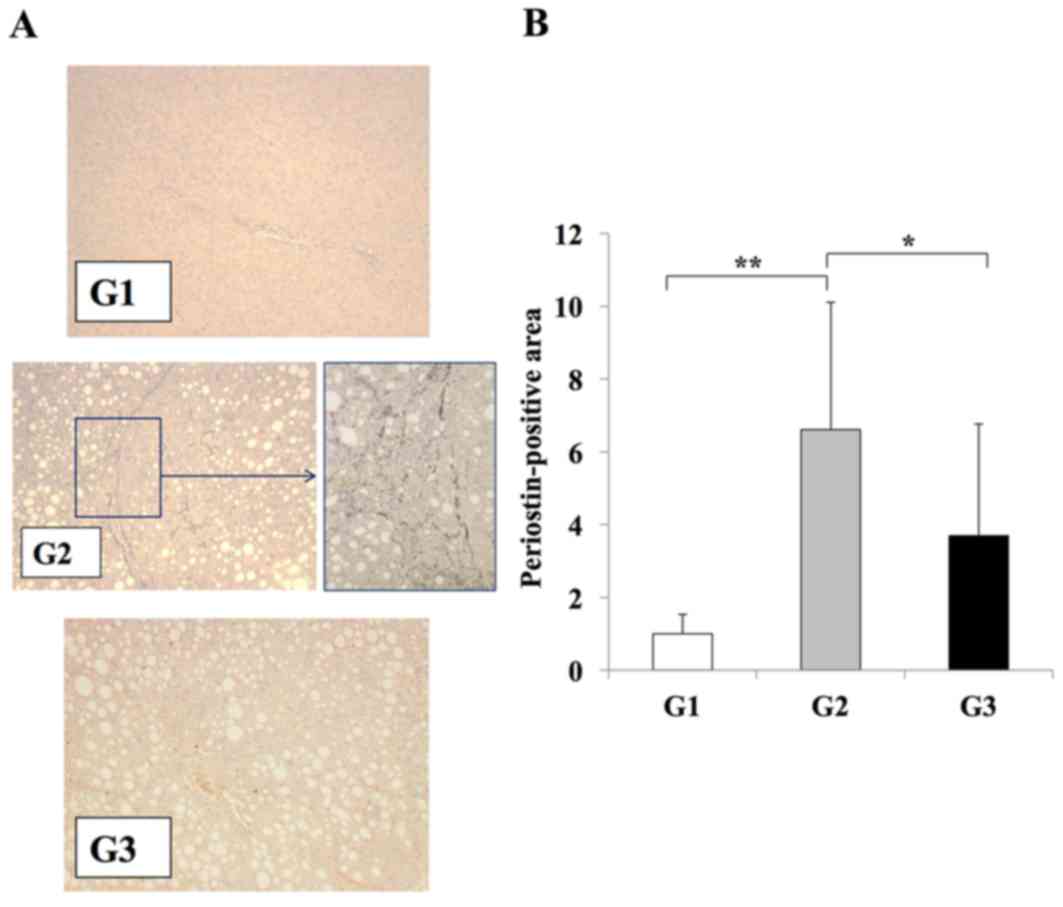 | Figure 3.Effects of losartan on periostin
expression during liver fibrosis. (A) Immunohistochemical analysis
of periostin expression in the liver tissues of rats from G1, G2
and G3 experimental groups (magnification: G1, G3, ×100; G2, ×100
(left) and ×400 (right) demonstrated that periostin expression was
induced in G2 group rats exclusively along the fibrotic septa. (B)
Semi-quantification of the periostin-positive area using an image
analyzer system. A significant reduction in periostin expression
was observed in the liver tissues of rats in the G3 group when
compared with the G2 group, whereas periostin expression was weak
in rat liver tissues from the G1 group. The results are presented
as the mean ± standard deviation (G1 and G2, n=6; G3, n=10).
*P<0.05 and **P<0.01, as indicated. G1, choline-supplemented
amino acid diet-fed control rats; G2, CDAA diet-fed rats; G3,
losartan-treated CDAA diet-fed rats; CDAA, choline-deficient
L-amino acid. |
RT-qPCR analysis indicated an inhibitory effect of
losartan on the expansion of Ac-HSCs. This inhibitory effect was
demonstrated by a decrease in the mRNA expression levels of
Tgfb1 and Col1a1, which are representative markers of
Ac-HSC expansion and directly correlate with liver fibrosis
development (3) (Fig. 4). In addition, it was revealed that
hepatic periostin RNA and protein levels were significantly
increased in rats from the G2 group when compared with the G1 group
(Fig. 5). By contrast, rats in the
G3 group exhibited a significant reduction in periostin RNA and
protein levels when compared with rats in the G2 group (Fig. 5). These results indicated that
periostin expression may be induced during liver fibrosis, and this
effect is inhibited by treatment with the losartan ARB.
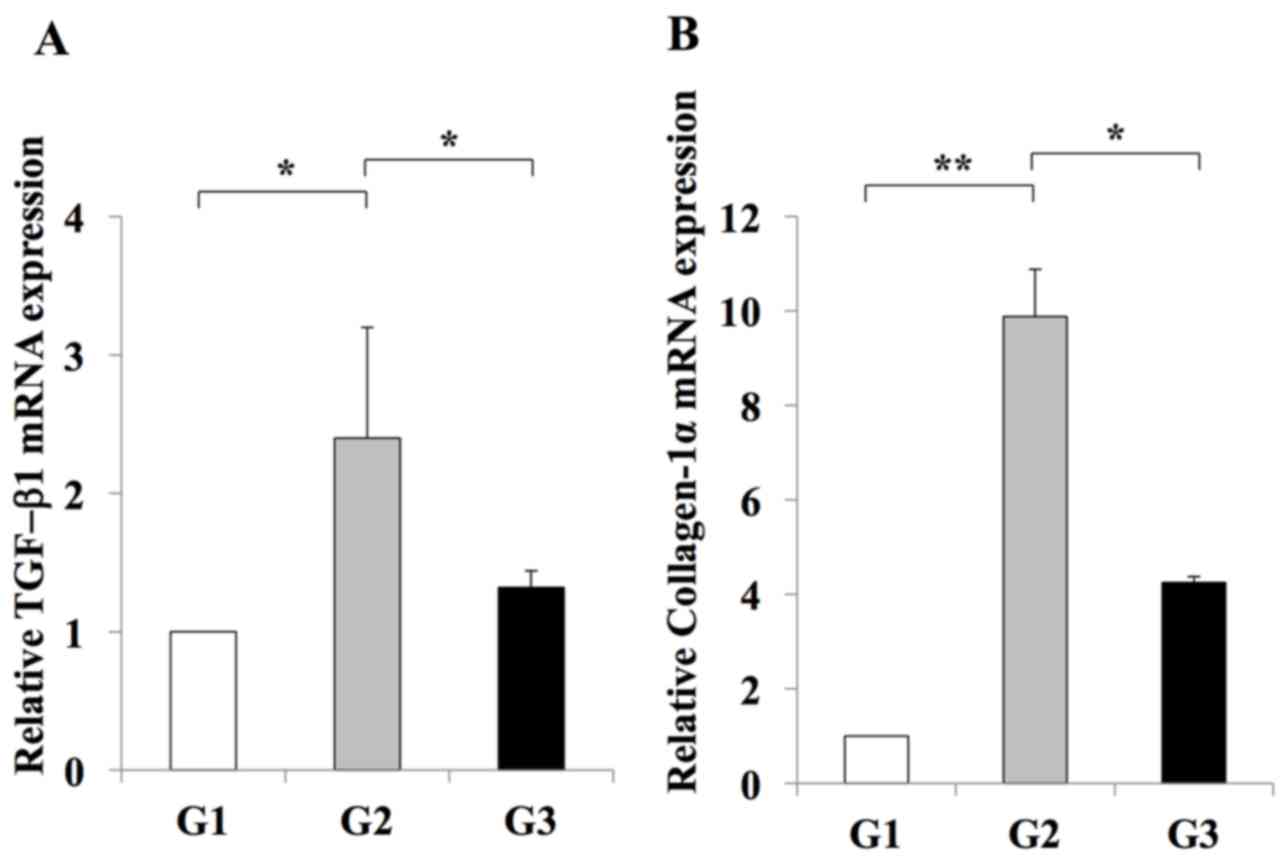 | Figure 4.Effect of losartan on the hepatic
expression of profibrotic genes. The expression levels of (A) TGF-β
and (B) Col1a1 mRNA in the livers of rats in the G2 group were
significantly increased when compared with those in the G1 group.
Treatment with 30 mg/kg/day losartan significantly suppressed the
expression of TGF-β1 and Col1a1 in the liver. The results are
presented as the mean ± standard deviation (G1 and G2, n=6; G3,
n=10). *P<0.05 and **P<0.01, as indicated. G1,
choline-supplemented amino acid diet-fed control rats; G2, CDAA
diet-fed rats; G3, losartan-treated CDAA diet-fed rats; CDAA,
choline-deficient L-amino acid; CDAA, choline-deficient L-amino
acid; TGF, transforming growth factor; Col1a1, collagen type 1
α1. |
In vitro analysis of the effects of
periostin on Ac-HSCs
To further examine the possible involvement of
periostin in liver fibrosis, in vitro assays were performed
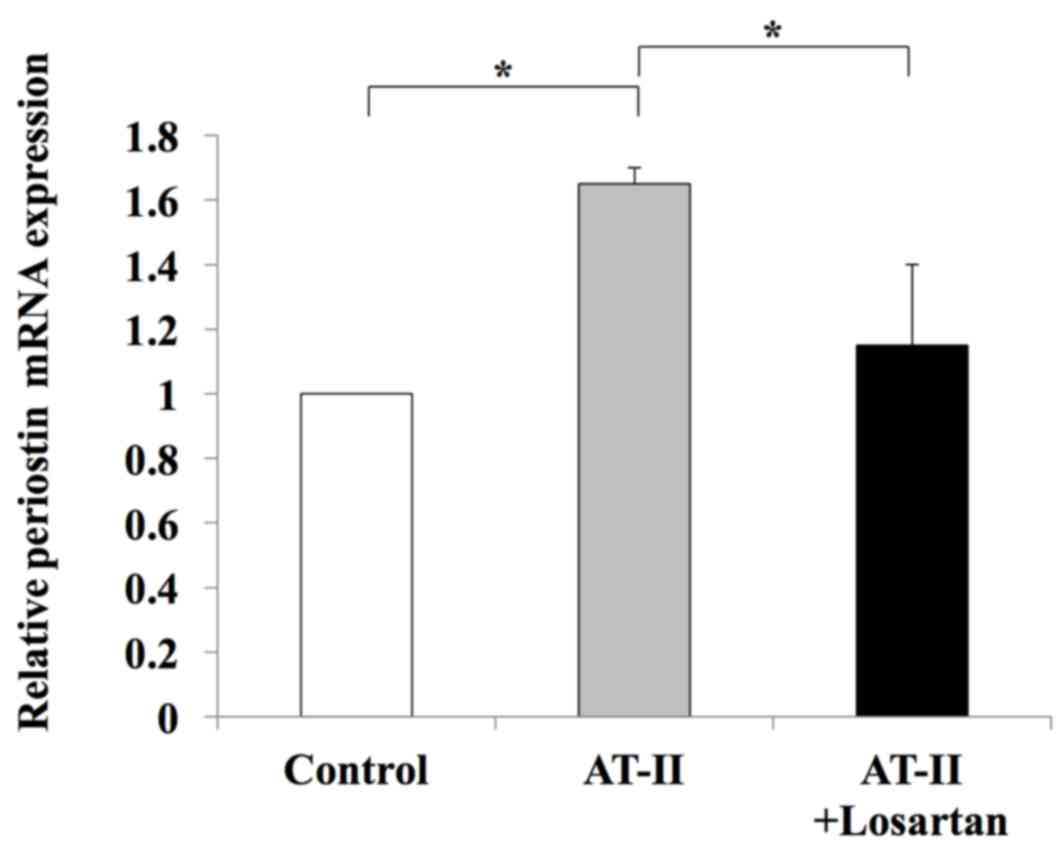
using the human LX2 Ac-HSC line. Periostin mRNA expression was
confirmed in LX2 cells (data not shown). The mRNA expression levels
of periostin in LX2 cells was significantly enhanced following
treatment with 1 µM AT-II; however, this effect was significantly
attenuated by supplementation with losartan (Fig. 6). This suggests that the RAS
signaling pathway may positively regulate periostin expression. The
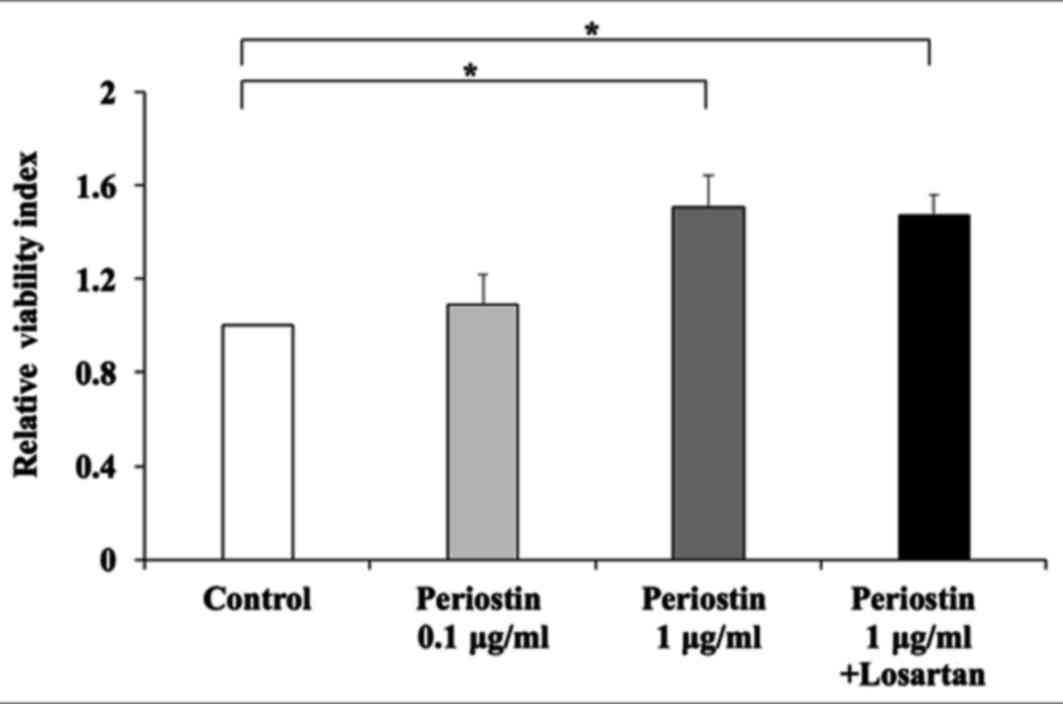
direct effect of periostin on the viability of HSCs was then
investigated. Exposure to 1 µg/ml periostin significantly induced
the viability of LX2 cells (Fig.
6). Notably, this was not inhibited by treatment with losartan
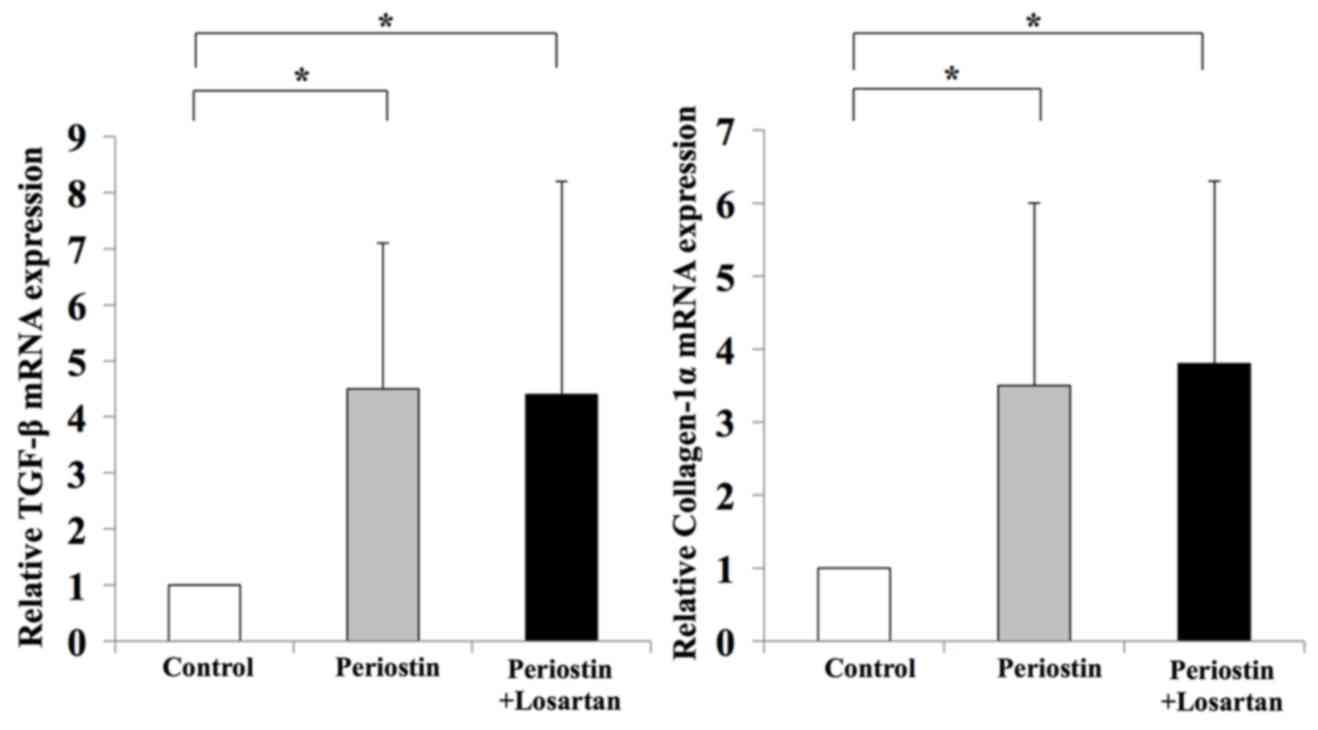
(Fig. 7). In addition, periostin
significantly promoted the expression of TGF-β1 and Col1a1 in LX2
cells when compared with controls; however, treatment with losartan
demonstrated no significant effect on the expression levels of
these genes when compared with periostin-only treated cells
(Fig. 8). These results suggest
that AT-II may positively regulate periostin expression in HSCs,
and periostin may serve an important autocrine role in the
viability and activation of HSCs.
Discussion
Periostin, also known as osteoblast-specific factor
2, is a recently characterized matricellular protein that binds to
ECM components, such as type I collagen and fibronectin, and has
been implicated in collagen fibrosis (14). This protein transmits signals from
the ECM to cellular receptors to regulate a number of cellular
functions, including cell adhesion, proliferation migration and
tissue angiogenesis (8).
The potential involvement of AT-II-induced periostin
in fibrosis development was first demonstrated in the heart
(15). Cardiac fibroblasts, the
predominant secretory cells that produce ECM, are important targets
of AT-II and are key mediators of cardiac fibrosis (16). Continuous AT-II infusion in a rat
cardiac fibrosis model demonstrated extensive interstitial fibrosis
and the abundant accumulation of periostin within the interstitial
space, as determined by immunofluorescence analysis (9). In cultured adult rat cardiac
fibroblasts, AT-II induced the expression of periostin mRNA and
protein via the Ras/p38-mitogen activated protein kinase/cyclic
adenosine monophosphate responsive element binding protein 1 and
extracellular signal-related kinase 1/2-TGF-β1 signaling pathways
(9,17). Taken together, these results
suggest the involvement of an AT-II/periostin signaling pathway in
cardiac fibrosis.
A recent report demonstrated an upregulation of
periostin in cirrhotic liver tissues and activated HSCs, which
suggested that periostin may be a potential biomarker for hepatic
fibrosis (18). In addition,
previous studies have demonstrated a possible involvement of AT-II
in HSC-mediated liver fibrosis development (3–6,19). A
previous report demonstrated that AT-II directly stimulated HSC
proliferation in vitro, and RAS inhibitors, including ACE-I,
ARB and SAB, attenuated hepatic fibrosis and suppressed the
proliferation of Ac-HSCs (3–6,19).
These medications are commonly used antihypertensive agents that
reportedly suppress the progression of hepatic fibrosis. Bataller
et al (20) demonstrated
that activated but not quiescent HSCs produce AT-II, which
stimulate HSC proliferation in an autocrine manner. However, the
association between RAS and periostin in liver fibrosis development
has not yet been elucidated. The current study demonstrated that
inhibition of periostin with losartan markedly inhibited the
development of liver fibrosis, as evidenced by a reduced number of
Ac-HSCs in the liver. These results suggested a possible
interaction between the RAS and periostin in liver fibrosis
development.
In the current study, in vitro analysis of
LX2 cells demonstrated that AT-II was able to induce periostin
expression in Ac-HSCs, and this may serve a central role in liver
fibrosis. In addition, these results suggested that Ac-HSCs may be
a source of periostin. In addition, periostin treatment improved
viability and induced the expression of profibrotic genes TGF-β1
and Col1a1 in Ac-HSCs, which supports the hypothesis that periostin
directly affects Ac-HSCs by augmenting liver fibrosis. Notably,
this direct effect of periostin was not reversed by inhibition of
the RAS with losartan. The authors hypothesize that the RAS may
partially induce periostin expression in Ac-HSCs in an autocrine
manner. Therefore, antifibrotic treatments that target periostin
directly may provide an additional anti-fibrotic effect on ARB
treatment. Notably, periostin has recently been investigated as a
novel target for anti-fibrotic therapy in the liver (21,22).
Previous reports have demonstrated that loss of periostin in mice
reduced the development of experimental liver fibrosis induced by a
methionine-choline-deficient diet or treatment with carbon
tetrachloride (21,22). In addition, small interfering
RNA-induced loss of periostin reduced the proliferation and
expression of Col1a1 and αSMA mRNA in HSCs following treatment with
TGF-β (18). These observations
indicate the positive involvement of periostin on HSC activation
and proliferation, which serves a central role in liver fibrosis.
In addition, a successful anti-fibrotic treatment targeting a
receptor of periostin (αV integrin), has been reported to be a
potential alternative to anti-periostin treatment (23). Further examinations are required to
discover novel anti-fibrotic treatment modalities targeting
periostin.
In conclusion, the present study demonstrated that
AT-II-induced periostin serves an important role in liver fibrosis
development. Hepatic periostin expression was significantly
attenuated in parallel with hepatic fibrosis development by a
pharmacological blockade of the AT-II signal. These experiments
indicated that AT-II can augment the activity of HSCs by the
expression of TGF-β1 and collagen type I α1 via periostin
expression, which may be crucial for liver fibrosis. The results of
the present study suggest that periostin may function as a novel
regulator of HSC activation, and targeting periostin may therefore
present a useful strategy for the treatment of liver fibrosis.
Further studies, which may employ a genetically altered periostin
in a rodent liver fibrosis model, would allow further investigation
into the role of periostin in the development of liver
fibrosis.
Glossary
Abbreviations
Abbreviations:
|
AT-II
|
angiotensin II
|
|
TGF-β
|
transforming growth factor-β
|
|
CDAA
|
choline-deficient L-amino-acid
|
|
ARB
|
angiotensin II type 1 receptor
blocker
|
|
Col1A1
|
collagen type I α1
|
|
ECM
|
extracellular matrix
|
|
HSC
|
hepatic stellate cells
|
|
ACE
|
angiotensin I converting enzyme
|
|
Ac-HSC
|
activated hepatic stellate cell
|
|
CSAA
|
choline-supplemented amino acid
|
|
ALT
|
alanine aminotransferase
|
|
RT-qPCR
|
reverse transcription quantitative
polymerase chain reaction
|
References
|
1
|
Friedman SL: Mechanisms of hepatic
fibrogenesis. Gastroenterology. 134:1655–1669. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bataller R and Brenner DA: Liver fibrosis.
J Clin Invest. 115:209–218. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yoshiji H, Kuriyama S, Yoshii J, Ikenaka
Y, Noguchi R, Nakatani T, Tsujinoue H and Fukui H: Angiotensin-II
type 1 receptor interaction is a major regulator for liver fibrosis
development in rats. Hepatology. 34:745–750. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Debernardi-Venon W, Martini S, Biasi F,
Vizio B, Termine A, Poli G, Brunello F, Alessandria C, Bonardi R,
Saracco G, et al: AT1 receptor antagonist Candesartan in selected
cirrhotic patients: Effect on portal pressure and liver fibrosis
markers. J Hepatol. 46:1026–1033. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Matono T, Koda M, Tokunaga S, Sugihara T,
Ueki M and Murawaki Y: The effects of the selective
mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist eplerenone on hepatic
fibrosis induced by bile duct ligation in rat. Int J Mol Med.
25:875–882. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Noguchi R, Yoshiji H, Ikenaka Y, Kaji K,
Shirai Y, Aihara Y, Yamazaki M, Namisaki T, Kitade M, Yoshii J, et
al: Selective aldosterone blocker ameliorates the progression of
non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in rats. Int J Mol Med. 26:407–413.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yoshiji H, Kuriyama S, Yoshii J, Ikenaka
Y, Noguchi R, Yanase K, Namisaki T, Yamazaki M, Tsujinoue H, Imazu
H and Fukui H: Angiotensin-II induces the tissue inhibitor of
metalloproteinases-1 through the protein kinase-C signaling pathway
in rat liver fibrosis development. Hepatol Res. 27:51–56. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Horiuchi K, Amizuka N, Takeshita S,
Takamatsu H, Katsuura M, Ozawa H, Toyama Y, Bonewald LF and Kudo A:
Identification and characterization of a novel protein, periostin,
with restricted expression to periosteum and periodontal ligament
and increased expression by transforming growth factor beta. J Bone
Miner Res. 14:1239–1249. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li L, Fan D, Wang C, Wang JY, Cui XB, Wu
D, Zhou Y and Wu LL: Angiotensin II increases periostin expression
via Ras/p38 MAPK/CREB and ERK1/2/TGF-β1 pathways in cardiac
fibroblasts. Cardiovasc Res. 91:80–89. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yoshiji H, Kuriyama S, Kawata M, Yoshii J,
Ikenaka Y, Noguchi R, Nakatani T, Tsujinoue H and Fukui H: The
angiotensin-I-converting enzyme inhibitor perindopril suppresses
tumor growth and angiogenesis: Possible role of the vascular
endothelial growth factor. Clin Cancer Res. 7:1073–1078.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kaji K, Yoshiji H, Ikenaka Y, Noguchi R,
Aihara Y, Douhara A, Moriya K, Kawaratani H, Shirai Y, Yoshii J, et
al: Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor attenuates hepatic fibrosis
via suppression of activated hepatic stellate cell in rats. J
Gastroenterol. 49:481–491. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kanda Y: Investigation of the freely
available easy-to use software ‘EZR’ for medical statics. Bone
Marrow Transplant. 48:452–458. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kudo A: Periostin in fibrillogenesis for
tissue regeneration: Periostin actions inside and outside the cell.
Cell Mol Life Sci. 68:3201–3207. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Snider P, Hinton RB, Moreno-Rodriguez RA,
Wang J, Rogers R, Lindsley A, Li F, Ingram DA, Menick D, Field L,
et al: Periostin is required for maturation and extracellular
matrix stabilization of noncardiomyocyte lineages of the heart.
Circ Res. 102:752–760. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Brown RD, Ambler SK, Mitchell MD and Long
CS: The cardiac fibroblast: Therapeutic target in myocardial
remodeling and failure. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 45:657–687.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Iekushi K, Taniyama Y, Azuma J, Katsuragi
N, Dosaka N, Sanada F, Koibuchi N, Nagao K, Ogihara T and Morishita
R: Novel mechanisms of valsartan on the treatment of acute
myocardial infarction through inhibition of the antiadhesion
molecule periostin. Hypertension. 49:1409–1414. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hong L, Shejiao D, Fenrong C, Gang Z and
Lei D: Periostin down-regulation attenuates the pro-fibrogenic
response of hepatic stellate cells induced by TGF-β1. J Cell Mol
Med. 19:2462–2468. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Noguchi R, Yoshiji H, Ikenaka Y, Kaji K,
Aihara Y, Shirai Y, Namisaki T, Kitade M, Douhara A, Moriya K and
Fukui H: Dual blockade of angiotensin-II and aldosterone suppresses
the progression of a non-diabetic rat model of steatohepatitis.
Hepatol Res. 43:765–774. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bataller R, Sancho-Bru P, Gines P, Lora
JM, Al-Garawi A, Solé M, Colmenero J, Nicolás JM, Jiménez W, Weich
N, et al: Activated human hepatic stellate cells express the
renin-angiotensin system and synthesize angiotensin II.
Gastroenterology. 125:117–125. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li Y, Wu S, Xiong S and Ouyang G:
Deficiency of periostin protects mice against
methionine-choline-deficient diet-induced non-alcoholic
steatohepatitis. J Hepatol. 62:495–497. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Huang Y, Liu W, Xiao H, Maitikabili A, Lin
Q, Wu T, Huang Z, Nicolás JM, Jiménez W and Weich N: Matricellular
protein periostin contributes to hepatic inflammation and fibrosis.
Am J Pathol. 185:786–797. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Henderson NC, Arnold TD, Katamura Y,
Giacomini MM, Rodriguez JD, McCarty JH, Pellicoro A, Raschperger E,
Betsholtz C, Ruminski PG, et al: Targeting of αv integrin
identifies a core molecular pathway that regulates fibrosis in
several organs. Nat Med. 19:1617–1624. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|