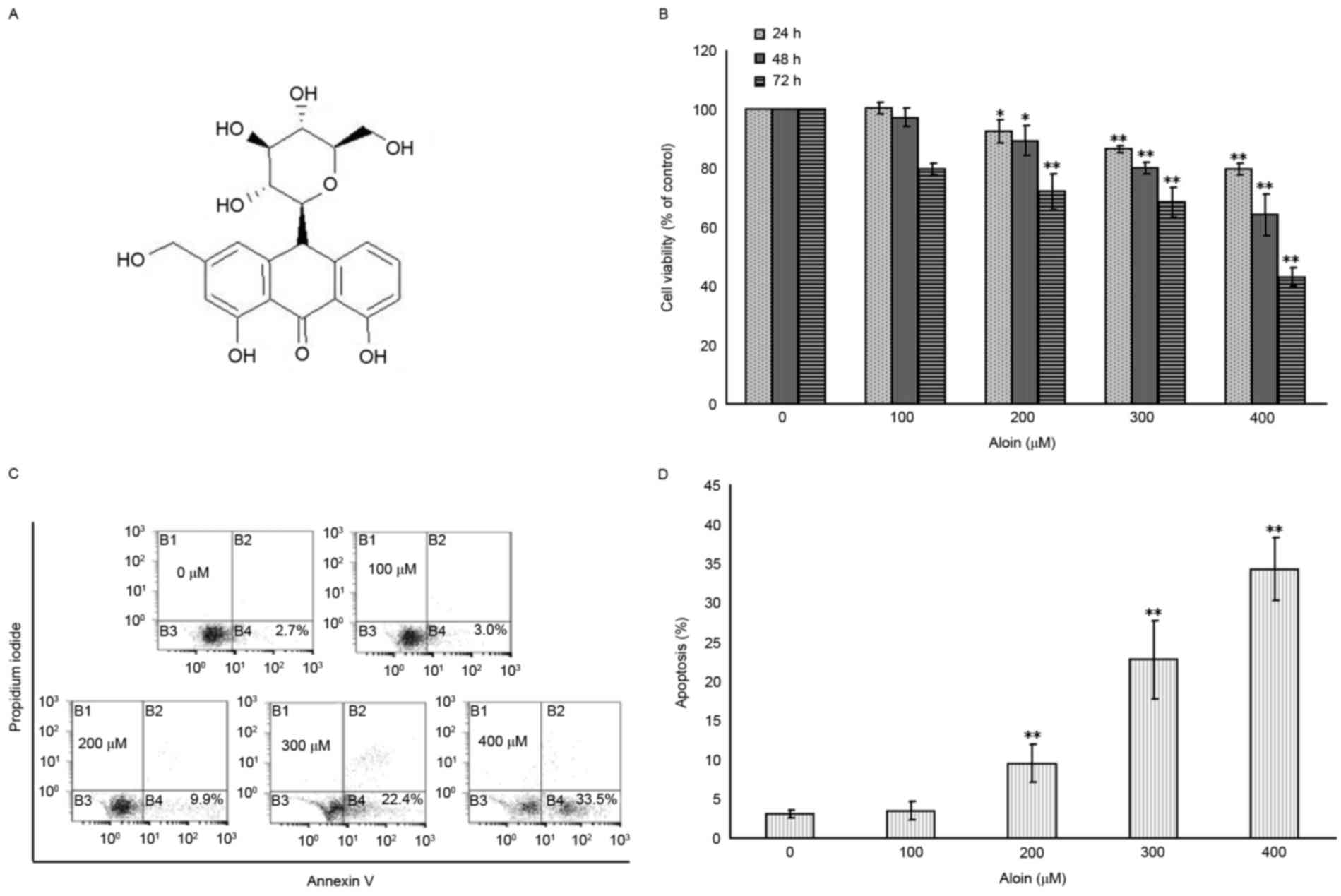
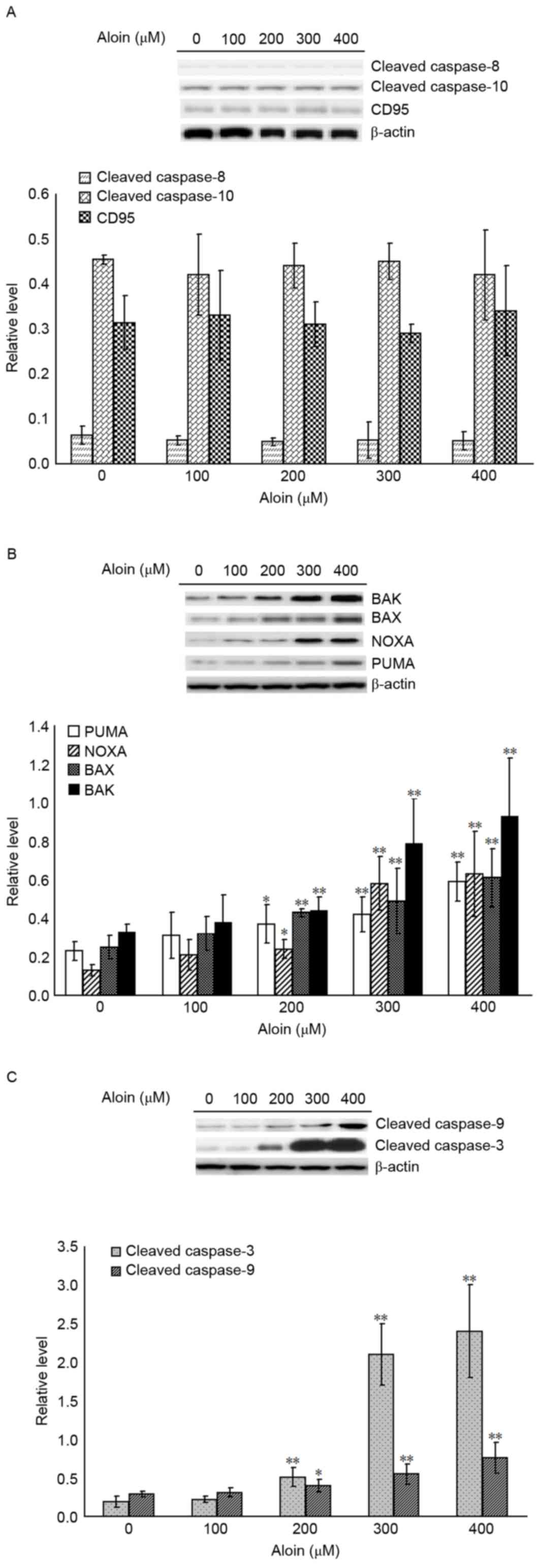
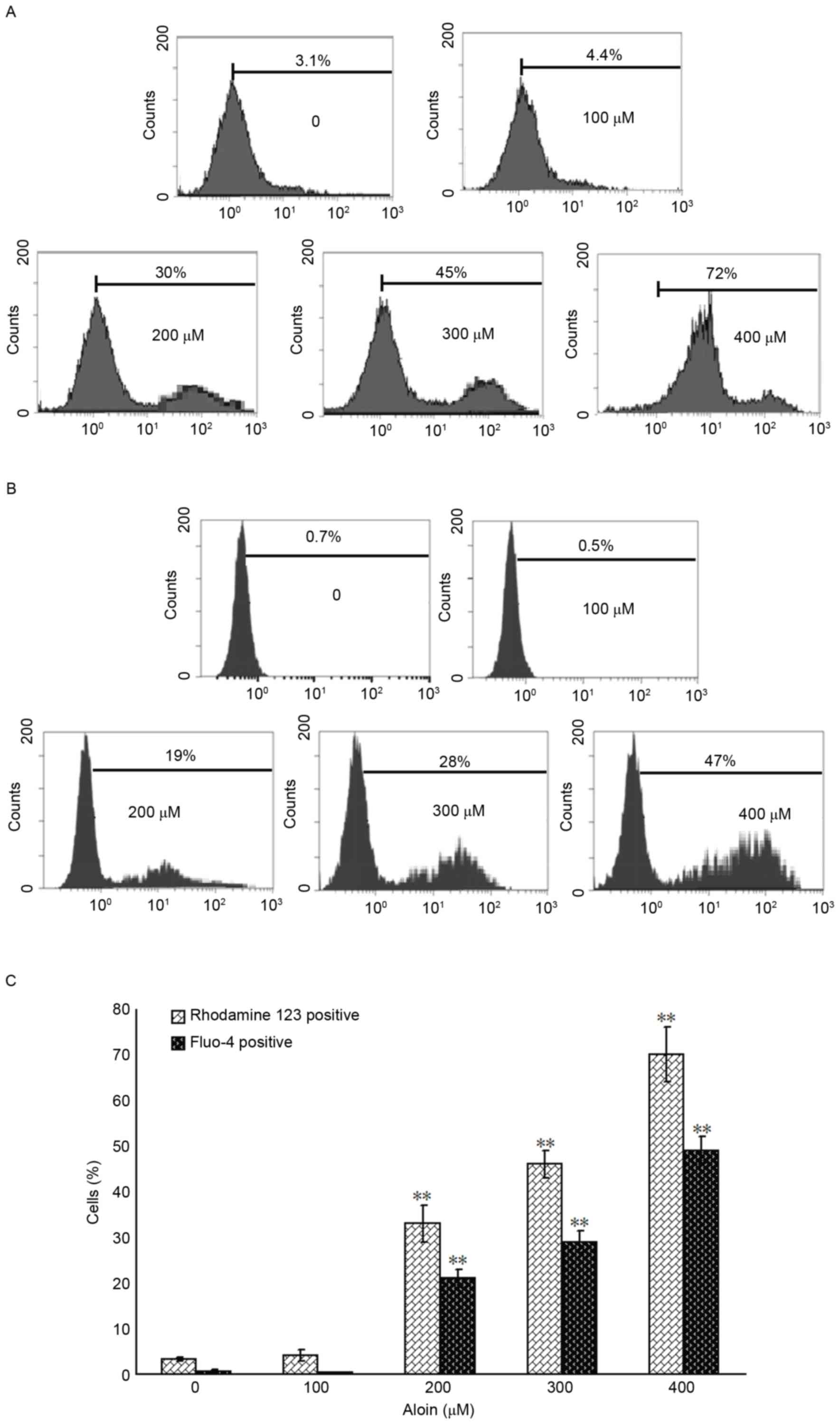
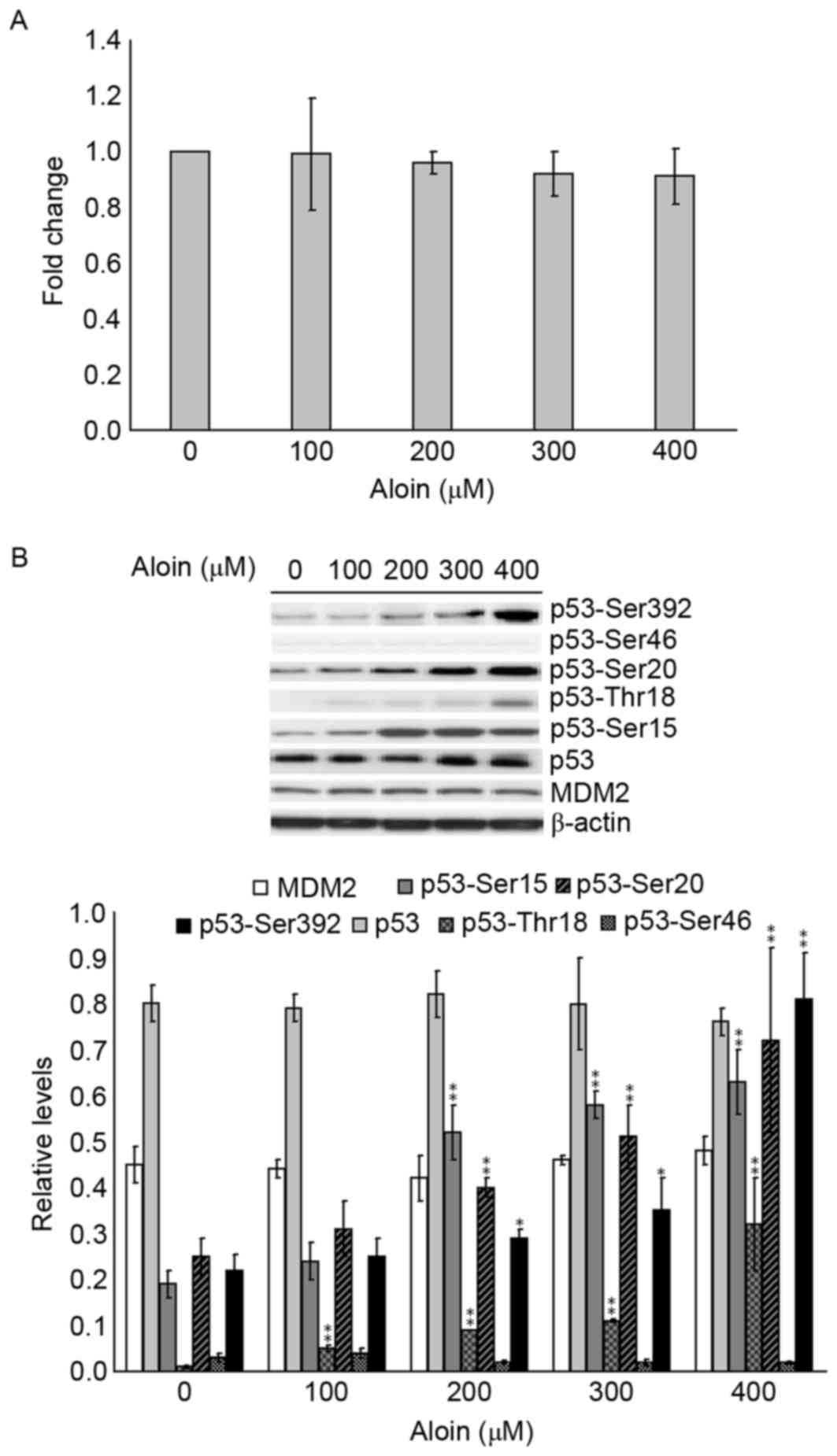
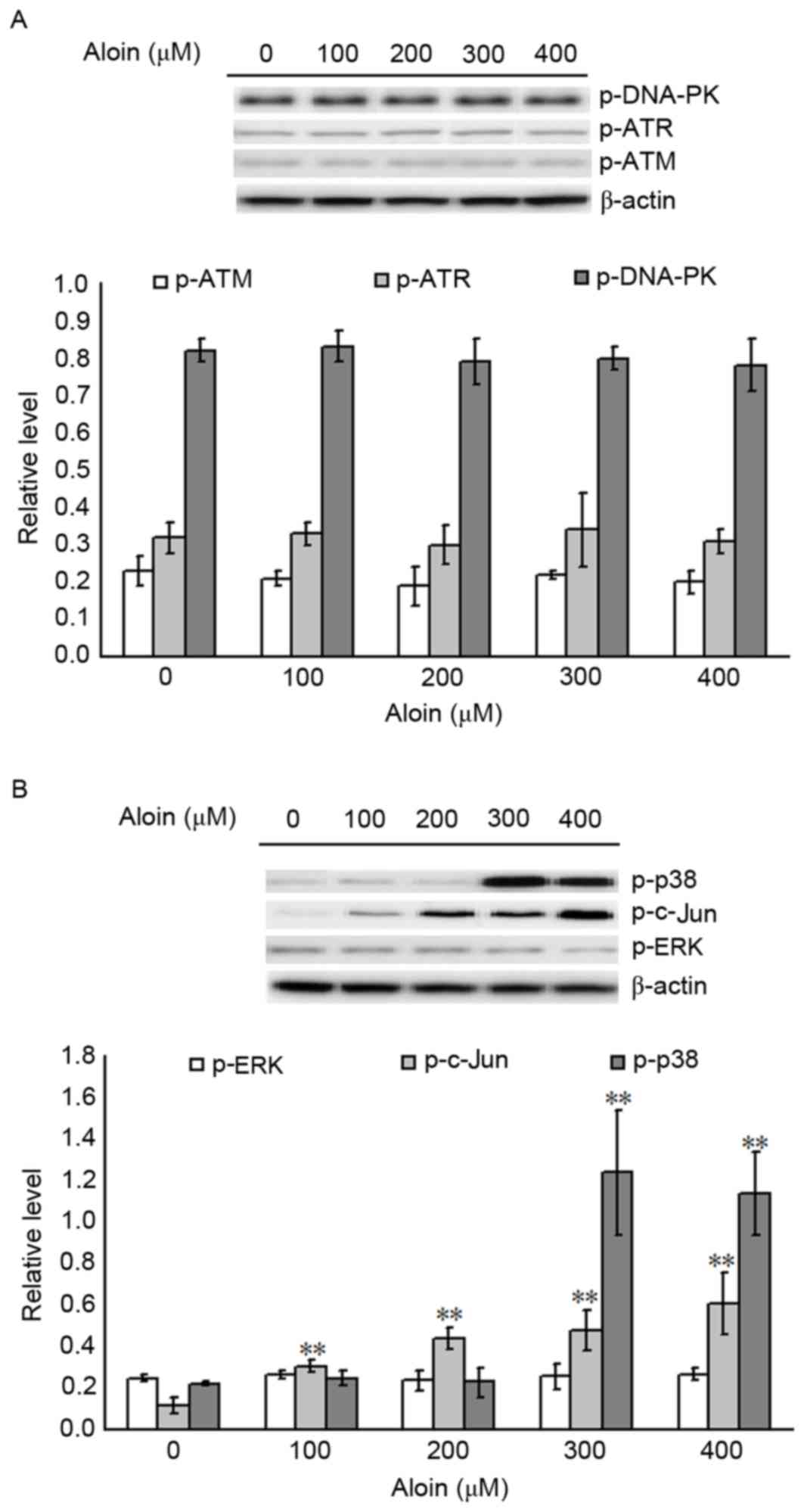
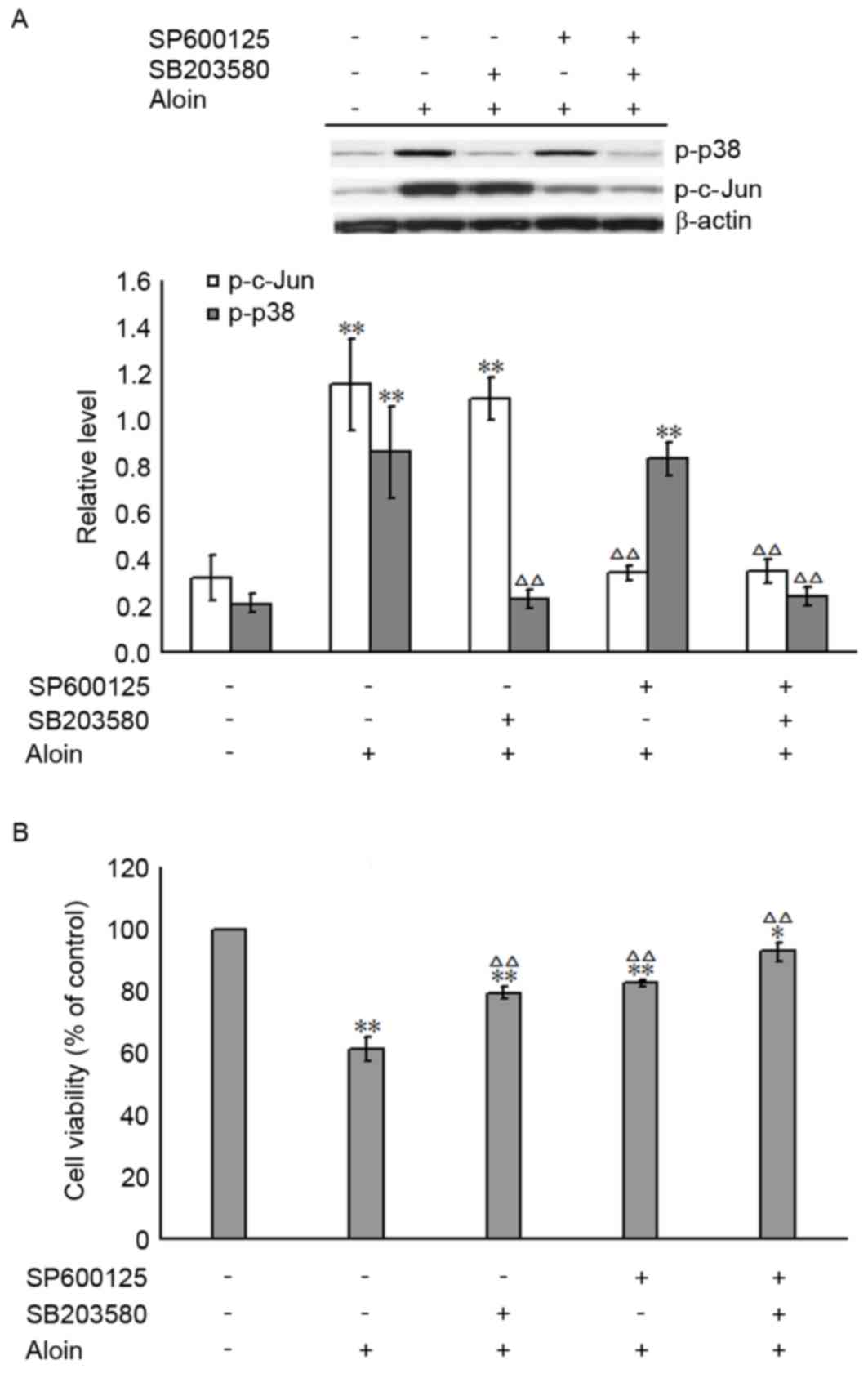
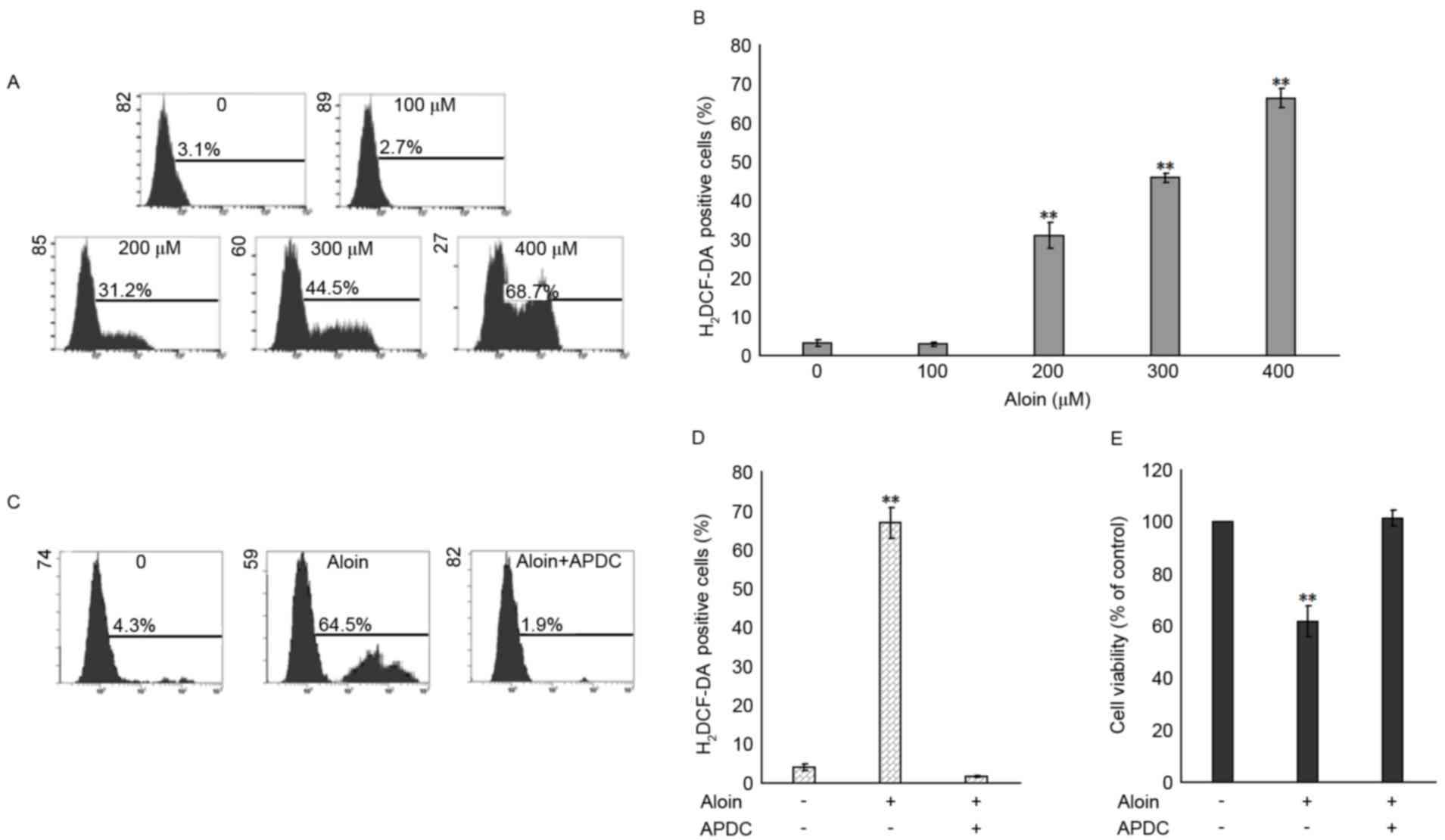
|
1
|
Gutterman Y and Chauser-Volfson E: The
content of secondary phenol metabolites in pruned leaves of Aloe
arborescens, a comparison between two methods: Leaf exudates and
leaf water extract. J Nat Med. 62:430–435. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tabolacci C, Rossi S, Lentini A,
Provenzano B, Turcano L, Facchiano F and Beninati S: Aloin enhances
cisplatin antineoplastic activity in B16-F10 melanoma cells by
transglutaminase-induced differentiation. Amino Acids. 44:293–300.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Buenz EJ: Aloin induces apoptosis in
Jurkat cells. Toxicol In Vitro. 22:422–429. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pronin AN, Xu H, Tang H, Zhang L, Li Q and
Li X: Specific alleles of bitter receptor genes influence human
sensitivity to the bitterness of aloin and saccharin. Curr Biol.
16:1403–1408. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Michael D and Oren M: The p53 and Mdm2
families in cancer. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 12:53–59. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jiang Y, Rao K, Yang G, Chen X, Wang Q,
Liu A, Zheng H and Yuan J: Benzo(a)pyrene induces p73 mRNA
expression and necrosis in human lung adenocarcinoma H1299 cells.
Environ Toxicol. 27:202–210. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Callén E, Jankovic M, Wong N, Zha S, Chen
HT, Difilippantonio S, Di Virgilio M, Heidkamp G, Alt FW,
Nussenzweig A and Nussenzweig M: Essential role for DNA-PKcs in DNA
double-strand break repair and apoptosis in ATM-deficient
lymphocytes. Mol Cell. 34:285–297. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Saxena N, Ansari KM, Kumar R, Dhawan A,
Dwivedi PD and Das M: Patulin causes DNA damage leading to cell
cycle arrest and apoptosis through modulation of Bax, p(53) and
p(21/WAF1) proteins in skin of mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
234:192–201. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sheikh MS and Fornace AJ Jr: Role of p53
family members in apoptosis. J Cell Physiol. 182:171–181. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang C, Gao C, Chen Y, Yin J, Wang P and
Lv X: Expression pattern of the apoptosis-stimulating protein of
p53 family in p53+ human breast cancer cell lines. Cancer Cell
International. 13:1162013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Deb SP, Singh S and Deb S: MDM2
overexpression, activation of signaling networks and cell
proliferation. Subcell Biochem. 85:215–234. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Krzesniak M, Zajkowicz A, Matuszczyk I and
Rusin M: Rapamycin prevents strong phosphorylation of p53 on serine
46 and attenuates activation of the p53 pathway in A549 lung cancer
cells exposed to actinomycin D. Mech Ageing Dev. 139:11–21. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jabbur JR, Huang P and Zhang W: DNA
damage-induced phosphorylation of p53 at serine 20 correlates with
p21 and Mdm-2 induction in vivo. Oncogene. 19:6203–6208. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tichý A, Záskodová D, Zoelzer F, Vávrová
J, Sinkorová Z, Pejchal J, Osterreicher J and Rezácová M:
Gamma-radiation-induced phosphorylation of p53 on serine 15 is
dose-dependent in MOLT-4 leukaemia cells. Folia Biol (Praha).
55:41–44. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tampio M, Loikkanen J, Myllynen P,
Mertanen A and Vahakangas KH: Benzo(a)pyrene increases
phosphorylation of p53 at serine 392 in relation to p53 induction
and cell death in MCF-7 cells. Toxicol Lett. 178:152–159. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sluss HK, Armata H, Gallant J and Jones
SN: Phosphorylation of serine 18 regulates distinct p53 functions
in mice. Mol Cell Biol. 24:976–984. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lee KB, Kim KR, Huh TL and Lee YM: Proton
induces apoptosis of hypoxic tumor cells by the p53-dependent and
p38/JNK MAPK signaling pathways. Int J Oncol. 33:1247–1256.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Brown L and Benchimol S: The involvement
of MAPK signaling pathways in determining the cellular response to
p53 activation: Cell cycle arrest or apoptosis. J Biol Chem.
281:3832–3840. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Huang J, Wu L, Tashiro S, Onodera S and
Ikejima T: Reactive oxygen species mediate oridonin-induced HepG2
apoptosis through p53, MAPK and mitochondrial signaling pathways. J
Pharmacol Sci. 107:370–379. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Salles-Passador I, Fotedar A and Fotedar
R: Cellular response to DNA damage. Link between p53 and DNA-PK. C
R Acad Sci III. 322:113–120. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gatz SA, Keimling M, Baumann C, Dörk T,
Debatin KM, Fulda S and Wiesmüller L: Resveratrol modulates DNA
double-strand break repair pathways in an ATM/ATR-p53- and
-Nbs1-dependent manner. Carcinogenesis. 29:519–527. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chène P: Inhibiting the p53-MDM2
interaction: An important target for cancer therapy. Nat Rev
Cancer. 3:102–109. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Huang X, Wu Z, Mei Y and Wu M: XIAP
inhibits autophagy via XIAP-Mdm2-p53 signalling. EMBO J.
32:2204–2216. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zheng M, Yang J, Xu X, Sebolt JT, Wang S
and Sun Y: Efficacy of MDM2 inhibitor MI-219 against lung cancer
cells alone or in combination with MDM2 knockdown, a XIAP inhibitor
or etoposide. Anticancer Res. 30:3321–3331. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lan YH, Chiang JH, Huang WW, Lu CC, Chung
JG, Wu TS, Jhan JH, Lin KL, Pai SJ, Chiu YJ, et al: Activations of
both extrinsic and intrinsic pathways in HCT 116 human colorectal
cancer cells contribute to apoptosis through p53-Mediated ATM/Fas
signaling by emilia sonchifolia extract, a folklore medicinal
plant. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012:1781782012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Seitz SJ, Schleithoff ES, Koch A, Schuster
A, Teufel A, Staib F, Stremmel W, Melino G, Krammer PH, Schilling T
and Müller M: Chemotherapy-induced apoptosis in hepatocellular
carcinoma involves the p53 family and is mediated via the extrinsic
and the intrinsic pathway. Int J Cancer. 126:2049–2066.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liu T, Laurell C, Selivanova G, Lundeberg
J, Nilsson P and Wiman KG: Hypoxia induces p53-dependent
transactivation and Fas/CD95-dependent apoptosis. Cell Death
Differ. 14:411–421. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lee MC, Liao JD, Huang WL, Jiang FY, Jheng
YZ, Jin YY and Tseng YS: Aloin-induced cell growth arrest, cell
apoptosis, and autophagy in human non-small cell lung cancer cells.
Biomarkers and Genomic Medicine. 6:144–149. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Camins A, Sureda FX, Gabriel C, Pallàs M,
Escubedo E and Camarasa J: Modulation of neuronal mitochondrial
membrane potential by the NMDA receptor: Role of arachidonic acid.
Brain Res. 777:69–74. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cao XH, Zhao SS, Liu DY, Wang Z, Niu LL,
Hou LH and Wang CL: ROS-Ca(2+) is associated with mitochondria
permeability transition pore involved in surfactin-induced MCF-7
cells apoptosis. Chem Biol Interact. 190:16–27. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liu J, Chang F, Li F, Fu H, Wang J, Zhang
S, Zhao J and Yin D: Palmitate promotes autophagy and apoptosis
through ROS-dependent JNK and p38 MAPK. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
463:262–267. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sato A, Okada M, Shibuya K, Watanabe E,
Seino S, Narita Y, Shibui S, Kayama T and Kitanaka C: Pivotal role
for ROS activation of p38 MAPK in the control of differentiation
and tumor-initiating capacity of glioma-initiating cells. Stem Cell
Res. 12:119–131. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liu WH, Cheng YC and Chang LS:
ROS-mediated p38alpha MAPK activation and ERK inactivation
responsible for upregulation of Fas and FasL and autocrine
Fas-mediated cell death in Taiwan cobra phospholipase A(2)-treated
U937 cells. J Cell Physiol. 219:642–651. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Colin DJ, Limagne E, Ragot K, Lizard G,
Ghiringhelli F, Solary É, Chauffert B, Latruffe N and Delmas D: The
role of reactive oxygen species and subsequent DNA-damage response
in the emergence of resistance towards resveratrol in colon cancer
models. Cell Death Dis. 5:e15332014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lapidus RG, Carter-Cooper BA, Sadowska M,
Choi EY, Wonodi O, Muvarak N, Natarajan K, Pidugu LS, Jaiswal A,
Toth EA, et al: Hydroxylated dimeric naphthoquinones increase the
generation of reactive oxygen species, induce apoptosis of acute
myeloid leukemia cells and are not substrates of the multidrug
resistance proteins abcb1 and abcg2. Pharmaceuticals (Basel).
9(pii): E42016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hsieh CJ, Kuo PL, Hsu YC, Huang YF, Tsai
EM and Hsu YL: Arctigenin, a dietary phytoestrogen, induces
apoptosis of estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer cells through
the ROS/p38 MAPK pathway and epigenetic regulation. Free Radic Biol
Med. 67:159–170. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sanada M, Kuroda K and Ueda M: ROS
production and apoptosis induction by formation of Gts1p-mediated
protein aggregates. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 75:1546–1553. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Derouet-Hümbert E, Drăgan CA, Hakki T and
Bureik M: ROS production by adrenodoxin does not cause apoptosis in
fission yeast. Apoptosis. 12:2135–2142. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Jiang H, Hou C, Zhang S, Xie H, Zhou W,
Jin Q, Cheng X, Qian R and Zhang X: Matrine upregulates the cell
cycle protein E2F-1 and triggers apoptosis via the mitochondrial
pathway in K562 cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 559:98–108. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Pei D, Zhang Y and Zheng J: Regulation of
p53: A collaboration between Mdm2 and Mdmx. Oncotarget. 3:228–235.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Walker G and Box N: Ribosomal stress, p53
activation and the tanning response. Expert Rev Dermatol.
3:649–656. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Yang J, Ahmed A and Ashcroft M: Activation
of a unique p53-dependent DNA damage response. Cell Cycle.
8:1630–1632. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Pabla N, Huang S, Mi QS, Daniel R and Dong
Z: ATR-Chk2 signaling in p53 activation and DNA damage response
during cisplatin-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 283:6572–6583.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Cheng F, Liu J, Teh C, Chong SW, Korzh V,
Jiang YJ and Deng LW: Camptothecin-induced downregulation of MLL5
contributes to the activation of tumor suppressor p53. Oncogene.
30:3599–3611. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Fraser M, Bai T and Tsang BK: Akt promotes
cisplatin resistance in human ovarian cancer cells through
inhibition of p53 phosphorylation and nuclear function. Int J
Cancer. 122:534–546. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Katayama A, Ogino T, Bandoh N, Takahara M,
Kishibe K, Nonaka S and Harabuchi Y: Overexpression of small
ubiquitin-related modifier-1 and sumoylated Mdm2 in oral squamous
cell carcinoma: Possible involvement in tumor proliferation and
prognosis. Int J Oncol. 31:517–524. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Saito S, Goodarzi AA, Higashimoto Y, Noda
Y, Lees-Miller SP, Appella E and Anderson CW: ATM mediates
phosphorylation at multiple p53 sites, including Ser(46), in
response to ionizing radiation. J Biol Chem. 277:12491–12494. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Yamauchi M, Suzuki K, Kodama S and
Watanabe M: Stabilization of alanine substituted p53 protein at
Ser15, Thr18, and Ser20 in response to ionizing radiation. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 323:906–911. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Momand J, Villegas A and Belyi VA: The
evolution of MDM2 family genes. Gene. 486:23–30. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Ongkeko WM, Wang XQ, Siu WY, Lau AW,
Yamashita K, Harris AL, Cox LS and Poon RY: MDM2 and MDMX bind and
stabilize the p53-related protein p73. Curr Biol. 9:829–832. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Yoou MS, Park CL, Kim MH, Kim HM and Jeong
HJ: Inhibition of MDM2 expression by rosmarinic acid in
TSLP-stimulated mast cell. Eur J Pharmacol. 771:191–198. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Kao CL, Hsu HS, Chen HW and Cheng TH:
Rapamycin increases the p53/MDM2 protein ratio and p53-dependent
apoptosis by translational inhibition of mdm2 in cancer cells.
Cancer Lett. 286:250–259. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Inoue T, Geyer RK, Yu ZK and Maki CG:
Downregulation of MDM2 stabilizes p53 by inhibiting p53
ubiquitination in response to specific alkylating agents. FEBS
Lett. 490:196–201. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Huang M, Zhang H, Liu T, Tian D, Gu L and
Zhou M: Triptolide inhibits MDM2 and induces apoptosis in acute
lymphoblastic leukemia cells through a p53-independent pathway. Mol
Cancer Ther. 12:184–194. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Vitale I, Senovilla L, Galluzzi L, Criollo
A, Vivet S, Castedo M and Kroemer G: Chk1 inhibition activates p53
through p38 MAPK in tetraploid cancer cells. Cell Cycle.
7:1956–1961. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Zhang JQ, Li YM, Liu T, He WT, Chen YT,
Chen XH, Li X, Zhou WC, Yi JF and Ren ZJ: Antitumor effect of
matrine in human hepatoma G2 cells by inducing apoptosis and
autophagy. World J Gastroenterol. 16:4281–4290. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Taylor CA, Zheng Q, Liu Z and Thompson JE:
Role of p38 and JNK MAPK signaling pathways and tumor suppressor
p53 on induction of apoptosis in response to Ad-eIF5A1 in A549 lung
cancer cells. Mol Cancer. 12:352013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|